- Causes
- Diagnostics
- Kinds
- Surgery
- Therapeutic treatment
- Video
- Photo
- Main
Micromastia is a pathology of the development of one or both mammary glands, manifested in the form of their insufficient development. Micromastia can accompany a woman from adolescence, but also develops after breastfeeding, weight loss and as a result of aging .
Underdevelopment of the mammary glands can be detected only after puberty is completed, that is, at 16–17 years of age. In the rarest cases, examination reveals that there is a complete absence of glandular tissue in the mammary glands; this developmental pathology is called amastia, it can be either one-sided or bilateral and is a special case of micromastia. Do not forget that the shape and size of each woman’s breasts are individual, just as her weight, height and physique are individual, which must be taken into account when diagnosing micromastia, because the breasts should look natural and harmonious. So, with a height of 160 centimeters and a weight of 48 kilograms, a woman will look excellent with size “B” breasts , but a larger size of mammary glands will not decorate her, but will disrupt the proportions of her graceful figure. Although, many women can only dream of breasts of this size: according to statistics, almost 30% of women are not without reason dissatisfied with the size of their mammary glands; moreover, they consider small breasts to be the cause of all their misfortunes.
Girls who “hate” their small breasts should follow the example of British actress Keira Knightley, who is rich, famous and in demand in her profession, despite the lack of a magnificent bust.
Table of contents
- Etiology and pathogenesis
- Clinical manifestations
- Principles of treatment
Gynecomastia in men is a benign enlargement of the male breast (usually bilateral, but sometimes unilateral) resulting from proliferation of the glandular component of breast tissue. Gynecomastia should be distinguished from pseudogynecomastia ( lipomastia ), which is characterized by fat deposition without proliferation of the glandular component.
In our company you can purchase the following equipment for the treatment of gynecomastia in men:
- VASER (Solta Medical)
According to data on requests for medical help, gynecomastia in men most often occurs for the following reasons:
- Medicines - 10–25%
- Persistent pubertal gynecomastia - 25%
- Idiopathic gynecomastia (no reason) - 25%
- Cirrhosis or chronic digestive disorders - 8%
- Primary hypogonadism - 8%
- Testicular tumors - 3%
- Secondary hypogonadism - 2%
- Hyperthyroidism - 1.5%
- Chronic renal failure - 1%
Types of micromastia
Micromastia can be unilateral, when only one of the mammary glands is underdeveloped, and bilateral, if both glands are underdeveloped. In addition, types of pathology are distinguished depending on the cause of the disease:
- Congenital micromastia , caused by heredity and developmental disorders of the fetus, is usually combined with other congenital diseases.
- Primary micromastia , the appearance of which is associated with hormonal problems;
- Secondary micromastia is a pathology that develops as a result of age-related changes, breastfeeding, sudden weight loss or exposure to other external factors.
- Aesthetic micromastia only causes a woman moral discomfort, since it is not accompanied by changes in hormonal levels and congenital malformations.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The normal ratio of androgen (testosterone) to estrogen production is 100:1, and their concentration in the bloodstream is 300:1. Gynecomastia occurs as a result of a change in this balance in favor of estrogens . Another cause of the disease is an increase in the sensitivity of the glandular tissue of the breast to the normal level of estrogen circulating in the blood.
Estrogens cause hyperplasia of the ductal epithelium, their elongation and branching, proliferation of periductal fibroblasts and increased vascularization. The histological picture of the male breast as a whole becomes similar to the female mammary gland ( Fig. 1 ).
Estrogen production in men occurs primarily through the conversion of androgens (testosterone and androstenedione) to estradiol and estrone by the enzyme aromatase , primarily in muscle, skin, and fat tissue. The testes produce 6–10 mg estradiol and 2.5 mg estrone per day. An increase in estrogen production and/or tissue sensitivity to it can occur in one of two locations:
- In the testes - associated with tumors or ectopic production of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). The latter option occurs with extragonadal gonocytomas, as well as with metastases of lung, kidney and gastrointestinal cancer.
- In the periphery - associated with increased aromatase activity in chronic liver diseases, digestive disorders, hyperthyroidism, adrenal tumors or familial gynecomastia.
Physiological gynecomastia is observed in newborns, adolescents and the elderly. This condition usually does not require treatment (except in cases of excessive breast hypertrophy). For example, pubertal gynecomastia ( Fig. 2 ) in 90% of patients goes away on its own within a period of several weeks to three years.
Pathological gynecomastia is caused by an increase in the production of estrogens and/or an increase in the sensitivity of tissues to them, as well as a decrease in the production of androgens and/or a decrease in the sensitivity of tissues to them. In addition, gynecomastia can be idiopathic , that is, for no apparent reason. This diagnosis is made after a complete examination of the patient, when the provoking factor cannot be identified.
Causes of pathological gynecomastia:
- Testicular injury - the damaged organ produces androgens worse.
- Viral orchitis - an inflammatory process in the testicle reduces the production of androgens.
- Congenital anorchia - the absence of testicles introduces an imbalance in the antrogen-estrogens ligament.
- Malignancies that increase serum human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels.
- Pituitary tumors or abnormalities leading to hyper- or hyposecretion of luteinizing hormone.
- Hyperthyroidism - gynecomastia is caused by increased aromatase activity and increased levels of sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG).
- Chronic digestive disorders - cause a decrease in the level of gonadotropin and testosterone compared to estrogen. Moreover, after normalization of nutrition, the patient’s condition may worsen due to an accelerated increase in the production of estradiol compared to testosterone.
- Klinefelter syndrome is a hereditary disease characterized by the presence of small, dense testicles and gynecomastia in men.
- Kallmann syndrome is a combination of hypogonadism with olfactory disorders and insufficient secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
Some drugs can cause gynecomastia in men - antiandrogens (ketoconazole, finasteride, spironolactone), cytostatics (methotrexate), antihypertensive drugs (digoxin, amiodarone), hormonal drugs (phenothiazine derivatives), anti-infectives (isoniazid, metronidazole), drugs (amphetamines, methadone) etc.
Rice. 1. Differences between normal male breast structure ( left ) and gynecomastia ( right ). With gynecomastia, in addition to fat and muscle tissue , hyperplastic glandular tissue ( glandular tissue ) is noticeable (Mayo Foundation)
Rice. 2. Pubertal gynecomastia (www.medscape.com)
Aesthetic parameters of breast perception
Ideally, the breasts should be in the shape of a cone or hemisphere. Its base should be on the chest wall, and the protruding part should be the nipple. When drawing an imaginary line through the nipples, an axis of the mammary gland should be formed, on both sides of which it is evenly convex and has the same weight. The ideal breast has a small interbreast space, the side part of the gland is close to the edge of the torso or protrudes beyond it (due to this the waist appears thinner), a natural shape with a full lower part. In this case, the diameter of the nipple should be 0.8 cm, and the areola - 3.5-4.5 cm.
Clinical manifestations
Generally speaking, gynecomastia in men is manifested by enlarged breasts. In this case, one should distinguish between true gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia.
Pseudogynecomastia occurs in overweight men. In this case, fat deposits are found only in the subareolar area (around the nipple), on both sides. Over time, such breasts do not change shape or size, unless there is a significant increase in aromatase activity in the adipose tissue - then true gynecomastia can occur.
Differential diagnosis of these conditions is carried out as follows. The patient is placed on his back with his hands behind his head. Then the doctor places the thumb and index finger on the outside of the nipple opposite each other, as if he wants to pinch it. Next, he begins to slowly bring his fingers together—to “pinch.” With true gynecomastia, a glandular mobile mass characteristic of the female breast will be felt in the area of the areola. With pseudogynecomastia, the moving mass is not felt.
If you suspect gynecomastia in a man, you should evaluate his appearance (eunuch-like habitus), examine the testicles (reduction in size, pronounced asymmetry, etc.), and look for signs of chronic diseases of the liver, thyroid gland or kidneys.
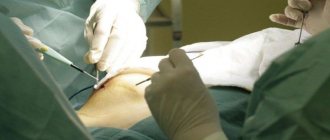
Surgical treatment of micromastia
Changing the shape of the mammary glands surgically is called mammoplasty; patients suffering from micromastia undergo endoprosthetics of the mammary glands (silicone implants are inserted). It is worth knowing that injections of biogels into gland tissue are absolutely not suitable for these purposes (indeed, they are prohibited!) , but there is a hyaluronic filler designed specifically for increasing the volume of the mammary glands, buttocks and calves - Macroline (Sweden), injections of which will help ( albeit temporarily) increase your bust. Mammoplasty is performed by a plastic surgeon and only for patients who have reached the age of majority.
In each case, the specialist individually determines where exactly the implant will be placed and selects the incision site taking into account the characteristics of the constitution - this could be the armpit, the perimeter of the areola, the area under the mammary gland, or even the navel. Usually the endoprosthesis is placed directly under the mammary gland, although it is often installed under the muscle located below.
Video - Gynecomastia in men
VASER
Plastic surgeons about the VASER technique and training course
Body contouring and surgical treatment of cellulite using VASER-associated liposuction.
VASER
Master class by Alfredo Hoyos Total Definer at the Osnova clinic
On April 26-29, 2020, a master class by Alfredo Hoyos was held on body contouring and lipotransfer in one operation.
Z Wave | ZLipo Med
Combination of Z Lipo and Z wave devices (Zimmer)
The RUWT procedure, carried out immediately after the end of the cryolipolysis procedure, increases the effectiveness of the latter by 2 times.
All Videos
The main thing about micromastia
| Question | Answer |
| Synonyms | small breasts. |
| Causes | heredity, hormonal imbalance, age-related changes. |
| Symptoms | underdevelopment or absence of glandular tissue. |
| Surgery | mammoplasty surgery (installation of implants). |
| Drug treatment | use of hormonal drugs, including birth control pills. |
| Nutritional supplements | Dietary supplements based on phytoestrogens. |
| Cosmetic preparations | breast enlargement creams. |
| See a doctor | gynecologist, mammologist, surgeon. |
Characteristics of breast implants
All implants have a shell: smooth or textured. Its function is to hold the filler. In addition, it plays an important role in engraftment. It must be strong to withstand all loads, and at the same time soft and thin so as not to injure surrounding tissues. Most modern dentures have a textured surface. It comes into contact with a large number of surrounding tissues, due to which the implant takes root faster and better, and the risk of complications is significantly reduced.
Implants can be round or teardrop-shaped. Teardrop-shaped are anatomical prostheses. They look natural and suit most women. Most often, doctors prefer prostheses of this particular shape. But round implants are not bad either. In some situations, the surgeon may recommend using them. During the operation they can be given the desired shape.
The profile of the prosthesis is the ratio of the height and width of the base. The surgeon can choose implants with different profiles. It depends on what result the patient wants to get.
Today, implants are filled with a special gel. It is viscous, so even if the implant is damaged, it will not leak. This gel has several types of fluidity: soft, elastic and dense. There are also dentures that are filled with saline solution. There are also combined prostheses with 2 chambers. Moreover, one of them is filled with gel, and the other with saline solution. With saline implants, breast size can be increased or decreased by increasing or decreasing the volume of fluid in the implant. Double-chamber prostheses are most often used in reconstructive mammoplasty.
Expander implants are also used in reconstructive mammoplasty. During the operation, the doctor inserts them into the chest and fills them with saline solution. Thus, over the course of several weeks or months, the specialist creates a place for installing a silicone implant.
Principles of plastic correction of small breasts
Mammoplasty is one of the most popular procedures in plastic surgery. Every year, about 1 million girls around the world have their breasts enlarged. Thanks to mammoplasty, you can not only change the shape and give an aesthetic appearance to the breast, but also correct a defect such as micromastia. Treatment with mammoplasty is also carried out for breast sagging, asymmetry, hypertrophy or after removal of the mammary glands.
Most plastic surgeries on the breast are associated with breast enlargement. The majority of women who decide to undergo this operation have normal breast structure and no endocrine diseases, but their breasts do not correspond to modern ideals, which is why women can have difficult mental experiences.
Another group of people wishing to enlarge their breasts are women with initially normal breast size, which decreased after breastfeeding a child.
Endoprosthetics is possible only after breast growth has finished, that is, after 18-20 years. Before the operation, the patient must undergo a complete examination, after which the surgeon will take the necessary measurements and recommend implants of the most suitable shape and size.
At the moment there is a huge selection of implants of different shapes and sizes. During the operation, the doctor can only enlarge the breasts or, if the patient wishes, also perform a breast lift.
The result after surgery is influenced by the woman’s psychological state, the initial appearance of the breast, possible allergies or previous surgical interventions performed on the breast, and a tendency to bleeding or scarring. All these points are discussed with the doctor before the intervention.