Welcome to the pages of a medical blog designed to help everyone. On the current agenda is such a problem as dermatitis. Let's figure out where it comes from and how to treat dermatitis on the face of an adult, and most importantly, what standards to adhere to so as not to encounter this problem again.
It's no secret that some diseases that were rare twenty or thirty years ago have now become commonplace.
Human skin is a kind of barometer of the body, which means that it often signals us about various kinds of internal problems and problems. One of the most widespread skin diseases today is dermatitis.
Dermatitis - what is it?
Dermatitis is an inflammatory disease of the skin. In the vast majority of cases, dermatitis, one way or another, affects the surface of the skin on the face, causing not only physical inconvenience, but also directly bringing with it psychological problems.
Just half a century ago, skin dermatitis was considered the province of children, but now this disease often affects adults as well.
Symptoms of dermatitis
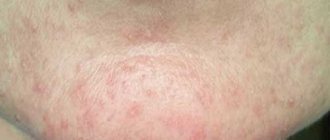
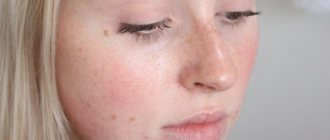
The main harbinger of dermatitis is itching of the skin and its redness. The body temperature remains at a normal level, or rises to 37.2 degrees, no more. In the allergic form, inflammation spreads very quickly, and the affected area also increases. Papules appear only in rosacea-like, oral form, when the causative agent is a bacterial infection.
The skin at the site of inflammation does not rise, like acne. A compaction may only appear. In this case, the place where the redness is noticeable is very itchy. But the more the patient scratches it, the more of the skin is affected by dermatitis. As a rule, the area of inflammation does not increase over time. After a few hours, the skin acquires a lighter shade and remains so until the irritant factor is eliminated.
Elena Malysheva spoke in some detail about the symptoms of dermatitis on the face. It is recommended to watch a recording of a video broadcast dedicated to this particular problem:
Dermatitis in adults
More and more often, nowadays, adults - men and women - turn to dermatologists for help due to the appearance of unpleasant rashes on the skin of the face, due to irritation and itching.
Among the reasons, experts increasingly see the irritating effects of modern cosmetics and household chemicals, allergies to various substances, including sometimes medications.
Many skin diseases clearly manifest themselves in adulthood. But there are some exceptions. So, for example, atopic dermatitis begins in childhood as a diathesis to certain products, accompanying a person throughout his life.
It is noteworthy that in adults, dermatitis differs in the nature of its course. There are also some differences here based on the type and variety of dermatitis; we’ll talk about this in more detail below.
Dermatitis in adults - stages of the disease:
- The acute period is the formation of swelling and red spots, the appearance of blisters filled with an unpleasant serous fluid. This period is often accompanied by an unpleasant burning sensation on the face and intense heat.
- The subacute period is the time when scales and scabs form on the skin, causing a lot of trouble for the patient due to severe itching and general anxiety.
- The chronic period is the time when dermatitis reaches a stage that is difficult to treat. The disease at this time manifests itself seasonally and recurrently.
Types of skin dermatitis
Each type of disease has different causes.
Allergic
Allergic dermatitis is the body's reaction to an allergen.
Allergic dermatitis can be caused by:
- Food (fruits, berries, nuts and other highly allergenic products).
- Plant pollen.
- Street or household dust.
- Medications.
- Chemical substances.
- Household chemicals.
- Cosmetics and care products.
- Animal fur.
This type of dermatitis occurs more often in people whose bodies are more prone to allergies.
Atopic
Atopic dermatitis is the most severe form of the disease. Symptoms first appear in childhood and later recur in adulthood. In adults, this form of the disease most often occurs due to constant stress or exposure to allergens.
The occurrence of atopic dermatitis is due to a genetic factor.
If one of the parents has experienced acute dermatitis, then with a 50% chance the child will develop atopic dermatitis. If the father or mother has atopic dermatitis, then the risk of this disease in the child is 80%. In many cases, atopic dermatitis is accompanied by bronchial asthma and allergic rhinitis.
Types of dermatitis on the face in adults
In addition to general risk factors, there are also narrowly targeted causes that become the causes of various types of disease. This disease is a real Serpent-Gorynych with different dangerous types.
NOTE!
To quickly get rid of blackheads, acne and pimples, as well as to rejuvenate your facial skin, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with this effective remedy .
Find out more...
There are different types of dermatitis, each with its own symptoms, specific treatment and complexity of its course.
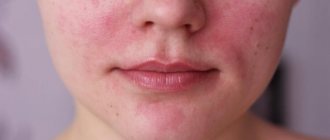
Allergic dermatitis
From the name itself it is clear: who is to blame for the disease. We are talking about the body's individual reaction to a specific allergen or irritant.
In this case, many things can act as an allergen: plant pollen, dust, animal hair, various food products, cosmetics and household chemicals. Dermatitis manifests itself in varying degrees: areas of rash, slight redness, runny nose, swelling and lacrimation.
The allergen itself is not terrible - it is too small. However, once in the bloodstream it quickly binds to blood proteins. It is this compound that acts as a provocateur of the disease. The main signs of the disease show themselves 5-6 days after contact with the allergen itself.
In order to get rid of such dermatitis, you need to find the irritant and remove it. However, this must be done from the first stages of the disease. This type of dermatitis quickly develops into complicated forms.
Rapid deterioration in health, appearance of scars on the face and severe headaches. Over time, the disease develops into a more serious atopic form.
Atopic dermatitis
Often, incorrectly or not treated at all, allergic dermatitis leads to a new stage - atopic dermatitis. This type of disease manifests itself as itchy and unpleasant, rather bright red spots on the face, which can be weeping crusts.
We are talking about eczema - a disease that is dangerous due to its fairly rapid transition to the chronic stage.
This type of dermatitis is characterized by an allergic basis; heredity often plays a large role in its appearance. This disease can peacefully sleep in the body for decades, suddenly awakening under the influence of certain factors.
In this case, the trigger can be, for example, a nervous shock, a hormonal surge, or improper skin care. This type of disease is considered the most widespread.
Contact dermatitis
This type of disease is very similar to allergic. The only difference is that only areas of the skin that came into contact with the allergen are susceptible to such inflammation. We are talking about clothing, cosmetics, household items (for example, a latex pillow), jewelry (containing nickel), medications, and unsuitable care products.
This dermatitis is characterized by a long period of manifestation. Only after a couple of weeks a person can detect the first signs of the disease on the face. This type also includes sun allergy (photodermatitis).
This type of disease is the easiest to treat and most often goes away without consequences. However, if you ignore the situation, the disease can lead to complications. On the face, simple redness over time may well develop into unpleasant itchy blisters and peeling.
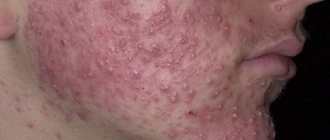
Oral dermatitis
Oral (rosacea-like) often affects adults aged 20-30 years. The disease manifests itself in the form of rashes in the area around the mouth, sometimes spreading to the skin of the eyelids and bridge of the nose. It is easy to recognize by its spots ranging from pink to bright red. Such spots often change color (depending on weather conditions).
The culprits of this disease are long-term use of external products (cosmetics, toothpaste, cream, ointments, lipstick). A stimulating factor is a metabolic disorder, nervous and digestive system, as well as the intake of hormonal substances.
Treatment of this type of dermatitis is not so difficult if the disease is mild. In this case, you need to carefully monitor your face and become more demanding in choosing care products.
If you do not focus on painless spots, then you soon run the risk of noticing not the most beautiful and sometimes even lumpy thickenings on them.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Often this disease is simply called “salt discharge.” The culprit of the disease is the saprophytic flora that exists in each of us. It suddenly begins to spread in large numbers.
At the same time, the products of her life activities quickly change the chemical composition of the secretion of the sebaceous glands, which acts as a provocateur for the onset of the disease.
And, of course, nothing happens for nothing - everything happens for a reason. The impetus for the development of this type of disease is the human immune system, which clearly fails. And here it is customary to distinguish between two types of illness:
- Dry - the skin is very flaky, the face is quickly covered with whitish itchy scales, which are difficult to get rid of.
- Oily – the skin becomes covered with a pustular rash (acne or black comedones). The face quickly takes on a grayish and slightly shiny color.
This type of dermatitis can affect an adult of any age. And here an attentive approach and comprehensive, competent treatment are important.
Allergic dermatitis
In dermatology, it is customary to distinguish several types of allergic dermatitis: allergic contact and atopic. As for the first, it is provoked by interaction with the allergen. To form a persistent allergic reaction, regular contact with the allergen for two weeks is sufficient. Atopic dermatitis on the face is considered a more severe disease because it is a chronic inflammation of the skin. As a rule, atopic dermatitis appears in childhood and then remains for life.
Treatment of allergic dermatitis on the face primarily involves completely avoiding the allergen or limiting contact with it. To do this, the patient must first undergo a series of tests to identify the allergen. Anything can be an allergen. If it is any product, it should be removed from the diet; household chemicals should be replaced with less harmful ones. As for drug therapy, allergic contact dermatitis is treated with antihistamines (for example, Erius or Zyrtec). It is advisable to choose drugs of the current generation, since they do not have side effects such as impaired coordination of movements, decreased concentration, and drowsiness.
Atopic dermatitis in a patient is indicated by symptoms such as dry skin, roughening and thickening of the skin on the face, cracks on the lips and behind the ears, atopic palms, skin lesions around the nipples, peeling and redness of the skin. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes tests for the allergen, a blood test, the Fadiatop test, and an analysis for the concentration of immunoglobulins E in the blood. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor draws up a treatment regimen for the disease, which should include drug therapy, diet therapy, and the creation of the most optimal psycho-emotional environment.
In the acute period of the disease, therapy with antihistamines, glucocorticosteroids and membrane stabilizers is indicated. If the patient is diagnosed with an infection, then antibiotics are also included in the treatment regimen. After the inflammation subsides, the doctor prescribes maintenance therapy: taking sorbents, vitamins, immunomodulators. For the treatment of atopic dermatitis on the face, the following local and systemic drugs are recommended:
- Glucocorticosteroids are traditional drugs that can be used both topically in the form of ointments and intravenously in the form of tablets. These medications include Elokom, hydrocortisone, Dermovate, Afloderm. They have a powerful anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effect, relieve swelling, and inhibit allergic reactions.
- Antihistamines have an antiallergic effect. Because they block the release of histamine, the drugs also eliminate redness, itching and swelling. They are prescribed mainly in the form of tablets, less often - injections. This group of medications includes clemastine, suprastin, loratidine.
- Immunosuppressors of the macrolide class - these medications block the release of inflammatory mediators, thereby providing an antiallergic effect. Often, patients are prescribed Elidel ointment, which must be applied twice a day for a week to the affected areas of the skin on the face.
- Moisturizers are preparations for eliminating excessive dryness of affected skin on the face. Moisturizing creams, lotions and ointments can only be used during the chronic or subacute period of the disease. Since during the disease there is severe damage to the skin on the face and a violation of its integrity, patients are also prescribed agents that accelerate the regeneration of the epidermis and epithelialization processes. Effective emollients include Topicrem, Atoderm, Lipikar, and those that accelerate skin healing include Actovegin, solcoseryl, and methyluracil ointment.
- Sedatives are required to be taken during treatment of the disease. The fact is that patients are bothered by constant painful itching, which often leads to psycho-emotional disorders. You can eliminate irritability, depressed mood and tension by taking herbal sedatives (motherwort tincture) and tranquilizers (tofisopam).
- Drugs to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract are prescribed for up to ten days during the acute period of the disease. First of all, patients are recommended to take drugs that destroy toxins in the intestines (lignin, smectin). At the end of therapy, it is advisable to take a course of sorbents that restore the protective properties of the intestine and normalize its microflora (eubiotics and probiotics).
Dermatitis - causes of pathology
What are the hidden causes of such an unpleasant illness? Why do the exocrine glands simply stop functioning normally at some point?
Key risk factors are poor heredity, poor lifestyle and nutrition. Hormonal imbalances, the use of low-quality cosmetics, stress, constant fatigue, bad habits - all this quickly attracts dermatitis to itself like a magnet.
The reasons can be both internal and external:
- Disorder of the exocrine glands.
- Use of low-quality care products and cosmetics.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Disorders of the digestive and hormonal system.
- Bad habits.
- Insufficient oxygen supply.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Poor nutrition.
- Prolonged stress.
- Emotional stress.
- Neuroses and depression.
- Chronic fatigue.
In the case of poor nutrition, lifestyle, frequent stress, and the use of inappropriate cosmetics, dermatitis appears on the face.
In order to prevent the development of the disease, doctors advise adhering to preventive measures: treating existing diseases in a timely manner, leading a correct lifestyle, and paying attention to sports.
There are certain irritants that cause the formation of common dermatitis:
- temperature regime;
- pressure and friction;
- acids and alkalis;
- ionizing radiation;
- some plants.
Diagnosis of dermatitis
In case of the first signs of itching and rashes - key signs of dermatitis, it is important to immediately contact an allergist or dermatologist. For the most part, these experts conduct the examination, so to speak, together.
In individual situations, a diagnosis can be made and the cause established based on the results of a survey and initial examination. And yet, more often you have to be patient and pass the required list of tests.
A clinical blood test will make it possible to assess the level of inflammation activity, and a biochemical analysis will show changes in the activity of internal organs, which may be the cause of dermatitis.
If an allergic origin of the disease is suspected, the specialist will prescribe a blood test for immunoglobulin E and carry out the required allergy tests.
To comprehensively exclude dermatitis caused by food, there are studies that determine the body’s increased sensitivity (sensitization) to certain foods in the blood and skin using the scarification method.
If allergic contact dermatitis is suspected, skin testing with a range of allergens should be performed. In addition to the allergist and dermatologist, consultation with other experts is often required: gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, neuropsychiatrist, and so on.
Treatment of any facial dermatitis begins with a visit to a specialist - a dermatologist. It is the doctor who will help you timely establish the true causes of the formation of the disease, give useful advice, tell you how to cure facial dermatitis, and create a personal treatment regimen.
Dermatitis - folk remedies
Treatment of facial dermatitis with the help of folk remedies is most often aimed at actually muting the symptoms. There are many variations that complement the prescriptions of doctors in complex and most advanced forms of the disease, or will help to get rid of the problem once and for all from the first stages.
- Ointments
Homemade ointment is particularly effective. In addition to the antiallergic creams recommended by experts, you can also make an ointment at home, which will certainly help reduce itching and reduce inflammation.
- Tar. Take a tube of shaving cream and mix it with tar (6 grams), heat it to a temperature of +60° C. Apply the cream to the affected areas two to three times a day.
- Lactic-glycerin. Mix milk (15 grams) with glycerin (16 ml). After this, add rice starch in volume to the mixture to thicken the mixture. Apply the mixture in the evenings and leave it on your face overnight.
- Potato. Grate the potatoes (100 grams) on a fine grater and add liquid honey (7 ml). Apply the ointment to your face overnight.
- Herbal decoctions and tinctures
Treatment of dermatitis using herbs is considered effective. It is worth making healing mixtures in advance. Store such decoctions in a cool place, but no more than 3 days. We wipe the skin with herbs two to three times a day. The course is one month.
- Walnut decoction. Grind seven walnut leaves, add a glass of water, put on low heat and boil for 6 minutes. Let the jar of broth sit for two hours.
- Wine tincture. Grind four plantain leaves, add a third of a glass of white wine. Infuse the mixture for several hours.
- Intoxicating tincture. Mix the string and hops (10 grams each) with boiling water (150 ml). Let it sit for 40 minutes.
It is beneficial to consume celery juice 30 minutes before meals 3 times a day. Pass the celery root through a meat grinder and squeeze out all the juice from the resulting mixture. We take 15 ml.
- Vegetable and essential oils
An excellent remedy for combating dermatitis is a mixture of different oils. They effectively relieve itching and irritation and soften the skin. We apply healing agents to all problem areas two to three times a day.
- Take baby cream with anti-allergenic ingredients (10 grams) and add myrrh and cypress essential oils (2 drops each).
- Mix cosmetic oils of wheat germ and jojoba (17 grams), St. John's wort or amaranth (34 grams). We also add 3 drops of orange essential oil (or rose, fir, sandalwood, patchouli, tea tree or rosemary).
- Take milk (16 ml), add essential oils of cedar and geranium (5 drops each), mint (3 drops).
In undiluted form, essential oils help: tamanu, black currant, almond and sea buckthorn oils, jojoba and macadamia oils, jojoba, as well as apricot and chamomile oils, geranium and cedar, ylang-ylang and leuzea, frankincense and lavender. It is customary to apply them pointwise to the affected areas 2-3 times a day.
Treatment
Having discovered various kinds of rashes and neoplasms on the face, everyone begins to worry about the question of how to treat them. Folk remedies can relieve symptoms by making the spots paler and temporarily eliminating itching. But you need to understand that the disease itself will not go away until it is diagnosed and treated. And for this you will need to undergo laboratory tests.
Eliminating the root cause is the goal of treating dermatosis on the face of any type. Among the most effective techniques are the following.
Preparations for internal use
If it is a parasitic dermatosis, antiparasitic drugs are used to remove pathogens from the body. Vermox, Vormil, Nemazol, Pyrantel, Dekaris, Medamin, ditrazine citrate, Fensal, Ivermek, Akrikhin, Chloxyl, Bithionol, Perchlorethylene, Cesol, Azinox, Biltricid and others are prescribed. Glucocorticosteroid drugs can be used to relieve inflammation.
Products for external use
External medications (ointments, creams, lotions) have anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, deepening, antiparasitic, antifungal, and antibacterial effects.
For example, the multifunctional ointment for dermatosis Rederm is often prescribed; the cream for dermatosis Advantan has received good recommendations. Dermatologists suggest using zinc ointment, Elokom, Radevit, Afloderm, Trixera, Indomethacin, Solcoseryl.
Dermatitis - prevention and prognosis
Most often, facial dermatitis does not have the best prognosis. However, if you go to the hospital in a timely manner, recovery is often possible. Nevertheless, it is important to always remember: having suffered from dermatitis at least once, you need to once and for all eliminate contact with the irritant that caused the pathology.
In the absence of proper therapy, the disease can become chronic, making it difficult to respond to treatment itself. In such a situation, pathology will remind itself from time to time.
Often a person in such a situation develops eczema, wet ulcers appear, and peeling of the skin does not give rest. Modern medicine has created many variations in the treatment of this disease.
To prevent the disease, you need to adhere to the rules of hygiene, as well as monitor the condition of the skin on your face, use hypoallergenic products and creams. In addition, you should exclude from your diet foods that promote the production of subcutaneous fat.
Strengthening the immune system, as well as timely treatment of diseases and normalization of digestion, including chronic ones, will help to avoid pathology.
Only if you follow all the advice can you actually avoid the development of the disease. In addition, you should not rely on self-medication, because dermatitis is a serious disease that requires a special approach in terms of treatment. Only timely contact with a dermatologist really reduces the risk of complications and unpleasant consequences.