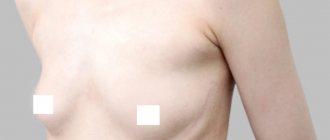
Features of additional shares
Accessory lobe of mammary gland in the armpit
Polymastia, or an additional lobe of the mammary gland, is included in the ICD-10 classification and refers to congenital developmental anomalies that are associated with deformities and chromosomal abnormalities.
Polymastia is associated with an atypical position of the glandular tissue of the breast, most often indicating an additional lobe under the armpit.
Also, the breast lobule can be located between the mammary glands, directly under the collarbone or deep in the armpit. The most rare and remote cases of the position are outside the milky line, right between the shoulder blades or in the pelvic area.
Additional lobe of the mammary gland
In some women, a mass is often found in the armpit. It can be represented by a lobe of the mammary gland.
This condition is a birth defect. The lobes can be found not only in the armpit, but also in other parts of the body (on the neck, back and external genitalia).
This pathology is a cosmetic defect, as the appearance of the breast changes. The accessory mammary gland does not have a nipple, but it is characterized by the following features:
- may increase during pregnancy and feeding of the baby;
- may suffer from infectious or any other pathology;
- movable;
- elastic.
The exact reasons for the development of this pathology have not been established. The most common is the genetic theory.
According to it, the anomaly develops due to a violation of embryogenesis. The outcome is improper formation of the gland.
Normally, additional lobes are formed during another 1–2 months of gestation, but then they involute. Only 2 glands remain.
An additional lobule under the armpit is often discovered during adolescence. The triggering factor is puberty. Axillary localization of the additional lobe is observed in 4 - 6% of cases.
Main clinical manifestations
Symptoms of an additional lobule of the mammary gland may be absent for a long time. The main signs of pathology are:
- physical discomfort in the armpit area;
- the presence of a bulge in the armpit;
- pain.
This pathology causes psychological discomfort. The main symptom of this congenital anomaly is a lump under the armpit.
It is dense and elastic. If inflammation develops against the background of an infectious pathology, edema may occur.
The swelling may be painful or painless. Only in some cases, upon examination, can a point or nipple be detected.
After childbirth, before menstruation and during pregnancy, the accessory organ enlarges. It is located downwards from the chest.
The size of the formation is several centimeters. An axillary cavity with an additional lobe is a cosmetic defect.
There is no direct connection between this pathology and malignant neoplasms (cancer).
Despite this, constant mechanical trauma to the lump increases the risk of developing cancer.
This anomaly under the arm during pregnancy does not affect lactation. If a woman experiences symptoms of intoxication and pain, this may indicate an inflammatory process (mastitis).
Reasons for the formation of a false lobe
Among the factors influencing the formation of anomalies are the severe stress of a pregnant woman
The appearance of an additional lobule of mammary gland under the arm is most often associated with genetic abnormalities and disorders during embryonic development. There are no other confirmed causes for this condition. However, doctors often identify factors that may contribute to the anomaly:
- severe stress of a pregnant woman, as well as poor diet and bad habits;
- genetic mutation at week 6, when the most important parameters of adipose tissue are established;
- sharp changes in hormonal levels during adolescence in a woman who has an additional lobe;
- hereditary predisposition - risks increase to 90% if the woman’s mother or grandmother had polymastia.
A separate factor that can be identified is that a pregnant woman takes certain groups of medications that contribute to the development of pathology: anticonvulsants, contraceptives, drugs to reduce the activity of the thyroid gland, as well as medications to normalize blood clotting. Chemotherapy, ionizing radiation and radiation treatments for cancerous tumors are especially dangerous.
Intrauterine infections are a provoking factor in the development of abnormalities
Some household chemicals and industrial compounds with which a woman interacts can contribute to problems during pregnancy. Other factors cannot be ruled out:
- mental disorders of the expectant mother, frequent stress and emotional tension;
- chronic diseases;
- intrauterine infections;
- prolonged exposure to extremely low or high temperatures that do not correspond to the natural conditions to which a woman is accustomed;
- mechanical damage to the fetus in the 1st-3rd trimester after an accident, falls, blows.
Identifying these factors is a very complex process, since some of them may not be noticed by a woman or may not be assessed by her as dangerous.
Causes of extra mammary glands under the armpit
The reasons for the appearance of this anomaly have not yet been fully determined. More precisely, there is still no consensus regarding the factors contributing to their development.
Typically, additional lobes of the mammary glands appear due to genetic disorders. This happens against the background of a hormonal imbalance or surge. For example, this could be the same menopause, pregnancy or puberty.
Accessory glands have always been classified as pathologies. In fact, this is an anomaly. A woman's breasts have a symmetrical arrangement. Naturally, it consists of only 2 glands. Additional
The “growth” can be located under normal glands. But there are also more “interesting” places where they stay. So, most often the anomaly develops on the neck, armpits and back. It is extremely rare that an additional organ can appear on the genitals.
Often the cause lies in the improper development of the mammary gland. This happens due to developmental problems. This process begins as early as the 6th week of development. Usually, by the 10th week, all excess “growths” are eliminated on their own, leaving only two mammary glands in the place where they should be. But, in some cases, elimination never occurs.
Symptoms of the development of polymastia
With the development of mastopathy of the accessory lobe, a compaction is formed
If the accessory mammary gland is small in size, it will not manifest itself for a long time. The following conditions can provoke symptoms of additional lobules:
- Pregnancy. The lobe becomes rounded and becomes distinct even before the delay occurs. Under the influence of prolactin, the mammary glands are transformed, which also affects the additional elements. This can be noticed by swelling, discomfort and even pain in the armpit area.
- Childbirth and lactation. On the 5th day, a woman experiences maximum milk production, which leads to breast enlargement, increased density and sensitivity. The same thing happens with the extra slice.
- The occurrence of inflammatory processes. Inflammation may or may not be associated with the feeding process. Often inflammation - mastitis - manifests itself long before and after lactation. Outwardly, it looks like an enlarged lymph node - the formation is quite dense, localized in the middle of the armpit. But inflammation can also indicate another disorder - a cancerous tumor. In this case, the formation may not hurt in the initial stages; it will be mobile, independent of other tissues.
- Development of mastopathy. In the axillary area, pain occurs in the second phase of the menstrual cycle, but with the onset of menstruation, the discomfort goes away. In some patients with mastopathy of the accessory lobe, a small compaction forms.
The additional lobe that appears does not have additional symptoms, such as fever or effects on general well-being.
Polymastia
- Between two normal mammary glands
- Below the collarbone
- In the armpit
- On the skin of the genital organs, near the anus, between the shoulder blades on the back (very rare)
Occasionally, an accessory gland is found that has only a nipple or only an areola, and even more rarely, false mammary glands with a nipple, which originate not from the glandular tissue, but from the adipose tissue. In most cases, pathology is detected in women.
The area of localization in the armpit is most likely for both polymastia and accessory lobules. Located in the armpit, the formation may be associated with the normal mammary gland, but not always. With this arrangement, the accessory gland is not only regularly injured, but also causes serious physical and aesthetic discomfort.
The development of the mammary glands starts from the 6th week of the embryonic period. The emerging strands of epithelial tissue grow, form ducts, and their excess parts disappear by the 4th month. If this process fails, a person may be left with an extra lobule or gland after birth.
Hormonal imbalances can lead to the formation of additional lobules even throughout life. So, in some women they were discovered only during pregnancy. Sometimes pathology is detected during puberty.
Signs and symptoms
Outwardly, it is almost impossible not to notice a problem in the body, so the patient’s psychological discomfort can be significant.
The lobules and glands protrude outward, sometimes resembling a normal mammary gland, but more often looking like a small lump on the skin.
Symptoms may include:
- Nipple soreness
- Aching pain in the gland itself
- Increase in size during menstruation
- Milk discharge from the nipple in nursing mothers
In some patients, oncological formations develop in additional lobules or with polymastia.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pathology is carried out by a mammologist, mammologist-oncologist. After asking for help, the doctor will conduct a physical examination (palpation) of the formation and recommend a number of instrumental studies:
- Ultrasound of the gland. It will help clarify the size, location, structure.
- Mammography, MRI or CT. More precise methods are necessary to differentiate polymastia from a tumor process, lipoma, or cyst.
At the age of over 35-40 years, a woman is prescribed a puncture of a lobule or additional mammary gland to clarify the diagnosis and exclude oncology.
If there are no complaints, wait-and-see tactics are acceptable. There is no drug treatment for polymastia, so the only way to get rid of the gland or lobule is through surgery. Restoring the aesthetics of the breast is possible through liposuction if the formation consists of adipose tissue.
- Pain in the accessory gland
- Family history of breast cancer
- Aesthetic discomfort, psychological need to get rid of a defect
The prognosis after treatment is favorable. With observational tactics, timely diagnosis of changes in the accessory mammary gland is mandatory (ultrasound once a year). Typically, its location contributes to trauma and friction, which are potential risk factors for malignant degeneration. If the formation grows rapidly, its emergency removal is recommended.
https://www.ginomedic.ru/mammologiya/novoobrazovaniya/polimastiya.html
Health Hazard
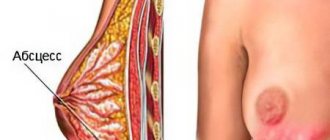
If the appearance of an additional lobe of mammary gland under the arm is not associated with pain and unpleasant symptoms and it does not bother the woman in any way, there is no need to worry about the condition of the formation. In itself, it is not dangerous to health. The rate of growth into a malignant tumor is no greater than the formation of nodes in the normal mammary gland.
However, pathological processes in this part of the gland may be diagnosed too late, which will slow down treatment. It often turns out that it is possible to detect pathology even with an advanced abscess or stage 3-4 tumor. This can be avoided if you regularly undergo examinations by doctors - a gynecologist and a mammologist.
Symptoms of extra mammary glands under the arm
Symptoms are exclusively visual. But it is worth noting that this pathology can also be painful. In some cases, a woman develops a complex. After all, this affects her psychological state and brings a lot of inconvenience. This leads to fears and lack of love for one’s own body.
Accessory organs are characterized by a three-dimensional shape. In some cases, they have a nipple. Sometimes the neoplasm has a special shape or looks like an ordinary mammary gland. Usually its location is in the axillary area.
A few days before the onset of menstruation, the anomaly may change significantly in volume. Before menstruation, breasts often become enlarged. As for the additional organ, it follows its example. During pregnancy and after childbirth, it may even leak breast milk.
This anomaly is not oncology. But we should not exclude the possibility of its “transformation” into malignant. Such cases actually occurred. The risk of developing cancer remains in those people whose accessory organs are constantly injured, for example, by clothing.
Additional lobule of mammary gland under the armpit
A completely familiar habitat for this anomaly is an additional lobule. Sometimes, the location of the dislocation is in other areas, but this one is the most pronounced. It is worth noting that not in all cases this mammary gland has something in common with the main one.
Under the armpit, a neoplasm occurs in almost 6% of all cases. The growth takes its development from the rudiments of the embryo. This process lasts throughout the entire milk line. There are eight types of anomalies in total. Half of them do not contain glandular tissue. But despite this, it has a completely full-fledged nipple. Experts do not consider these anomalies life-threatening. Yes, this is a neoplasm, but it is not malignant and it cannot develop into this form. True, this issue has not been thoroughly studied.
Women with an accessory gland agree to surgery. They make this decision because of constant discomfort. The presence of this organ burdens them and causes a number of complexes. Indeed, in many cases, the accessory gland interferes with normal existence and creates a number of inconveniences.
Looking at the anomaly on an x-ray, you can see a low-intensity zone, usually it is darkened. Basically it is surrounded by special fibers.
Diagnosis of the condition of the accessory lobe
Often an accessory mammary gland is detected during a comprehensive ultrasound examination
To make a diagnosis, doctors require precise instrumental examination techniques:
- Ultrasound. Very often, an additional lobe is found by chance during a comprehensive ultrasound.
- CT and MRI. They are used when a tumor is suspected and to clarify the nature of the tumor.
- Mammography. Allows targeted examination of the axillary and chest areas.
- Puncture. It is carried out for mastopathy and other signs of inflammatory processes to be sent for histological examination.
If there is a serious suspicion of cancer, a woman is prescribed blood tests to determine tumor markers.
It is impossible to diagnose an additional lobule of the mammary gland by visual examination and palpation alone. An experienced mammologist always prescribes an instrumental examination to accurately exclude unfavorable factors and pathological processes.
Is education dangerous for health?
As a rule, polymastia does not pose a health risk. However, it can lead to such troubles as:
- lactostasis – stagnation of milk during lactation;
- mastitis – inflammation of the mammary gland of an infectious nature;
- mastopathy – thickening of glandular structures as a result of hormonal changes in the female body;
- benign tumors and cysts;
- oncology.
In addition, a large accessory mammary gland and pain accompanying polymastia can lead to emotional distress, irritability, tearfulness, fear and anxiety, as well as psychological problems (depression, hypochondria).
Need for surgery
Acute psychological discomfort or the presence of diseases in the additional lobule are indications for surgery
Treatment of the additional lobe of the mammary gland under the arm is possible only by removing the pathological formation: in the presence of cysts, tumors, abscesses. In other cases, doctors do not recommend touching the lobule if it causes purely aesthetic discomfort.
Indications for surgery will be:
- detection of cysts, malignant tumors and fibroadenomas;
- regular pain and swelling of unknown origin;
- large size of the accessory gland;
- acute psychological discomfort.
Sometimes therapy with drugs for mastopathy is prescribed if the symptoms appear rarely and are mild. These medications are good at relieving swelling, discomfort, and mild pain. Hormonal contraceptives are often used to eliminate signs of polymastia.
Prevention
Prevention of additional mammary glands under the arm is, in principle, impossible. It is not possible to control this process or do anything to prevent it. After all, as mentioned above, this is an ordinary anomaly. Nothing affects its development. The only factor may be hormonal imbalance or heredity. It's impossible to do anything about it.
Adolescence, the beginning of the menstrual cycle, pregnancy - all this occurs with the participation of a large number of hormones. These processes cannot be prevented, unless it is the latter. Therefore, the only way to get rid of the problem is to simply remove the tumor.
There is nothing scary or dangerous in this procedure. It's just an operation and that's it. Then the woman will be able to live without much discomfort. If you don't want to, you can leave everything as is. But, it is worth repeating again, it is not possible to prevent the appearance of this neoplasm.
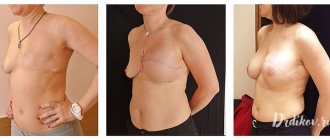
Methods for removing an additional lobe
Removed additional milk lobe
There are several methods for surgical removal of the accessory lobe of the mammary gland. The most common among them:
- Excision and suturing. Through an incision in the skin, the doctor removes the glandular tissue and the nipple, if present. The skin is then excised and the tissue is sutured. The removed tissue can be sent for biopsy to identify the causes of the formation of an additional lobule.
- Liposuction. During the operation, fat deposits are sucked out from the accessory lobule.
For up to 5 days after surgery, the doctor will install a drainage tube to prevent pus and other secretions from accumulating in the area. The recovery period takes on average 1 month.
Reasons for the appearance of an additional lobe of the mammary gland
It is necessary to distinguish between the concepts of “additional lobule” and “gland”. The pathologies are somewhat similar, but there are significant differences. The accessory breast (polymastia), in addition to glandular tissue, has a direct excretory duct, its own areolar zone and nipple. This is like a full-fledged mammary gland, only in a rudimentary size.
An additional lobule is just a piece of glandular tissue that, due to some circumstances, has ectopized into another zone. Its duct opens into a common one for all on the main chest.
No reliable reasons for the formation of an additional lobe of the mammary gland have been established. The generally accepted opinion is that this occurs even during the period of embryonic development under the influence of some unfavorable factors. As a result, some of the cells remain in the armpit area, and all the rest migrate to the usual location of the breast.
This can be either the influence of harmful environmental factors, or medications in the early stages of pregnancy, infectious diseases during this period, etc.
A hereditary predisposition to this feature has been noted, so it is possible that the pathology is associated with mutations of some specific genes.
Prevention and prognosis
A woman who has this anomaly genetically cannot prevent the formation of an additional lobule. This is due to the fact that reliable information about the causes of the disease has not been collected. However, to avoid the growth of glandular breast tissue during pregnancy, a woman needs to stop taking provoking medications, reduce stress levels and monitor her health to exclude infectious and viral lesions.
If a woman has developed an additional lobe, she needs to be examined every year with an ultrasound. After 35 years, it is necessary to undergo mammography every 6 months in order to exclude cancer processes. It is not recommended to injure this area, as injuries can cause inflammation.
The prognosis for control of the additional lobule is favorable. The appearance of a malignant tumor in it is the exception in medical practices rather than the rule. It is also noted that after menopause, some anomalies may disappear without surgical intervention.
Is it necessary to have surgery?
If the additional lobule of the mammary gland is not complicated by anything (abscess, cyst, tumor, etc.), there is no need to remove it. Even if it brings tolerable discomfort during breastfeeding or on the eve of menstruation, this is not an indication for surgery.
- with large sizes;
- if it is accompanied by severe pain, swelling;
- if a cyst, fibroadenoma or even a malignant tumor is found in it;
- at the request of the woman, if it brings her psychological or cosmetic discomfort.
If a girl is bothered by some minimal symptoms, you can try treatment with drugs intended for the treatment of mastopathy. This way you can reduce the manifestation of pain, discomfort, swelling, and slightly reduce the size of the formation. Using properly selected hormonal contraception also helps relieve all symptoms.
Watch the video about benign breast tumors:
Medical diagnostics
The entire abnormal process of formation and development of the lobule under the arm cannot be diagnosed at the stage of development and formation. The presence or defect can be determined by the signs that a woman feels. To do this, the following procedures are additionally carried out:
- palpation by a mammologist;
- MRM (mammographic examination);
- Ultrasound;
- education puncture.
Mammography and ultrasound are needed in order to understand whether the lobe is a common defect in the development of the gland, or whether it is a benign tumor. Cancer in this case is impossible, since there are pronounced symptoms indicating the development of a viral formation.
With cancerous formations, fever and chills appear at the 3-4 stage of the formation of the disease. It is impossible to diagnose them, since symptoms appear long before the tumor in the glandular structure begins to develop and cover the surrounding tissues.
If you constantly injure the lobules, an inflammatory process will begin, which will lead to pain and mastitis of the additional lobe. It is difficult to recognize a disease in a place that should not be in the body, since the tumor-like lobe itself is a foreign body that needs to be punctured and removed. If such a lobe is found under the armpit of a woman over 40 years of age, additional testing may be necessary, such as an atypical test for cancer cells.
The entire abnormal process of formation and development of the lobule under the arm cannot be diagnosed at the stage of development and formation. The presence or defect can be determined by the signs that a woman feels. To do this, the following procedures are additionally carried out:
- palpation by a mammologist;
- MRM (mammographic examination);
- Ultrasound;
- education puncture.
Mammography and ultrasound are needed in order to understand whether the lobe is a common defect in the development of the gland, or whether it is a benign tumor. Cancer in this case is impossible, since there are pronounced symptoms indicating the development of a viral formation.
With cancerous formations, fever and chills appear at the 3-4 stage of the formation of the disease. It is impossible to diagnose them, since symptoms appear long before the tumor in the glandular structure begins to develop and cover the surrounding tissues.
If you constantly injure the lobules, an inflammatory process will begin, which will lead to pain and mastitis of the additional lobe. It is difficult to recognize a disease in a place that should not be in the body, since the tumor-like lobe itself is a foreign body that needs to be punctured and removed. If such a lobe is found under the armpit of a woman over 40 years of age, additional testing may be necessary, such as an atypical test for cancer cells.