Oncological diseases of the breast are the most pressing problem of modern healthcare.
According to the World Health Organization, they rank first among cancer pathologies in women. 16% of all cancers in females occur in the mammary glands. The previously held opinion that breast cancer is a disease that develops more often in first world countries has now exhausted itself. The incidence rate in underdeveloped countries is increasing sharply.
To date, doctors all over the world are organizing various associations, congresses, and conferences that are dedicated to breast diseases. These events are aimed at exchanging experience and information regarding early diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer processes. Such international assistance makes it possible to treat breast cancer at a high level anywhere in the world. However, after breast cancer surgery, the body may still be at risk. What does this mean and how to avoid it?
What is breast cancer and why does it occur?
Cancer is a disease that is caused by the appearance of atypical (undifferentiated) cells in the body, their further growth and replacement of healthy tissue. The appearance of these cells is associated primarily with disruption of the immune system (this is the main modern theory regarding the occurrence of cancer). Every minute hundreds of atypical cells appear in our body, but the immune system recognizes them and destroys them with lightning speed, which prevents the development of cancer. Under the influence of various factors, this process is disrupted, which leads to the appearance of cancer.
Associated symptoms during the rehabilitation period
Injury to tissue in the bust area or the introduction of a foreign body causes consequences that manifest differently in each patient:
- Pain . You can't do without it. Immediately after the anesthesia wears off, my nipples and back hurt, and my glands swell. At first the syndrome increases, then subsides and disappears completely. To alleviate the condition, the woman is prescribed analgesics. How much breast pain after mammoplasty depends on various factors. Usually the symptom subsides after two weeks.
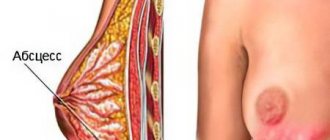
- Suppuration and burning. The condition indicates infection of the wound and penetration of bacteria through the injured tissue. A burning sensation in the chest is accompanied by high fever, back pain, and prolonged wound healing with the release of pus. To solve the problem, antibacterial therapy is prescribed, drainage and lavage are performed. If the burning sensation does not go away after the procedures, it may be necessary to remove the implant.
- Hematoma. Appears if bleeding begins from a damaged vessel or normal circulation is restored in the area where the lymph has clotted during surgery. Hematoma after mammoplasty can be recognized by a dark clot visible through the skin and a small thickening. It is removed with a scalpel or physiotherapeutic methods.
- Allergy. If the wrong material is chosen, the breast implant presses and burns. More often, the symptom manifests itself as a result of an omission during the preliminary examination, when the possible reaction of the body to a foreign body was not thoroughly studied. In this case, the endoprostheses will have to be removed. A manifestation of an allergy to drugs may be atypical swelling, which is accompanied by a change in skin color.
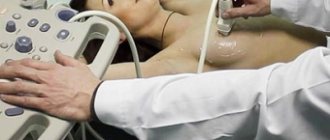
- Seroma. Fluid accumulates under the implant on one or both sides. Externally, seroma looks like uneven swelling and is detected only by ultrasound. The liquid is removed with a syringe, observing its exact location using ultrasound.
- Displacement of the endoprosthesis. It is impossible to predict how natural fabrics will behave. Excessive compaction may cause deformation or displacement of the implant. Surgeon errors and improper pocket formation are also possible.
- Loss of skin sensitivity. This is a normal phenomenon due to a violation of the integrity of the nerve endings, which should resolve within six months. In very rare cases, nipple sensitivity may be affected.
Risk factors for developing breast cancer:
1. Hormone-dependent factors. Breast cancer is a disease that develops only in females (only 1% of all breast cancer pathologies occur in men). This is primarily due to hormonal characteristics. The dominance of one or another sex hormone in a woman’s body directly depends on the phase of the cycle. In the first phase (from the first day of menstruation to ovulation), estrogen and follicle-stimulating hormone predominate, in the second phase (after ovulation until the first day of menstrual bleeding) - progesterone and luteinizing hormone. Various disturbances in the cyclicity of these processes can indirectly affect the occurrence of breast cancer. These factors are divided into:
· Internal (exogenous). These include: early onset of menstruation, late onset of menopause, absence of pregnancies resulting in childbirth or late first birth;
· External (exogenous). Taking hormonal therapy for another disease, long-term continuous (more than 1 year) use of oral contraceptives, which over time disrupt the natural cyclic change of hormones in a woman’s body.
2. Factors related to the ecological situation of the environment. It's no secret that people living in rural areas, in areas with a sea or mountain climate, get sick much less often than people living in large cities or industrial centers. The polluted environment, which affects the human body every day (and for some from birth), has a powerful negative effect on the functioning of the immune system, which causes the development of oncological pathologies in the future, including breast cancer.
A person’s lifestyle also applies to external factors. No wonder they say: “We are what we eat.”
Negative environmental factors are divided into:
· Ionizing radiation;
· Geolocation;
· Nutrition;
· Drinking alcoholic beverages of various strengths;
· Tobacco smoking.
3. Features of individual anamnesis. The older a person is, the more background diseases and pathological conditions he “accumulates.” This fact has a strong impact on the immune system, depleting it and making it more vulnerable. As a result, it is not able to “reject” cancer cells and destroy them.
Individual factors include:
· Age;
· Presence of previous oncological diseases of the breast (primarily mastopathy) and organs of the female reproductive system (ovaries, uterus);
4. Genealogical history. Some diseases, including cancer, can be inherited. This does not mean that all women in the family will suffer from breast cancer, but they are more susceptible to this disease than women in whose family there have been no such cases.
Currently, genes that determine the development of familial cases of breast cancer have been identified. Therefore, even before the development of a dangerous condition, it is possible to predict its risk. If it is high, then the mammary gland can be removed preventively. A striking example of this approach is the story of Angelina Jolie.
Prevention of complications
Most complications after a mastectomy are considered inevitable . But it is important to detect them in a timely manner:
- To prevent bleeding, a special power tool is used that stops bleeding from small vessels.
- To prevent infections, skin treatment with a special disinfectant is used.
- To prevent the occurrence of lymphostasis, it is necessary to follow the prescribed preventive measures. It is necessary to prevent the possibility of infection.
- If you suspect the occurrence of erysipelas, you must visit a doctor in order to begin the necessary therapy.
- If lumps, swelling of the breast or arm occur, you should immediately visit a doctor.
- Diet, special nutrition.
- Exercise therapy and proper breast care.
- Under no circumstances should you use your injured arm to draw blood, measure blood pressure, or give injections.
Mastectomy is an effective treatment option. In order to save her life, a woman needs to decide to take such a step. In general, the prognosis after a mastectomy is quite favorable. It is considered favorable when it is detected at an early stage. And also with proper treatment.
In due time, removal of the tumor and a course of therapy can preserve the patient’s normal life for a long time. This disease progresses without treatment, leading to disability and death . A woman who has learned about her illness should set herself up for a good outcome, because this helps in confronting the disease. According to statistics, a favorable outcome in the first stage is about 99.9%, and in the second stage – 80% of recovery.
If you want to be the first to know about the release of new articles or you are simply more accustomed to reading on VKontakte, then join our group “Beauty Secrets” and stay up to date with all the news in the beauty industry.
Subscribe!
A woman's well-being after breast surgery
There are two types of operations for oncological process in the mammary gland:
1. Non-radical (sparing) - the scope of the operation is limited to the removal of only the tumor-like formation and a small part of the tissue around it.
2. Radical - complete removal of breast tissue, surrounding subcutaneous fat, regional (closest) lymph nodes, and sometimes resort to removal of nearby muscles.
Lymphostasis of the breast after surgery
Partial breast surgery:
This surgical option is chosen by women for aesthetic reasons, but there remains a high risk of disease recurrence. In addition, it can only be performed on cancer in situ, i.e. with minimal changes to the organ. With a gentle version of the operation, the mammary gland and nipple are preserved. It is possible to change the volume of the operated mammary gland, taking into account the removal of not only pathological tissue, but also healthy tissue. However, this problem can be easily corrected with clothing or special underwear.
After breast cancer surgery, in addition to the general complications that can occur after any operation, the following come to the fore:
1. Compaction of postoperative scars;
2. Tumor recurrence;
3. Proliferation of connective tissue along the ducts of the mammary gland near the surgical field.
1. Consolidation of the postoperative scar
For a woman, this complication, as a rule, does not cause inconvenience. The compaction is determined only by palpation (feeling) of the mammary gland. This fact is of particular importance for doctors. Due to the deposition of calcium salts in the suture area, further examination of the woman to identify a possible relapse is difficult. A compacted scar interferes with both x-ray and ultrasound examinations carried out over time in patients with oncological processes.
2. Tumor recurrence.
Unfortunately, non-radical operations increase the risk of tumor recurrence. Incomplete removal of the mammary gland does not exclude the possibility that atypical cells have already immigrated into visually healthy tissue, which will cause a relapse of the malignant neoplasm.
3. Proliferation of connective tissue along the ducts of the mammary gland.
An inflammation process is observed near the surgical field after breast cancer surgery. The body does not tolerate emptiness, and instead of the removed tissue, connective tissue begins to form. Often, the growth of connective tissue spreads to healthy areas of the breast.
Clinically, this complication is manifested by pronounced thickening and heaviness of the operated breast. This causes discomfort in women.
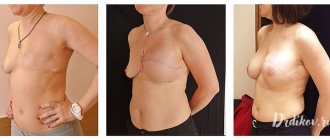
Complete removal of the mammary gland (radical surgery)
After breast cancer surgery, recovery is complicated not only by somatic, but also by psychological problems faced by both patients and their attending physicians. All complications are usually divided into early and late (delayed).
Early complications
Early complications after radical breast surgery:
1. suppuration of the surgical wound;
2. development of early bleeding;
3. fever;
4. failure of postoperative sutures;
5. psychological rejection of a new body with the development of depression or, conversely, aggression.
1. Development of postoperative bleeding.
If the ligature slips from a blood vessel, early postoperative bleeding may develop. The operated patient feels increasing weakness, dizziness, and a feeling of chilliness. The bandage applied to the seam is abundantly saturated with scarlet blood.
To prevent this complication, electrocoagulation of blood vessels has recently been used.
2. Fever.
The feeling of chills associated with an increase in body temperature is a frequent companion of the postoperative period. This condition is associated with a violation of the integrity of tissues, the development of an inflammatory process in them, and the body’s active attempts to cope with this inflammation. The “depressed” the state of the immune system, the less pronounced this condition. However, such a reaction is not a good prognostic sign.
3. Failure of postoperative sutures.
Usually detected after patients begin to walk or actively move their arms. Clinically, the complication is manifested by pain in the area of the surgical suture, blood leakage and inflammatory processes. The woman's body temperature rises, and the skin near the seam turns red and becomes hot.
4. Psychological rejection of the new body.
Complete removal of one breast is a serious psychological problem for every woman. That is why, before surgery (during the period of preoperative preparation) and after breast cancer surgery, close cooperation with a psychologist is necessary. This specialist will help every woman set the right priorities and make it clear that saving life is above all, and the beauty of the body can be restored by various methods (operative and non-operative).
Exoprostheses and special underwear after mastectomy
Exoprostheses are artificial overlays made of soft materials. They imitate the shape and size of the patient's real breasts. Exoprostheses are selected individually for each woman and are worn continuously after the permission of the attending physician. A correctly selected exoprosthesis will give a woman confidence, and will also become a therapeutic and prophylactic means of rapid post-operative adaptation.
The exoprosthesis compensates for weight imbalance, preventing secondary body deformations such as curvature of the spine, drooping shoulders, and poor posture. It is also worth noting the importance of special underwear that will secure the exoprosthesis. Special bras are worn together with exoprostheses. They provide safety and comfort when wearing exoprostheses.
The straps of special bras are padded, widened in the shoulder area, do not cut into the skin, and reduce pressure on the shoulders, preventing lymphedema. The underwear should fit tightly so that the prosthesis does not change position when moving and bending.