A nevus is a special type of benign congenital skin formation, which in some cases affects, among other things, the mucous membrane and conjunctiva of the eye.
Sometimes this pathology in the literature is called a noncellular or melanocytic pigment spot. A problem arises due to the accumulation of a large amount of melanin in nevocytes.
These cells are difficult to influence by hormones or other substances. In appearance, they resemble melanocytes without corresponding processes.
Elimination of age spots in most cases occurs due to the need for aesthetic correction of a person’s appearance. However, in certain cases, this pathology provokes the development of complications, which requires the elimination of the formation for medical reasons.
Pigmented nevus: what is it, photo
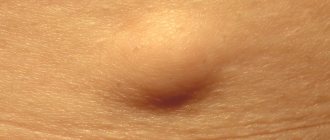
It's no secret that almost every person has moles on their skin. However, not everyone knows that a synonym for these formations is “pigmented nevus”. However, this concept is much broader. It includes not only small moles, but also age spots that reach large sizes. Nevi can be located on the skin, as well as on the mucous membranes and even on the iris of the eye. Formations consisting of melanocytes differ in size, thickness, shape and color. So, what is a pigmented nevus? Photos of such formations can be found in specialized literature on dermatology, cosmetology or oncology. Looking at pictures of different nevi will help you get an idea of their types. Despite this, to verify the origin of the mole, you need to consult a specialist.
In most cases, pigmented skin nevi appear in early childhood. Small brown formations that slightly rise above the surface of the epidermis are called moles. They grow almost imperceptibly and do not bother the baby in any way. Birthmarks are also classified as nevi. These formations are larger in size and have different shapes. They rarely rise above the surface of the skin. A child is born with these pigment spots, and they grow with him.
All nevi consist of a pigment - melanin, which gives color to our skin, iris and hair. The amount of this substance varies. The pigment content in the body is higher in dark-haired and dark-skinned people. The accumulation of melanin in one place leads to the formation of nevi. They can be located anywhere, including on internal organs and muscles. Pigmented nevus is a benign neoplasm that normally does not bother a person. Most often, birthmarks cannot be treated if they do not cause aesthetic discomfort. Several years ago it was believed that small pigment formations on the face, on the contrary, impart beauty. It is now known that not all moles are harmless. In cases where there is a risk of malignancy of a benign neoplasm, it should be removed.
Causes and characteristics of nevi
Doctors call all moles nevi. Regardless of the origin, the mechanism of formation of the growth corresponds to the mechanism of the appearance of a benign tumor.
Most nevi are formed from normal cells of the epidermis and dermis due to local accumulation in a small area of skin. In addition to structural cells, they necessarily contain melanocytes, which produce pigment that changes the color of moles. The color of nevi can be very different: from pink to dark brown.
It is worth noting that melanocytes in moles remain unchanged and produce the usual amount of pigment. There are simply too many of them in a small area, which leads to the concentration of this substance. This makes it very noticeable against the background of the rest of the skin. For this reason, nevi in fair-skinned people are pinkish or light brown, while in those with dark skin they are dark brown and black.
Moles can be congenital or acquired.
In the first case, they do not appear immediately after birth, but after some time. They need time to grow in size. Congenital moles, unlike acquired ones, grow with a person. Initially, they are tiny and almost invisible, but as the child grows, they become noticeable to the naked eye.
In the second case, nevi appear on a person’s skin throughout his life. Moreover, doctors are confident that there are no age restrictions for this process. Most moles appear on the skin during hormonal changes in the body. We are talking about puberty, pregnancy, menopause, etc. Under the influence of hormones, moles can change shape and color.
Most nevi are benign neoplasms. They are not prone to malignant degeneration. Actually, for this reason they are not touched unnecessarily.
In some cases, moles can become malignant and then begin to pose a serious threat to human health and life. Such neoplasms cannot be left without attention and treatment.
You should not think that any dark spot on the skin is a possible focus of cancer cells. In fact, the vast majority of skin cancers develop in areas of the skin that are devoid of visible growths.
Causes of nevi
All pigmented nevi of the skin can be divided into congenital and acquired. This classification is not scientifically based, since it is still unknown when exactly clusters of melanocytes are formed. This division is based only on the time of appearance of nevi. If areas of the skin become dark in color in early childhood, then the formations are considered congenital. Acquired nevi appear in adolescents or adults.
The causes of congenital age spots are unknown. It is believed that pathological migration of melanoblasts occurs during intrauterine development. Risk factors include illness during pregnancy, medications or other chemical exposures, and hormonal imbalances. A possible cause of the appearance of congenital nevi is considered to be genetic predisposition. This explains the appearance of “Mongolian spots” in children of Asian origin.
Acquired nevi are considered more dangerous, since the frequency of transformation of these neoplasms into cancer is higher. However, according to other data, all areas of pigmentation are formed at the stage of fetal development, and their appearance indicates the adverse effects of provoking factors. Regardless of this, the following causes of nevi are identified:
- Hormonal changes in the body.
- Skin infections.
- Solar insolation.
- Visit to the solarium.
- Skin damage.
In fact, the identification of such provoking factors is quite justified. Hormonal imbalance develops during puberty and pregnancy. During these periods, the incidence of moles is much higher. In addition, age spots often appear in women using hormonal contraceptives.
Chronic skin pathologies (atopic dermatitis, acne) and physical damage often provoke the appearance of pigmented nevi on the face, neck and shoulder area. The main reason for the appearance of moles is considered to be solar insolation. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation not only affects the occurrence of pigmentation, but also increases the risk of malignancy of formations. Therefore, people with problem skin should not be exposed to direct sunlight for a long time.
Reasons for education
Nevi are the growth of special skin cells (nevocytes) containing a huge amount of melanin pigment. In appearance, these formations are similar to small brown tubercles on the surface of the skin.
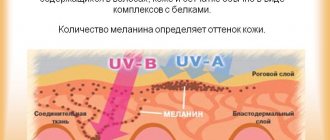
What is melanin and what role does it play in the formation of moles? This pigment is called a natural dye; it is found in the hair, brain, and eyes. Our appearance is determined by the amount of melanin, even how our skin tans, what color the tan will be - all this is thanks to the pigment.
The formation of a nevus is a very interesting process: melanocytes (special cells with processes) absorb the hormone thyroxine. After oxidation, this hormone turns into melanin, then penetrates the cells through the processes of melantocytes, accumulating there. The result of this process is the appearance of birthmarks of various sizes.
Why do you think we need melanin? It performs many functions necessary for our body:
- this pigment protects us from stress;
- helps cope with excessive emotionality;
- acts as an excellent antioxidant, helping to cope with various pathogenic factors that affect us.
The following factors contribute to the formation of congenital nevi:
- genetic predisposition;
- infectious diseases in pregnant women;
- the influence of various toxic substances, exposure of a pregnant woman to radiation, frequent stress.
How to get rid of closed comedones on the face? Learn traditional recipes and modern methods.
What causes stretch marks on legs and how to get rid of them? Read the answer on this page.
Therefore, future mothers, be attentive and careful during such an important period of life, take care of the baby, do not be nervous, and avoid the influence of negative factors.
The reasons for the appearance of moles in adulthood are:
- weakened immune system;
- pregnancy;
- dermatological diseases;
- failure of the endocrine system;
- use of certain medications;
- taking hormonal contraceptives;
- ultraviolet radiation.
Interesting! Caucasians are most susceptible to developing moles, especially people with fair skin, blue eyes and pink freckles.
Classification of pigment formations
Based on their histological structure, there are about 50 types of nevi. Of these, the most significant are 10 types of benign formations, differing in origin and clinical picture. Doctors distinguish 2 main groups of nevi, each of which includes several types of age spots. The classification is based on the risk of malignancy of the formation. The first group includes melanogenic nevi. The risk of malignancy of such formations is low. These include the following types of age spots:
- Papillomatous nevus. It differs in that it looks like melanoma: it has an uneven, bumpy surface and rises above the surface of the skin. The hair on this growth continues to grow, but changes color. Papillomatous nevus has a dark brown tint. The localization of such a mole is the torso, limbs and scalp.
- Mongolian spot. It has different shapes and large sizes. This congenital pigmented nevus occurs in most children of the Mongoloid race. It does not rise above the epidermis and disappears on its own by the age of 20.
- Halonevus refers to acquired benign skin formations. It has an oval or round shape. The peculiarity of this mole is that there is a light rim around it. Such a formation can be located on any part of the skin or mucous membranes. With age, the mole becomes lighter and disappears.
- Intradermal pigmented nevus. It is characterized by small size and peculiar localization: the neck area and skin folds. Appears most often during puberty. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, it can malignize into melanoma. A complex pigmented nevus has a similar structure. It is a small pigmented formation resembling a papule.
- Fibroepithelial nevus. This formation consists of connective tissue and rarely undergoes malignancy. It protrudes significantly above the surface of the skin and has a light brown or pinkish tint. This mole has a round shape and a smooth surface. The formation can be congenital, but more often occurs in older people.
Non-melanogenic nevi rarely become malignant, but they require observation. The lack of growth of such moles indicates a favorable prognosis.
Symptoms and signs of pigmented nevi
A neoplasm can be identified by the presence of external signs of spots:
- flat or protruding above the surface of the skin;
- yellow, brown, red, blue or black;
- rounded, symmetrical, with smooth, regular boundaries;
- the skin pattern remains on the surface; roughness, tubercles, papillae may be present, similar to the convolutions of the brain or a wart;
- if the accumulation of cells is located deep in the dermis, then hairs can grow on the surface of the nevus;
- sizes vary from a few millimeters to tens of centimeters;
- pigmented nevi can be soft or hardened to the touch;
- Most often the neoplasms are single, less often multiple. In the latter case, one of the moles is larger than the others.
Melanoma-dangerous skin nevi
Melanoma-dangerous nevi include benign skin neoplasms, the likelihood of which becomes malignant is high. Therefore, they require constant monitoring or radical treatment. Similar pigment spots include the following formations:
- Blue nevus of Jadassohn-Tiche. Despite the fact that it consists of differentiated pigment cells, the pathology refers to precancerous conditions. The blue nevus is small in size (up to 1 cm) and protrudes slightly above the surface of the epidermis. In some cases, it is represented by a nodule located deep in the skin. The formation has a purple or dark blue color.
- Borderline pigmented nevus. Refers to congenital formations. Such a mole protrudes above the surface of the skin and is dark in color. The color of the pathological area can be purple, brown or dark gray. The size of the nevus does not exceed 1.2 cm. The name of this formation is due to the fact that the pigment cells of which it consists are located on the border of the epidermis and dermis.
- Giant nevus. This pigment spot is large (more than 20 cm) and can occupy a significant area of the body. A giant nevus has a rough surface and dark color. Increased hair growth is observed in the pathological area of the skin.
- Nevus of Otta. A disease characterized by the presence of bluish spots on the skin of the face, lips, and mucous membranes of the eyes. It is often a congenital defect, but can also occur during adolescence. The risk of developing such a disease increases significantly among representatives of the Mongoloid race.
- Clark's nevus. It is characterized by asymmetry of contours, a flat surface and different colors. The size of the skin defect ranges from 5 mm to 6 cm. The nevus can be located in the back, along the back of the thighs, or around the genitals. It refers to dysplastic formations that are highly likely to transform into oncological pathology.
Melanoma nevi are a large group of pathological conditions that require diagnosis and treatment. In some cases, when removal of the formation is impossible, constant prevention of malignancy is necessary.
Types of moles
There are several classifications of nevi. In our country, doctors prefer to use two of them: histological and potential threat.
The first is based on understanding from which cells the neoplasm grew . The second divides all moles into melanoma-hazardous and melanoma-safe. That is, no harm can be expected from some neoplasms, while others have some chance of turning into malignant ones.
According to histological classification, nevi are divided into the following types:
- Borderline. Formed by border cells between the upper and deep layers of the skin. Outwardly it looks like a spot with a slightly raised edge. Usually colored dark gray or brown. A borderline nevus can reach 3 mm in diameter.
- Epidermal. This neoplasm is based on epidermal cells. It has the appearance of an elevation with clearly defined edges. Can be painted in different colors.
- Intradermal. This nevus is formed from cells located deep in the skin. Outwardly, it looks like a hemisphere, slightly raised above the surface of the epidermis and painted in dark colors. The size of such a neoplasm can reach 1 cm in diameter.
- Seborrheic. This type of mole looks like a flesh-colored spot with a rough surface. Very often it is formed in children due to improper development of skin cells. Moreover, the reasons for the abnormal development have not yet been clarified. Seborrheic moles can be either congenital or acquired.
- Difficult. This neoplasm consists of deep and superficial layers of the skin. Outwardly, it looks like a flat tubercle. It happens both individually and in groups.
- Epithelioid. This mole looks very similar to melanoma, but it is not. Moreover, she is never reborn. However, if it is present, doctors warn the patient about the high risk of developing skin cancer.
- Galonevus. Outwardly, it is an ordinary brown spot with a wide light rim. Such formations appear on the skin of people over 30 years of age. Over time they may increase or decrease. In some cases, they disappear completely , but after them a white spot remains on the skin.
- Mongolian spot. This is a single formation, detected at birth in the buttocks or back. It can be painted in different colors. Its surface rises slightly above the skin.
- Blue mole. It got its name from its color. This is an epidermal neoplasm in which melanocytes produce a bluish-black pigment. Externally, it looks like a small nodule with a diameter of 1 to 3 cm. It appears mainly on the lower back, buttocks, feet and hands.
- Dysplastic. It may also be called Clark's nevus. This is a single or group growth of an oval or round shape with uneven edges. Its color is red or light red. In the very center, the spot has a small protrusion above the surface of the surrounding skin. The diameter of the formation is small - 6 mm.
- Papillomatous. This is a type of epidermal mole. Its surface consists of irregularities and outgrowths of the skin, which is why it is very similar to cabbage. It has a brownish or pinkish color. Because of its appearance, it is often confused with pedunculated papilloma.
- Fibroepithelial. This type of nevus is quite rare. Its peculiarity is a large number of connective fibers inside the neoplasm. It always feels soft and elastic to the touch.
- Pink melanocytic mole. It most often appears in people with fair skin and can be pink or light red in color. Sometimes it is colorless and stands out only because it protrudes above the surface of the skin.
- Verucous. This neoplasm is also called warty. It has the shape of an elongated dark brown spot. Formed from epidermal cells. Most often manifests itself in childhood.
Congenital and acquired moles are very similar in appearance. It's easy to confuse them. But doctors know one external sign that allows them to be distinguished. Congenital moles always have a diameter greater than 1.5 cm.
Nevus of the eye: features
The accumulation of melanocytes is observed not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes. An example is pigmented nevus of the eye. Another name for this formation is a benign choroidal tumor. It belongs to congenital pathologies, but begins to manifest itself only at 10-12 years of age. This is due to the fact that at this age there is an increased formation of pigment. There are 3 types of choroidal nevi:
- Stationary.
- Progressive.
- Atypical.
All of them belong to benign eye tumors, but under the influence of provoking factors they tend to malignancy. Like skin lesions, choroidal tumors are characterized by discoloration. So, what are pigmented nevi of the eye? Photos of such tumors are abundantly presented in the literature for ophthalmologists and oncologists, as well as on medical websites. Nevi are small spots in the eye, the color of which differs from the color of the iris.
Skin nevi such as hamartoma (sebaceous, verrucous, Becker's).
Skin hamartomas are formations that appear from errors during embryonic development. They are characterized by an incorrect arrangement of various types of cells (epidermis, vascular glands, etc.) relative to each other and with impaired cell maturation.
Sebaceous nevus or seborrheic.
A sebaceous nevus (seborrheic) is a large mole with a disturbed structure of many types of cells at once: epidermis, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, sweat glands. Noticeable already at birth or discovered later. The size of a sebaceous nevus is from 1 to 6 cm. The surface is often smooth, lumpy, waxy with a yellowish or orange tint. There is no hair. With age, from flat it becomes more and more convex and lumpy. Most often found on the head, upper chest. The main danger of such moles is the increased likelihood of developing other skin tumors on their surface. Most often these are benign trichoblastoma and syringocystadenoma of the skin, but many other rare tumors also occur. Malignant basal cell carcinoma develops with a frequency of 1 to 10% according to various authors. Removal of a sebaceous nevus with a laser or cryodestruction significantly improves the cosmetic result, however, it does not completely eliminate the appearance of secondary tumors. Removal with a scalpel can lead to disfiguring scars, but it eliminates the appearance of secondary formations as much as possible.
In the photo there is a seborrheic or sebaceous nevus in the shape of the letter V. It can serve as a source of malignant and benign tumors.
The photo shows a blue nevus of the hand. It is rather gray in color. Firm to the touch.
Warty skin nevus.
As mentioned above, this formation should not be confused with papillomatous nevus. A verrucous nevus is essentially a hamartoma that affects only the epidermis. Despite the fact that it is formed during embryogenesis, it resembles a wart not only externally, but also under a microscope. The mole has the appearance of tubercles and plaques with horny overlays and processes. The tubercles often form lines. A warty nevus does not increase the risk of cancer and does not develop into anything. Mole removal is possible using laser, liquid nitrogen, electrocoagulation and radio wave method.
Becker's nevus.
Becker's nevus is another hamartoma that affects hair follicles, skin fibers and blood vessels. There are very few melanocytes in it; the color is due to a change in the orientation of the dense fibers of the skin. The size of the mole is from 10 to 15 cm. Becker's nevus is divided into a colored part and a part covered with hair. They do not completely overlap each other; in some places one or the other may be present. It differs from congenital nevus in the smooth surface under the hair, the absence of tubercles and seals. With age, the mole becomes more noticeable due to hair growth and darker coloring. Does not increase the likelihood of skin cancer, but can be combined with underdevelopment of muscles and skeleton on the side of the formation. Cosmetic treatment to reduce hair growth and color intensity is acceptable. Complete removal for large sizes is impractical.
Types of choroidal tumors
A stationary nevus of the eye is characterized by clear or feathery contours. It has a greenish or gray color. The shape, size and color of the formation do not change throughout life. Such tumors practically do not become malignant.
A progressing nevus is distinguished by the fact that it has a yellow rim around the main accumulation of pigment. The color and shape of the defect may change. In addition, such nevi increase in size, which increases the risk of vascular compression and a decrease in visual fields. Therefore, this type of pathology requires medical supervision.
Atypical nevi have a poor prognosis. Therefore, the slightest change or growth requires urgent surgical treatment. Such formations are light in color and are accompanied by deterioration of vision.
Diagnosis of pigmented tumors
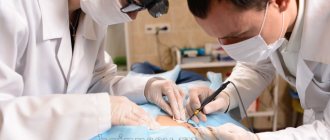
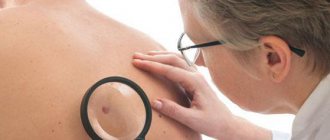
If the nevus changes or appears, you should consult an oncologist. He will be able to make a differential diagnosis between various skin tumors and choose treatment tactics. An important study is dermatoscopy, which allows you to see the pigment spot under high magnification. If a tumor is suspected of malignancy, a complete laboratory diagnosis, chest x-ray and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity are performed. To establish the histological type of nevus, wide excision of the formation is performed. A biopsy is performed only in emergency situations, as it can lead to malignancy and spread of tumor cells.
Diagnostic methods
It is impossible to accurately determine the type of nevus on your own, since there are several dozen varieties. A dermatologist or oncologist can do this based on the following data:
- taking anamnesis;
- visual inspection;
- dermatoscopy using a magnifying glass and camera;
- biopsy - excision of part of the material and examination of it under a microscope;
- SIAscopy - determination of the location of blood vessels and the amount of melanin, as well as collagen and hemoglobin. This is one of the most accurate and reliable analyzes that assess the condition of the cells in the deep layers of the skin. All results are displayed on a computer monitor in the form of a three-dimensional image. For
- Dynamics determinations use the graphics overlay method;
- studying the surface of a mole directly on the body under a fluorescent microscope; laboratory diagnostics - detection in the blood of tumor markers that appear only in malignant tumors.
⛔ If you suspect melanoma, it is strictly forbidden to do a biopsy of a mole or a scraping for preliminary analysis: tumor cells will instantly disperse throughout the body
The most dangerous type is melanocytic nevus, which is considered a prerequisite for the development of melanoma, a malignant formation. According to statistics, in the Russian Federation melanomas are diagnosed in 4 cases out of 100.
Pigmented nevus: treatment
Photos depicting nevi can be found in many sources on relevant topics. However, only a doctor can definitively determine what kind of tumor it is. Treatment of pigmented nevi is not always carried out. In cases where the mole is harmless and does not cause cosmetic discomfort, dynamic observation is indicated. Nevi, which are often subject to trauma, must be removed. You can remove the formation using liquid nitrogen or a laser. If there is a risk of malignancy, surgical removal of pigmented nevi is required. In this case, they retreat 2 cm from the spot and capture healthy tissue. The resulting material is sent to the histology laboratory.
Possible complications with nevi
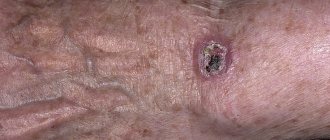
The main complication of nevi is the transformation of normal pigment cells into melanoma. The following signs of malignancy are distinguished:
- Sudden increase in education.
- Bleeding or ulcers.
- Change in color of a mole.
- Painful sensations.
- Itching and burning.
If any of these symptoms are present, you should immediately contact an oncologist and have the tumor removed. Only timely surgical treatment will help avoid cancer.