Reasons for the appearance of molluscum contagiosum on the face
The causative agent of the disease is Molluscum contagiosum. It is viral in nature, contains DNA and belongs to the group that includes the smallpox virus. There are 4 types of molluscum contagiosum, designated MCV 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Infection occurs through contact (through household items, clothing, bed linen, towels, toys, when swimming in the pool) and through sexual contact. The liquid contents of the papular rash spread in the environment and can lead to infection of other people.
Molluscum contagiosum virus can survive on dust particles for a long time. This leads to widespread spread of the disease in children's groups. The development of the disease is facilitated by infrequent and insufficiently thorough cleaning of premises, neglect of personal hygiene rules, decreased immunity, long-term use of cytostatics and hormonal drugs.
If left untreated, a papular rash on the face or other parts of the body lasts 6–8 months, in some cases up to 4 years, and then may disappear.
The virus does not cause significant harm to the body. But with a weakened immune system, relapses of the disease may occur and become chronic.
To date, there are no medications that can completely destroy DNA-containing viruses. Therapy aimed at strengthening the immune system helps prevent relapses of molluscum contagiosum.
Since epithelioma is contagious and occurs in people with a deficiency of immunity, there is a very high probability of the body being affected by other infections, for the detection of which it is necessary to undergo additional examination.
Result and prospects
If a person has a healthy immune system, the infection will go away on its own. There will be no traces or memories of her. This will not happen very quickly, the event will last about a year. The exact timing is difficult to determine; everything will depend on the patient’s immunity and skin condition. There is good news - as soon as the nodules disappear, the virus will go away with them. However, as long as there is a rash, the patient is contagious.
Unfortunately, although the causative agent of molluscum contagiosum is a relative of the chickenpox virus, it does not leave behind lasting immunity. Therefore, new contact with him will bring a new wave of the disease. Obviously, the best prevention of the disease is the absence of contact with sick people. This is quite difficult to do, since the rashes are not always noticeable. However, following a few rules can prevent the spread of infection:
- You should wash your hands well with warm water and soap.
- Parents should teach their children proper hand-washing techniques, as the easiest way for a child to become infected is through touching a friend or a toy.
- If possible, you should not exchange hygiene items or personal items, such as towels, combs, or even soap.
- You should try not to use someone else's sports equipment. This includes all equipment that could come into contact with the naked body of a stranger.
- If rashes do appear, you should try not to touch them with your hands so as not to spread the infection over a large area.
- Where nodules appear, you should not use a razor; any damage will spread the infection. If the formation is very disturbing, it is better to consult a doctor and raise the question of options for removing single rashes.
- You should refrain from sexual intercourse if there are foci of infection on the genitals or groin area.
Unfortunately, when a person has AIDS or another disease associated with immunodeficiency, molluscum contagiosum will not go away on its own. Nodules will not disappear without special treatment, like in healthy people. For such patients, doctors offer combined treatment methods in order to reduce the number of rashes. Complete removal of all lesions in such situations is impossible.
Symptomatic manifestations of the disease
The duration of the incubation period for infection with molluscum contagiosum can be different - the minimum period for the development of the disease before the appearance of the first symptoms is 2 weeks, the maximum is 6 months. Invading epidermal cells, the virus integrates its genome into it, which leads to the reproduction of new intracellular parasites.
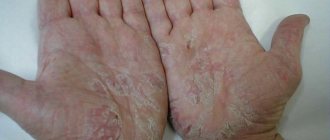
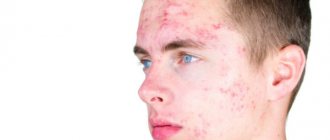
Visually, this process is the formation of papules on the skin - dense yellowish-pink nodules, shaped like hemispheres with a smooth and shiny surface. On the face, they most often appear on the skin of the eyelids and forehead; other places where the rash is localized are the neck, arms, thighs, lower abdomen, and external genitalia.
The rapid multiplication of the pathogen leads to an increase in the size of the rash. They can be located either in the form of single formations or in groups, the fusion of which leads to an expansion of the area of the affected skin areas up to 2–3 cm.
The upper part of the papules is slightly pressed inward and filled with white cheesy contents, which contain mollusc-shaped formations. Usually the rash is not painful; in rare cases, itching occurs. The inflammatory process appears when a secondary infection occurs.
Forms of the disease
Based on the symptomatic manifestations of molluscum contagiosum, three forms of the disease are distinguished: typical, generalized and complicated. In the first stage, there are few rashes, all the characteristic symptoms of the disease are manifested, the papules are located on one specific area of the body close to each other. With a generalized course of molluscum contagiosum, there are many neoplasms; they can be located at a considerable distance and in different parts of the body.
If the disease has progressed to a complicated stage, in addition to the main infection, a secondary one is added, which leads to inflammation and hyperemia of the skin surrounding the papules. In these areas, pus begins to secrete, causing pain.
This form of molluscum contagiosum is characteristic mainly of HIV-infected people. The spread of infection can occur during shaving, causing papules to appear on the chin.
The doctor talks about the causes, signs, and general symptoms of the manifestation of molluscum contagiosum on the skin of the face.
Classification and forms of the disease
According to the nature of their distribution, five varieties are distinguished:
- The classic form is diagnosed when the mollusks are located singly.
- The giant form suggests the presence of fused individual elements grouped within one plaque with a diameter of 5 cm.
- The formation of the pedicular variety involves mollusks fused into one plaque, which holds onto the skin with a thin leg. The number of nodules can reach 10 pieces.
- The generalized form is a profuse rash. The number of mollusks on the affected area of skin can be several dozen.
- The mylar variety is similar to the generalized one. The difference is that the mollusks are smaller.
Diagnosing the disease and establishing the form is not difficult for an experienced dermatologist. This requires an examination and history taking, on the basis of which conclusions are drawn and treatment is prescribed. In cases where doubts arise related to the similarity of the neoplasm with other rashes (for example, vulgar warts, keratoacanthomas, milia), the doctor orders a biopsy. The affected skin fragment is examined under a microscope. The conversation about how to get rid of a cosmetic defect will begin after receiving the results of the biopsy.
Diagnostics
When making a diagnosis, the clinical picture of the disease is taken into account. If difficulties arise, for differential diagnosis with other diseases (lichen planus, syphilis, warts, chickenpox, allergic manifestations, tumors), a histological examination of the internal contents of the pustules is carried out under a microscope to detect molluscan bodies.
They form in the deep layers of the epithelium and, continuously multiplying, fill the affected skin cells.
Compared to the rash of molluscum contagiosum, papular syphilide does not have similar inclusions inside the papules. Chicken pox occurs with fever, headache, and itching in the area of the rash. The chickenpox rash appears as clear blisters filled with liquid. In severe cases, pus may accumulate in them.
Lichen ruber is characterized by the formation of light plaques with a pearlescent surface, but not filled with liquid contents inside. To make an accurate diagnosis, you should consult a dermatovenerologist.
Symptoms
A sign of the disease are small pimples themselves (from 2 to 5 mm in diameter), usually the number of nodules does not exceed twenty. Externally, these are pimples with a dimple in the center, dome-shaped and flesh-colored, at first dense, then becoming softer. The nodules appear to be filled with a white, waxy substance.
Pimples usually do not cause pain, but are sometimes accompanied by itching.
People with reduced immunity and AIDS patients are at particular risk - their damage associated with exposure to molluscum contagiosum may be more pronounced.
Treatment methods for molluscum contagiosum
In many cases, after accurately determining the type of disease, specialists do not prescribe drug therapy, since if the body is in good shape, all symptoms will go away on their own within 6 months. If the immune system is in a normal state, it will be possible to avoid relapses of molluscum contagiosum in the future without taking special medications.
But if the disease occurs against a background of reduced immunity, for example, when a person is infected with HIV, it becomes chronic and to prevent its recurrence it is necessary to constantly strengthen the immune system.
Use of general drug therapy
When choosing medications, the doctor takes into account the duration of the disease, age and health status of the patient. Immunomodulators (Amiksin, Cycloferon) and treatment of affected areas with antiviral ointments (Acyclovir, Oksolinovaya) are prescribed.
For the generalized form of molluscum contagiosum, accompanied by profuse rashes, tetracycline antibiotics (Doxycycline, Tetracycline, Metacycline) are used.
Removing papules using laser
When exposed to a laser beam, the skin layer at the site of the virus concentration heats up, its temperature rises to 150°C. This contributes to the complete destruction of the infection and the elimination of affected cells through evaporation. The penetration depth of laser radiation does not exceed 5 mm, which guarantees no adverse effects on the underlying tissue. The procedure is safe and can be performed on both adults and children.
Removal of rashes prevents pathogens from reaching other areas of the skin and the development of complications in the form of sepsis or a purulent process, ensures the sterility of the treated surface, and is painless.
After treatment, you should protect the areas of skin where the papules were removed from contact with water for 3 days. Visits to the pool and water procedures in the bathhouse are prohibited. You should not stay in the bright rays of the sun for a long time or visit a solarium.
How to treat using liquid nitrogen?
The cryodestruction method is based on exposing the papule to liquid nitrogen cooled to −170 °C. Freezing the internal contents of the rash leads to the destruction of the pathogen and the destruction of the tissue damaged by it.
The procedure is completely painless, eliminates damage to healthy areas of the skin, and is not accompanied by bleeding or scarring. The technique can be used to eliminate papules in children and does not require bandages or medication.
How to remove papules using electrocoagulation
Cauterization of nodules in spray coagulation mode using a variable frequency current allows you to destroy the bodies of molluscum contagiosum and the epidermal cells affected by them. Anesthesia of the affected areas during electrocoagulation is provided by local anesthesia. Upon completion of the procedure, a dry crust remains at the site of the papule; after healing of the wound surface, no scars remain.
Surgical curettage of the contents of papules using curettage
Used for minor rashes. The area of skin on which the procedure will be performed is lubricated with the anesthetic drug EMLA, which is a cream containing a mixture of anesthetics Prilocaine and Lidocaine, 1 hour before the removal of foci of infection. A sealed bandage is applied to the treated surface. After an hour, the anesthetic is washed off and the operation begins.
A double-sided curette (Volkmann spoon) is used to scrape out the contents of the papules. Instead, a wooden spatula with a pointed surface can be used.
In some cases, tweezers are used to remove the internal contents of the nodules. Then the surface of the skin is treated with iodine solution, Podophyllin or Chlorhexidine. During the procedure, bleeding may occur, and scars sometimes form on the wounds.
Removing papules using chemicals
The method consists of regular daily lubrication of the nodules with ointments and solutions containing components that have antiviral activity.
The recommended frequency of treatment of papules is 1 or 2 times a day. The principle of applying the drugs is spot-on, on the surface of the nodules themselves, excluding the contact of the products on the skin bordering the papules. Typically, the rashes disappear within 3-12 weeks with this method.
When choosing a drug, it should be taken into account that the safest are Fluorouracil and Oxaline ointments, as well as gels containing Benzoyl peroxide.
In addition to these drugs, the following drugs are used:
- Tretinoin - applied for 6 hours, then washed off;
- Imiquimod - papules are smeared 3 times a day;
- Cantharidin;
- Acyclovir;
- Vartek;
- Infagel;
- Kondilin;
- 3% solution of Trichloroacetic acid - applied once a day, spot-on for 30 minutes, followed by rinsing;
- Chlorophyllipt - frequency of use 2-3 times a day;
- 3% salicylic acid solution - applied twice a day.
Diagnosis and treatment
Examination is the main tool for diagnosing this disease. The rashes may have an unusual shape and resemble, for example, warts, chickenpox pockmarks, and even manifestations of skin cancer. When in doubt, a dermatologist will most likely take a scraping and use a microscope to determine the exact nature of the disease.
Since children are very often infected with this virus, as a rule, everything goes away on its own, parents do not even have time to think about how to remove the mollusks. The skin cleanses itself, the process takes from a year to a year and a half. The child is not treated with medications, nor are laser procedures performed, since all these actions have side effects.
However, it should be noted that although the disease often goes away without outside help, its treatment is definitely useful:
- is a prevention of the spread of the virus to other parts of the body;
- does not allow you to infect others;
- prevents the appearance of new rashes.
The doctor selects treatment methods individually, focusing on the patient’s age and the condition of his skin. Procedures can be of several types:
- A dermatologist freezes the nodules with liquid nitrogen - cryosurgery.
- Curettage. Using a special instrument - a curette, the molluscum contagiosum is mechanically removed. The doctor actually scrapes the growth from the surface of the skin.
- The use of various acids to remove rashes. The principle of operation of this method is the destruction of the upper layers of the skin; removing mollusks on the face in this way is controversial.
- Laser removal of molluscum contagiosum. The main advantage of this type of treatment is accuracy, that is, damage to unnecessary areas of skin is practically eliminated, which is very important for people with reduced immunity.
If there are a lot of rashes, the dermatologist may remove them at intervals of several weeks. This is done in order to allow damaged areas of the skin to recover. For home use, your doctor may prescribe retinoids, which will also need to be applied to the nodules.
Traditional methods of treating molluscum contagiosum
Traditional healers have developed many effective ways to treat this disease. They involve the use of both herbal components and medications - potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide, iodine.
Recipes using garlic
You need to prepare a paste of crushed garlic cloves and butter (1:1), apply it to a gauze swab, apply it to the papule and secure it with an adhesive plaster. The lotions are changed to fresh ones in the morning, at lunchtime and in the evening. You can also, instead of applying the mixture, wipe the affected areas with a garlic clove cut in half or the juice squeezed out of it 3-4 times a day.
The duration of treatment is 3–7 weeks. The papules decrease in size, then become covered with a crust, which disappears after a while.
Application of potassium permanganate solution
The rashes are cauterized with a cotton swab dipped in a concentrated (dark purple) solution of potassium permanganate. Avoid contact of the product with surrounding tissues, as it may cause burns.
Cauterization with iodine, hydrogen peroxide, calendula tincture
At home, this procedure must be carried out very carefully to prevent the infection from spreading to healthy areas of the skin.
The skin surrounding the papules and tweezers are treated with medical alcohol. Then the contents of the nodule are squeezed out and removed with a cotton swab moistened with alcohol, and its surface is cauterized with iodine, calendula tincture or hydrogen peroxide.
To exclude the possibility of re-infection, clothing and bedding must be changed. The wound surface should not be moistened with water for several days; it should be treated daily with iodine, and after a crust has formed, Oxolinic ointment should be applied until the affected area is completely healed.
The process of regeneration of the epidermis in the wound can be accelerated by lubrication with juice obtained from bird cherry leaves.
Treatment of rashes with celandine and dandelion juice
Lubricating papules with celandine or dandelion juice gives a good healing effect. They can also be treated with calendula or eucalyptus tincture without removing the contents with tweezers.
Compliance with general rules
The child should not attend the children's group until complete recovery. This will prevent other children from becoming infected. All things used by a sick child are washed and disinfected.
In an apartment or private house, general cleaning is carried out to remove as much dust as possible, on which the virus can remain viable for a long time. During treatment, taking water procedures in the bath, visiting a bathhouse, or visiting a swimming pool are excluded.
It is necessary to ensure that the baby does not scratch the nodules that appear and regularly washes his hands with soap. Foci of infection should be wiped daily with Chlorhexidine or another type of antiseptic.
To reduce the likelihood of an adult patient infecting other people, sealing the pustules with an adhesive bandage. It is not advisable to shave the hair at the site of the rash. Lubricating the skin with cream will prevent the appearance of cracks and inflammation at the location of the pustules.
Features of the recovery period
The formation of immunity to the molluscum contagiosum virus takes a significant period of time - from 3 to 18 months. At this point, the symptoms of the disease disappear without a trace. In some cases, it takes several years for the body to develop immunity.
During the recovery period, you should strengthen your immune system by hardening the body, eat well, and include fresh vegetables, fruits, and nuts in your diet. Moderate physical activity, staying in a pine forest, and walking in the fresh air are beneficial.
Getting rid of molluscum contagiosum at home
Molluscum contagiosum can be removed using unconventional methods. They include the use of alcohol infusions, lotions, and ointments. When using traditional methods of treatment, it is important to know that herbal remedies can cause an allergic reaction.
Use of celandine
Celandine is a unique plant, tinctures from which help to quickly remove tumors on the skin. Due to toxicity, this method is not suitable for getting rid of molluscs in childhood. All celandine-based products can cause damage to the skin. In this regard, it is very important to be careful when using. Only nodules can be treated with the tincture, while avoiding the healthy surface.
To treat molluscum contagiosum, you can use fresh celandine juice or tincture from this plant. It is recommended to do it at home. The leaves are collected in the middle of the first month of summer. They are placed in a glass container, vodka is added and placed in a dark place for 2 weeks. The skin nodules are then treated twice a day. After some time, a dark crust will appear at the site of the formations. It goes away as it dries immediately with the papule.
Treatment with iodine
If molluscum contagiosum appears in a child, it is better to use a safe and inexpensive remedy - iodine. It has a strong antiseptic effect and helps prevent further spread of nodules throughout the body. Iodine is best used in cases of a small number of viral formations and the absence of pathologies in the thyroid gland. This remedy is not used for multiple rashes and hyperthyroidism.
Before applying iodine to the nodule, it must be carefully removed with hands thoroughly disinfected with chlorhexidine or other antiseptic solution. The product must be applied pointwise. Before use, it is important to pay attention to the expiration date of the drug. Treatment is carried out twice a day until the infection completely disappears.
Application of potassium permanganate
You can get rid of molluscum contagiosum by using potassium permanganate. A weak solution in this case will not have a therapeutic effect. It is recommended to make it so strong that the shade of the liquid becomes dark.
Potassium permanganate should only be applied pointwise. Treatment is carried out until a crust appears at the sites where nodules form. This method is used until the skin is completely cleansed.
Complications
The disease usually has a favorable course and, in the absence of special treatment, goes away on its own. But if a secondary infection in the form of pathogenic bacteria gets into the wounds that occur when scratching the nodules, an inflammatory process can begin. Symptomatically, it is manifested by swelling and redness of the skin, the formation of pus.
If this process is started, inflammation will lead to the development of dermatitis, which requires long-term treatment and threatens the appearance of unaesthetic scars on the skin.
Symptoms (3 forms of the disease)
Diagnosed mollusks on the face of a child and an adult undergo an initial incubation period lasting from 2 weeks to six months. Only after this the first symptoms appear.
When the virus penetrates deep into the layers of the dermis, a favorable environment is created for the reproduction of other parasites and intracellular spread.
Molluscs on the face (as in the photo) in adults and children are rounded nodules (papules) of pinkish-yellow color with a smooth surface. They are localized mainly on the eyelids and eyebrows.
Due to the intensive reproduction of pathogens, the rash spreads quite close.
When you press on the formations from the inside, a thick, cheesy component is released.
According to the clinical picture of molluscum contagiosum, 3 forms of development are distinguished:
- Typical - single rashes and on a specific area of the epidermis.
- Generalized – there are quite a lot of papules, located relatively far from each other. They begin to spread throughout the body.
- Complicated - inflammatory processes with purulent discharge from the skin near the tumors are observed (a stage inherent in HIV-infected patients).
Mollusks on a child’s face often take on an unusual shape – profuse. With it, the bubbles do not have a concavity, and they are small in size.
A similar course of the disease is typical for children suffering from leukemia, HIV infection, atopic dermatitis or immunodeficiency.
Preventive measures
Infection with molluscum contagiosum can be prevented by isolating a sick child and at home by providing him with individual tableware and bedding, hygiene products, and towels. The baby’s toys must be disinfected, clothes and linen washed in hot water, followed by ironing.
Among the adult population, the elimination of casual sexual intercourse helps prevent the transmission of the pathogen through sexual contact. Improving the state of the body's immune system is facilitated by a healthy lifestyle, minimizing stress, and a balanced diet rich in vitamins and microelements.
Use of ointments
It is easy to prepare products for external use yourself. There are several ways to treat molluscum contagiosum.
The ointment can be made from garlic and butter. The mixture should be applied to the affected skin three times a day. If garlic juice is well tolerated in its pure form, you can treat papules only with it. The easiest way is to peel a clove of garlic, make a few cuts and lubricate the knots.
The herbal infusion also helps get rid of molluscum contagiosum. To prepare, you need to take 1 tablespoon each of eucalyptus, yarrow, juniper and calendula. The mixture must be infused in a glass of boiling water for at least an hour. The medicinal drink should be drunk twice a day, 120 ml. Course - 14 days. This method is contraindicated if there is intolerance to any component.
To get rid of molluscum contagiosum, you can use a decoction of pine needles. It has a powerful antiseptic property and promotes rapid healing of the skin.