Causes
Xanthomatosis is usually caused by high levels of lipids, that is, fats, in the blood. Also, xanthomas on the skin appear in diseases accompanied by lipid metabolism disorders:
- atherosclerosis;
- diabetes;
- hypothyroidism;
- primary biliary cirrhosis of the liver;
- cholelithiasis and other types of cholestasis;
- nephrotic syndrome in kidney disease;
- hematological diseases;
- malignant tumors;
- side effect of taking prednisolone, tamoxifen or cyclosporine.
One of the reasons for the appearance of xanthoma on the skin in young people is familial hyperlipidemia, accompanied by an increase in the level of triglycerides and cholesterol in the blood.
Xanthomas themselves are not dangerous. However, it is necessary to identify their cause. First of all, you need a consultation with a dermatologist and an examination by a therapist. If necessary, the patient continues treatment with a cardiologist, endocrinologist, nephrologist, hepatologist, hematologist, or oncologist.
Specifics of the therapeutic course
The goal of drug treatment is to eliminate cholesterol accumulations, as well as normalize lipid metabolism. If cholesterol levels are significantly elevated, the use of statins is indicated, which help inhibit the production of food enzymes that ensure the formation of cholesterol. In this situation, medications such as:
- Atomax, Atoris;
- Simvastol, Akorta;
- Roxera, Torvacard;
- Cardiostatin, Rosacard;
- Liptonorm.
These medications can compete with drugs that are made from natural raw materials. An excellent example is Polycanazole, which is produced from sugar cane. This product has virtually no side effects.
Thanks to bile acid sequestrants, it is possible to perform lipid metabolism and also fight hypercholesterolemia. Doctors prescribe proton pump inhibitors, which include Pravastatin, Simvastatin. You can take fibric acid derivatives: Gemfibrozil, Fenofibrate and Clofibrate. Probucol is often prescribed - a mild drug that has an excellent effect on the body.
Folk remedies that are actively used in the fight against xanthoma deserve special attention. The most popular of them are:
- Garlic perfectly regulates blood cholesterol levels.
- Vitamins. Vitamin B3, a natural statin present in green vegetables, meat, milk, and cereals, deserves special attention. Ascorbic acid inhibits the production of lipoproteins.
- Soy products, as well as those that contain a large amount of fiber (legumes, oats, barley, carrots).
- Fish oil is the best way to control lipid metabolism. It is recommended to eat fatty fish.
- Linseed oil.
- Products that contain resveratrol. These include: cocoa, dark grapes and peanuts.
This decoction helps perfectly: 5 tablespoons of spruce needles, 200 grams of rose hips, pour 1.5 liters of water, cook for twenty minutes. Take one hundred milliliters twice a day for one month.
Gastric xanthoma is a benign formation that requires timely treatment. During therapy, you need to adhere to a strict diet to help restore balance. It is mandatory to remove cream, butter, sour cream, fatty foods and alcoholic beverages from the diet. It is undesirable to eat lamb, pork and lard
If symptoms appear, it is important to immediately visit a doctor and not self-medicate.
Symptoms
Xanthomas on the skin associated with the accumulation of fats are clinically divided into several options:
- flat;
- intertriginous;
- palmar;
- tendon;
- tuberose;
- flat eruptive.
Sometimes there is a combination of several types.
Flat
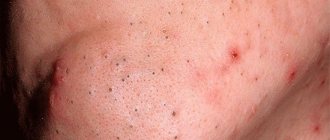
The most common type of formation. Xanthomas are asymptomatic and appear on the skin as soft, velvety, flat, polygonal yellow elements. Most often, a flat xanthoma of the eyelids is observed, at the inner corner of the eye. Sometimes they reach gigantic sizes.
Tuberous (lumpy)
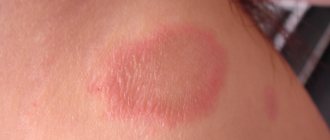
These are firm, painless, red-yellow nodules. Lesions on the skin can be multiple and merging. Such xanthomas usually develop in places of friction and pressure, for example, on the extensor surfaces of the knees, elbows, and buttocks. Sometimes they appear on the skin of the cheeks or the bridge of the nose.
Tendon
Slowly enlarging subcutaneous nodules associated with tendon and ligament tissue. These include gouty tophi, affecting the big toe. Such xanthomas most often occur in the extensor area of the upper limbs and in the Achilles tendon.
Eruptive
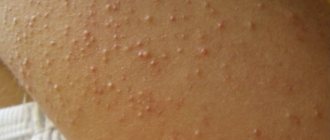
Eruptive xanthomas on the skin are localized mainly on the buttocks, shoulders, and extensor surfaces of the limbs. Sometimes the mucous membrane of the mouth and face are affected. The lesions are rashes of red-yellow papules on reddened skin. They are accompanied by itching and sensitivity to the touch.
Xanthomas on the palms look like spots; they can appear on other parts of the body. The palmar fold is most often affected by type 3 dyslipoproteinemia.
In patients with normal blood lipid levels, special disseminated and verrucous forms of xanthomatosis occur.
1. Tendon xanthoma 2. Eruptive xanthoma
Disseminated form
The disseminated form of xanthomatosis is observed mainly in adults and looks like multiple red-yellow tubercles and nodules located in the folds of the skin, as well as numerous xanthelasmas on the eyelids. In diffuse xanthomatosis, the skin is affected in the form of yellow plaques under the eyes, on the neck, upper torso, buttocks and in skin folds. In rare cases, the oral cavity is additionally involved.
Verrucous form
Such xanthomas occur primarily in the oral cavity of adults. These are single asymptomatic lesions. They can also be localized on the forearms, limbs, anogenital area, as well as on the walls of the esophagus, making swallowing difficult.
Xanthelasma
A type of xanthoma. Xanthoma is similar in appearance to a yellow subcutaneous formation that appears on the limbs, buttocks and other areas of the skin, and xanthelasma rises above the skin surface, forming a tumor-like formation, primarily around the eyes.
Diet for xanthomas
Proper nutrition, based on a balance of consumption of normal amounts of fats, proteins and carbohydrates, is the basis for the treatment of all disorders leading to the appearance of xanthomas. Diet recommendations should correspond to the original etiology of the disease and the age of the patient. If the indicated nutritional conditions are observed, multiple xanthomas in children and patients under 25 years of age decrease in size or disappear altogether. A diet for xanthelasma helps prevent the appearance of new tumors and the proliferation of old ones.
A diet aimed at regulating lipid metabolism in children diagnosed with xanthomatosis due to diabetes and obesity involves, in addition to limiting animal fats, reducing the daily calorie intake.
Prohibited products include: lard and pork in any form, duck and goose meat, butter, sour cream, fatty fish (mackerel, salmon). It is also not recommended to consume fresh whole milk. You can eat eggs, but no more than one per day and no more than two per week. When preparing dishes with eggs, try to use only the whites.
It is recommended to eat steamed or baked food. Preference should be given to protein and plant foods. Patients with congestion in the liver are recommended to drink more vegetable juices and eat fresh salads seasoned with olive or sesame oil. It is known that fermented milk products, especially cheese, cottage cheese, kefir and yogurt, increase the amount of bound cholesterol, so they should definitely be included in the diet. Preference should be given to fermented milk products with reduced fat content. Products with a fat content of 0% and 0.5% are considered useless for combating metabolic disorders. Fermented milk drinks should be chosen with a fat content of 1-1.5%, cottage cheese 5-6% and cheese no more than 45%.
For diseases associated with impaired absorption of lipid compounds, it is not recommended to eat meat by-products (liver, heart). When cooking chicken or turkey, you must remove the skin.
For recovery and prevention of xanthomas, it is recommended to regularly include in the diet foods that accelerate metabolism, the so-called natural fat burners. These products include: grapefruit, green tea, celery, cinnamon and ginger. It is also recommended to consume foods high in vegetable fats, proteins and amino acids. These foods include mushrooms, avocado and spinach.
We recommend reading
Scabies - symptoms, photos and first signs
Surgitron device and treatment method
Causes of Acanthosis Nigricans and Treatment Methods
How and what napkins help in the treatment of trophic ulcers
Complications of xanthomatosis
Typically, xanthomas on the skin do not cause any complications. Health problems can arise if you do not pay attention to the causes of this condition. In this case, the likelihood of hypertensive crises, angina pectoris and myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke and even death increases.
As a rule, most xanthomas on the eyelids do not affect vision. However, there is a small chance that a large formation will cause ptosis - drooping eyelid. As a result, vision in the affected eye gradually deteriorates.
Large xanthomas on the skin can change the patient's appearance, causing cosmetic defects.
Types of xanthoma
Depending on the structure, location and appearance of the formations, there are several types of xanthoma.
Based on the location of lipid deposits, formations are divided into 2 groups.
- Cutaneous neoplasms. The patient's skin is covered with xanthomas on top. The formations are easily amenable to therapeutic effects.
- Internal xanthomas. The formations are localized on the meninges, tendons, and muscle surfaces. The pathology is difficult to diagnose and requires long-term therapeutic intervention. Tendon or Achilles xanthoma is especially dangerous.
Experts also classify xanthomas according to the nature of their formation.
- Eruptive xanthoma. A distinctive feature is the acquired red color. Then the eruptive xanthoma changes color to a characteristic yellow. The tumor retains a burgundy rim for a long time. The formations are round or spherical in shape, small and medium in size.
- Tuberous xanthoma. A distinctive feature is symmetry in arrangement and a yellow or brown tint. The formations are large in size.
- Flat xanthoma. The formations have a round, slightly convex shape. Their localization occurs on the hands and palms. Sizes range from small to large.
- Xanthelasma of the eyelids. Medium-sized formations. They have a yellow or brown tint. Cover the upper eyelid and area around the eyes.
Separately, experts distinguish gastric xanthoma. Fatty growths are localized on the mucous tissues of the gastrointestinal tract. The formations are benign, but can develop into cancerous tumors.
Gastric xanthomas are asymptomatic. They are diagnosed by gastroscopy. They are typical for patients with diabetes, gastritis, and atherosclerosis. The antrum of the stomach is most often susceptible to xanthomas. Therapy involves taking lipid-lowering drugs and prescribing a diet. No surgery required.
Cutaneous xanthomas are easily treated.
Associated conditions
The presence of skin xanthoma in a patient may indicate the possibility of the following diseases and conditions:
- myocardial infarction, aortic valve pathology, as well as pancreatitis;
- large single flat elements sometimes accompany chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, mastocytoma, and ultraviolet ray damage;
- POEMS syndrome (polyneuropathy, organomegaly, pathology of the endocrine glands, skin changes caused by M protein), systemic sarcoidosis and insufficient number of liver bile ducts;
- primary or secondary hyperlipidemia - an increase in fat content in the blood caused by hereditary diseases or atherosclerosis.
Disseminated xanthomatosis affects various internal organs, and patients experience difficulty swallowing, shortness of breath, and blurred vision. The functioning of the central nervous system and musculoskeletal system is disrupted. Such xanthomatosis is often associated with lymphoproliferative diseases and hematological malignancies, such as leukemia. In addition, these patients have an increased likelihood of oral candidiasis, Budd-Chiari syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and Hand-Schuler-Christian disease.
The verrucous form of xanthomatosis accompanies the following diseases:
- lichen planus;
- Paget's disease;
- epidermal nevus;
- discoid lupus erythematosus;
- pemphigus vulgaris;
- dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa;
- chronic graft-versus-host disease;
- actinic keratosis;
- squamous cell carcinoma;
- congenital developmental defects;
- consequences of PUVA therapy with psoralen or radiation treatment;
- period after bone marrow transplantation.
Forecast
The prognosis of the disorder directly depends on the factors that provoked it. This is due to the fact that in some cases xanthomas can disappear on their own, while in others they can lead to consequences such as atherosclerosis of the coronary or cerebral vessels, heart disease and an increase in liver size. However, the most common danger of the disease lies in its frequent relapses.
In addition, patients should not forget about the possible formation of complications of the underlying disease. Often, in addition to cosmetic inconveniences, xanthomas do not cause any other discomfort, which is why the prognosis of the disease is favorable.
Diagnosis of xanthomatosis
The doctor studies the state of lipid metabolism to identify primary and secondary hyperlipidemia. Blood tests are used for cholesterol, low- and high-density lipoproteins, and triglycerides. Liver and kidney function tests are performed.
To confirm xanthomatosis of the Achilles tendon, ultrasound and MRI are used. For disseminated xanthomatosis, positron emission computed tomography can be used to identify the severity of the disease and assess the effectiveness of treatment.
In doubtful cases, a histological examination of tissue obtained from these formations is prescribed. In this case, vacuolated or foamy macrophages are determined - cells that have absorbed fat, which dissolved during processing of the biopsy sample.
Eruptive foci may contain inflammatory infiltrates; verrucous, tendinous and tuberous - connective tissue.
Prevention of pathology
Prevention of xanthomatosis consists of measures aimed at maintaining a healthy lipid balance, as well as timely identification of diseases that affect it.
These measures include:
- moderate consumption of carbohydrates and animal fats in the diet;
- periodic weighing and weight loss;
- avoidance of excessive alcohol consumption;
- annual preventive medical examination and laboratory tests.
Harmless-looking rashes, even if they do not cause discomfort, should not be taken lightly. The disturbances in the body that they indicate can be very serious. If a xanthoma rash appears on the body, a medical examination is mandatory.
Treatment of xanthomatosis
Eruptive xanthomatosis
Is it possible to remove xanthoma and how to do it
Xanthomatosis is treated with medications or surgery.
Xanthomas are not always associated with hyperlipidemia, but if it is present, it requires mandatory treatment. This will not only reduce the risk of complications of atherosclerosis, but also reduce the size of the pathological formation itself. In severe hypertriglyceridemia, the main goal of treatment is the prevention of pancreatitis.
To treat hyperlipidemia, a special diet and lipid-lowering drugs are used. The latter include statins, fibrates, bile acids, resins, probucol and niacin. After starting to take them, eruptive xanthomas begin to disappear within a week, tuberous xanthomas after a few months, and tendinous xanthomas within several years.
The formation itself can be removed using trichloroacetic acid applications.
If drug therapy is ineffective or inappropriate, xanthomatosis is treated surgically, but lipid-lowering drugs are still not canceled to reduce the risk of systemic complications of hyperlipidemia.
Removing xanthomas using excision with a scalpel is a very effective, but also the most traumatic method. During surgery, bleeding inevitably occurs and there is a risk of infection. After the intervention, almost all patients are left with small scars.
Usually the formation is removed with a laser, excision followed by skin grafting, removal using cryodestruction or electrocoagulation.
Laser technique is the most popular for the treatment of xanthomatosis. Its effectiveness largely depends on the skill of the surgeon. An experienced doctor can remove all lesions in one session without damaging the dermis and thereby minimizing the risk of scarring. The operation is performed under local anesthesia, the patient's eyes are protected with special glasses.
Electrocoagulation (cauterization using high temperature) has the following advantages:
- lower cost than laser removal;
- no risk of retinal burns.
Cryotherapy is rarely used to eliminate xanthelasmas. This is due to the difficulty of protecting the eyes from the effects of low temperatures, as well as the greater likelihood of scarring compared to other methods. However, the advantage of such an intervention is the extremely low risk of infectious complications.
After surgery, relapses of xanthomatosis and complications are possible, for example:
- temporary redness of the skin;
- infectious complications, suppuration;
- scarring;
- formation of dark spots - hyperpigmentation.
With disseminated xanthomatosis, various internal organs may be involved in the process, which determines the severity of the disease. In other cases, the disease has a benign course. In some cases, xanthomas may disappear spontaneously. They never turn into skin cancer.
Xanthoma and biopsy
Where is the entrance to the vagina in the photo
Most experts argue that there is no need to take a biopsy from the formation and conduct research. But some malignant neoplasms can be similar to xanthomas, and they can only be identified through analysis. In this case, it is necessary to conduct a thorough morphological study and carry out dynamic monitoring of patients. The inconsistency of data about the disease makes it necessary to study this disease. Doctors conduct scientific research, during which they study the mechanisms of the formation of precancerous conditions against the background of the influence of exogenous and endogenous factors. It is necessary to substantiate the principles of inhibition of pathological processes and the frequency of xanthoma formation in patients with chronic gastritis.
For this purpose, a certain group was examined that had chronic gastritis. A full examination was carried out for them - histological, endoscopic, cytological analyses. A multivariate analysis was carried out based on all the data obtained.
Many endoscopy specialists do not diagnose xanthomas for several reasons. They do not attach much importance to these formations. In addition, xanthomas may be invisible due to the fact that the stomach foams. Special preparations that extinguish foam quickly clear the stomach of mucus. After this, a detailed inspection can be carried out. Endoscopic examination becomes accessible, and microscopic pathologies and xanthomas can be viewed without problems.
Numerous tests have confirmed that gastric xanthomas are an important endoscopic sign. The frequency and distribution of lipid formations increased if morphological, atrophic microscopic changes and hyperplasia of the mucous membrane in the stomach increased. This gave grounds for the fact that such formations are not serious changes, but are a significant diagnostic mark or signal of precancerous conditions in the gastric mucosa (dysplasia, metaplasia, atrophic manifestations).
Despite the fact that xanthomas are small formations, diagnosis should not be neglected. Physicians conducting endoscopic examinations must necessarily indicate the presence of such formations in endoscopic protocols. If they have been identified, this indicates the need to conduct thorough examinations of the patient so that it is possible to timely diagnose the cancerous condition of the gastric mucosa in the initial stages.
Lotions
Xanthelasma of the eyelids: treatment with folk remedies can be carried out using butter (60 g) and freshly squeezed watercress juice (3 tablespoons). The oil is pre-softened and juice is added to it, mixed thoroughly. Apply the composition to the growth daily until it disappears.
You can use vegetable oil, which is heated in a steam bath and salt is added to it. After this, the growth is cauterized with a cotton swab dipped in oil. The procedure should be carried out until a crust appears. After this, you should wait until it disappears along with the xanthelasma.
Good reviews for the following recipe:
- lard (100 g);
- chopped garlic (50 g).
The lard is melted in a water bath, garlic is added and heated for 3 minutes. After this, the composition is cooled. Every day the mass is applied to the growth and covered with a cabbage leaf, fixed.
Treatment with folk remedies for xanthelasma of the eyelids without surgery can be carried out with a mixture of wheat grains and vegetable oil. The composition requires half a teaspoon of ground wheat grains. They are filled with vegetable oil. You can use olive or sea buckthorn. You will need so much oil until you get a mixture that has a consistency similar to thick sour cream. The composition is applied to the damaged area of skin for 10 minutes daily. Lotions should be applied until the growth opens.
The remedy can be prepared from badger fat. 20 grams of fat is dissolved in a water bath until it melts. Apply to plaques while hot, but not scalding. The product can even be rubbed in for several minutes.
Patient reviews
- I've had high cholesterol all my life, it's hereditary. New plaques constantly appear on the eyelids. I had it removed by a surgeon, with a laser, and tried compresses and lotions. They still appear. Herbal decoctions are the only thing that at least increases the intervals between relapses. Alina, Moscow .
- I removed xanthelasma surgically. They appeared again. I'm thinking about laser, but I'm afraid. For now I drink propolis and apply zinc ointment. I try to follow a diet, but I love butter, which is fatty, which may be why there is little result. Alexey, Ekaterinburg .
- Growths suddenly appeared on both the upper and lower eyelids. They got bigger and looked ugly. She refused to remove it. They treated the liver and fat metabolism. I follow a strict diet, drink a decoction with mint, and apply hydrocortisone. The plaques have stopped growing and in some places seem to have shrunk. I hope for a more visible result. Galina, St. Petersburg .