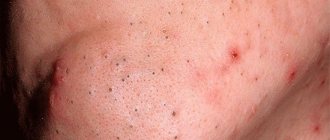
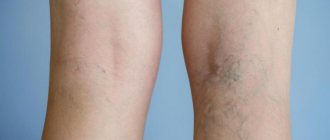
Keratosis - main symptoms:
- Itchy skin
- Hair loss
- Dry skin
- Skin pigmentation
- Hair fragility
- The appearance of blisters
- Pain syndrome
- New growths on the skin
- Appearance of warts
- Dandruff
- Cracks in the skin
- Dull hair
- Scales on the skin
- Dry hair
- Split ends
- Skin roughness
- Formation of areas with keratinized skin
- Thickening of the skin
- Change in skin tone
- Bleeding skin
Causes of keratosis
The causes of keratosis are endogenous and exogenous factors, depending on the form of the disease.
Common reasons include:
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation is the most common cause of keratosis of the facial skin;
- damage by aggressive chemicals;
- injuries;
- insect bites that produce toxins;
- skin infection for various reasons;
- inflammatory processes of the skin, exposure to bacteria, fungi, viruses;
- somatic diseases, especially inflammation of the digestive system, nervous diseases, pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- metabolic disorder;
- decreased immune status;
- hematopoietic disorder;
- endocrine disorders;
- benign and malignant neoplasms, especially blood and skin;
- allergic reactions;
- hormonal changes;
- old age;
- heredity (Darier's disease, Mibelli's poroquetosis, Miescher-Lutz elastosis).
Keratosis in a child can develop as a result of intrauterine intoxication. There are frequent cases of pathology developing against the background of other skin diseases, for example, atopic dermatitis (allergic reactions associated with genetic disorders).
Reasons for appearance
The exact causes of the disease have not yet been established. The main one is regular exposure to ultraviolet radiation. It affects the dermis, epidermal layers, blood vessels, sebaceous glands, and melonocytes.
Gradually, under the influence of sunlight, the disturbances increase, reaching the peak of the disease.
The following factors contribute to the development of pathology:
- genetic predisposition;
- weakened immune system;
- influence on the skin of chemicals (resinous substances, oil, sand, etc.);
- past infections;
- age-related changes (the disease most often affects people over 50 years of age).
Due to weak immunity, AIDS carriers, people with problems with the nervous and endocrine systems, as well as patients who have undergone chemotherapy or complex operations are more prone to the appearance of keratosis.
Some types of keratoses often affect young people. This usually applies to red-haired or fair-haired people with gray, blue or green eyes. Research shows that by the age of 40, 60% of the population has at least one element of keratosis.
Over the age of 80, everyone has some type of this pathology.
Classification
Conventionally, pathology is divided into several types.
By degree of distribution:
- Diffuse - almost the entire surface of the skin is affected.
- Localized (focal) - specific areas of the body are affected.
By origin:
- Congenital - the prerequisites for the disease are laid in intrauterine development.
- Acquired - occurs at any age under the influence of external or internal factors.
- Symptomatic is one of the manifestations of dermatosis.
By localization:
- Keratosis of the cervix.
- Follicular (hyperkeratosis) - blockage of the hair follicle by epidermal scales.
- Keratosis of the facial skin.
- The scalp.
- Plantar keratosis.
- Keratosis of the vulva.
- Keratosis of the feet.
For development reasons:
- Solar keratosis (actinic) is a reaction to excessive exposure to sunlight. In older people, senile keratosis, a precancerous condition, may occur.
- Actinic keratosis or seborrheic - “senile warts”, basal cell papilloma.
- Pilar keratosis (pilaris) is inherited, the most common (50–80% of all skin pathologies in adolescents, 40% in adults).
- Lichenoid keratosis - develops as a result of infection of skin formations that, when inflamed, resemble lichen planus.
- Professional – associated with constant skin contact with aggressive environments.
- Ichthyosis occurs when protein metabolism is disrupted due to a gene mutation.
The classification is conditional. As such, there is no classification of keratosis due to the variety of manifestations and causes.
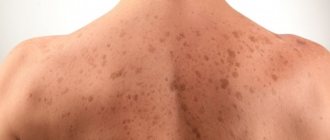
Follicular keratosis photo.
Prevention of occurrence
Foot disease can be prevented if it is not caused by internal factors. To prevent keratinized areas from appearing on the sole, you should:
- Choose the right shoes. It is better if it is made of natural materials with orthopedic insoles. The model should be comfortable, and the size should match the foot.
- Get rid of excess weight, which puts pressure on the feet, which provokes the formation of “corns”. By avoiding the accumulation of extra pounds, you can prevent yourself from developing hyperkeratosis on the sole.
- Perform regular foot care routines. Timely removal of the stratum corneum using pumice and the use of moisturizing creams will prevent the appearance of hyperkeratosis.
- Treat foot lesions with mycosis in a timely manner using effective anti-fungal medications.
If keratinized areas of skin appear on the soles, this indicates the presence of foot deformities or internal health problems. The formation of epidermal compactions should not be neglected. A cosmetic defect can develop into a serious complication.
The article has been verified by the editors
Symptoms of keratosis
Provoking factors in the development of clinical manifestations may be:
- avitaminosis;
- stress;
- use of oral contraceptives;
- unhealthy food;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- cold weather.
General symptoms:
- pigmented skin;
- keratinization;
- the appearance of various formations or thickenings;
- itching;
- possible pain syndrome;
- bleeding
The nature of skin formations and symptoms vary depending on the form of the disease and location.
With palmoplantar keratosis, keratinization, deep cracks, and blisters appear on the heels. Roughness of the skin on the hands and feet occurs in 100% of cases, a change in the shade of the dermis from amber to brown - in 90%, increased sweating of the soles and palms - in 70%, painful cracks - in 60% of cases. Keratosis of the feet can occur when wearing uncomfortable shoes or an unsuccessful pedicure.
Keratosis symptoms
The first symptom of keratosis of the scalp is dry skin and hair, deterioration of hair condition (brittleness, dullness, split ends), dandruff. Next, keratinization appears in the area of the hair follicles, irregularities and tubercles are felt on the head, which can bleed if damaged.
As the disease progresses, hair begins to fall out in individual areas or over the entire surface at once. At the site of baldness, hair does not grow back, which is due to the death of the hair follicles.
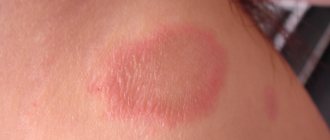
The seborrheic form is characterized by the appearance of hyper-pigmented spots, which transform into warts or plaques with clearly defined boundaries, covered with crusts. Plaques can occur anywhere on the body, plural or singular. The color of the formation varies, from flesh-colored to black. When subjected to mechanical damage (rubbing, squeezing), warts bleed.
Symptoms of the follicular form usually appear at an early age. The first manifestation is dry dermis. Next, nodules with hairs on top appear, which are located symmetrically on the skin. A peculiarity in children is keratosis on the face, usually without any unpleasant sensations other than aesthetic ones. Often these manifestations disappear during adolescence due to hormonal changes.
Skin damage in the solar (actinic) form of the pathology occurs in open areas with direct exposure to ultraviolet radiation. At risk are older people, those who spend a long time in the sun, people with fair skin, HIV-infected people, and those with age spots.
The senile form is characterized by the formation of multiple fused hard scales on open areas of the body. Round or oval lesions up to one centimeter in size are difficult and painful to remove. At risk are men, people with skin photosensitivity types I – III, who are exposed to ultraviolet radiation for a long time.
Seborrheic keratosis photo.
What is keratosis
The pathology consists in the compaction of epithelial cells, which provokes the development of a neoplasm with defined boundaries.
A keratoma may look like:
- plaque;
- spot;
- crust;
- node;
- growth
Keratosis of the skin, photos in adults are presented below, belongs to the category of age-related pathologies. But some types can be diagnosed in children. Keratosis usually affects people over 40 years of age. The peak incidence occurs between the ages of 55 and 65 years.
The disease develops in both men and women. In some cases it disappears without therapy. The neoplasm is classified as benign, but can develop into a malignant form. Flat cells are similar in morphology to malignant cells, so if pathology appears, it is advisable to immediately seek help from a specialist.
Diagnostics
The clinical picture of the disease is pronounced, so an experienced specialist can make a diagnosis based on a visual examination. To clarify the form of pathology and differentiation, a microscopic examination is carried out. Modern devices have great capabilities and provide information sufficient for a clear understanding of the disease.
The main method for the final diagnosis is histological examination of a biopsy specimen, which makes it possible to establish the type of skin formation, stage, nature of the pathological process, and obtain other accurate indicators based on which adequate treatment is selected.
Stages and degrees of the disease
Keratosis of the skin develops gradually. Each type has its own clinical picture. In the cyanide form, as the tumor grows, the area of the skin affected by the pathology becomes dark and loose. At the second stage, cysts form in the tissues.
The skin becomes lumpy and begins to peel. When the keratoma is damaged, it begins to bleed and becomes painful. Sometimes an inflammatory process occurs.
In the initial stages of angiokeratoma, blue-black vascular nodules, the diameter of which is 2-5 mm, form on the patient’s skin. They are based on dermal cells. At the second stage, the nodules become rough and begin to peel off. At the last stage, the nodules begin to bleed and become inflamed. This form of disease also occurs in newborns.
The pathological process is localized in the area:
- scrotum;
- belly;
- hips;
- buttocks;
- armpits;
- oral cavity;
- vulva;
- stop;
- lips;
- cheeks;
- fingers.
Keratosis of the skin.
Photos of adults show what neoplasms may look like. The follicular form most often develops in women. It is characterized by the formation of flesh-colored keratinized plugs on the hair follicles. New growths are uneven. Their structure resembles flat, silvery scales. The size of the neoplasms is no more than 1.5 cm.
Most often localized in the area:
- faces;
- buttocks;
- neck;
- armpits.
Keratosis of the skin (the photo in adults shows only external symptoms) begins in the cold season. In warm weather, the symptoms are erased. At a late stage of the disease, the nodules increase in size. The surface of the skin becomes rough. At the last stage, they may begin to bleed and hurt. The seborrheic appearance is characterized by slow development and chronic course.
A spot on the skin of a yellowish tint reaches a diameter of 3 cm. It has a dense morphology with scabs. At the second stage, the spot begins to increase in size and many layers form in it. The neoplasm becomes crusty. The thickness of the stain reaches 1.5 cm. On the last steel, the seal begins to turn black, crack and bleed.
Treatment of keratosis
You can get rid of keratosis with the help of comprehensive treatment after identifying the cause of the disease. The treatment is carried out by a dermatologist; you may need to consult a geneticist, endocrinologist, nutritionist, or oncologist.
The treatment complex includes:
- systemic therapy;
- diet therapy;
- symptomatic treatment;
- surgical intervention;
- local treatment;
- traditional methods.
Vitamins (A, D), fish oil, calcium and iron supplements are prescribed, and, if necessary, painkillers. The specific treatment regimen is selected individually, taking into account the causes and manifestations.
For topical use, creams, sprays, and gels based on sodium chlorite are used with a moisturizing and anti-inflammatory effect.
If you have hyperkeratosis of the feet, you should consult a podiatrist. For keratosis of the foot, treatment is aimed at careful care and hygiene procedures. First, you should soften the stratum corneum using salt baths or softening cosmetic products. The hard layer is then removed and then sanded.
A competent podiatrist carefully removes the rough layer to reveal healthy skin. To remove corns and rough skin, using a sugar cone is effective - a pedicure milling machine with a garnet-coated cutter can be used both at home and in beauty salons. Hardware procedures are hygienic and effective.
Treating keratosis at home
To treat keratosis at home, caring emollient oils (lavender, rosemary, pine oil), hand and foot baths, special lotions, and gels are used. It is especially effective to use herbal baths in the morning and evening hours before abrasive procedures, after which a medicinal ointment or oil is applied. Compresses are made from herbs with anti-inflammatory and healing effects (chamomile, sage, aloe, etc.). The main goal is to soften the formation and carefully remove it.
Lavender oil photo.
The healing properties of tar soap in the fight against skin diseases have been known since ancient times. Tar soap removes excess sebum, preventing clogging of pores, reduces sweating, dries out inflammation on the skin, fights dandruff, and makes hair stronger and thicker. Due to the content of tannins and oils in soap, it has an anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and moisturizing effect. Skin and hair look well-groomed after using soap.
It is recommended to eat a diet that excludes canned foods, spicy, fatty, pickled foods, baked goods, sweet carbonated drinks, alcohol and those foods to which the patient may develop an allergic reaction. It is recommended to consume large amounts of vitamins contained in fresh fruits and vegetables, seafood, and cereals.
How to remove skin tags
Gentle surgical and cosmetic techniques are used to remove growths:
- Cryotherapy is indicated for large lesions; the technology involves the effect of liquid nitrogen on the formation. After freezing, the plaques undergo necrosis and are removed. A possible complication of cryotherapy is hyperpigmentation.
- Laser therapy - laser removal. The manipulation involves the impact of a laser beam on pathological lesions. This is the most effective method of combating keratotic formations, characterized by painlessness, speed, and absence of consequences.
- Diathermocoagulation - removal of lesions with electric current is performed under anesthesia. There is a high risk of scarring and pigmented spots.
- Phototherapy is the treatment of keratotic lesions with a special agent that increases the sensitivity of the epidermis to light waves of a certain length. The plaques are then exposed to light rays without damaging healthy tissue. After the procedure, you should not stay in the sun for 48 hours.
- Plasmolifting - plasma injections to stimulate local immunity and skin regeneration.
- Biorevitalization - injections of hyaluronic acid improve the condition of the skin, rejuvenate it, and increase its ability to regenerate.
For minor lesions, chemical peeling (glycolic, lactic, glycolic-salicylic) helps - the use of acids for a chemical effect on warts.
Solar keratoses are treated using curettage, a surgical technique in which localized affected areas are scraped out using a curette. Curettage is not used to remove actinic lesions on the face, since the manipulation may leave a scar.
For ichthyosis skin lesions (“fish scales”), warm alkaline baths (up to 39 degrees) help, after which the patient is wrapped in a blanket for two hours and given hot herbal tea to drink. Heat dilates blood vessels, promotes sweating, exfoliation, moisturizing the skin, and stimulates the muscle and vasomotor reflex.
An hour after the bath, the body is lubricated with salicylic acid in combination with oil or fat. Combining baths with massage is effective. The treatment is long-term.
Treatment
The treatment regimen depends on the form of keratosis and its severity.
The goal of treatment is to eliminate the provoking factor (fungal or bacterial infection, hormonal disorders, etc.). The patient must be prescribed a therapy regimen that allows him to adjust the production of keratin.
Is keratosis of the palmoplantar region treated with medications?
The main drug for treating this problem is the drug Niotigazon. It belongs to the group of antipsoriatic drugs, helps regulate the processes of renewal and keratinization of the epidermis. The dosage and course of administration are selected individually. In this case, the severity of keratoderma, age and weight of the patient must be taken into account.
If for some reason the patient cannot take Niotigazon, he is prescribed the following drugs:
- keratolytics (help exfoliate dead skin areas);
- retinoids in the form of ointments (stop the further process of proliferation of epidermal cells).
The complex treatment necessarily includes physiotherapeutic procedures (UV therapy, dithermocoagulation, baths, etc.).
When a secondary bacterial infection occurs, a course of antibacterial agents is prescribed. If the cause of keratosis is a fungal microflora, then the patient is prescribed antimycotic drugs.
How to treat keratosis of the nails
Antifungal drugs, both external and internal, are used for treatment.
Common and effective drugs include Clotrimazole, Nystatin, Pimafucin, Clotrimazole, etc. The course of treatment is long - from several months to six months. These products help relieve inflammation, itching, flaking of the skin and other unpleasant symptoms.
Folk remedies for the treatment of nail hyperkeratosis are also popular. This includes baths of sea salt or herbal infusions, rubbing in essential oils, etc. Experts recommend using such treatment methods in combination with the use of medications to obtain maximum results.
How is plantar pathology treated in children?
Children of childhood are prescribed long-term use of retinol, iron supplements, and in severe cases, glucocorticosteroids are used (mainly agents for external application). Phonophoresis with vitamins must be prescribed; the number of courses is determined individually (on average 25-30 sessions). This treatment is carried out several times a year (with exacerbation of symptoms).
Is it possible to treat with folk remedies?
Traditional medicine methods are used in combination with drug therapy. The most common and effective are:
- compresses made from fresh aloe or burdock leaves (have an anti-inflammatory effect, soften keratinized areas);
- rubbing essential oils of lavender, jasmine, etc. into the affected areas.
Regular baths with sea salt will help remove dead skin. After steaming, rub your palms or soles with pumice. After the procedure, be sure to lubricate the treated areas with a moisturizer. Before starting treatment with traditional methods, you should definitely consult your doctor.
Vitamin therapy
Taking a complex of vitamins is considered a prerequisite for a positive treatment result.
It includes vitamin A, group B, C, PP, etc. Patients are also prescribed immunostimulants and angioprotectors. The course and dosage are determined by the doctor individually. Palmoplantar keratoderma is a genetic disease that occurs in a chronic form. The development is based on a mutation of the genes responsible for the production of keratin complexes in the body. Depending on the type and severity of keratosis, the patient is selected an appropriate treatment regimen. Therapy lasts a long time, and the patient is often prescribed preventive courses of medications to reduce the risk of repeated relapses.
Forecasts
The outcome of the disease depends on the type and extent of the keratotic process. In general, the prognosis is favorable with timely treatment and compliance with medical recommendations. In the absence of proper treatment, the development of microbial eczema, malignant neoplasm, tooth loss, hyperpigmentation, disruption of the endocrine system, and the development of depression are possible.
The most unfavorable prognosis is considered to be the senile form of keratosis. Plaques do not disappear on their own, as, for example, with the follicular form. This is a precancerous condition: in the absence of treatment, irrational therapy, and constant trauma to the lesions, degeneration into squamous cell carcinoma is possible. Malignancy occurs in 2–5% of cases.
Ichthyosis can be complicated by metabolic disorders, folliculitis, progression of chronic diseases, and the addition of new systemic diseases. If ichthyosis is detected in the fetus, it is recommended to terminate the pregnancy.
The risk group includes people with fair skin, a family history, those living in a sunny, hot climate, those who have undergone radiation and chemotherapy, and those who are HIV-infected.
Treatment methods for skin on feet
Therapy for hyperkeratosis on the legs is complex. To get rid of the pathology, it is recommended to perform foot peeling, hardware medical pedicure, take medications, make foot baths and use special care products.
Drug treatment
Hyperkeratosis of the feet is accompanied by dryness of the outer skin, therefore, for its treatment, retinoids and products with vitamin D are prescribed, which help accelerate the process of shedding the keratinized epidermis and the formation of new cells in its place.
Tigazon
Contains vitamin A and belongs to the category of retinoids. The medicine normalizes the processes of cell formation and desquamation of the skin. Prescribed at the rate of 0.5-1 mg per 1 kg of body weight, taken for 2-3 months.
Calcipotriol
It is an active form of vitamin D and is used to treat areas of the nail bed and skin of the feet affected by hyperkeratosis. The first results of drug therapy are visible after two weeks of use.
Lipamide
The active components of the product are similar in their pharmacological properties to lipoic acid, but are better absorbed by the body. The use of the medication normalizes metabolic processes in the body and improves fat balance.
Ointments
When small areas of the feet are affected by hyperkeratosis, fatty ointments have a good effect, helping to retain moisture and soften the outer covering. Useful active substances are urea, panthenol, salicylic and lactic (fruit) acids, corticosteroids. Let's consider the most popular local remedies:
- Belosalik. The ointment has keratolytic and anti-inflammatory properties. The drug is applied in a thin layer to the affected areas 1-2 times a day. For mild illness, several applications of the ointment are sufficient; in advanced cases, the course of treatment lasts 3-4 weeks.
- Solkokerasal. Helps soften the skin of the feet and prevents the appearance of cracks. Salicylic acid, which is part of the ointment, produces an antiseptic effect, and urea softens the stratum corneum. The fatty base of the drug combats dry skin.
- Hydrocortisone ointment. Glucocorticosteroids in this product give a quick but short-lasting effect, normalize the process of epithelial discharge, and minimize irritation and inflammation. The ointment is applied with light rubbing circular movements onto the affected areas of the skin twice a day. The duration of use depends on the degree of manifestation of hyperkeratosis and the use of other means of therapy.
Solcokerasal does not contain steroid components, so it can be used for long-term treatment of foot hyperkeratosis without fear of side effects.
Treatment in the podiatrist's office
Therapy for foot hyperkeratosis begins with a visit to a highly specialized doctor – a podiatrist. The doctor, after a thorough examination and detailed study of the medical history, will be able to make a diagnosis. Health-improving activities are carried out according to a scheme developed over many years. It consists of several stages: softening of the hardened epidermis; cleansing of the stratum corneum; polishing the surface of the feet. At the moment, there is no universal remedy that allows you to remove rough skin without using a scalpel. To eliminate the defect, it is necessary to go through all stages of treatment for foot hyperkeratosis.
Prevention
Keratotic skin lesions are a complex problem that is difficult to eliminate. In order not to encounter the disease, it is recommended:
- avoid prolonged exposure to the sun, especially for people at risk, do not be in the sun from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.;
- do not sunbathe in the sun or in a solarium, especially if the patient has solar keratosis;
- use sunscreen, wear glasses with UV filters, sick people - wear natural, light clothing with long sleeves, comfortable shoes;
- take care of the immune system, strengthen it, eat rationally;
- do not overcool;
- maintain hygiene;
- avoid injury to the skin.
People suffering from dermatoses should undergo regular medical examinations with a dermatologist and preventive treatment, and eliminate irritating and provoking factors.
Possible causes of the disease
Fraxel - laser therapy for facial skin
There are several possible causes of hyperkeratosis. All of them can be divided into two groups: external factors and internal ones. Considering each potential cause, the disease is completely avoidable.
External factors include the following:
There are several possible causes of hyperkeratosis.
- influence of chemicals (for example, if a person’s work involves constant contact with chemicals);
- failure to comply with hygiene rules (inadequate compliance);
- staying in direct sunlight or strong wind for too long;
- washing with low-quality (hard) water.
Internal factors for the development of hyperkeratosis are:
- diabetes;
- genetic mutations;
- circulatory disorders;
- psoriasis;
- problems in the gastrointestinal tract;
- psychosomatic manifestations;
- lichen;
- ichthyosis.
What to do?
If you think you have Keratosis
and symptoms characteristic of this disease, then doctors can help you: dermatologist, podologist.
We wish everyone good health!
Diseases with similar symptoms
Ringworm (overlapping symptoms: 5 out of 20)
Ringworm is a fungal disease that affects the human skin. The disease is accompanied by skin rashes (in the form of spots), peeling and slight itching. The disease mainly affects children and people aged 30 to 70 years. Ringworm affects both men and women equally.
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks:
Symptoms of hyperkeratosis on the skin
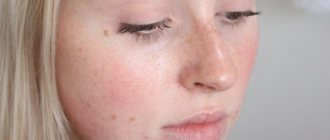
Follicular hyperkeratosis appears as small bumps located around the hairs on the facial skin. These are dense red formations that peel and itch. The external signs of the formations resemble the “goose bumps” that occur during a chill.
With the lenticular form of hyperkeratosis, papules of horny tissue ranging in size from 1 mm to 5 mm are formed. The formations are reddish-brown or yellow-orange in color.
After removal, a weeping surface prone to bleeding can be found under the papule. Papules are single and do not tend to merge. They do not cause much discomfort to the patient except for moderate itching, which rarely occurs.
In the disseminated form of hyperkeratosis, various elements are formed on the skin that resemble short and thick hairs. In some cases, they unite several follicles, taking the shape of a brush. They are characterized by active peeling.
Regardless of the form of hyperkeratosis, the patient’s skin is dry and pigmented. With tactile contact, distinct seals can be seen. Most often, elements of hyperkeratosis are localized in the space between the eyebrows, wings and sinuses of the nose. This is due to the abundance of sebaceous and sweat glands in these areas, which are susceptible to various types of infections.