What is swelling on skin areas
Almost every person suffered from swelling on the body. Often their appearance is not associated with any pathological cause, so the symptom gradually goes away on its own. But there are cases when it is difficult to establish the provoking factor and it is very difficult to differentiate the disease.
With edematous syndrome, fluid accumulates in different areas of the skin in natural cavities, which provokes a change in the volume of tissues, their functions and physical properties.
This video will tell you about swelling of the hands and feet:
How to tell if an infection has entered a wound: 9 dangerous signs
A simple wound is not so terrible - many people think so. But if not handled well, it can quickly become a serious problem. Here's how to identify the signs of a developing infection so you can get rid of it before it causes real trouble.
Dirt and particles are still present on your skin
Depending on the circumstances that caused the scratch (for example, you fell on a sandy sidewalk), various small particles could get into the wound.
It is extremely important to clean it immediately and remove any elements or dirt to prevent the wound from becoming infected.
However, if you find that a splinter or dirt has penetrated too deep under the skin for you to reach it yourself, consult a doctor. Don't think that just because you cleaned the wound, infection can be avoided.
Do you use soap to treat microtraumas?
Surprised to see soap on this list? This is just one common health product that could be harmful to you and your family. Regular hand soap can sometimes irritate the skin, which can slow down the healing process and, in turn, lead to infection of the wound.
Of course, each person reacts differently to different cleansers, all this is purely individual. But why take the risk and use soap to treat microtraumas? It is best to avoid using harsh ingredients, namely soap, and use soft moisturizing gels and ointments.
They are much more useful than soap.
Neglecting bandages
If you think it's a good idea to let your skin breathe after initially treating any microtrauma, think again. By not covering the wound with a bandage, you expose the skin to infection. New cells must migrate to the appropriate areas for the wound to heal faster.
By covering it with a bandage, you make this process easier and faster. The best way to help prevent infection is to apply an ointment to the wound, which you should always have in your home. If you haven't visited a doctor, then at least keep Vaseline in your medicine cabinet.
As you know, it prevents the wound from drying out and scabs forming, and accordingly, it heals faster.
You cut yourself with rusty metal, the wound is too deep
Do you have a deep cut because your skin was damaged by a rusty blade or any other metal? This does not guarantee that after you treat the wound, you will not get infected.
But this means you should see a doctor immediately. Do not attempt to treat deep cuts or scrapes yourself.
You are not a doctor, and a simple bandage and Vaseline will not save you, since in such situations, you will probably need stitches on the wound. And only a doctor can do this.
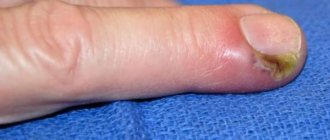
Redness and swelling around the wound
It's normal for the skin around a wound or scratch to look a little different. Redness, swelling and even a small bruise appear. The main thing is not to confuse this with an accumulation of pus. You should only panic if these symptoms worsen and the wound does not heal.
For example, redness and slight swelling around a cut or scrape are often signs of healing. But when this color does not disappear for a long time or the swelling increases, this indicates that the process of infection of the wound has begun.
Do not delay, consult a doctor as soon as possible to avoid dire consequences.
The pain doesn't subside
Obviously, cuts and scrapes hurt a little, some of them a lot. But if your pain does not subside, but only intensifies, you are unable to endure it, this means that an infection has entered the wound, that is, it is time to see a doctor.
The pus is green and has a foul odor
If you have a wound or deep scratch on your body, there are two things you need to watch closely: color and smell. If you see green pus oozing from the wound or a foul odor coming from it, this is a sign that you have a purulent infection.
You need to urgently run to the doctor. But what if a yellowish film-like substance has formed on a wound or scratch? No need to worry. Doctors say it's actually called granulation tissue, which is part of the healing process.
However, it should not be confused with pus.
You're not feeling well
Although it seems like signs of a skin infection will only appear on your skin, this is not always the case. As the infection spreads, your body mounts a counterattack.
And it can lead to systemic symptoms such as fever, nausea, mental confusion or just mild malaise. Although everything is purely individual, if you feel unwell and your wound does not heal for a long time, consult a doctor.
Let him examine the wound and study your symptoms. An abrasion or scratch may become a more serious problem.
When your infection becomes something more serious
Skin infections can become serious and can happen literally overnight. Staphylococcus is a good example. Infections are caused by staph bacteria, microbes that are commonly found on the skin of healthy people. This is usually not as problematic when bacteria invade your body.
But a staph infection can be fatal to a person. There are many types of infections caused by staph bacteria. They are characterized by redness, swelling, ulcers and usually affect areas of the skin on the legs. Impetigo is a dangerous skin disease caused by staphylococcus bacteria.
This is a contagious and painful rash that usually results in large blisters, oozing fluid, and a golden crust. Be sure to see your doctor if you have any of these symptoms or suspect that the infection has gotten worse.
The doctor will prescribe antibiotics and treat the lesion to improve your condition.
Found a violation? Report content
Source: https://FB.ru/post/diseases-and-conditions/2017/12/20/18457
His classifications
For development reasons
Edema is divided according to a variety of criteria. For example, they are divided according to development reasons:
- Hypoproteinemic . The level of albumin in plasma decreases.
- Hydrostatic . There is an increase in pressure in the capillary.
- Membranogenic . The permeability of the capillary network increases because it is damaged.
Edema is divided into 2 main types - general and local. In the latter case, the phenomenon is limited to one or several small areas.
By stage of formation
According to the stage of formation there are:
- predotek (the process of fluid retention in the body begins);
- pronounced swelling, which is easily determined upon examination.
According to the type of edematous fluid
Classification is also carried out according to the type of edematous fluid:
- Slime . It usually consists of organic acids, interstitial tissue colloids, and water. This form of the disease is commonly called myxedema.
- Exudate is a liquid with blood elements, often containing up to 8% protein.
- Transudate . A liquid similar to the previous form, but with a reduced protein content (no more than 2%).
According to the rate of development of the pathological condition
The speed of development of the pathological condition also plays a role:
- chronic (forms up to several weeks);
- acute (appears within a few hours);
- fulminant.
Self-diagnosis of edematous syndrome is described below.
Swelling of the penis with erosive balanoposthitis
With balanoposthitis, the head and prepuce become inflamed. If not only redness and swelling appears on the penis, but also erosions and ulcers, then the erosive form of this pathology is diagnosed. It can be caused by various pathogens.
Most often this is:
- herpes
- syphilis
- scabies
Scabies is not an infection. This is a parasitic disease. It is caused by a tick. Accompanied by severe itching. Toxic swelling of the penis appears. A secondary bacterial infection occurs.
Less commonly, erosive balanoposthitis can be caused by:
- Trichomonas
- staphylococcus
- streptococcus
Very rarely, the causative agent is an amoeba or the Epstein-Barr virus.
How to identify a symptom in yourself
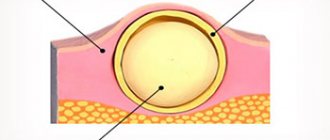
It is impossible to determine the process of fluid accumulation independently at the initial stage. Perhaps this is only when it becomes visible. The affected area will rise above the skin and become soft. Typically, touching the area will leave an imprint, although sometimes the swelling will be firm.
As for other symptoms, they depend entirely on the cause of the disease. This can be pain in the heart, cyanosis, shortness of breath, or just general malaise.
Read below about the causes of skin swelling, independent and accompanied by inflammation, redness and itching.
The video below will tell you about edematous syndrome:
Swelling of the penis due to STDs
Sexually transmitted infections sometimes cause swelling of the penis. Although most sexually transmitted diseases in men affect the urethra, inflammation can spread to the glans.
This occurs with the following infections:
- herpes
- gonorrhea
- chlamydia
- gardnerellosis
- candidiasis
In addition to swelling of the skin on the penis, these pathologies are manifested by other symptoms. Rashes appear.
A discharge may appear on the surface of the penis.
Discharge may also be present in the urethra. Sometimes pain is felt during sexual intercourse and urination.
STDs are treated with antimicrobial drugs. Which ones exactly depend on the type of infection. First, laboratory tests are performed. Their goal is to identify the pathogen.
After identifying the type of microorganism that causes the penis to swell after sex, medications are prescribed. For gonorrhea, this is usually ceftriaxone. Fluconazole is prescribed to treat candidiasis.
In the case of gardnerellosis, ornidazole is used. Sometimes STDs cause complications. If swelling of the scrotum and penis is observed, this often indicates infectious inflammation of the testicles and appendages.
More often than not, the process is one-sided. With orchiepididymitis there is a threat of infertility. Therefore, it is advisable to begin treatment as quickly as possible if this disease develops.
Diseases and disorders
Edema in many cardiovascular diseases is one of the important indicators of the presence of a problem. So, if it is localized in the lower extremities, on the lower back, then this indicates heart failure. If swelling of the skin begins to flow into the subcutaneous tissue and begins to accumulate in the peritoneum or pleural cavity, then this is a clear sign of an advanced form of the disease.
General swelling
The formation of edema (and sometimes its location in certain areas of the body) can indicate other diseases:
- Cirrhosis of the liver. The symptom is accompanied by severe ascites and affects the abdominal wall, lower back, and legs.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Nephritis and other renal pathologies. Water retention occurs throughout the body, but more on the face and under the eyes. The skin in such places is pale and soft.
- Hormonal disorders. The symptom often accompanies dysfunction of organs and glands that produce hormones.
- Neurosis, a weakened autonomic system. Organ dysfunction occurs and substances are produced that promote the accumulation of salts and moisture in the body.
- Exhaustion. The hypoproteinemic form of edema accompanies fasting, prolonged alcohol intoxication, and gastrointestinal diseases.
- Pulmonary failure. Fluid accumulation occurs in the lower part of the body, in the legs.
- Swelling of the skin due to allergies is very dangerous, since it is usually concentrated in the area of the neck and face. Growth in the volume of the larynx can lead to a blockage of oxygen.
For all the diseases listed above, general edema is often diagnosed.
Local swelling
Local accompanies the following pathologies:
- Thrombophlebitis. The swollen limb is very painful, the skin area is dense, and in the area of thrombosis it has a brown tint and is inflamed.
- Lymphedema. If the disease is in its initial form, then only the feet and legs are affected, but later the fluid accumulates over the entire area up to the thigh. The advanced course is determined by dense tissue; fibrous growths begin on the skin of the legs.
- Varicose veins It can be asymmetrical. It usually appears after prolonged stress on the limbs, or during prolonged standing.
- Postthrombophlebitic syndrome. Edema accompanies blockage of the vessel constantly and has different sizes. After some time, it is accompanied by trophic disorders, pigmentation, and varicose veins.
- Brain diseases, especially encephalitis, are accompanied by fluid accumulation, numbness in the area and sometimes even paralysis.
- In case of joint diseases, swelling forms around the joint.
- Obliterating atherosclerosis. The symptom appears due to the need to constantly lower the legs down to reduce pain.
- Phlebolymphedema is a combination of varicose veins and lymphedema. Fluid accumulation is bilateral.
- Disruption of lymphatic drainage. A swelling appears in the area of the lymph nodes, it is compacted and pale.
- Inflammatory process. Palpation is painful, the skin is red due to the influx of a large volume of blood to the area. This is often observed with erysipelas, burns, boils, etc.
- Problems with blood pressure.
It is also possible to distinguish an idiopathic form of edema, when it is not possible to accurately determine the root cause. Young women are very susceptible to this, especially those whose work involves the need to constantly stand.
Read below about the treatment of edematous syndrome.
Causes of wound redness: what symptoms indicate an inflammatory process
Wounds
Redness around the wound is the first symptom of a pathological process in the area of the damaged skin. Scratches, abrasions and other injuries can occur due to mechanical stress on the epidermis. The condition may go away on its own if the affected area is shallow.
Causes of wound inflammation
The appearance of a wound is accompanied by redness around the pathological area and pain. Manifestations depend on the nature of the damage:
- bleeding;
- discharge of pus;
- ichor;
- deep wound.
There are reasons that provoke the occurrence of unpleasant sensations and provoke painful recovery, redness around the injured area.
Influencing factors:
- Dirt getting into the cavity. The human immune system is able to independently fight bacteria that enter the body, provided that the human protective functions are functioning normally. When a wound is received, the integrity of the skin is disrupted, and free access to blood, internal tissues and muscles of the body appears. Resisting possible infection, inflammation begins. Redness is a symptom of a pathological process. Failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene and proper hand washing can lead to consequences. Experts recommend paying attention to health to avoid complications.
- Infectious and colds. A condition that increases inflammation. The deterioration of a person’s well-being is caused by a cold, virus, infection in combination with the resulting damage to the skin. Bacteria slow down treatment and cause an increase in the infected area.
- Repeated damage. When the area tightens, it becomes crusty and traumatizes. The area begins to swell, redness occurs, and pain intensifies. Signs indicate re-inflammation.
- The pathological process when using hirudotherapy is a method of eliminating various diseases, which involves the use of leeches. Animals stick to the body and leave small wounds. To avoid redness and other complications, it is necessary to treat with medical alcohol and hydrogen peroxide. Neglecting the rules of asepsis can lead to redness and other manifestations that cause discomfort.
- Wound inflammation after CABG – coronary artery bypass grafting. During the operation, a segment of the femoral vein is sutured to the aorta, an artery of the heart, creating an additional source of coronary circulation to the myocardium. The postoperative suture is located in the middle of the chest. Inappropriate processing and violation of hygiene rules threaten inflammation. The process is accompanied by redness and acute pain.
To organize effective treatment, it is necessary to identify the cause. Once the source of infection is eliminated, the doctor will select medications and prescribe procedures to promote tissue healing.
Signs of wound inflammation
Symptoms may be internal sensations, external indicators caused by the removal of a mole, wart, or other surgical intervention. The condition requires treatment. It is advisable to use home therapy methods in combination with drug therapy.
When traumatized, the healed wound is swollen and painful; the symptoms are caused by mechanical impact. Redness is a symptom of a pathological process. A red spot appears around the damaged area, accompanied by swelling. When pressing with fingers, pain is observed.
Redness
The injured surface acquires a reddish tint around the resulting hematoma or wound. The burn provokes redness of the epidermis, severe itching and burning appears.
There is a desire to place the damaged part of the body in ice water. For minor lesions, experts recommend using panthenol-based ointments.
It is forbidden to use products containing oils or immerse limbs in hot water.
Edema
Swelling around the wound often occurs. As a result of the damage, swelling is observed. Externally it is characterized by smoothed skin. If the lips are severely damaged, the cheeks and face may swell. Experts recommend using cold compresses. To prevent complications, you should consult a doctor. After an examination, the doctor may prescribe medications that can eliminate the problem.
There is a crust on the wound
On the wound, swelling and crusting occurs due to the recovery phase. A protective layer is formed to prevent water and dirt from entering the cavity, indicating an independent healing process. Swelling and redness are signs of inflammation. To avoid consequences, you must consult a doctor.
Pain
Unpleasant sensations - a symptom indicates errors in following the rules of asepsis, indicates an insufficient course of drug therapy, including antibiotics.
It is necessary to pay attention to wounds on the legs with diabetes. Failure to maintain personal hygiene can lead to consequences.
The sign is a confirmation of the inflammatory process in the body, accompanied by redness and swelling of the affected area.
Other
There is an increase in local and regional body temperature. The clinical picture is similar to those caused by a cold. A deep cut or laceration requires careful treatment of the damaged area with antiseptics.
The development of the inflammatory process, accompanied by redness and swelling, must be stopped to avoid infection.
Possible complications:
- Discharge of pus. The affected surface must be disinfected to prevent tissue infection through blood. An effective remedy is Syntomycin ointment.
- Itching indicates that bacteria have entered the bloodstream. Balsamic liniment according to Vishnevsky is used.
- A rash around the wound indicates an allergic reaction caused by components of the medications being treated.
Malignant diseases
1. Epithelial skin tumors
Basal cell carcinoma (basal cell carcinoma) has a pronounced destructive growth, often recurs, and usually does not metastasize. It occurs in people of both sexes, usually in old age. It grows very slowly and often ulcerates.
Clinically it is a plaque or nodule; in advanced stages it is a large, deep ulcer. Around the erosion or ulcer you can usually see a dense cushion the color of ordinary skin. When you stretch the skin, you can see that this roller consists of individual small “pearls”. As the process spreads deeper, the tumor loses mobility.
Treatment: removal of the tumor within healthy tissue. Usually cryodestruction, diathermocoagulation, surgical excision, prospidine or colchamine ointment are used.
Squamous cell epidermal carcinoma is more common in older men. Occurs against the background of senile keratosis or leukoplakia. It is a dense spherical formation, thicker than the skin, the size of a pea, then acquires an exo- or endophytic shape. In the exophytic form, the tumor rises above the level of the skin, its surface is uneven and warty. At the same time, such a tumor grows deeper. Subsequently, it ulcerates. In the endophytic form, this is usually an ulcerative-infiltrative process in the thickness of the skin. Tumor growth leads to significant destruction of surrounding tissues, metastases quickly appear, and death occurs after 2-3 years from cachexia or bleeding during tumor disintegration. The diagnosis is confirmed histologically; one should not forget about metastases to regional lymph nodes.
Treatment: carried out by an oncologist, the tumor is surgically excised within healthy tissue, and chemotherapy is administered if necessary.
Sebaceous gland cancer - occurs in older people, grows slowly, and is prone to relapse and metastasis. In appearance it resembles liposarcoma.
Treatment: surgical.
Sweat gland cancer is rare, has rapid growth and metastasis. A heterogeneous nodule in the thickness of the skin sometimes reaches very large sizes.
Treatment: surgical.
Metastatic cancer is a more malignant variant of basal cell carcinoma with pronounced invasiveness and the ability to metastasize.
Treatment: surgical only.
2. Tumors from pigment-forming tissue
Melanoma (melanoblastoma, melanocarcinoma) is an extremely malignant tumor, the primary focus of which is most often in the skin. Skin melanoma occurs predominantly against the background of a pigmented nevus after its injury, severe insolation, etc.
Clinic: a nevus, usually hairless, round or oval in shape, begins to enlarge after a single or repeated mechanical injury or massive insolation. It increases gradually in the plane of the skin or exophytically, sometimes changes color, becomes rough and begins to peel off. As a result, the nevus becomes easily vulnerable, often bleeds at the slightest trauma, becomes infected and becomes wet. Each subsequent injury increases exophytic growth. Gradually, the tumor takes the form of a dense nodule with a rough surface on a wide base, covered with loose bloody crusts. Most often, melanoma is heterogeneous in color.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of histological examination, urgently, right on the surgical table. For diagnosis, a radiophosphorus test is also used, based on the ability of melanoma to accumulate radioactive phosphorus ten times more than normal skin, as well as thermography, since the temperature of melanoma is 4 degrees higher. In the presence of erosion and ulcers, a cytological examination can be performed by taking smears of impressions from the surface of the tumor.
Treatment: carried out in oncology hospitals by surgical excision of the tumor within healthy tissue (minimum 0.5 cm), followed by the use of chemotherapy and immunotherapy.
3. Soft tissue tumors
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is characterized by slow growth and a tendency to relapse. Metastases are rare. At the beginning it looks like a nodule, gradually enlarging, turning into a dense, tuberous, often ulcerated nodule. Color ranges from flesh to brown. Often located on the torso and limbs.
Fibrosarcoma is a malignant tumor of fibrous connective tissue.
Clinic: the tumor has clear contours and infiltrative growth. Color varies from normal skin to pale brown.
Liposarcoma is a malignant tumor of adipose tissue. It is more common in men at any age. These tumors do not metastasize for a long time. The consistency is denser than lipomas. When cut, the surface is mottled with areas of necrosis and hemorrhage.
Angiosarcoma is an extremely malignant tumor consisting of vascular endothelial cells. It occurs most often against the background of lymphostasis of the upper limb after radical mastectomy (Stewart-Treves syndrome); angiosarcoma of the face and scalp also occurs. Angiosarcoma presents as erythematous or hemorrhagic spots and plaques. Gradually, centrifugal infiltration occurs, leading to the fact that the entire face or scalp is affected. Nodules and ulcerations are noted. Metastases to the cervical lymph nodes, as well as hematogenously to the lungs, liver and other organs.
Treatment: surgical, but rarely successful due to the occurrence of several foci and widespread distribution over the surface of the skin.
4. Metastatic (secondary) tumors
The spread of cancer of internal organs into the skin occurs by local infiltration, as well as by lymphogenous and hematogenous routes.
The most common source of skin metastases in women are:
| Mammary cancer | 69 % |
| Colon cancer | 9 % |
| Ovarian cancer | 4 % |
The most common source of skin metastases in men are:
| Lungs' cancer | 24 % |
| Colon cancer | 19 % |
| Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral mucosa | 12 % |
| Kidney cancer | 6 % |
As a rule, metastases to the skin appear from a nearby primary tumor through the lymphogenous route, and distant metastases through the hematogenous route.
Clinic: metastases in the skin usually look like a node or a group of nodes that are mobile or fused to the underlying structures. In color, they may not differ from the surrounding skin or be purple and red. Very sparsely pigmented. The epidermis is usually involved in the process. Sometimes erosions and ulcers appear. Clinically, metastases may resemble primary skin lesions, including epidermoid cysts, lipomas, primary skin cancers, pyogenic granulomas, cellulitis, and even dermatitis.
Diagnosis: established by biopsy with processing of biopsy specimens in formaldehyde for routine examination.
Metastases to the skin usually correspond to a poor prognosis, and this symptom usually indicates multiple already existing metastases of internal organs.
5. Precancerous diseases of the oral mucosa
and the red border of the lips
Classification of precancerous diseases of the oral mucosa
A. Obligate (with a high incidence of malignancy)
- Bowen's disease
B. Optional (with a low incidence of malignancy)
- Leukoplakia (verrucous and erosive)
- Papillomatosis
- Erosive-ulcerative and hyperkeratotic form of lupus erythematosus and lichen planus
- Post-radiation stomatitis
Classification of precancerous diseases of the red border of the lips
A. Obligate
- Warty precancer
- Limited precancerous hyperkeratosis
- Abrasive precancrosis cheilitis Manganotti
B. Optional
- Leukoplakia
- Keratoacanthoma
- Cutaneous horn
- Papilloma with keratinization
- Erosive-ulcerative and hyperkeratotic form of lupus erythematosus and lichen planus
- Post-radiation cheilitis
Bowen's disease
Occurs more often in men.
Localization: soft palate, uvula, retromolar region and tongue.
Clinic: most often this is a macular nodular lesion; due to keratinization, it is similar to leukoplakia and lichen planus. Erosion may appear. Subsequently, atrophy appears, then the lesion sinks slightly. There are no subjective sensations. The course is usually severe. Early invasive growth is observed when localized on the oral mucosa. Since histology shows the picture of Cancer in situ in the spinous layer of the epithelium, this disease is classified as cancer. Diagnosis is usually difficult, so diagnosis is made based on histological findings.
Treatment: surgical excision of the lesion within healthy tissue. If this is not possible, then close-focus radiotherapy should be used. Without treatment, the prognosis is poor.
Warty precancer
Described in 1965 by A.L. Mashkilleyson. It develops mainly in men over 40 years of age on the red border of the lips.
Clinic: strictly on the red border of the lips there is an element up to one centimeter of spherical shape. It has a dense consistency. The color of such an element ranges from normal to stagnant red. Sometimes the surface is covered with dense scales. The nodule is painless on palpation. The surrounding tissue is not changed. Malignancy occurs 1-2 months after the start of the process. The diagnosis is confirmed histologically. Treatment is surgical. The prognosis without treatment is unfavorable.
Limited precancerous hyperkeratosis
Described in 1965 by A.L. Mashkilleyson. Occurs in men after 30 years of age. Localized on the lower lip, strictly on the red border of the lips. It is a sharply limited area of polygonal shape up to 1.5 cm in size. The surface is covered with thin, dense scales and has a grayish-white color. Usually the lesion sinks, but with a large number of scales it rises. Malignancy begins after 6 months. The diagnosis is made based on the results of a biopsy.
Treatment: surgical with mandatory histological examination.
Abrasive precancrosis cheilitis Manganotti
Manganotti cheilitis is a common disease that occurs in men over 60 years of age and progresses to squamous cell carcinoma. Rapid malignancy is observed.
Clinic: the manifestation of the disease is very diverse. Usually this is erosion of various shapes with a smooth surface that has a rich red color. Often crusts form on the surface of the erosion; when they are traumatized, bleeding occurs, while traumatizing erosion without crusts does not cause bleeding. An inflammatory reaction is observed up to 1.5 cm from the erosion border. Lesions tend to rapidly epithelialize and recur. The course is chronic from 3 months to 30 years.
Treatment: agents that stimulate epithelization are used, treatment of gastrointestinal pathologies, sanitation of the oral cavity and prosthetics. It is effective to use vitamin A concentrate 10 drops 3 times a day, Nerobol and other drugs that prevent aging of the body and improve blood circulation. Vitamin A applications, fucorcin, lorinden C, and ointments containing methyluracil and solcoseryl are prescribed locally. The prognosis is usually favorable.
Leukoplakia
It is a keratinization of the oral mucosa, red border of the lips and genitals. Accompanied by inflammation, occurs in response to chronic irritation. An important place in the etiology of leukoplakia is occupied by gastrointestinal pathology, leading to a decrease in the resistance of the mucous membrane to irritants and a lack of vitamin A. It usually occurs in people who smoke and in the presence of prostheses made of different metals.
Clinic: leukoplakia is usually localized on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, at the corners of the mouth, on the lower lip. There are flat (48%), verrucous (39%), and erosive leukoplakia (10%). Usually the lesion is an inflammatory spot with an element of keratinization (flat), then the leukoplakia begins to rise (verrucous) and ulcerate (ulcerative). The last two forms are most prone to malignancy. Diagnosis is based on clinical data, confirmed in doubtful cases by histological results.
Treatment: sanitation of the oral cavity, elimination of the irritant. It is recommended to take vitamins B6, A, applications of vitamin A solution, borax with glycerin. The use of cauterizing agents is strictly contraindicated. With proper treatment, recovery occurs within 8-12 months.
Cutaneous horn
This is an area limited by epithelial hyperplasia with huge hyperkeratosis. This is a hearth with a diameter of up to 1 cm, a cone shape and a height of up to 1 cm. Gray or brown in color, tightly fused to the base. Treatment is surgical followed by histology.
Keratoacanthoma (horny molluscum)
Very rare. It manifests itself as a grayish-red hemispherical nodule with a depression in the center. It grows very quickly, is not fused with the underlying tissues, is almost painless, and regresses after 6-8 months. The diagnosis is not difficult. Treatment is surgical.
Symptoms and types of hemangioma
Quite often you can see hemangioma on the skin of adults. This is a tumor based on a vascular formation. Hemangioma can be divided into several types, they will depend on which specific vessels are involved in the process. Let's look at the types of hemangioma on the skin in adults and children:
- Cavernous. This hemangioma is located deep in the skin and is a limited subcutaneous node covered with a bluish-colored cover. As a rule, such a hemangioma is diagnosed immediately after the birth of a child, and it is localized on the head or neck.
- Simple capillary. Such a neoplasm is detected on the surface of the skin. This hemangioma is very large in size. The color can range from reddish to dark blue. The tumor is growing around the periphery.
- Combined. This hemangioma is a combination of cavernous and simple forms of this tumor.
- Mixed. In this case, both blood vessels and nearby tissues are involved in the process. As a rule, connective tissues are involved.
If the hemangioma is located on the eyelid or on the face, then radiation therapy is used for removal. In other situations, sclerotherapy, cryotherapy, and hormone therapy are prescribed. The surgical intervention method is used only if the hemangioma is located too deep.
Where to go if your penis is swollen
If swelling of the penis appears and you do not know what to do, contact our clinic. You will be examined by an experienced urologist. He will determine the cause of the swelling.
After assessing the clinical symptoms, the doctor will prescribe a series of diagnostic procedures. They will allow you to accurately determine the cause of swelling of the penis.
Then the urologist at our clinic will suggest the optimal treatment method. The most common cause is infection. After a course of therapy and eradication of the pathogen, the swelling will go away.
If there is swelling of the penis, contact the author of this article, a venereologist in Moscow with many years of experience.
Treatment of swelling of the penis
Different diseases are treated differently. Both conservative and surgical techniques are used.
In most cases, it is possible to manage with medications. Because the main group of causes of penis swelling is infection.
The drugs are used externally and systemically.
They are used externally in the form of solutions, creams, and ointments. The doctor may prescribe baths with antiseptics. In case of fungal inflammation, creams with antifungals are used.
In case of viral origin of the disease, local agents with acyclovir are used in addition to systemic drugs. Oral antibiotics are often prescribed. Which ones exactly depend on the pathogen isolated.
You should not self-medicate. Because it is impossible to guess what infection caused the swelling of the penis.
This can only be determined through laboratory tests. Therefore, antibiotics, treatment regimens and drug dosages are selected exclusively by the doctor.