Almost all people have small cosmetic defects of various types and sizes on their skin. Some of them are safe, although not very aesthetically pleasing, while others are better to get rid of quickly. To figure out what yours are, contact an experienced cosmetologist-dermatologist.
It is best to remove all excess from the skin in winter - the absence of sunlight and heat will allow the healing process to proceed calmly.
Skin formations that a cosmetologist removes are divided into two groups:
- those whose appearance is caused by infection,
- a benign enlargement of any skin element not associated with infection.
Benign enlargement of any skin element
These skin defects have a number of features in common.
- They usually do not pose a health risk, but if they tend to become inflamed, which is common in people with weakened immune systems, they may require removal.
- Gradually they can become quite large, so for cosmetic purposes it is better to remove them while they are small.
- They are removed using electrocoagulation (electric current). Emla anesthetic cream is applied to the skin for 40 minutes, then each element is cauterized with a thin coagulator electrode. A crust remains at the site of removal, which must be treated daily with an antiseptic. After the crust falls off, a slightly pinkish spot remains, or less often a small pit, which gradually disappears. After removal, you should not sunbathe for at least a month.
- These formations can be deep, therefore, in order for the healing process to proceed faster and better, a few days before removal it is advisable to undergo a mesotherapy procedure (intradermal injections) with vitamins, antioxidants and hyaluronic acid.
Hyperplasia (thickening) of the sebaceous glands
What does it look like? Round lesions ranging in size from 2 mm to 1 cm with a slightly granular surface and a “umbilical” depression in the center. They hardly differ in color from normal skin or have a slightly noticeable yellowish tint. They protrude slightly above the surface of the skin.
Where? Hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands is most often unevenly “scattered” over the skin of the forehead, cheeks, temples and near the nose.
How to get rid of it? Using electrocoagulation. It is better to remove foci of hyperplasia while they are small, since with age they can become quite large, and then at the site of their removal (especially on the forehead) a pit may remain for quite a long time. Increased sebum secretion can contribute to the faster development of hyperplasia, therefore, after removal and falling off of the crusts, it is advisable to use cosmetics that reduce sebum secretion.
Syringoma
What does it look like? Syringomas are thickenings of sweat glands - small round, slightly loose compactions no larger than a match head. In color they either do not differ from the surrounding skin, or have a slightly yellowish tint - as if many lumps are deep in the skin and shine through it. Syringomas can occur in people of any age, starting from adolescence.
Where? On the skin around the eyes, mainly under the lower eyelids.
How to get rid of it? Using electrocoagulation.
Xanthelasma
What does it look like? Xanthelasmas look like small “bags of fat” scattered unevenly in the skin of the eyelids. They are irregular in shape, soft, yellow-white in color, and can be quite large - from 1 to 4-5 match heads. Most often found in people over 30 with high cholesterol levels.
Where? On the skin around the eyes, mainly on the upper eyelids.
How to get rid of it? Using electrocoagulation. If the level of cholesterol in the blood remains high, xanthelasma may appear again after removal. Therefore, it is advisable to combine cosmetic procedures with treatment aimed at lowering cholesterol levels, which is carried out by a therapist. This includes diet and special medications.
Milia
What do they look like? Small white “dots”, smooth, regular in shape. In essence, this is a blockage of the sebaceous glands, similar in origin to “blackheads” on the nose.
Where? On the skin of the eyelids and face.
How to get rid of it? Milia are superficial formations, sometimes they can be removed simply with a needle, but often they can be deeper and then require the use of a coagulator. Unlike the previously described formations, milia can go away on their own. But if there are a lot of them, and they are clearly increasing in number and size, it is better to contact a cosmetologist to remove them and find out the reasons for their appearance.
Keratoma (seborrheic wart)
What does it look like? A round or oval flat formation of a yellow-brownish hue. Keratomas can be either small “dots” or large “blobs” covered with loose yellow-brown crusts. The sudden, abundant appearance of “flocks” of keratomas scattered throughout the skin may indicate problems in the body.
Where? Typically, keratomas are located on the chest, neck, and face, although theoretically they can appear on any part of the skin. They often occur in tanning enthusiasts on the face, décolleté, neck and abdomen, although they can also “please” those who sunbathe infrequently.
How to get rid of it? Keratomas are not dangerous to health. They must be removed if they quickly enlarge, darken, become inflamed or bleed. In this case, the doctor will send the questionable area for histological examination. Keratomas develop in people whose upper layer of skin is prone to excessive thickening, so they are advised to use peelings, home or professional, scrubs, medicated body milk with fruit acids or urea.
Elimination of various skin defects
Cost of services
40.165 Removal of neoplasms of the face Nevi (moles), fibromas, keratomas, cutaneous horn on the face, warts ranging in size from 1mm-4mm 1 pc. 500 40.166 Removal of neoplasms of the face Nevi (moles), fibromas, keratomas, cutaneous horn on the face, warts ranging in size from 5mm-1cm 1 pc. 1000 40.167 Removal of tumors on the body: from 1 mm in diameter (1 pc.) 400 40.168 Removal of tumors on the body: size from 5mm-1cm (1 piece) 900 40.169 Fibroids (up to 5 mm.) 1000 40.170 Papillomas, soft Face: size from 1 mm - 2 mm (1 piece) 300 40.171 Papillomas, soft Face: size from 5 mm - 1 cm 400 40.172 Papillomas, soft Body: size from 1 mm - 4 mm 300 40.173 Papillomas, soft - body: size from 4 mm - 10 mm 400 40.174 Papilomas from 5 to 15 pieces. 3000 40.175 Papilomas from 15 to 20 pcs. 3500 40.176 Papilomas from 20 to 30 pcs. 4500 40.177 Papilomas from 30 to 40 pcs. 5500 40.178 Milia 250 40.179 Genital warts 1 piece 1000 40.180 Removal of molluscum contagiosum (per element) - Mechanical (with tweezers) 200 40.181 Removal of molluscum contagiosum (per element) – Laser 400 40.182 Xanthelasmas - up to 4 mm 1400 40.183 Xanthelasmas - more than 4 mm 1800 40.185 Surgical excision of atheromas and dermatofibromas - Body: 1 mm/diameter (up to 5 cm) 400 40.186 Surgical excision of atheromas and dermatofibromas (5 cm or more) 200 40.187 Surgical excision of atheromas and dermatofibromas Face: 1 mm/diameter 500 40.188 Surgical excision of body scars: Surgical excision of body scars - 1 cm 2000 40.189 Surgical excision of scars on the body: Surgical excision of scars on the face - 1 cm 5000 40.190 Surgical excision of facial scars: Surgical excision of facial scars - mm/diameter 500
Moles, freckles, papillomas, warts are on the body of almost every person. They arise due to excessive growth of tissue in a specific place and are called “neoplasms”.
There are hundreds of types of skin tumors, which can be divided into three categories: benign, precancerous and malignant. There is no need to panic, but you definitely need to check the formations on your skin. This is especially true for any tumors, spots, moles that are large or localized in areas of friction - the armpit, neck, groin. And if the formations begin to grow, change visually, or, even worse, get sick, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible!
Please note that diagnosis is only possible after a series of examinations. Determining the exact nature of the tumor “by eye” is not realistic.
CLASSIFICATION OF SKIN NEOPROMATS
BENIGN EDUCATIONS are not dangerous to human life. But this does not mean that they can be ignored. Especially if the tumor is large and poorly located on the body, regularly subject to friction. In some cases, these tumors can develop into cancer or disrupt the functioning of body systems or individual organs, so their nature should be studied and, if possible, removed. The removal procedure is performed on an outpatient basis and is painless and effective.
There are congenital and acquired benign formations, among them: atheroma, hemangioma, lymphangioma, lipoma, papilloma, mole, nevus, fibroma, neurofibroma.
MALIGNANT TUMORS behave aggressively, grow quickly, affecting surrounding tissues. The earlier a tumor is detected, the greater the chance of cure.
Important! Treatment of malignant tumors is carried out exclusively by an oncologist.
PRE-CANCEROR CONDITIONS of the skin include senile keratoma, xeroderma pigmentosum, cutaneous horn, and Bowen's dermatosis. Each type has its own characteristics; treatment requires contacting an oncologist.
DETAILS ABOUT BENIGN NEOPLASMS
Benign formations, as a rule, have smooth, clear edges, are symmetrical, and uniform in color and structure. Their size usually does not exceed seven centimeters.
Let's look at the most common ones.
MOLES (nevi) appear as excessive pigmentation and come in different shapes, sizes and colors - from light brown to black (related to the amount of pigment - melanin). They have a smooth surface, but sometimes rise above the skin.
ü capable of degenerating into malignant formations
WARTS and PAPILLOMAS look like nodules, have clear contours, and the color is different shades of brown. They arise due to the presence of the papilloma virus in the human body. They have a bumpy surface.
ü capable of degenerating into malignant formations
When they appear, KERATOMS have a flat base and are rough to the touch. In later stages, they become like warts covered with fat. They can be of different colors, often a group of keratomas is immediately formed. A possible reason is decreased immunity.
- can degenerate into malignant formations
LIPOMS are formed from adipose tissue, which is why they are also called wen. There are several types of lipomas, all of which are recommended to be removed. They are prone to active growth and can grow between muscles or vascular bundles to the periosteum.
ü can cause pain
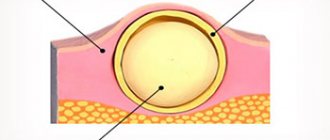
ATHEROMAS or sebaceous gland cysts look like pimples and have a smooth red surface. They appear where there is hair - on the back, face, head, in the groin area.
- dangerous due to inflammation
MILIUMS are white or yellowish nodules that rise above the skin. They arise due to the active work of the sebaceous glands. They often appear on the face and are a cosmetic problem.
- cosmetic defect
HAMANGIOMAS are formed due to the atypical behavior of blood vessel cells and represent the proliferation of a vascular network on the surface of the skin. They can reach large sizes and come in colors from red to black.
- dangerous due to the possibility of the appearance of cancer cells among benign
DIAGNOSTICS
So, we briefly talked about common benign neoplasms. If you come across a description of your problem, then you should definitely make an appointment with a dermatologist. It has been proven that congenital moles and nevi pose the greatest danger, so experts recommend that they be examined and removed immediately.
At the appointment, the doctor will collect an anamnesis, carefully examine the neoplasm and, if necessary, conduct a histological examination to identify atypical cells.
If a decision is made to remove the tumor, you will need to undergo a series of blood and urine tests, a cardiogram and fluorography. Additional research may be carried out.
MODERN METHODS FOR REMOVAL OF NEW TUMORS
Today in aesthetic medicine several methods are used to remove skin lesions. The specific type of intervention is determined by the doctor based on the individual characteristics of each patient. The cost of the intervention will depend on the specific tumor (its size, location) and the chosen method of removal.
CRYODESTRATION
Removal of tumors occurs using liquid nitrogen, which has a very low temperature and freezes tumors, destroying their structure. This method requires special professionalism and experience from the doctor, since it is impossible to control the depth of exposure.
The procedure is quick and painless, leaving no scars. Cryodestruction is well suited for removing tumors in the face and neck.
RADIO WAVE METHOD
Radioknife, as a modern alternative to a scalpel, is considered the safest of all methods of exposure. The method involves exposing tissue to radio waves, which remove the tumor by heating and destroying cells. It is important that the tumor is not damaged and is transferred for further research intact.
The operation is painless and is performed using local anesthetics. After the procedure, no stitches are required and no scars are left. Recovery takes 5-7 days.
The “Medina” clinic uses the “Surgitron” radioknife.
SURGICAL METHOD
In some cases, it is advisable to remove formations using the classical surgical method. For example, excision with a scalpel is carried out if malignancy is suspected (degeneration into a malignant tumor). If the doctor recommends surgical removal according to indications, you should definitely listen.
The operation is performed using local anesthesia. Rehabilitation takes up to three weeks.
REHABILITATION
The duration of rehabilitation depends on the chosen method of removing the formation. Recovery can take from three days using modern methods to three weeks with surgery.
It is not recommended to sunbathe, visit the sauna and swimming pool. If pain occurs, it can be relieved with local anesthetics. If the removal was carried out on the facial skin, you should not use cosmetics until complete healing. The surgical site should be protected from sunlight to avoid post-traumatic pigmentation.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Contraindications to the removal of benign formations are severe mental disorders, infections in the acute stage, psoriasis, diabetes mellitus, exacerbation of herpes, dermatological diseases in the area of education, low blood clotting, severe vascular and heart diseases, pregnancy and lactation.
If, as a result of histological examination, there is a suspicion that the neoplasm is malignant, the patient must consult an oncologist.
ADVIСE
In the first days after surgery, swelling, redness, and pain may occur. This is fine. But if these problems do not go away, you need to consult a doctor to take action.
To ensure that rough scars do not remain at the surgical site, you should carefully follow the doctor’s recommendations and properly care for the sutures.
Contact only professionals. After unprofessional cryodestruction, it is possible to get burns, resulting in scars on the skin.
Removing tumors is part of the treatment. Experts recommend subsequent therapy aimed at eliminating the cause. Only an integrated approach prevents relapse.
Skin defects of infectious nature
These formations are removed using electrocoagulation with the parallel use of immunomodulatory methods.
Papillomas
What do they look like? Like tiny “bags” or “droplets” the color of normal skin, hanging on a thin stalk or sitting like a rounded “button”. They can be either single or abundantly covering the skin. The appearance of papillomas indicates a weakening of local immunity to the human papillomavirus.
Where? On the skin of the neck, armpits and under the breasts, less often on other areas of the skin. Almost everyone has papillomas, “relatives” of warts.
How to get rid of it? It is advisable to combine electrocoagulation of papillomas with strengthening the local immunity of the skin. It is advisable to use oxygen-ozone therapy (daily application of ozonated oil and injection of an oxygen-ozone mixture twice a week 7-10 times), local use of ointments with an immunomodulatory effect (ointments with interferon).
Papillomas are superficial formations, so the skin heals quickly after their removal.
If there are a very large number of papillomas or their reappearance after their removal, systemic immunocorrection is prescribed: oral administration of immunomodulators or an injection course. For this, Lykopid, Immunomax, Panavir, Polyoxidonium, Kagocel and a number of other drugs are used (as prescribed by a doctor).
Warts
What do they look like? Formations of irregular shape with a rough surface. They can be quite large. The appearance of warts near the nail or on the sole of the foot is especially unpleasant - in these areas, their removal is most labor-intensive.
Where? Most often on the skin of the hands and feet, although they can be located anywhere.
How to get rid of it? Warts must be removed, as they are contagious - this is the most famous viral skin problem. Warts are removed by electrocoagulation or cauterization with liquid nitrogen. Electrocoagulation is preferable, as it allows you to “target” more accurately and not injure the skin around the wart, and the healing process is easier under the crust, and not under the bubble, as when using liquid nitrogen. Before removing a wart, it is advisable to inject an anesthetic, lidocaine or ultracaine, under it, which will eliminate pain.
For multiple warts, systemic immunocorrection is necessary, as well as examination to identify possible causes that contribute to decreased immunity.