9750
0
A malignant tumor that is localized in the basal layer of the skin and spreads to healthy skin is called melanoma. Its development is ensured by pigment cells that have degenerated into cancer cells.
This disease appears due to the degeneration of an ordinary and harmless (at first glance) nevus or mole on various parts of the human body or in the mucous membrane. It proceeds aggressively and quickly. Melanoma affects both men and women aged 35 to 50 years.
Doctors are not always able to diagnose this disease at an early stage. It is detected when metastasis appears. This is why it is difficult, and in some cases impossible, to cure melanoma.
What it is
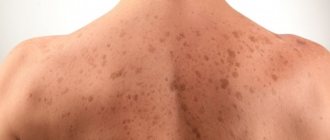
Melanosis, or melasma, is the formation of coffee-colored pigment spots on the skin.
Pathology most often occurs in women against the background of hormonal imbalance, when the concentration of progesterone and estrogen in the body does not correspond to the norm.
Pigment spots form in women:
- carrying a child;
- using oral contraceptives;
- resorting to hormone therapy during menopause.
Pigment spots are formed under the influence of sunlight. They occur in women living in southern countries. Summer is a period of risk. Increased solar activity provokes the development of pigmentation on epithelial tissues.
Stages and types of disease
In medical practice, there is a definition for staging skin melanoma. It is very difficult for a person without medical education to understand the classification of the disease, but we will try to tell you about the stages in simpler language.
Stages of skin melanoma:
- According to Clark, when the tumor penetrates the layers of the epidermis.
- According to Breslow, in this case the thickness of the formation changes.
In the picture presented you can see that the Clark classification consists of 5 degrees, each of which has its own characteristics in the clinical picture.
The prognosis for skin melanoma according to the second classification is difficult. The fact is that according to Breslow there are only 4 stages. But if you look closely at the picture, you will notice that according to Breslow there are two stages with stage I and stage II, everything depends on the thickness of the primary melanoma.
Causes
Doctors have identified several factors that cause melanosis of the skin. The causes of pathology include:
- concomitant diseases affecting the pituitary gland, ovaries and adrenal glands;
- impaired functioning of the thyroid gland;
- intoxication of the body with toxic substances - arsenic, resins and other aggressive hydrocarbons;
- infectious diseases prone to progression - syphilis, tuberculosis, dysentery, malaria;
- pediculosis in severe form with damage to the mucous membranes;
- avitaminosis;
- poor nutrition, leading to disruption of metabolic processes in epithelial cells;
- heredity (pathology is transmitted mainly from mother to child).
The causes of melasma are interconnected with the type of pigmentation, concomitant diseases and genetic predisposition to certain pathologies. When drawing up a treatment regimen, the doctor selects drugs that can combat the cosmetic defect and the root causes of the disease.
Treatment
Treatment of skin melanoma should be comprehensive.
Medication methods include:
- Chemotherapy.
- Hormonal therapy.
- Immunotherapy.
Ankylation and vinca alkaloid drugs are used as chemotherapy. For example: Vincristine or Cisplastine, read the instructions before use.
Immunotherapy helps fight tumor cells well; treatment is carried out with the drug Bleomycin.
In order to prevent disability due to skin melanoma, doctors resort to surgery. The main goal of surgery is to remove the malignant tumor, thereby preventing the spread of metastases. The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
Types of melanosis
Doctors distinguish between several types of pathological pigmentation. The classification of the disease is based on provoking factors and symptoms. There are 5 types of melasma:
- Uremic. Occurs against the background of renal failure.
- Hepatic. Caused by liver disease (usually cirrhosis).
- Kakhetic. Caused by severe forms of tuberculosis, impaired functioning of the adrenal glands.
- Endocrine. Caused by diseases of the thyroid gland, a disorder of the pituitary gland.
- Toxic (arsenic). Appears against the background of severe intoxication caused by arsenic and hydrocarbons. Gasoline, kerosene, motor oil and other petroleum products lead to poisoning.
In addition to the general large categories, specific types of melanosis are distinguished. These diseases are severe and threaten the health and life of patients. Such pathologies are eliminated mainly by surgical methods.
The following types of melasma are distinguished:
- Chloasma. The development of pathology is provoked by hormonal imbalance. Occurs in women during pregnancy and menopause.
- Becker's melanosis. Benign spots appear in young men.
- Dubreuil's melanosis. The disease affects women over 50 years of age. The formations can degenerate into cancerous tumors.
- Lentigo. Flat pigmented nevi appear on the epithelium.
- Moynahan syndrome. A huge number of brown spots that are benign in nature form on the epidermis of patients.
Classification
Depending on the manifestations of the disease, external signs, degree of malignancy and a number of other factors, the disease is classified into the following types:
- Melanoma – develops in pigment cells called melanocytes. It belongs to the category of the most aggressive facial anomalies. Prone to early metastasis and frequent relapses. Difficult to treat;
- squamous cell - this form has a high damaging ability, but fortunately, it is rarely diagnosed. In this case, the compaction grows very quickly in size, the transition from stage to stage is short-term and has no clear boundaries. Metastases already at the second stage affect neighboring lymph node connections;
- superficial - manifests itself in the form of an external rash of a reddish hue with a slightly raised marginal zone. The outer surface is shiny and smooth. The area of the body discussed in this article is rarely diagnosed;
- nodular - similar to inflammatory focal manifestations of a dense structure. Pigmentation changes from pink to deep red. It is characterized by rapid cell division, due to which the pathology rapidly increases in size, which greatly disfigures the face;
- flat - is a spot of almost flat shape, has a flat surface, clear boundaries and rounded edges, partially curved in the upper direction;
- basal cell – diagnosed in more than 70% of identified cases of skin cancer of the face. It develops in the basal tissues of the epidermis, hence its name.
A specific feature is slow progression, minimal risk of metastasis and almost complete absence of recurrent processes. This type of disease is often interpreted as an intermediate tumor state.
Photo: basal cell carcinoma
Everyone should know the very first signs of skin cancer. This article describes what squamous cell skin cancer looks like.
Why does melanoma often form on the legs?
Symptoms
Pigmentation on the epithelial tissues of the face is the main symptom of melanosis. Brown-brown defects cause incredible psychological and physical anxiety. Unnatural coloring affects the skin of the forehead, cheeks, nose, and upper lip. The spots are located symmetrically, appearing simultaneously on both sides of the face, armpits, genitals and other places on the body.
Common symptoms of the disease include:
- diffuse pigmentation of epithelial tissues (found in newborns);
- hypersensitivity of the skin to ultraviolet radiation;
- merging of affected areas into large foci;
- swelling;
- compaction and coarsening of the stratum corneum;
- atrophy of epithelial tissues;
- impaired functioning of the nervous and endocrine systems.
The affected skin is constantly irritated. Patients feel itching and burning in the area of age spots.
Forecast
The mortality rate for oncological lesions of the facial area is much lower compared to other malignant diseases. How optimal the prognosis will be depends on the type and form of pathology, the degree of aggressiveness of atypical cells, and the presence or absence of metastases.
For example, the basal cell type of anomaly is practically not prone to relapses or metastasis and has the best prognosis for complete recovery. The situation is worst when diagnosing melanomas - here, even with therapy, only every second patient overcomes the five-year mark.
On average, against the background of effective treatment, the following people can live through the specified life threshold, depending on the stage:
- Stage 1 – more than 96% of patients;
- Stage 2 – about 68% of people;
- Stage 3 – about 42%;
- Stage 4 – no more than 15%.
In this case, the relative error of such a forecast should be taken into account, since in patients with melanoma or nodular form of pathology, these indicators are much lower due to the strong aggressiveness of cancer cells and their tendency to early metastasis.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Therapy methods
A doctor of appropriate qualifications can determine the type of melasma and draw up a treatment regimen. Having identified the provocateurs of the disease, the doctor selects medications to eliminate the root cause of the pathology and age spots from epithelial tissues.
Drug therapy
To treat melanosis use:
- vitamins C, A, E and PP;
- enterosorbents - Polysorb;
- hepatoprotectors with antioxidant properties - Hepatosan, Sirepar, Heptral, Gepabene, Karsil.
With the development of erythema (excessive redness of the skin resulting from dilation of blood capillaries), antihistamines are used:
- Suprastin;
- Tavegil;
- Zyrtec.
To treat melasma that has progressed to severe forms, corticosteroids are used:
- Hydrocortisone;
- Prednisolone;
- Prednisone.
In case of toxic melasma, the patient is isolated from the source of poisoning. Medicines are prescribed that can restore the functioning of internal organs affected by the effects of poisons. First of all, endocrine organs, kidneys and liver begin to be treated.
Reticular pigmentation is eliminated with local drugs. Coffee stains disappear under the influence of:
- hydrogen peroxide - a liquid with bleaching properties;
- ointments and creams with retinol - preparations containing vitamin A that can moisturize the skin and restore epithelial cells (Retinoic ointment);
- Salicylic ointment - a product that has an exfoliating and brightening effect;
- cosmetic creams with photoprotection that prevent the occurrence and progression of pigmentation (Shiseido Urban, Bioderma Photoderm, anti-sun cream from Biocon);
- 3% citric acid solution, which has a whitening effect.
Cosmetological methods
Skin defects are removed in beauty salons.
Hardware treatment methods are used if the patient has no contraindications and the pigment spots are benign.
Cosmetologists remove darkened areas of skin using the following procedures:
- Laser resurfacing. The specialist carefully treats damaged epithelial tissue without affecting healthy areas. The skin in problem areas is smoothed and brightened.
- Chemical peeling. During the procedure, damaged, keratinized skin is exfoliated.
- Photorejuvenation. The method allows you to cleanse the skin of the dead layer and improve the condition of the epithelium.
- Ultrasonic peeling. Pigment spots are cleaned with an ultrasonic scrubber.
- Enzyme peeling. Special enzymes are used to remove pigment. The procedure brightens and rejuvenates the skin.
- Biorevitalization or mesotherapy. Injection solutions that can whiten the skin are injected into the lesions.
Diagnostics
To select a more effective method for eliminating pathology and obtaining the most complete clinical picture of the progression of the disease, the following methods of qualitative diagnosis are used:
- blood tests - assess the general condition of the body, determine the presence of cancer cells using tumor markers;
- dermatoscopy – provides an external assessment of changes in the epithelial covers by multiple digital magnification;
- Siascopy – indicated for pigmented neoplasms. It consists of spectrometric scanning of anomalies through the use of special equipment and refers to non-invasive diagnostic options that provide complete information about the structural content, concentration of melanin and collagen components in the affected tissues;
- cytology - performed microscopically using stained smears taken from the surface area of the fragment under study. The material is taken during a biopsy or after surgery and amputation of the tumor.
Melanosis of the skin: causes, symptoms and prevention of manifestations
Melanosis is an excessive focal accumulation of melanin in organs and tissues. It appears as unaesthetic dark spots that foundation cannot cope with.
What is it and what are its features?
Melanin is a coloring pigment in the basal layer of the epidermis. It is produced by melanocyte cells to protect against UV radiation. The color of the skin and eyes is determined by the number of granules of a given pigment. They are a security system for DNA: they protect cell nuclei from genetic deformation by ultraviolet radiation.
Light-skinned people have little melanin, while dark-skinned people have the epidermis filled with it as much as possible. Melanocytes, regardless of the time of year, produce pigment. When the mechanism of melanin formation is balanced, the number of pigments is normal, and they are activated only under the influence of ultraviolet irradiation (sun, solarium), covering the body with a tan.
Sometimes the pigment begins to be deposited in excess in the skin and in those parts of the body where melanocytes do not exist (in the mucous membranes, in the brain, in the kidneys). This disorder is called melanosis.
Causes and symptoms
Cutaneous melanosis can be caused by:
- diseases of the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, ovaries;
- severe infectious diseases: syphilis, malaria, dysentery and tuberculosis;
- intoxication with petroleum products, resins, arsenic;
- taking furocoumarins, sulfanimods, tetracycline;
- extreme stage of lice infestation;
- vitamin deficiency (scurvy, pellarga);
- heredity.
Symptoms of melanosis (other names - melanopathy, melasma):
- spotty, diffuse pigmentation of the skin (may occur in newborns);
- increased sensitivity of the epidermis to ultraviolet rays;
- consolidation of focal pigmentation into large zones;
- dermatic edema, hyperkeratosis (thickening of the stratum corneum), atrophy of the dermis;
- itching and irritation of the affected areas;
- disorders of the nervous system and endocrine glands.
Kinds
Dermatologists distinguish two types of congenital melanosis:
Progressive reticular melasma is a disease of hypersensitivity to sunlight.
Characteristic signs of pathology are:
- extensive patchy pigmentation;
- the formation of melanophores (mobile pigment cells), accompanied by edema and keratosis.
Excessive melanoblastosis (neurocutaneous) is a tumor melanosis transmitted to the fetus through the placenta by maternal melanoma metastases. Symptoms:
- accumulations of melanophores on the body of a newborn;
- histological analysis shows a high concentration of melanin in brain cells and neurons.
Melanosis can develop in two layers of skin:
| Type of cutaneous melanosis | External symptoms | Laboratory results | Treatment effectiveness |
| Epidermal | Black, dark and light brown spots | Melanin in the superficial layers of the dermis. Melanocyte size is increased, dendrites are activated | He is being treated. Easy and in a short time |
| Dermal | Gray-blue spots | Macrophages in the superficial and middle layers of the dermis | He is being treated. Long and difficult to influence |
Melanopathies are divided into primary (the causes are not clear) and secondary (the results of disorders associated with other diseases).
Primary:
- hereditary pigmentation: freckles, melanism, Peutz-Jeghers-Touraine syndrome, lentiginosis;
- pigmented nevi (moles), juvenile lentigo;
- linear pigmentation of the forehead, chloasma, melasma, senile lentigo;
- cachectic melasma, Addison's disease, toxic hyperpigmentation of the dermis;
- drug-induced Riehl melanosis, Hofmann-Habermann toxomelanoderma, pigmented reticular poikiloderma of the neck and face;
- actinic melasma, Buschke-Eichorn marble pigmentation, parasitic hyperpigmentation.
Secondary:
- melanosis due to syphilis, tuberculosis;
- hyperpigmentosis after lichen planus, acne, neurodarmatitis, eczema.
Types of hypermelanosis that affect the face are considered unpleasant from an aesthetic point of view:
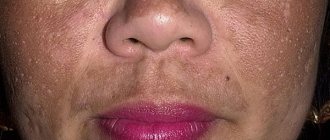
- juvenile and senile lentigo - pigment spots: in young men - rounded in shape, affecting the mucous membranes, in older people - accumulations of pigmented areas, a clear sign of skin aging;
- Becker's nevus is a hyperpigmented area of skin with increased hair growth;
- melasma – brownish-yellow and brown spots due to hormonal changes (pregnancy);
- photodermatosis - hypersensitivity to ultraviolet radiation in the form of a weeping rash and itchy redness (sun allergy);
- post-acne symptom - spots after acne.
Diagnostics
Hypermelanosis of the skin is fraught with potential danger: sometimes they provoke the appearance of a malignant melanoma tumor. Therefore, when pigmented areas appear on the body, it is important to consult a dermatologist who will conduct a diagnosis to establish the type of melanosis and determine the course of treatment.
Methods for diagnosing melanosis of the skin:
- Visual inspection (with a Wood's lamp) and palpation of the area.
- Finding out the medical history of the patient and his relatives.
- Dermoscopy (examination with a dermatoscope, which provides a multiple magnification of the examination area).
- Computer diagnostics (hardware examination of the skin and automatic comparison with the standard).
- Histological study of a microslide (section of the epidermis and dermis).
- Biopsy (in cases where there is confidence that hyperpigmentation has not led to the development of melanoma).
Treatment
The initial stage of melanosis can be treated with folk remedies, rubbing the skin with hydrogen peroxide, parsley or lemon juice, apple cider vinegar or salicylic acid. To defeat hypermelanosis, drug therapy will be required in several stages:
| Direction of treatment | Therapy |
| Eliminating irritants | Application of photoprotective creams |
| Elimination of contacts with toxic substances (polycyclic hydrocarbons) | |
| Treatment of provoking diseases (pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, nervous and endocrine systems) | |
| Basic treatment | Use of endocrine gland drugs |
| Anti-intoxication drugs | |
| Taking vitamins C, PP, A, E | |
| Pharmacy antioxidants: enterosorbents and hepatoprotectors | |
| Antihistamines | |
| Corticosteroids (for severe forms) | |
| Locally - lotions | |
| Removal of hypermelanotic lesions | Enzyme, electrical, chemical or ultrasonic peeling |
| Biorevitalization, mesotherapy (injections) | |
| Photothermolysis (a new key in treatment!) | |
| Laser resurfacing |
Forecast and prevention of occurrence
Skin melanosis can be successfully cured with timely consultation with a doctor. Many forms of hardware cosmetology allow you to completely remove hyperpigmentation and restore the epidermal cover.
The main preventive measure against melanosis is the use of protective agents against UV radiation. The filters they contain absorb, reflect and scatter ultraviolet rays.
Creams recommended:
- people with sensitive skin;
- predisposed to melanosis;
- after cosmetic procedures: dermabrasion, peeling, whitening, laser resurfacing, plastic surgery;
- during periods of physiological changes (adolescence, pregnancy).
The second measure is to carry out cosmetic peeling and whitening procedures during the season when the sun is least active. The best time is from October to January.
Proper nutrition and the use of vitamin complexes with vitamins C, PP, A and E are recommended.
The article has been verified by portal experts
articles:
(2 3.50 out of 5) Loading...
Traditional methods for strengthening the body
Treatment with folk remedies can be used for mild cases of the disease. As an immunomodulatory agent, you can prepare ginseng or an infusion of rosea radiola. You need to take a solution or decoction 20 drops per day.
If the patient has undergone removal, then after the operation it is better to take Leuzea extract. Take 25-30 drops per day. Course of treatment: month.
Schisandra or Eleutherococcus helps well with this disease. Such plants are natural adaptogens, therefore they have a good anti-cancer effect. Take in the dosage strictly prescribed by your doctor.
Many people ask whether melanoma can be treated with compresses? In fact, compresses made from medicinal plants can be used in treatment. However, not as the main medicine, but in complex therapy.
At home, you can prepare a compress from grated burdock root. To prepare you will need:
- burdock root;
- ointment based on catharanthus rosea.
Preparation: grind burdock root and mix with ointment in a 1:1 ratio.
Application: apply to affected areas, no more than once a day.
Birch is a good anti-cancer agent, because it contains bitulinic acids. Make a tincture of birch buds at home. For 500 ml of vodka you will need 100 grams of raw materials.
The prepared tincture should be wiped over the affected skin 2 times a day.
You cannot use traditional methods of treatment without first consulting a doctor, otherwise serious health complications may occur.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Endocrine disorders and hereditary predisposition play an important role in the formation of pathology.
At the same time, among the leading causes of melanosis are adrenocortical insufficiency of adrenal tissue, and, in addition, a decrease in the production of melanophore hormone by pituitary cells.
Among the forms of melanosis, pathological and physiological are distinguished. In the second case, pigmentation disorder is present in people with dark skin color and occurs under the influence of sunlight. In the case of a pathological condition, the melanin pigment is deposited in excess quantities in those areas where it is present normally (brain membranes, skin, eyes). Sometimes it appears in areas where it is not normally present (brain, kidneys, mucous membranes). Hyperpigmentation can be either focal or diffuse. In the tissues of the optical system, hyperpigmentation is often focal in nature.
Typically, such changes are diagnosed in patients of color.
Effect of ultraviolet radiation
Sunlight and solariums are the most common causes of skin melanoma. The appearance of oncology is promoted by intense and prolonged radiation. There is a frequent incidence of the disease in people living in hot, sunny climates, as well as people with fair skin, eyes and hair, because the melanocytes in their epidermis do not produce the required amount of melanin, from which the skin suffers more when exposed to sunlight. Sunburn, even during childhood and adolescence, can also lead to melanoma over time.
Symptoms
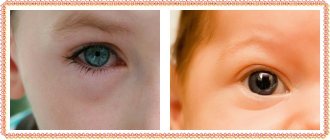
With melanosis of the eyes, dark spots appear in the skin of the eyelids, which can vary in size. Sometimes they are smooth, but in some cases they rise slightly above the surface. The intensity of the spots also varies, with a tendency to spread to the skin of the forehead and eyebrows. With melanosis of the conjunctiva, the area of the fornix and the lacrimal caruncle is affected. Sometimes melanosis spreads to the conjunctiva of the sclera.
The color of hyperpigmented areas directly depends on the location of the melanocytes; it can vary from blue and gray to brown and black. Due to the fact that the pigment itself is localized not in the conjunctiva, but in the episclera, the pigment formation does not shift when the conjunctiva is moved. When melanosis appears in patients with white skin, the risk of developing melanoma in the choroidal area increases.
Influence of nutrition
The appearance of melanoma is more often observed in people whose diet is dominated by high-calorie, fatty foods. Metabolic processes in the body are disrupted - this contributes to mutations in DNA. Also, patients in an oncology hospital are more often people whose weight exceeds 80 kilograms, but exactly how this affects the occurrence of a tumor is still not known. But contrary to existing belief, frequent consumption of drinks containing caffeine does not have any effect on the development of melanoma.
In 70 percent of cases, melanoma arises from nevi
Prevention
The use of protective creams against exposure to ultraviolet radiation is the main preventive measure against melasma. These cosmetics absorb, reflect and scatter UV rays.
Creams with filters must be used by people with hypersensitive skin and a predisposition to melasma, adolescents, pregnant women, women who have entered menopause, those who have undergone cosmetic procedures (peeling, laser therapy, skin lightening) and plastic surgery.
Doctors recommend adjusting the diet and creating a rational menu. Include in your diet foods enriched with C, A, E and PP (vegetables, fruits, herbs, vegetable oils, seafood, nuts, legumes).
Cosmetic procedures that eliminate pigmentation should be carried out during periods of reduced solar activity. The services of a cosmetologist are usually used in October-January.
If age spots occur, you should visit a dermatologist. The doctor will determine the nature of the disease, identify its cause and prescribe adequate treatment.
Influence of heredity
The chances of developing the disease increase if there is a family history of melanoma. A neoplasm in direct relatives increases the risk of its development by 50%. 10% of patients had a relative suffering from this disease.
Despite the fact that today medicine has made great strides in the treatment of melanoma, approximately 30% of cases of the disease are fatal. In half of the cases, the patient’s life is extended by up to 5 years. Therefore, it is so important to protect yourself from exposure to harmful factors. If you find that a mole has begun to change or a new growth has appeared on the skin, immediately contact an oncologist.
Complications and consequences of the disease
Pigmentless melanoma can be complicated by screenings of daughter tumors, metastases, and internal organs. This leads to a deterioration in their performance:
- metastases in the lungs impair blood oxygen saturation;
- brain metastases cause seizures, personality changes, and impaired movement and/or sensation in the limbs. Daughter tumors in the brain stem lead to disturbances in breathing, heartbeat, and maintaining normal blood pressure levels;
- metastases in the bones cause severe pain, bone destruction, difficulty in movements - up to their complete impossibility;
- metastases to the liver lead to indigestion, yellowing and itching of the skin, and deterioration of brain function;
- metastases to the skin cause pain.
When neoplasia is detected by the body's immune system, intoxication develops. It manifests itself as weakness, loss of appetite, drowsiness, and nausea. A person stops eating normally, and the body does not receive the nutrients it needs for life and to fight the tumor.
Over time, cancer cachexia develops - exhaustion. It is manifested by weight loss, constant weakness, and lack of appetite. Cachexia further worsens a person’s condition, disrupting metabolism and the functioning of all his internal organs.
Amelanotic melanoma - what is it?
This is a malignant tumor whose cells contain an extremely small amount of the pigment melanin (this is what gives the brown color to “regular” melanoma). As a result, neoplasia is very similar to various other skin growths, both malignant and benign. Therefore, it is quite difficult to diagnose achromatic melanocytic tumor at an early stage.
Melanoma containing little melanin is characterized by fairly rapid growth into fatty tissue and early ulceration. This creates conditions for metastasis.
A peculiarity of non-pigmented melanoma is the cessation of its growth after the sending of the first metastases. Moreover, after this, the primary tumor can completely disappear.
Colorless melanoma cells contain small amounts of melanin due to:
- insufficient content of the amino acid tyrosine in the body;
- disruption of melanin formation during tumor cell division.
Diagnosis and treatment of spindle cell melanoma
If a child has an incomprehensible formation on his body, you should definitely contact a dermatologist or oncologist. An external examination of the lesion site is not sufficient to confirm the diagnosis. It is necessary to collect tissue for histological examination. In addition, an MRI of the whole body is performed to identify possible metastases in distant organs or tissues.
The primary tumor can be removed in several ways.
In most cases, doctors recommend conventional surgical excision of the formation using a scalpel, which allows capturing a small amount of healthy tissue. This removal method can significantly reduce the risk of melanoma recurrence. In addition, the attending physician may choose to eliminate the tumor using liquid nitrogen and laser exposure. Such methods are less traumatic, but their use is recommended only if the formation is small in size.
If metastases have been identified in various organs, the use of toxic drugs is also required. As a rule, chemotherapy for spindle cell melanoma is carried out with interferon-based medications for 1 year. If there are tumors close to the primary melanoma, palliative chemotherapy may be indicated. Comprehensive treatment can improve survival prognosis.