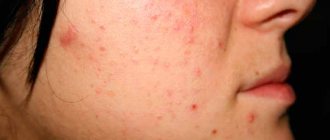
Infectious diseases include fungus on the face, which appears after contact with a person suffering from a fungal disease, or when using the personal belongings of an infected person. Often, pathogenic fungi get on the skin of the face or mucous membranes of the eyes after contact with animals with fungal diseases.
Fungus on the skin of the face occurs in adults and children, but it is not recommended to try to get rid of it on your own, since there is a high probability of causing great damage to the appearance and causing serious complications.
Symptoms
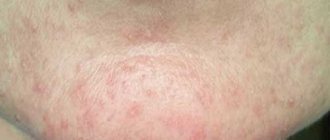
Clinical manifestations of classic fungal infection are characterized by extremely unpleasant syndromes. In this regard, the atypical course of the disease is more favorable, since it is not accompanied by the usual symptoms of mycosis in the form of severe itching and peeling. With all this, the following general symptoms of fungal infection have diagnostic significance:
- the appearance of red spots;
- the appearance of rashes on the face, cracks, ulcers;
- slight increase in temperature.
Fungus on a child's face
Due to the immature immune system, the growing organism is especially susceptible to mycosis. In most cases, facial skin fungus appears in children due to contact with sick people and poor personal hygiene. However, in young patients the symptoms of the disease manifest themselves much more intensely than in adults. Thus, in children, infection with mycosis is additionally accompanied by:
- dry skin;
- release of fluid from foci of infection;
- the appearance of a grayish coating on pathological areas.
Specific symptoms of different types of mycosis
Methods for treating fungus
For a fungal infection on the face, medications are prescribed
For fungus on the face, treatment should be timely. Some types of the disease are very contagious, so a person can pose a danger to others. Standard treatment regimen for any fungal skin diseases:
- careful hygiene;
- applying ointments against fungus on the face;
- immunomodulatory therapy.
Reasons for appearance
Scratches and microcracks on the face serve as gateways for infection. Once in the deep layers of the skin, the fungus begins to actively feed on the cells of the epidermis. Under favorable conditions, the pathogen finds opportunities for unlimited synthesis of mycelium threads. These processes do not go unnoticed on the skin of the face – it turns red, becomes dry, and itches. Among other predisposing factors for the development of fungal infection, experts name:
- diabetes;
- improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract;
- vascular pathologies;
- decreased immunity;
- excessive sweating of the dermis;
- hormonal imbalance;
- neglect of hygiene standards.
Types of fungal skin infections
Depending on the pathogen, the symptoms of mycosis may vary slightly in each individual clinical case. In order to verify the preliminary diagnosis, additional tests are prescribed. During the latter, as a rule, the direct causative agent of the disease is identified. Subsequently, based on the data obtained, one of the following diagnoses is made:
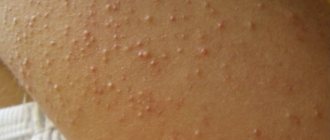
- Trichophytosis (ringworm) - the causative agent of the disease is fungi of the genus Trichophyton. As the latter penetrates into the deep layers of the dermis, bright red spots appear on the patient’s facial skin. The affected areas peel off and become covered with multiple nodules.
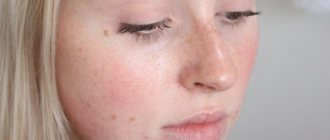
- Pityriasis versicolor (varicolored) - the pathology is caused by the yeast-like pathogenic fungi Malassezia furfur. Against the background of the disease, the infected person develops pink scaly spots, which subsequently increase significantly and merge into a single pathological focus.
- Seborrheic dermatitis - this type of lesion occurs due to infection with fungi of the genus Malassezia furfur. Focal manifestations of this disease are located mainly in places of greatest accumulation of sebum. In some cases, pathological formations are covered with a hemorrhagic crust. Seborrheic dermatitis is accompanied by itching.
- Rubromycosis - the causative agent of this type of mycotic infection is fungi of the genus Malassezia rubrum. With this form of lesion, large red spots appear on the patient’s skin, surrounded by a ridge of papules.
- Microsporia – this type of mycosis is caused by Microsporum. The disease is characterized by large red spots, above which rises a ridge covered with multiple blisters.
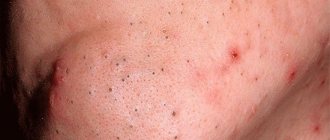
- Candidiasis is caused by a yeast fungus of the genus Candida. Along with the skin, the pathogen can infect mucous membranes. Thus, painful blisters filled with serous fluid are often found not only on the skin, but also in the patient’s mouth.
Traditional medicine recipes for fungus on the skin of the face
In parallel with traditional medicine, you can successfully use “grandmother’s” recipes, which help to quickly relieve symptoms and stop the spread of mycosis.
Below are effective remedies, recipes have been tested over the years:
- lotions with a decoction of celandine. To prepare a decoction, add 3 tablespoons to 1 liter of hot water. herbs, leave in a water bath for 15 minutes. The broth is filtered, cooled, and used to wipe the affected areas of the skin twice a day;
- rubbing with lemon juice. A simple and affordable way to stop mycosis, since the fungus does not like an acidic environment. The juice of 1 lemon is poured into a glass of boiling water. The solution is cooled and used to wipe the skin of the face;
- garlic ointment. To prepare the ointment, you need to grind a clove of garlic into porridge and mix it with butter 1:1. The ointment is applied to the spots, covered with a bandage and fixed until the morning;
- honey. If you are not allergic to bee products, you can use honey water to wipe your skin. Dilute natural honey in a ratio of 1:10 with boiled water.
Treatment
The essence of therapy for mycotic skin infections, first of all, comes down to the speedy elimination of the pathogenic agent from the affected area. In the background is the elimination of factors leading to infection. In view of this, in the treatment of mycoses, the use of systemic and local medications with an antifungal effect is justified. Regarding the former, it is important to say that the dosage and regimen of their use is determined individually for each patient.
Oral antimycotics are extremely toxic to the liver, so their use should be under strict medical supervision. In addition to systemic therapy with tablets, local agents are mandatory when treating fungus. Special ointments, creams and other medicinal formulations contain specific substances that are harmful to the fungus. Simultaneously with the treatment of mycosis, it is extremely important to take all measures necessary to strengthen the immune system:
- get rid of chronic diseases;
- maintain a sleep-wake schedule;
- lead an active lifestyle and adhere to the basics of proper nutrition;
- take vitamins and probiotics.
Drug treatment
Fungal diseases of the facial skin require effective treatment, which entirely depends on the correct diagnosis of the pathogen based on scraping tests of the patient’s skin flakes and visual examination. In the absence of adequate therapy, the pathogen begins to multiply unhindered, resulting in the disease taking a chronic course. In most cases, to combat a fungal infection, a comprehensive treatment regimen is developed using the following groups of drugs:
- multivitamin complexes;
- antihistamines;
- systemic drugs with fungicidal and fungistatic effects;
- external antifungal agents;
- enzymes and probiotics.
Systemic therapy for fungal infections involves oral administration of antifungals. The use of the latter promotes selective accumulation of the drug in the affected area in a concentration necessary to effectively suppress the development of the pathogen. For the purpose of systemic influence on a foreign agent, the following drugs are mostly used for internal use:
- Nizoral - the active ingredient of the drug is ketoconazole. Nizoral has a fungicidal, fungistatic effect. The medicine acts against dimorphic, yeast and other fungi. The drug is indicated for systemic lesions, mycoses of soft tissues and skin. The course of therapy is determined individually in each specific case. The average dosage for adults is 200 mg per day. Limitations for taking Nizoral include renal or liver failure. Side effects of the drug include hepatitis, paresthesia, and abdominal pain.
- Lamisil - the active component of the drug is terbinafine. This substance suppresses the early stage of sterol biosynthesis in the pathogen cell, which results in the death of the latter. Lamisil has a wide spectrum of action, so it is used for any type of fungal infection. For adults, the drug is prescribed 250 mg once a day. To treat mycosis caused by yeast, it is recommended to take the tablets for 2-4 weeks. The fight against other pathogens lasts about 2 months. The drug is contraindicated in persons with liver and kidney pathologies. Taking Lamisil can cause:
- headache;
- hepatitis;
- bile duct dysfunction;
- cutaneous lupus erythematosus;
- joint pain;
- dyspepsia.
Ointment
Complete treatment is impossible without the use of local drugs. Modern antimycotic ointments effectively eliminate inflammation and pathogenic flora, while providing a complex effect on the lesion. Local therapy for facial skin mycosis involves long-term use of the following antifungal agents for external use:
- Miconazole - this drug has a detrimental effect on almost all types of such infections. Miconazole ointment destroys pathogenic microorganisms by suppressing the production of ergosterol. The drug is indicated for lesions of the skin, nails, secondary infection with streptococci and staphylococci. Miconazole must be rubbed into the affected areas twice a day for 4 weeks. The ointment should not be used if you are intolerant of its individual components. The use of Miconazole, as a rule, does not cause side effects.
- Clotrimazole - the drug is an antimycotic with a wide spectrum of activity against most types of fungi. Clotrimazole inhibits the growth and reproduction of the pathogen by disrupting the synthesis of ergosterol. Indications for the use of the ointment are mycosis of the facial skin, pink and pityriasis versicolor. In order to eliminate the pathogenic agent, Clotrimazole is recommended to be applied to the affected area 2-3 times a day for 3 weeks. The drug should not be used if you are hypersensitive to its individual components. The use of ointment can cause:
- burning;
- itching;
- redness;
- swelling.
Prevention of fungal infections
To avoid the appearance of signs of mycotic lesions on the face, first of all, it is necessary to observe the rules of personal hygiene and carefully monitor the condition of the skin. In addition, experts advise avoiding contact with infected persons, as well as with their belongings, which must be disinfected. With all this, an important point in the fight against fungal infection is strengthening the immune system. In general, to prevent mycosis, doctors recommend:
- Do not use other people’s hygiene items (washcloths, brushes).
- Do not neglect the use of antiseptics even with minor damage to the skin.
- Eat properly.
- Avoid eating refined foods.
- Make time for walks and proper rest.
Prevention Tips
To prevent the development of fungus on the skin of the face, you must:
- strengthen general immunity;
- minimize contact with street animals;
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- carefully care for your facial skin.
Some cosmetics, especially antibacterial ones, can reduce local immunity, which gives a high chance of developing mycosis. Facial skin care should be thorough, but delicate. People with chronic diseases should pay special attention to the epidermis.
Despite the unpleasant symptoms, fungus on the face is quite easy to treat. Timely initiation of therapy will allow you to completely get rid of the symptoms of mycosis in an average of 2 weeks.
Yeast can affect not only the intestines, mucous membranes, skin of the feet and hands, but also the face.
Most often, mycosis is localized on the face in the area of skin near the lips; the scalp does not suffer from it.
The reasons for the appearance of yeast fungus on the skin of the face can be:
- general weakening of the immune system after illness or chronic diseases;
- damage to the entire skin;
- excessive consumption of products containing yeast (flour, alcohol, kvass, etc.);
As a result, fungal spores attack weakened areas of the skin and begin to actively multiply, causing its “owner” serious discomfort.
On the face, the fungus appears in the form of red, itchy spots with a diameter of 0.5 to 2-3 centimeters. In this area, the skin is noticeably rougher and begins to peel off. In rare cases, vesicles and pustules may appear.