Causes
Many patients wonder why inflammation occurs under or on the skin? The reasons are usually the following factors:
- penetration of various infectious agents under the skin, which are often pathogenic microorganisms;
- exposure to various physical irritants followed by the addition of an infectious process;
- various mechanical injuries, such as bruises, sprains, can lead to a purulent process;
- Contact with chemical agents is another common cause of skin problems.
Doctors believe that another key factor that is necessary for the development of infection under the skin or on it is a decrease in the body’s immune defense. Often, if immunity is not reduced, the disease simply does not develop even if the infection is in the affected area.
Varieties
Neoplasias have their own classification, since all their varieties have different properties, nature and structure. Depending on these criteria, the following types of skin tumors are distinguished:
- Basalioma is a neoplasm of a malignant nature, formed from epithelial cells and localized mainly on the face or on the skin of the neck. Read more about basalioma→
- A wart is a benign neoplasm that occurs due to infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). It often occurs in young people, children and the elderly, and is localized on the face, soles of the feet, chest, buttocks, armpits, neck and scalp. Read more about warts→
- Hemangioma is a red neoplasm formed from blood vessels. They are localized on the face, neck, skin behind the ear, but can also be located on the arms and epidermis of the legs. Read more about hemangioma→
- Lipoma or wen is a benign skin tumor formed from fat cells. It often forms in older people and is located in the legs, arms, and head.
- Keratoma is a group of benign neoplasms of gray or black color, formed from cells of the dermis, and located on the arms, upper legs, neck, different parts of the chest and torso.
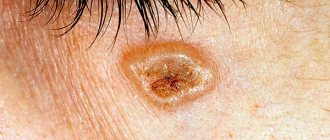
- Cutaneous horn is a precancerous neoplasm formed from horny masses and localized mainly on the skin of the face.
- Condyloma is a benign growth that occurs due to HPV infection. It is located in the buttocks, neck, armpits, and mucous membranes of the genitals. Read more about condyloma→
- Melanoma is a malignant skin tumor formed from melanocytes - pigment substances responsible for the natural color of the epidermis.
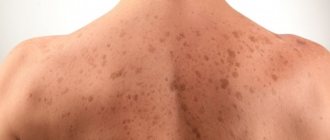
- A nevus or mole is a benign neoplasm that appears on the skin of a child, but can also develop in adults. It is formed due to the accumulation of melanocytes and is localized in the neck, back, chest, upper legs, arms, and scalp.
- Papilloma is a skin growth that is benign in origin and is a consequence of the development of human papillomavirus infection. Such neoplasms can be localized on the inner thighs, in the buttocks, on the face, arms, and neck.
- Fibroma is a benign skin tumor of a grayish or pinkish color, formed from mature cells of connective tissue structures.
- Queyra's erythroplasia is a tumor that develops in people over 60 years of age, localized in the genital area and having a bright red hue.
Symptoms
If an area under or on the skin becomes inflamed, patients usually complain of a number of characteristic symptoms, which are difficult to confuse with other diseases. Noteworthy:
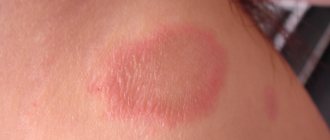
- the presence of local redness, strictly limited, without spreading in the initial stages;
- the presence of pain, which can be felt both at rest and when, for example, pressing on the problem area;
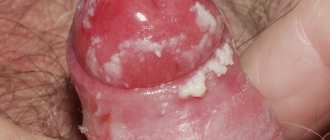
- formation in the affected area of a specific red protrusion, at the end of which there may be a white blotch (indicating the presence of a purulent core);
- local hyperthermia (increased skin temperature);
- with active processes affecting large areas, general symptoms may appear, such as increased body temperature, weakness, malaise, nausea, etc.
If general symptoms appear during infection, it is recommended to consult a doctor immediately, as this indicates the progression of the disease.
Kinds
Doctors today distinguish various types of skin inflammation. The division occurs based on the prevalence of the process, the location of the pathological focus and other data.
Abscess
An abscess is a purulent-necrotic process, which is often accompanied by the formation of a cavity, which is limited to the capsule.
Acne
Acne is a disease that most often develops on the face, accompanied by the formation of purulent foci due to improper functioning of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles. Read more about acne→
Hidradenitis
Hidradenitis is an inflammation not of adipose tissue, but of the sweat gland, which is often accompanied by the formation of an abscess (the sweat glands in the armpits and groin are mainly affected if the patient neglects the rules of hygiene). Read more about hidradenitis→
Atheroma
Atheroma is a type of inflammation under the skin that develops as a result of blockage of the sebaceous gland and is considered a tumor-like process.
Impetigo
Impetigo is a type of infectious skin lesion in children and adults, which is provoked by contact with streptococci or staphylococci. Read more about impetigo→
Carbuncle
A carbuncle is a large abscess, most often located on the surface of the skin (several hair follicles are involved in the pathological process).
Felon
Panaritium is an inflammation of the skin that affects only the fingers or toes (the upper extremities are more often affected; the nail plate may be involved in the process).
Paronychia
Paronychia is the localization of an infectious process in the area of the nail fold.
Pyoderma
Pyoderma is a complication that can result from dermatitis, minor injuries and skin cuts of various origins if an infection settles on the wounds.
Bedsores
Bedsores are necrotic changes in tissue due to constant pressure placed on them, often accompanied by a purulent process.
Pimples
Pimples are small formations on the skin filled with purulent contents.
Sycosis
Sycosis is an inflammatory process in the hair follicles that occurs chronically, with regular relapses.
Streptoderma
Streptoderma is an infectious skin disease caused by streptococci, which mainly affects young children.
Trophic ulcers
Trophic ulcers are initially not an infectious, but a trophic process, which over a long period can be complicated by the addition of pathogenic microflora.
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is the involvement of hair follicles in the pathological process, which is accompanied by the formation of small heads on the skin filled with pus.
Furuncle
Furuncle is a melting of the sebaceous gland and hair follicle, which is purulent-necrotic in nature.
What complications can there be?
At first glance, harmless growths can lead to serious complications. The most dangerous of them is the degeneration of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one. At the base of the leg there are roots, which, if improperly removed, can transform into metastases. Also, the risk of cancer increases if the papilloma is injured.
Growths do not always provoke serious changes in the body. But increased vigilance is required when they occur.
We advise you to read: What to do if papillomas appear during pregnancy
After all, the course of the disease can become complicated in some cases.
- If the papilloma is injured, bleeding may occur. If left unchecked, serious blood loss occurs.
- The papilloma may increase in size, which will create increased inconvenience for the woman. This increases the risk of injury to the tumor.
- In case of activation of HPV, a proliferation of filamentous papillomas is observed, which merge into a large lesion.
- A neoplasm that is injured may begin to fester. The risk of purulent infection of the body increases.
Therefore, doctors often suggest that the patient remove skin growths. This will avoid possible complications.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is often not difficult, since the pathological focus is located close to the surface of the skin and is visible to the naked eye. To make a diagnosis, a doctor usually needs to visually identify the pathological area.
Additionally, if necessary, it is possible to take discharge and ulcers with subsequent examination to identify the causative agent. Once the causative agent is known, antibiotic susceptibility testing is recommended to improve the effectiveness of therapy.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine offers to fight pedunculated papillomas in simple and accessible ways:
- Garlic. Prepare garlic paste. Lubricate the skin around the papilloma with cream, apply the paste to the formation, seal it with an adhesive plaster and leave for five hours. Do this daily until the papilloma dries.
- Celandine. To remove warts, use a freshly picked plant stem. Juice will be released at the cut site, which should be applied to the papilloma, being careful not to get it on healthy skin. It is best to lubricate it with cream first. Repeat the procedure every other day.
- Onion. Fresh juice is used to remove the formation. To do this, the onion is turned into a paste and applied to the papilloma, as is the case with garlic. Onion treatment will last longer.
- Iodine. To remove papilloma, it is recommended to lubricate it with iodine daily until it dries.
- Propolis. You will need an alcohol tincture of propolis, which you can buy at a pharmacy or prepare yourself. Soak a cotton ball in the tincture, apply it to the papilloma and fix it with a band-aid for two hours. Carry out the procedure daily.
- Castor oil. Lubricate the formation with it every day until it dries.
General principles of treatment
Purulent skin pathologies are not always easy to treat. In this regard, it is recommended to use different tactics for treating children and adults.
Children
If we are talking about a child, then it is recommended to start therapy with mild remedies that will cause minimal damage to the body. Preference is given to conservative treatment, as it is easier to tolerate. Recommended:
- local antibiotic therapy aimed at eliminating the infection;
- active vitamin therapy;
- prescribing a diet that will reduce the likelihood of relapses;
- physiotherapeutic and rehabilitation measures.
Adults
In adults, as in children, conservative treatment is preferred. It is possible to use antibiotics not only locally, but also systemically to achieve the best therapeutic effects. Symptomatic therapy is also carried out, aimed at eliminating signs of the disease that cause inconvenience to the patient (pain relief, dressings, eliminating symptoms of intoxication during an extensive process, etc.).
If the area of inflamed skin is very large, and the pus cannot be removed using conservative methods, surgical intervention is used.
Operating procedures
To restore the condition of the skin and get rid of papillomas on the leg, surgical intervention is recommended. The procedure can only be authorized by a doctor who first examines the condition of the tumors and determines the type of HPV that caused the skin manifestations.
Often women undergo surgery to correct a cosmetic defect. But sometimes tumors get in the way, constantly clinging to clothes. Removal is carried out using several modern minimally invasive methods:
- During cryodestruction, pedunculated papillomas are frozen with liquid nitrogen, which has a very low temperature.
- With laser coagulation, excision is performed with a device that distributes laser beams. The method is widely used as it does not leave marks on the skin. Wounds heal quickly, and papillomas do not form again.
- Removal of growths is carried out using electrocoagulation.
- Often, tumors are excised using radio waves.
- An unpleasant but effective method is chemical exposure. Papilloma is burned along with the affected tissues with the help of acid-containing and alkaline substances.
In some cases, the patient may be recommended traditional surgical excision. During the procedure, the papilloma itself is eliminated, as well as the tissues surrounding it. But the method has a significant drawback: scars may remain on the body. Therefore, it is used on areas of the body hidden under clothing.
Electrocoagulation is a minimally invasive method for removing papillomas
Prevention
Since purulent inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous tissue is often infectious in nature, to prevent pathology it is recommended:
- promptly treat all skin lesions;
- treat chronic diseases that can cause skin damage with the subsequent development of an infectious process;
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- Perform manicures and other similar manipulations with care.
An inflamed area of skin is always unpleasant, especially if the process is accompanied by the release of pus. A timely visit to a doctor will allow you to stop the process in time, preventing it from progressing too much.
Show all text
Skin neoplasms
Skin neoplasms are divided into several main types: benign, precancerous and malignant.
Most often, these are smooth single formations that resemble a tumor, no more than 1 cm in diameter. These dense skin protrusions of a red-brown hue are more common in young people, as well as in women. Any mechanical injury can provoke their inflammation, which can result in a bleeding ulcer.
It is a congenital or acquired vascular tumor that can occur in people of completely different ages, but most often occurs in children. Depending on the depth of the location of the vessels, it has many varieties: flat, stellate, branched. Such formations are treated in various ways: using cryotherapy, laser or photodestruction.