Removal of facial and scalp tumors
Various neoplasms appear in humans at birth or throughout life.
Some of them are benign and only cause aesthetic inconvenience. Others are malignant in nature and can provoke the development of cancer. In our medical center, removal of tumors of the face and scalp is carried out by doctors of the highest category with many years of experience. Surgeons use modern surgical methods, including laser surgery. Patients have the opportunity in a short time, without fear of negative consequences, to eliminate a cosmetic defect on the face and head.
Malignant neoplasms
Neoplasms on the skin of a malignant nature in the Russian Federation in the structure of cancer incidence today account for 9.8% and 13.7% in men and women, respectively. People living in areas with high photoinsolation and having fair skin are especially susceptible to the disease. The description of new cases of skin cancer has increased by a third over the past ten years.
Types of malignant neoplasms on the skin, their structure.
Malignant skin tumors include:
- basal cell carcinoma;
- Kaposi's sarcoma;
- liposarcoma;
- squamous cell carcinoma;
- melanoma, etc.
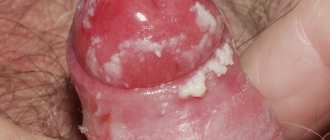
Basalioma
One of the most common epithelial skin tumors. It is formed from atypical cells of the basal layer of the epidermis, which is where it gets its name. The tumor is characterized by long-term progression, peripheral growth, during which the surrounding tissues are destroyed. Basalioma is not prone to metastasis.
This pathology develops mainly in elderly people and the elderly, and is localized mainly on the face, neck and head (its scalp). Sometimes basal cell carcinoma is classified as a precancer, because under the influence of certain factors it degenerates into metatypical cancer.
The first manifestation of a developing tumor is a dense, hemispherical nodule that does not rise above the skin. Its color usually matches the skin color or differs slightly (light pink tint).
At the initial stage, the patient does not complain. Over the course of several years, the papule grows, reaching 1 or 2 cm in diameter. Its center gradually collapses, bleeds and becomes crusty.
Under the latter, erosion or an ulcer with a narrow ridge along the edges is found, which over time scars and grows along the periphery.
Basalioma reaches a size of 10 centimeters or more. The once pink papule turns into either a flat plaque with peeling, or a noticeably raised node above the surface of the skin, or a deep ulcer that destroys the underlying tissue (down to the bone).
Liposarcoma
This is a neoplasm on the skin from fat cells of mesenchymal origin. In the photos below you can see how big these tumors reach. The description in clinical reference books speaks of liposarcoma as a formation that tends to appear on the buttocks, thighs and retroperitoneal tissue. It is more common in men over 40 years of age.
Initially, a swelling appears, then a node appears. There are no subjective sensations yet. On palpation, the nodule is dense, elastic, and mobile.
Subsequently, the tumor grows, turns red, and inflammatory processes begin. Large liposarcoma can compress nerves and blood vessels and even grow into them, causing disturbances in tissue trophism and pain.
Kaposi's sarcoma
This is a systemic multifocal disease of vascular origin with primary damage to the skin, lymphatic system and internal organs. It belongs to tumors of an endothelial nature and develops mainly in individuals with severe immunosuppression.
The morphology of skin lesions of sarcoma is quite diverse. They come in the form of spots, nodules, infiltrative plaques, etc.
There are several types of sarcoma:
- Classic (European).
- Endemic (African).
- Epidemic (for HIV).
- Immunosuppressive (immunodeficiency caused by medications and medical procedures).
The first type is observed in the elderly and the elderly and has a favorable course. The elements grow over a long period of time, decades in the proximal direction, and do not cause any discomfort to the patient. The formations are most often localized on the lower extremities, they are bluish-red spots up to 5 cm in diameter with smooth edges, reminiscent of hematomas.
As they grow, they transform into nodules and merge. Large nodes darken and eventually ulcerate. Swelling occurs along the edges of the elements, caused by stagnation of lymph in the lymphatic channel.
The African type is severe and affects young people. A fulminant course of the disease is often observed. African Kaposi's sarcoma manifests itself in several types of formations - from nodes to lymphadenopathy.
The most malignant type of elements of this type of sarcoma is considered to be “flowery” (growth in the form of vegetation - in appearance it resembles cauliflower). It is characterized by deep lesions of the dermis, subcutaneous tissue and underlying tissues down to the bone.
With HIV infection, the tumor can be located literally anywhere in the body, even affecting internal organs. The most typical places are the oral cavity, stomach and duodenum. The current is severe. The immunosuppressive type is similar in its manifestation to HIV-associated.
Squamous cell carcinoma
Malignant tumor of the epithelium. Formed from atypical keratinocytes that proliferate randomly. The process begins in the epidermis, gradually moving to deeper layers. The tumor is characterized by a tendency to metastatic process.
Squamous cell carcinoma occurs 10 times less frequently than basal cell carcinoma. It most often affects white-skinned men whose place of residence is a sunny, warm climate.
The localization of spinocellular epithelioma varies. The most favorite place for the formation of squamous cell carcinoma is the border between the mucous membrane and the skin. These areas include the lips and genitals.
At the initial stage of cancer development, an infiltrate appears with a raised hyperkeratotic (rough) surface. The color of the formation is usually gray or yellow-brown.
At first, as with basal cell carcinoma, there are no complaints. As the tumor grows, it can reach a size of up to 1 cm. At this moment, a dense node that continues to grow begins to be felt. Eventually, the carcinoma approaches the size of a walnut.
Description
Indications for tumor removal
In our clinic, doctors successfully perform operations to eliminate various tumors. Surgical intervention allows you to combat the following pathologies:
- moles are accumulations of melanin that have a flat or slightly voluminous shape and vary in size;
- Lipomas are benign accumulations of fatty tissue under the skin;
- keratomas - scaly growths on the skin that occur due to exposure to sunlight;
- atheroma - appears on the scalp due to blockage of the sebaceous gland;
- fibroma is a pathological accumulation of connective tissue on the skin and mucous membranes, round or oval in shape;
- xanthelasma - is benign in nature, appears as pale yellow plaques on the skin.
Malignant neoplasms include warts and their subtypes that arise due to HPV infection.
Indications for surgical removal of tumors are cosmetic or medical in nature. In the first case, the problem does not threaten the health and life of the patient. Treatment is carried out to eliminate cosmetic defects.
Medical indications for removal are:
- risk of degeneration into a malignant form;
- viral nature of formations;
- location of the pathology in places of permanent injury.
Before removing tumors of the scalp and face, our patients are required to undergo a preliminary examination. With its help, the doctor will determine the nature of the problem and select the appropriate treatment tactics.
Possible contraindications
There are a number of diseases and conditions of the human body in which surgical manipulation of the skin and mucous membranes is contraindicated. These include:
- hypertensive crisis;
- acute respiratory diseases;
- herpes in the acute stage;
- some types of malignant neoplasms;
- severe allergic reaction.
Doctors at our medical center, if they detect absolute or relative contraindications in a patient, will select a different tactic to combat the pathology.
Laser treatment of tumors
Exposure to pathological areas with a focused laser beam is a modern technique that does not cause pain to the patient. In our clinic, a semiconductor or CO2 laser is used to remove tumors on the face. This method has a number of advantages over conservative surgical methods:
- nearby tissues are not damaged;
- no bleeding;
- absence of pain;
- therapeutic efficacy;
- there is no need to stay in the inpatient department of the clinic.
Using a laser beam, you can remove almost all tumors - the device has three operating modes. Find out more about the terms of service and its cost. Contact the clinic doctor using the contacts listed on the website.
Growths on the scalp photo and name
- 01 August
- 0 rating
Patients refer to a variety of defects as skin growths. These can be small blisters and papillary outgrowths (papilomas, nevi), rough plaques and compactions (keratosis, cutaneous horn).
Knowing what diseases patients call “skin growths” and how often they are treated, I decided to write this article. So that the reader has an idea of what specific disease we are talking about and what danger the patient faces.
After all, some of the growths are safe, although they do not look aesthetically pleasing, while others need to be gotten rid of as quickly as possible.
According to my observations, the following are most often hidden under the name “skin growths”:
The most common growths on the skin are seborrheic keratosis.
Seborrheic keratoses are the most common growths on the skin. The disease develops in people over 35 years of age. Most often, at 45–50 years of age, as a result of impaired differentiation of the basal cells of the epidermis. Common causes are solar radiation and heredity.
The development of the disease occurs slowly, with age the size and number of growths increases. The appearance of the formations is extremely diverse. There are many types of seborrheic keratoses. Seborrheic keratosis is considered a benign tumor.
But, there is a low probability of formations turning into squamous cell skin cancer. So, it is better to remove large formations. The most suitable method is cryodestruction; it can remove very large growths on the skin without surgery and with minimal scarring.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with pigmented nevi, dermatofibroma, melanoma.
Skin growths such as seborrheic keratosis are characterized by the following manifestations:
- A spot of increased pigmentation, from light brown to black, which has clear boundaries, with a diameter of 3 mm to 5 - 6 cm.
- The appearance resembles a plaque or papule with a slightly scaly, bumpy or smooth surface.
- Skin lesions occur more often on the back, chest, less often on the face and neck. The disease does not affect the soles of the palm.
- Skin growths are more often multiple than single.
- Plaques of various shapes that rise above the skin, with a diameter of 0.5 to 4 cm.
Actinic keratosis - yellow growths
Solar or actinic keratosis is a precancerous disease. It occurs as a result of skin aging and prolonged exposure to sunlight. It is characterized by changes in the skin under the growths with their gradual transformation into malignant ones.
The disease occurs in people over 50 years of age. It appears on any part of the body, most often in areas exposed to solar radiation.
In contrast to seborrheic keratosis, the growths on the skin are flatter, have a reddish color at the base, and the horny layers have a yellowish tint. Sometimes, formations disappear on their own.
Dermatologists divide the forms of actinic keratosis: atrophic, hypertrophic, bowenoid. Specialists carry out differential diagnosis of pathology with basal cell carcinoma, seborrheic wart, disseminated lupus erythematosus.
- A flaky, rough, dry spot, slightly protruding above the skin, inflamed.
- Gradual growth of the stratum corneum of the skin in the form of a drop-shaped tubercle or a flat plaque with a yellow tint.
- Over time, the color of the formation changes. The skin at the base is redder, the horny masses are yellower.
- Possible loss of growths, in the future, the formation of a new lesion in the same place.
- The size of the formation in diameter ranges from a few millimeters to 2.5 - 3 cm.
- The skin around the growth is spotted and wrinkled.
Wart-like growths on the skin
People often consider only the most common warts - those on the fingers - to be warts. In addition to these common warts, there are other varieties. Few people know about periungual, plantar and filiform warts. They can well be called growths. All of these growths are caused by the human papillomavirus.
Growths on the skin near the nail
- A distinctive symptom of periungual warts is:
- The characteristic location of the growths is directly next to the nail or under it.
- Rough, rough surface.
- Flat or plaque-shaped growths.
- There are no clear boundaries.
- Gray or flesh-colored.
- Superficial location or deep penetration under the nail.
- Cause depletion, deformation, and destruction of the nail plate.
- Does not cause pain or itching.
Plantar growths on the skin
- The disease manifests itself outside the points of support and friction from shoes.
- Pain and discomfort when pressing on the sides of the growth while walking.
- The wart is brown or flesh-colored, with dots in the center.
- Absence of skin pattern on the wart.
- Itching in the area of the wart.
- Spread to the skin around the growth.
- Combination of warts and formation of mosaic clusters.
Infection occurs when:
- Direct contact from person to person,
- Walking barefoot in swimming pools and showers;
- Abrasions and cuts on the soles.
Growths on the skin of the body may be filamentous warts
- The appearance in no way resembles papillomas or thin papillae/
- They are called filamentous because they have spike-like growths on the surface.
The base is a dense, flesh-colored scaly plaque. These outgrowths protrude from the base. - Spiny outgrowths are not always found.
Sometimes they are washed off, steamed, and only rough lumps remain on the skin.
Papillomas are frequent growths on the skin
Papillomas are papillary growths on the skin. They have a color from light to brown. The disease is caused by a group of papillomaviruses, which are transmitted through household and contact from sick to healthy. When infected, changes occur in the cells, which leads to their proliferation.
Locations of growths: facial skin, mucous membranes of the mouth and nose, ligaments, limbs. The types of papillomas completely depend on the type of virus that provoked them. There are darkish pigmented growths. Dimensions from a millimeter to 1 cm. Different types of papilloma virus manifest themselves in different ways.
Condylomas are growths on the skin in the groin and anus
The reason is the same - the papilloma virus. Characteristic smooth or rough growths, ranging in size from one millimeter to 3 cm. They can be single or merged. Localized in the genital and anus areas. In men - near the head and crown of the penis, frenulum.
In women, they are located on the labia, clitoris, less often on the cervix, inside the vagina. Growths on the skin in the genital areas during sexual intercourse cause discomfort and complicate the birth process. Multiple proliferation of condylomas is a sign of a weakened immune system.
Infection with growths occurs during sexual intercourse with a carrier of the virus, very rarely through household means.
Soft fibroma - large growths on the skin
Soft skin fibroma - growths on the skin of quite large sizes. They can protrude several millimeters or centimeters above the surface of the skin. A single neoplasm that has clear boundaries.
The base is usually somewhat narrowed, widening at the top, and the ends are soft to the touch. Often appears in middle-aged people. Skin growths are painless. When injured, an inflammatory process can develop.
The reasons for the development of growths have not been studied, but a characteristic role is played by hereditary factors, hormonal changes, and senile skin changes.
Intradermal nevi are frequent growths on the skin of the face
Intradermal nevi are dense nodules, covered with or without hairs. Usually light flesh-colored or light brown. Very often growths of this type are found on the face and spoil the beauty. In general, pigmented nevi are a group of congenital neoplasms on the skin of a benign nature.
It is characterized by an accumulation of cells (nevocytes) in a certain limited area. Often pigmented nevi appear in embryos, and their appearance is observed with age. The typical development of growths throughout life is a gradual transition from flat shapes to increasingly convex ones, and a gradual loss of color.
Pigment cells can lie quite deep, the larger the outer growth, the further to these pigment cells. A dangerous complication of any type of nevus is the transition of the disease to a malignant form, in which the growth gradually turns into melanoma of the skin. However, this is a rare occurrence for this education.
When diagnosing, this formation must be distinguished from melanoma, senile warts, and dermatofibroma.
Such growths on the skin appear for the following reasons:
- Hormone level disturbances, hormonal changes.
- Genetic disorders.
- Infections of the urinary and reproductive system.
- Action of toxic substances.
Cutaneous horn - a horny growth on the skin
Skin growths of this type appear in people over 45 years of age against the background of hormonal changes in the body and its general aging. The skin disease manifests itself as a certain painless, roughened area, which gradually increases, acquiring a conical horn shape.
The growth can be single or multiple, yellow or brown in color, and can grow to enormous sizes. The surface of the formation is uneven, covered with jagged scales, with a rounded inflammatory area in the center. It is most often localized in the face area.
Horny growths on the skin in most cases eventually develop into squamous cell skin cancer. It is necessary to be treated before it turns into skin cancer, it will be easier and calmer.
Source: https://papillomnet.ru/papillomy/narosty-na-kozhe-golovy-foto-i-nazvanie.html
Neoplasms on the scalp
Neoplasms (papillomas, atheromas, wen) that appear on the scalp should be a reason for you to immediately consult a doctor. Why are they dangerous? It is important to understand that any benign formations (nevi, keratomas, papillomas) located on the scalp are very often injured as a result of washing the hair, using a hair dryer, hair dyes, combs, or wearing a tight hat. And trauma, as is known, can cause a benign tumor to develop into a malignant one .
Atheromas (sebaceous gland cysts) are benign formations.
In addition to an extremely unaesthetic appearance, atheromas can fester, hurt, and cause fever and swelling. A suppurated arethroma can break out on its own. This leads to the need for urgent surgery - emergency surgery to remove atheroma on the head. Therefore, in this case, you also need to consult a doctor as soon as possible for planned surgical removal, which is often more expedient and less traumatic.
Types and varieties
A formation that appears on any part of the head is called a fibroma. It is considered a benign tumor, not dangerous. In addition, its growth is very slow, which makes it possible to diagnose it at the initial stage before it reaches a large size. Fibroma of the head occurs in an adult or child, regardless of gender.
Depending on the location they distinguish:
Breast fibroma. The second name is fibroadenoma, which is a type of mastopathy.
Uterus. More often it is called fibroids, it forms in the body of the uterus, ranging in size from 1-2 mm to 20 cm. A woman can have single or multiple fibroids. The disease occurs without pronounced symptoms and is not prone to degeneration into a malignant neoplasm.
Fibroma of the lower extremities. This type of swelling is divided into localization of the disease in any area of the lower limb or just the foot. In the first case, it is formed in any area of the limb, having a different color, but a round shape. In this case, it appears only on the foot.
Skin. The size starts from 1-2 cm, with clearly defined boundaries, the fibroma is located under the scalp.
Skin fibroids are divided into hard and soft. Solids have a dense structure with limited mobility . When pressed, they go deep into the skin, leaving a concavity. Do not cause pain or physical discomfort. Most often they occur on the mucous membranes of the body and skin. Men and women are equally susceptible to them. Externally they can be convex or concave.
Soft fibroids look like a large mole or wart with varying color changes: from pale pink to purple. Most often they affect women over 40 years of age, as well as people suffering from excess weight. The location of fibroma is the armpits, chest and folds under it, scalp, ears, eyelids, and the front of the neck. Over time, multiple tumors appear in this area.
Even if a person notices the appearance of a mole or wart, it is worth consulting a dermatologist. Perhaps the formation is located in a place that is constantly exposed to mechanical damage, then the risk of its degeneration will increase.
Features of treatment of scalp tumors at Neo Skin Medical Center
First of all, the patient receives advice from a qualified dermatologist regarding his problem. The doctor listens carefully to the patient’s complaints, asks questions, and conducts a direct examination. If it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis, preoperative treatment may be prescribed. Depending on the feasibility, surgical treatment will be performed by an experienced surgeon.
Communication with a doctor takes place individually, without the presence of strangers, in compliance with strict confidentiality. Surgical treatment occurs under local anesthesia (drugs are selected individually).
When suturing a wound, only the highest quality materials are used.
Doctors at the Neo Skin center pay great attention to good cosmetic results.
- When removing tumors, only cosmetic (intradermal) sutures are used, which protects against the formation of rough scars.
- The area where the operation is performed is not trimmed (shaved), as happens in ordinary public hospitals, which very often causes patients to delay the moment of seeing a doctor.
- The postoperative period proceeds unnoticed by others. The patient does not drop out of everyday life.
After surgical treatment, the attending physician needs no more than three to four visits in a two-week period for a follow-up examination.
Treatment effectiveness
There are no relapses at the site of radical removal of benign formations of the skin and subcutaneous fat (the exception is lipomas, which recur in 5% of cases). This way you will get rid of the cosmetic effect and take care of your health. Unfortunately, there are a large number of growths or formations on the human body, these include not only formations on the head, but also tumors on the genitals.
Contact the Neo Skin medical center and get an effective solution to the problem of neoplasms of the scalp!
Causes
Scientists have not identified the main causes of scalp fibromas, but have identified predisposing factors. These include:
- Heredity.
- Injuries received. At the site of the injury, scar tissue forms, which is the optimal environment for the emergence and growth of scalp fibroids.
- Hormonal imbalance. When hormone levels are disrupted, the body experiences a disruption in the proliferation of connective tissue cells.
- Diabetes. This disease causes systematic metabolic disorders throughout the body, causing pathological processes.
- Having bad habits. Harmful substances contained in alcohol and tobacco products promote mutations in fibrous tissue, resulting in active cell reproduction.
- Papillomavirus.
- Decrease in the body's defenses.
- Age. Elderly people are more often susceptible to this type of disease.
- In addition to these main factors, radiation exposure also plays an important role.
What is it and why did it appear?
The scalp, with the exception of thick hair, is essentially not much different from neighboring areas of the body. It is also subject to pathological changes, among which proliferative processes occupy a special place. There are a number of additional factors that increase the risk of their development:
- Injury when combing or shaving.
- Exposure to chemicals (during painting, curling).
- Excessive insolation.
The most common benign growths include warts and papillomas. These are epithelial growths caused by papillomavirus. Typically, the pathogen penetrates through damaged skin in the presence of abrasions, scratches, and abrasions. Infection can occur in several ways:
- Contact household (use of shared towels, combs).
- Vertical (from mother to child during childbirth).
- Autoinoculation (during shaving).
There are more than 100 types of human papillomaviruses (HPV). Some of them do not manifest themselves in any way, others lead to the formation of warts, but there are also those that are dangerous for the development of precancerous and oncological processes. In addition to skin injury, predisposing factors are:
- Reduced immunological reactivity.
- Infectious diseases.
- Psycho-emotional stress.
- Vitamin deficiencies.
- Increased sweating.
Causes of pathology
Papilloma on the head, which can be clearly seen in photographs depicting people with HPV, does not arise without reason. Its appearance is provoked by various infections and bacteria. They are the ones who activate the dormant virus by penetrating the skin to the nerve endings.
Papilloma on the scalp can occur for the following reasons:
- Severe stress. Every second person finds himself in stressful situations every day, which have a detrimental effect on his overall health. Due to constant worries and worries, the virus awakens. It begins to move along the nerve canals and finds its way to the skin epithelium. If the virus penetrates cracks in the skin, it immediately appears on the top layer. Pathogenic growths begin to form on it, which indicate activation of HPV;
- Infection of damaged skin. Through small cracks, dirt enters the epidermis, which is an ideal environment for pathogenic microbes that activate HPV. This can happen even when simply combing your hair with a comb with too sharp teeth;
- Transmission of the virus from another carrier. People who often use hairdressing services and tattoo lovers are not immune from this problem. If the master did not properly handle the tools he used while cutting a haircut for a client with HPV, then there is a high probability that the disease will pass from him to a healthy person;
- Hormonal disorders. Skin growths in women often appear during complete hormonal changes. This usually occurs during pregnancy;
- Transmission of severe viral and infectious diseases. They greatly weaken the human immune system, which ceases to control the human immune system. For the same reason, papilloma appears on the head of a child whose immunity has not yet become sufficiently strong;
- Long-term use of potent medications. They are also capable of weakening the body’s defense system;
- Age. Doctors have come to the conclusion that papilloma in the head area is most often diagnosed in older people. It is believed that such growths are not capable of degenerating into cancer, so they are safe for human health.
Can papilloma appear on a child’s head?
The disease is both congenital and acquired, so there are cases of pathological growths being detected even in newborns. Also, in older children, pathological skin tumors appear due to HPV activity.
Usually, the appearance of papillomas on the scalp and body is blamed on a decrease in immunity for one reason or another. Therefore, in order to prevent the development of pathology, you need to be attentive to your own health and regularly strengthen your defense system with beneficial vitamins and microelements.
Types of skin tumors
Papilloma is a soft tissue formation of a papillary (thread-like) shape that is flesh-colored or brownish in color. As they grow, they can take on the appearance of a growth with a bumpy surface, similar to cauliflower. Usually, papillomas do not cause discomfort (except for aesthetic reasons), but if injured they can become inflamed or bleed.
Warts are defined as spherical or flat nodules with a keratinized, uneven surface. They have a dense structure, dry, painless. Sometimes warts merge into large plaques. Like papillomas, such growths do not cause discomfort, but with permanent damage they require increased attention.
Older people are more likely to develop keratoacanthoma, a benign tumor that originates from hair follicles. Such formations are round in shape, dense, and flesh-colored. Sometimes keratoacanthoma shows rapid growth, sometimes reaching 2–3 cm in diameter.
The most serious in terms of prognosis is melanoma - a malignant tumor of pigment cells with a high degree of aggressiveness. It looks like a small dark brown plaque with a rough surface and indistinct edges. The danger of melanoma lies in the rapid appearance of local screenings and distant metastases.
Another reason to visit an oncologist is basal cell carcinoma. This is a type of skin cancer that develops from cells of the basal layer of the epithelium. Such suspicion may arise when a flesh-colored or reddish nodule with a flaky or crusty surface is identified. After the latter falls off, the ulcerative defect is exposed. The tumor does not metastasize.
A red, bumpy formation under hair with a soft consistency usually turns out to be a hemangioma. This is a benign tumor that forms in the prenatal period due to a defect in the development of blood vessels. It rises above the surface of the skin, and when pressed, it collapses. When damaged, the hemangioma bleeds easily.
Not only papillomas and warts, but also other neoplasms, including malignant ones, can appear on the scalp.
Growths on the head in the hair
Neoplasms can appear on any part of the body. The scalp is no exception. However, this is a rather difficult place to independently determine the type of neoplasm that has appeared. Therefore, we have prepared a list of the most common growths on the head, dividing them into three groups: malignant, borderline and benign.
About neoplasms
In one of our articles “Skin growths: benign, malignant and borderline”. We have already talked about growths on the skin and classified them according to their danger to human health. Today we will look at those that are most often found on the head and are sometimes invisible under the hair.
Experts recommend regularly palpating and, if possible, examining the head for the presence of tumors, since the proximity of a malignant tumor to the brain can lead to irreparable consequences.
If you notice a strange growth on your head, immediately consult a dermatologist or oncologist.
The scalp is also the most traumatized and exposed area. Many people use combs with hard teeth, which can easily tear off the growth.
In addition, we wash our hair, dye it, apply masks that can corrode the tumor and provoke its degeneration into a malignant tumor. Another danger factor is prolonged exposure to the sun without a hat.
As you know, many moles tend to become malignant with prolonged and strong exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
That is why, if you feel or feel a growth in your hair that:
You need to urgently contact a specialist.
Types of neoplasms on the head
First, let's look at malignant neoplasms on the scalp.
First of all, malignant neoplasms include melanoma - skin cancer. You can find out more about it in our special article “Skin cancer: melanoma.” The neoplasm looks like a small plaque of light brown or black color with a rough surface.
Melanoma is dangerous, it metastasizes and can lead to irreparable consequences. Therefore, if it is detected on the scalp, you should immediately consult a doctor.
One of the most effective methods of treating melanoma is laser therapy; it helps skin cells regenerate faster and at the same time kills all harmful cells.
The second reason not to waste time and go for an examination to an oncologist may be a neoplasm that looks like a nodule with a crust, light pink or red in color - this is a basal cell carcinoma. It develops from the cells of the basal layer of the skin and is often accompanied by the formation of ulcers and erosions.
More information about this neoplasm can be found in our special article “Basal cell carcinoma. Skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma." An advanced treatment method for basal cell carcinoma is photodynamic therapy (for more details, see
PDT is a gentle treatment method that produces visible results after just a few sessions.
Skin epithelioma is a tumor that develops on the surface layer of the epidermis. Also distinguished is epithelioma of the sebaceous gland - a neoplasm that occurs on the scalp, with inflammation of the sebaceous glands.
Epithelioma looks like a pink or light brown growth and can reach 5 cm in diameter. This tumor is dangerous because it very quickly metastasizes to the lymph nodes.
It can occur against the background of previous dermatological diseases, as well as strong UV radiation.
Borderline neoplasms on the scalp
Scalp keratosis is a keratinization of the top layer of skin. Most often found on the face and scalp, it can be located either on a small area of the skin or affect the entire surface of the head. The neoplasm looks like multiple warts, ranging from light to dark brown in color.
Experts also identify seborrheic keratosis of the scalp; its appearance indicates pathologies occurring in the body. With this diagnosis, a thorough examination is necessary, since this may be evidence of cancer of the internal organs. Treatment for keratosis of the scalp is prescribed by an oncologist or dermatologist after receiving all the tests.
Treatment methods may include medications and peeling procedures, massage, and laser therapy.
Scalp keratoacanthoma is a benign tumor of the hair follicles that most often occurs in older people. It is a spherical dense neoplasm affecting the scalp.
Keratoacanthoma and its multiple forms are flesh-colored and can grow quickly, reaching 2-3 cm. In some cases, the neoplasm can become malignant, especially if it is often traumatized.
Treatment of keratoacanthoma is possible only with its complete excision using a scalpel, electric current or laser.
Benign neoplasms on the scalp
A mole is a small pigmented formation on the skin that can appear at any age and on any part of the skin, even on the head in the hair.
Moles can grow in large numbers during puberty, during hormonal imbalance or pregnancy, which you can read more about in our special article.
According to statistics, a mole on the scalp is not dangerous, and the likelihood of degeneration into skin cancer is extremely low. However, it is necessary to check moles; RTM diagnostics are the best way to deal with this.
Perhaps the most common neoplasms on the scalp are warts and papillomas. They appear due to the human papillomavirus, which is most often activated with reduced immunity, severe stress, infectious diseases, and a lack of vitamins in the body.
Find out more about what HPV is and how it manifests itself on the body in our article “Human Papilloma Virus”. Warts are classified as benign neoplasms, but if a wart on the head in the hair is often injured, then it must be removed.
The most effective method in such cases is laser removal.
Hemangioma of the scalp is a vascular tumor that appears due to improper development of blood vessels. It appears in infancy and most often forms on the face, neck or scalp. This is a benign neoplasm that does not cause harm to the body, except for aesthetic imperfection.
Hemangioma of the scalp is a racemous hemangioma; it is a lumpy pink, burgundy or red formation, reaching up to 5 cm in size, rising above the skin, and does not cause discomfort or pain when pressed. Removal of a hemangioma can be performed at any age, but first you need to consult a doctor.
Since removal of a hemangioma on the head may have a number of contraindications.
When treating any neoplasm on the head and hair, the most important thing is to consult a specialist in time. This will not only help identify a malignant tumor in the early stages, but also save life and health.
What is a blue nevus? Is this neoplasm dangerous?
Various remedies for warts in scalp hair
The appearance of skin tumors that resemble nodules and tubercles in appearance is caused by various reasons.
Typically, a wart on the head in the hair is a benign neoplasm that is not inflammatory in nature.
The growth has sharply defined contours and occurs against the background of infection with the papilloma virus. Melanomas, unlike warts, are malignant tumors of non-infectious origin.
Are growths on the head under the hair dangerous?
Hard or soft tubercles, elongated papillae on the skin cause a lot of trouble. Most people call any growths on the body “warts,” but skin tumors have different origins and require adequate treatment. There are warts of viral origin and non-infectious etiology.
The most common skin growths are usually benign or precancerous.
The appearance of the growth depends on the cause of the change and the properties of the skin of a particular person, the location and duration of the appearance of the tumor. Almost all types of warts initially look like flesh-colored or brown pimples. Large growths on the head under the hair and on the face can be flat and lumpy, relatively smooth and rough.
Why do the growths on the head increase in size?
Lumps under the hair on the head cause discomfort, although they are less noticeable than on the face and hands. However, the risk of damage is higher due to combing, cutting, and styling the hair. Getting rid of a wart on the head is especially difficult if the tumor becomes inflamed and increases in size. The reasons for unfavorable changes can be different, both internal and external.
Growths of different origins differ in appearance and tendency to malignancy (malignancy).
Factors influencing the increase in the number and size of warts on the face and under the hair on the head:
- unsuccessful attempts to self-treat skin tumors;
- diseases of internal organs, endocrine system;
- increased HPV activity with weakened immunity;
- injuries and any other damage to the skin;
- increased secretion of sebum by the sebaceous glands;
- profuse sweating, increased skin moisture;
- foci of infection in the body;
- dermatological diseases;
- taking certain medications;
- chronic stress.
A large number of people are susceptible to viral warts. Papillomavirus is present in the skin of 70–80% of the population, although it does not appear in every HPV carrier. Some skin growths go away on their own (without treatment). Most often, the number and size of warts increase with age, making it extremely difficult to get rid of them.
How to distinguish viral warts?
One or more benign lesions appear after infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). In the initial stages, the growths are flesh-colored or pinkish-pearl in color. They change with age and acquire a grayish-yellow or brown color. The diameter is up to 10 mm, and larger tumors are formed by the fusion of several growths.
The shape and size of warts of infectious origin depend on the type of virus (more than 100 different HPVs are known).
Human papillomavirus types 1, 2, 4 and 7 cause warts vulgaris. They have the form of hard growths with a rough horny surface and are localized on the head, face, arms and legs.
Juvenile warts occur when children and adolescents are infected with HPV-3, 10. These are round or polygonal nodules with a diameter of up to 5 mm, from flesh to grayish-yellow in color.
Condylomas are soft growths in the shape of a cockscomb, a mushroom on a knife, or cauliflower.
The difference between a wart of viral origin and a mole or atheroma:
- spread from the site of initial growth to other areas of the head, face, neck and upper body;
- gradual increase in size, tendency to merge;
- absence of hairs growing from the nodule;
- there is no skin pattern on the surface.
HPV infection occurs through domestic and sexual contact, and the virus is also transmitted to the child from the mother during childbirth. The virus infects the layer of skin at the border of the epidermis and dermis, where increased proliferation and keratinization of cells begins.
From the moment of infection to the formation of a growth, it takes from several weeks to 10–15 years.
Source: https://dermatitoff.ru/narosty-na-golove-v-volosah.html
Treatment of pathology
Based on the reason for the development of growths and their nature, various methods of therapeutic correction can be used. The doctor will tell you which of them is best to use in a particular case.
Methods for removing papillomas
Papillomas are recommended to be removed in several situations: the presence of a cosmetic defect, frequent trauma, the patient’s desire. Typically, minimally invasive methods are used for this:
- Cryotherapy (liquid nitrogen).
- Electrocoagulation.
- Laser destruction.
Such methods have a number of advantages - speed, low risk of side effects, quick recovery. If the growths are large and fused, instrumental excision (with a scalpel) may be required to remove them.
An alternative to radical removal using minimally invasive and surgical methods may be the use of local medications with destructive and cytostatic properties. These include:
- Podophyllin (Vartek, Condilin).
- Imiquimod (Keravort, Aldara).
- Synecatechin (Veregen).
- Solcoderm.
- 5-fluorouracil.
At the same time, you should undergo a course of treatment for HPV infection. Usually drugs with antiviral and immunomodulatory properties are prescribed: interferon, Panavir, Isoprinosine, Immunomax. Vitamins are also used to increase the body's nonspecific resistance.
To remove papillomas on the scalp, minimally invasive, surgical and medicinal methods are used.
Treatment methods
Methods for eliminating soft or hard bumps on the head depend on their origin, the severity of symptoms, and the age of the patient. If it does not increase in size and does not interfere with a person’s normal lifestyle, then doctors adhere to a wait-and-see approach. Only with its sudden growth will conservative or surgical treatment be carried out.
Ointments, gels, creams, balms
Immediately after a head injury, it is advisable to use a cold compress. A plastic bag should be filled with ice cubes and then wrapped in a thick cloth. Apply the compress every hour for 10 minutes. If a lump does form, external remedies will help. What to do to eliminate pain, what medications to use:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Ketorol, Nise, Voltaren. Ointments and gels relieve pain, relieve inflammation, and prevent the formation of edema;
- angioprotectors, venoprotectors - Troxevasin, Troxerutin, Lyoton, heparin ointment. They restore the integrity of damaged capillaries and eliminate bleeding.
Time-tested remedies have proven themselves well in resolving bumps on the head - balsamic liniment according to Vishnevsky, Naftaderm, balms with comfrey or cinquefoil. They are characterized by complex effects. The components remove excess fluid so that it does not compress sensitive nerve endings and reduce the severity of pain.
Tablets, capsules, dragees
The formation of bumps on the head, large and painful, often signals infection of the tissues. A similar situation usually arises when a doctor’s prohibition is violated - do not touch the lump, be careful when washing your hair. Staphylococcus aureus and epidermal staphylococci and opportunistic fungi penetrate into microcracks. An infectious-inflammatory process starts, which can only be stopped by taking antibiotics or antimycotics:
- macrolides Clarithromycin or Azithromycin;
- semisynthetic penicillins Amoxiclav, Augmentin;
- cephalosporins Ceftriaxone, Cefazolin;
- antimycotic agents Flucostat, Nystatin.
What to do with other formations?
The tactics of treating tumors of the scalp boils down to removing the formation itself and preventing metastasis (in case of malignant processes). The main method is surgical excision within healthy tissues or extended - with nearby lymph nodes.
For some tumors (keratoacanthoma, basal cell carcinoma, angiomas), laser therapy and cryodestruction are in demand. Late stages of melanoma are treated with chemotherapy, immunotherapy and radiotherapy. Gene therapy for the tumor is at the research stage.
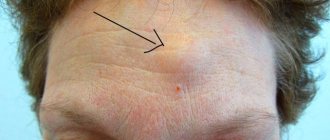
Atheroma
A lump on the head can reach the size of a chicken egg if the cause of its occurrence is atheroma. Atheroma is a fast-growing benign tumor that is formed due to the closure of the sebaceous gland duct. Typically, such a formation is painless, dense to the touch and increases in size over time.
Trauma, abrasions or friction of the skin over the atheroma contribute to the penetration of bacteria and the occurrence of a purulent-inflammatory process, leading to an increase in body temperature and pain in the area of the lump. An atheroma that has already arisen cannot disappear on its own, so surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
Neoplasms on the scalp
Neoplasms (papillomas, atheromas, wen) that appear on the scalp should be a reason for you to immediately consult a doctor. Why are they dangerous? It is important to understand that any benign formations (nevi, keratomas, papillomas) located on the scalp are very often injured as a result of washing the hair, using a hair dryer, hair dyes, combs, or wearing a tight hat. And trauma, as is known, can cause a benign tumor to develop into a malignant one .
Atheromas (sebaceous gland cysts) are benign formations. In addition to an extremely unaesthetic appearance, atheromas can fester, hurt, and cause fever and swelling. A suppurated arethroma can break out on its own. This leads to the need for urgent surgery - emergency surgery to remove atheroma on the head. Therefore, in this case, you also need to consult a doctor as soon as possible for planned surgical removal, which is often more expedient and less traumatic.
Formations such as lipomas do not develop into a malignant tumor, but they are characterized by active growth. Thus, over time, a pronounced cosmetic defect is formed. Therefore, you should also not delay the removal of lipomas on your head.
Remember , self-medication of such neoplasms is EXTREMELY contraindicated, as it can lead to the spread of the process.
If you suspect the appearance of neoplasms of the skin or subcutaneous fat of the scalp, you should immediately consult a doctor!
At the Neo Skin medical center you can receive a full range of services for the diagnosis and treatment of tumors of the scalp.
The center provides surgical treatment of tumor diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue of the scalp (benign and malignant tumors of the skin), atheromas (sebaceous gland cyst), lipomas (benign tumor of the subcutaneous fatty tissue), etc.
Possible reasons
Hematoma most often appears in children after a bruise, has a purple tint due to subcutaneous hemorrhage
Experts have identified the main factors that cause the growth of compaction. These include injuries, insect bites, inflammatory processes in soft tissues, as well as various subcutaneous formations. A treatment regimen is selected in accordance with the causes of the pathology.
Injuries
A large bump on the head often grows after a severe bruise. As a result of an impact or fall, a closed traumatic injury is formed. It is often accompanied by concussion and skull injuries.
Since the skin on the head is practically devoid of fatty tissue and fits tightly to the bone part, in case of injury, blood concentrates at the site of impact and forms a kind of compaction. This neoplasm is characterized by severe pain, especially at the moment of touch, hyperemia, swelling, extensive hematoma and hemorrhage.
As the injured area on the head heals, the skin tone changes from bright purple to yellow. Gradually the volume of the lump decreases and it disappears completely. A visit to a specialist is required, especially if the injury is accompanied by severe swelling, pain, bleeding, dizziness and nausea. Some of these symptoms indicate a concussion, which will require careful treatment.
Urgent medical care is necessary if a child is injured, or if an adult’s blow or fall has damaged not only soft tissues, but also the skull. First aid for the victim at home involves applying an ice pack to the injury site.
Allergy to insect bites
A large number of small bumps may indicate allergies or eczema
Allergies to insect bites are not common. However, depending on the degree of the body's reaction, the lump can grow up to several centimeters in diameter. It is accompanied by severe itching, swelling, and redness.
With constant scratching, when the skin receives microtrauma, there is a high risk of bacterial infection. This is especially true for young children, who are most susceptible to allergic reactions to the bites of gadflies, wasps, bees, and mosquitoes.
You can avoid the appearance of allergic seals with the help of antihistamines. For some time, you should exclude citrus fruits, coffee, chocolate, lemonade, and alcoholic beverages from your diet.
Hemangioma
Hemangioma is a benign neoplasm that is formed as a result of improper functioning of blood vessels and capillaries. Often found in newborns. They occur on the crown, occipital region, next to the ear, on the right or left side of the longitudinal axis of the skull. Hemangioma is characterized by:
- painlessness on palpation;
- clear contours of the seal;
- does not move when pressed.
This type of neoplasm does not affect the health of infants. In most cases, hemangioma goes away on its own without medical intervention. Despite this, parents should notify the pediatrician. If the tumor continues to grow and rises above the surface of the skin, diagnosis and subsequent surgery will be required.
Atheroma
The danger of atheroma is the ability to suppurate
The tumor occurs as a result of disturbances in the functioning of the sebaceous gland. In essence, atheroma is a cyst or cavity with a pasty secretion inside.
Atheroma is located in the subcutaneous fat, it is round in shape, soft to the touch and easily moves to the sides. It grows slowly, but in the absence of proper therapy it sometimes reaches more than 10 cm in diameter.
The increase in volume occurs due to the secretion in the cavity, which continues to be produced. As it accumulates, it stretches the walls of the cyst and nearby tissues. At the same time, patients have no complaints of pain, itching, or other unpleasant sensations.
Atheroma does not go away on its own - you need to have surgery and remove the contents of the cyst. It is forbidden to squeeze it out, since there is a high risk of pathogenic microorganisms entering the wound.
Lipoma
Lipoma is a painless neoplasm, but it can grow large
Lipoma is a neoplasm consisting of adipose tissue. A hard lump on the head has a dense structure, most often it does not hurt, but if it grows excessively, it can compress the nerve endings, as a result of which the patient feels some discomfort.
Lipoma occurs on the scalp. The most likely causes of its formation are metabolic disorders. Growing to large sizes, the wen strongly compresses the blood vessels. This causes spasms and leads to frequent headaches. Lipoma requires surgical intervention, as it can sometimes degenerate into a malignant tumor - liposarcoma.
Fibroma
Fibroma is also a benign neoplasm that consists of connective tissue. The tumor can appear on different parts of the body and head, reaching large sizes. The causes of fibroma development are hormonal imbalances, metabolic disorders, and hereditary factors.
Often, fibroma develops into a malignant form. Sarcofibroma is dense to the touch and absolutely painless when pressed. She requires urgent treatment.
Warts
A wart on the skin is a benign lump of predominantly viral origin. It resembles a dense compact ball that is located above the surface of the skin. More often, warts are localized on the temples, crown, and behind the ears. They have some distinctive features:
- solid structure;
- skin tone does not change, but may acquire a slight brown or reddish color;
- can be multiple and merge into one.
Warts feel rough to the touch. Their main danger is that these formations are easily injured, so you need to get rid of them.
Epidermal cyst
An epidermal cyst under unfavorable conditions can develop into cancer
An epidermal cyst appears on the top or back of the head, but often pops up in an area with little hair. As a rule, the cyst does not grow more than 5 cm in diameter, but there are cases when it has grown to enormous sizes. On palpation it is painless and does not manifest itself with other unpleasant symptoms.
Despite the fact that an epidermal cyst is a benign neoplasm, under unfavorable circumstances it can develop into a malignant one. Therefore, a compaction of this nature requires medical supervision and timely removal. There is a high risk of pathogenic microorganisms entering the cyst. In such cases, the doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics.
pilar cyst
The pilar cyst has another name - trichilemmal. It forms on the hair follicle. The cyst is filled with liquid secretion. In some cases, it grows to enormous sizes and is quite painful to the touch. It develops into a malignant tumor only in isolated cases. Treatment consists of surgical removal.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a skin disease
Seborrheic dermatitis is an inflammatory disease of the skin on the scalp. This is a rather unpleasant pathology, which is manifested by profuse dandruff, itching, and redness. With severe pathology, the accumulation of dead skin areas creates unevenness and compaction.
The causes of seborrheic dermatitis can be prolonged stress, poor diet, poor scalp care, and hereditary factors. Treatment is prescribed after a series of laboratory tests.
Psoriasis
Small bumps on the scalp can be caused by psoriasis. The pathology is characterized by the appearance of small red spots that itch, gradually growing over the surface of the head. Patients complain of pain around the rash and an abundance of scales. One of the common causes of psoriasis is intestinal slagging, and genetic predisposition cannot be ruled out.
Features of treatment of scalp tumors at Neo Skin Medical Center
First of all, the patient receives advice from a qualified dermatologist regarding his problem. The doctor listens carefully to the patient’s complaints, asks questions, and conducts a direct examination. If it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis, preoperative treatment may be prescribed. Depending on the feasibility, surgical treatment will be performed by an experienced surgeon.
Communication with a doctor takes place individually, without the presence of strangers, in compliance with strict confidentiality. Surgical treatment occurs under local anesthesia (drugs are selected individually).
When suturing a wound, only the highest quality materials are used.
Doctors at the Neo Skin center pay great attention to good cosmetic results.
- When removing tumors, only cosmetic (intradermal) sutures are used, which protects against the formation of rough scars.
- The area where the operation is performed is not trimmed (shaved), as happens in ordinary public hospitals, which very often causes patients to delay the moment of seeing a doctor.
- The postoperative period proceeds unnoticed by others. The patient does not drop out of everyday life.
After surgical treatment, the attending physician needs no more than three to four visits in a two-week period for a follow-up examination.
Treatment effectiveness
There are no relapses at the site of radical removal of benign formations of the skin and subcutaneous fat (the exception is lipomas, which recur in 5% of cases). This way you will get rid of the cosmetic effect and take care of your health. Unfortunately, there are a large number of growths or formations on the human body, these include not only formations on the head, but also tumors on the genitals.
Contact the Neo Skin medical center and get an effective solution to the problem of neoplasms of the scalp!
The danger of papilloma on the head
As long as the skin growth on the scalp is small, it does not cause any particular problems. A person may not even notice its presence or simply not attach any importance to papilloma. But this is a wrong action.
Papillomas on the head in the hair must be removed in the initial stages of development. Thanks to this, it will be possible to avoid the possible degeneration of the growth into an oncological tumor. In addition, the papilloma will gradually grow and cause inconvenience.
A large growth will certainly be touched during the process of combing the hair, coloring it and shaping it into a hairstyle. An injured scalp papilloma will begin to become inflamed and painful. All this will lead to an even greater increase in size.
In addition, overgrown warts are much more difficult to remove. After them, noticeable marks remain on the skin. Due to the pronounced inflammatory process, serious suppuration can occur, which is extremely undesirable to allow.