Skin rashes are a consequence of complex systemic diseases.
Cosmetic procedures are not enough.
It is important to conduct a differential diagnosis and begin adequate treatment.
Find the answer
Are you having any problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease.
The site provides reference information. Adequate diagnosis and treatment of the disease is possible under the supervision of a conscientious doctor. Any medications have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist is required, as well as detailed study of the instructions! Here you can make an appointment with a doctor.
Skin rash, its different types
Pathological changes on the skin, characterized by rashes of varying localization and degree of damage, are caused by several hundred different diseases.
Some of them are dangerous and require careful diagnosis followed by adequate therapy.
All types of rashes are infectious and non-infectious:
- Infectious manifestations of the rash are characteristic of the development of rubella, scarlet fever, measles, chickenpox, typhus, herpes, lichen, meningococcemia, erythema, mononucleosis, urticaria.
- Non-infectious ones are formed due to allergic reactions, pathologies of the hematopoietic and vascular system, and problems with connective tissue.
- Diseases that primarily affect the skin or are limited in manifestation only to the skin. The rash is not a manifestation of other diseases, but affects only the skin.
Skin rashes can manifest themselves morphologically: blisters, ulcers, blisters, spots, nodules, tubercles, scales, scars, cracks, ulcers.
These rashes come in different locations and color intensities. All of them require diagnosis and treatment. Dermatologists do not recommend using the simplest home recipes to eliminate rashes on your own.
Skin pathologies may be accompanied by a number of other symptoms. Only the specific features of the symptoms of most diseases help make the correct diagnosis.
To prescribe adequate treatment, a dermatologist needs to examine the patient at the very beginning of the pathological rash.
In addition to the doctor for skin problems, the patient is prescribed consultations with other specialists:
- Gastroenterologist;
- Endocrinologist;
- Therapist;
- Gynecologist;
- Surgeon.
There is no need to delay contacting a doctor or ignore prescribed treatment. An advanced skin rash can provoke the appearance of extensive skin pathologies with multiple complications.
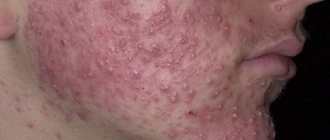
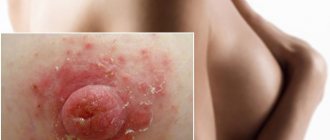
Red rash on the body with black dots
Human skin is the largest organ, which, like a litmus test, reflects what is happening inside the body. Any rash is the first sign of disease or infection, so do not hesitate if a rash appears on your body. If you have skin rashes, you should see a dermatologist, and if the rash appears in the genital area, you should see a gynecologist or urologist.
A rash is a visual change in the structure and color of the skin; it is characterized by redness, itching, peeling and even pain. The halo of the rash, despite its external integrity, consists of individual elements, which include:
- ulcers (defects on the surface of the epidermis caused by slowing down the regenerative processes in the upper layers of the skin);
- erosion (superficial epithelial defect without scar formation)
- papule (dense nodule located above the surface of the skin);
- vesicle (a fluid-filled capsule located in the upper layers of the epidermis);
- pustule (a cavity formation on the surface of the skin filled with pus);
- blister (an element on the surface of the skin caused by inflammation and swelling of the papillary dermis);
- nodes (dense, painless nodules on the skin);
- hemorrhages (subcutaneous hemorrhages caused by high permeability of the vascular walls);
- petechiae (pinpoint subcutaneous hemorrhages caused by capillary injury);
- ulcers (deeply located formations filled with pus).
Depending on the location of the skin rash, the source of the problem can be determined. In particular:
- Allergic reactions cause a rash on the hands and face;
- Infections are characterized by rashes on the torso (abdomen, back);
- STIs are localized on the genitals, inner thighs and skin around the anus;
- Stress weakens the immune system, so the rash is localized throughout the body (but, unlike allergies or rashes due to infections, the reaction to allergens and immunoglobulin will be negative)%;
- Problems of the gastrointestinal tract are expressed in the form of serious skin abnormalities (with ulcerative colitis - erythema nodosum (inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue and blood vessels in the form of nodes), with problems with the pancreas - atopic dermatitis, intestinal infections provoke pyoderma - ulcers on the skin);
- Rashes due to problems with blood or blood vessels appear on the abdomen and then spread throughout the body. It is characterized by the absence of itching.
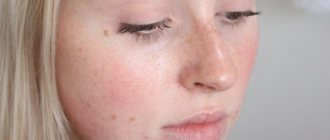
Allergy skin rashes are not caused by an immune reaction of the blood to allergic elements. This is due to haptens - simple chemical compounds that are not immunogenic. But they tend to bind to the carrier protein.
Attaching to a macromolecule, the newly formed complex synthesizes immunoglobulins. The body perceives it as foreign, causing an increase in the level of leukocytes.
As a result, the skin becomes covered with red spots of different sizes and different locations.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4q_FgHF7-II
An allergic rash is characterized by the following characteristics:
- It does not always cause itching and fever;
- Accompanied by swelling of the face, eyelids, runny nose;
- The area of the rash corresponds to the places where the skin comes into contact with the allergen (if you are allergic to jewelry - on the wrist or fingers, to deodorant - in the armpits, to cosmetics - on the eyelids or around the mouth);
- A blood test shows an increase in the number of eosinophils;
- The biochemical blood test remains unchanged.
The most common form of allergy rash is hives. In appearance, it resembles pink spots that appear on the skin after contact with nettles. Hives are a reaction to pollen, cosmetics, and dust. Often localized on the bends of the elbows, knees and wrists. Accompanied by severe itching and peeling of the skin.
Depending on the allergen, the rash has the following types:
- Allergy to food . It is an erythematous rash in the form of rough spots rising above the surface of the epidermis. A characteristic feature of food allergies is severe itching.
- Cold allergy . Occurs when exposed areas of skin come into contact with cold (air, water). Although cold does not directly provoke an allergic reaction, it is a trigger for an allergic reaction to improper functioning of the thyroid gland, spleen, etc. Cold allergies are accompanied by lacrimation, nasal discharge, as well as the appearance of whitish and pink, scratch-like spots on the skin, which disappear on their own after some time. If a person has ever had an allergy to cold, he needs to see a doctor to find out the true cause of the malfunction of the body.
- Allergy (atopic dermatitis) to dust/animal hair . It is often diagnosed in children. It manifests itself in the form of an itchy rash, accompanied by increased dryness of the skin. In some cases there are weeping ulcers. The simplest test to identify atopic dermatitis: take an ordinary school ruler and press on the area of the rash for 20 seconds. If a white streak remains on the skin after a few minutes, it is atopic dermatitis. If the skin has regained its previous shade, this is a rash of a different nature.
- Allergy to alcohol . Alcohol has a vasodilating effect. Accordingly, more substances, including toxic ones, are absorbed into the blood. The more components in an alcoholic drink, the stronger the allergy to it. The most “dangerous” drink is absinthe, which contains wormwood, anise, fennel, coriander, and lemon balm. The skin becomes covered with red spots, as if from burns. In chronic alcoholics who drink cheap wine every day, a red, weather-beaten face is a consequence of constant alcohol intoxication of the body. If such a reaction occurs in an ordinary person, he needs to find out the source of the allergy and consult a doctor. The biggest danger is Quincke's edema, when the lungs swell and the person dies within a few minutes.
There are 4 types of allergic rashes: food, contact, respiratory and respiratory. The biggest allergy sufferers are children. It should be remembered that not all products consumed by adults are suitable for children.
A child’s rash should not be ignored. The most dangerous is the rash caused by meningococcal infection. Outwardly, it resembles a food allergy, but at the same time the body temperature rises. It’s better to be on the safe side, and if your baby has any rash, you should consult a doctor.
The distinctive features of an allergic rash are vesicles (capsules with liquid inside), papules (grain-like compactions) and pustules (bubbles with pus). An infectious rash has these symptoms.
Various infections and viruses entering the body damage, first of all, the mucous membrane, as well as the skin. Unlike an allergic rash, an infectious rash is always accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
Also characteristic signs of infection:
- body intoxication, vomiting, headache
- fast fatiguability
- phasing, spread of the rash to other parts of the body with each new day
- enlarged lymph nodes
- rashes look like papules, vesicles and pustules
- the skin dries out and flakes off.
The infection rash is not itchy, but touching it is painful. The causes of rashes are the following diseases:
- Herpes: depending on the type of virus, the skin of the face (lips) or the genitals (head of the penis, labia) are affected. The rash looks like blisters, which gradually open up and ulcers form in their place. Upon completion, a crust will form that should not be touched;
- Scabies: The causative agent is a microscopic mite that leaves tiny tunnels under the skin. Unbearable itching occurs;
- Chickenpox: The rash resembles a mosquito bite, filled with serous fluid. Vesicles spread throughout the body, including the scalp. The soles and palms remain intact;
- Scarlet fever: the rash looks like roseola - pinpoint pink spots of various shapes. After a few days, the rash fades and turns brownish. After the temperature normalizes, the skin peels and flakes. A characteristic feature is redness of the tongue and enlargement of the papillae;
- Measles: the rash looks like papules, which are localized on the inside of the cheeks and gums. The rash spreads from the neck down the back, lastly moving to the limbs. The mucous membrane of the eyes becomes inflamed;
- Rubella: the skin becomes covered with red spots, localized in the thighs and buttocks, and malaise is observed;
- Infectious mononucleosis: lymph nodes enlarge, adenoids swell. The rash is observed throughout the body, including on the roof of the mouth;
- Meningococcal infection: This is an extremely dangerous infection that can lead to the death or disability of a child. It is by the appearance of the rash that one can notice the symptoms of the disease on the first day of infection. A rash with meningococcal infection is a consequence of exposure to toxins caused by the activity of meningococcus, which increase vascular permeability. The rash is hemorrhagic in nature, that is, it looks like small hemorrhages. Mainly localized on the buttocks and limbs.
There is an effective test to distinguish meningococcal rash from other rashes. You need to take a glass, turn it over, press on the area of the rash and twist it a little until the skin around it turns white. If the skin turns pale at the site of the rash, then it is not a meningococcal infection. If the rash remains the same color, you should immediately call an ambulance.
A rash due to diseases of the blood or blood vessels is caused by damage to the walls of the capillaries, as a result of which petechiae - small bright red dots - appear on the surface of the skin. Unlike ordinary hemorrhages, a rash due to blood diseases does not change color when pressed. Other signs indicate the disease:
- joint pain (knees, ankles);
- black stools, diarrhea, sharp pain in the abdomen as if poisoned;
- the rash covers the entire body.
Diseases that cause hemorrhagic rash include:
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (Werlhof's disease) is a blood disease in which small arteries and capillaries are blocked by blood clots. Mainly found in children, especially newborns.
The disease has autoimmune causes of unknown etymology. Those. Your own immune cells perceive platelets as a foreign body and attack them.
The rash is painless, occurs as a reaction to the administration of any medication, and is localized at the injection site.
Hemoblastosis. This is a malignant tumor that occurs very often in childhood. The rash has several types:
- hemispheres of red-brown color, covered with a crust;
- blisters with serous fluid inside;
- rashes similar to bruises, both large in size and in the form of bloody dots that appear without any reason.
In all cases, the rash causes severe itching. Blood tests for hemoblastosis show a significant increase in the number of leukocytes due to decreased immunity. Hemoglobin drops, lymph nodes enlarge.
Platelet counts drop and the child gets tired quickly. The cause of a rash in diseases of the blood or blood vessels is a decrease in the number of platelets and a disruption in the synthesis of proteins involved in blood clot formation.
This rash also occurs when taking medications that thin the blood (Aspirin, Warfarin, Heparin).
Diabetic angiopathy. This is a violation of the vascular capacity of the lower extremities, provoked by type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Due to the disease, the walls of blood vessels become thinner and become fragile. This causes skin dystrophy. Ulcers and erosions appear on the skin.
The condition of the skin largely depends on the functioning of the internal organs. Using a map of rashes on the face, you can determine which organs have problems.
- pimples on the forehead indicate problems with the intestines;
- a rash along the hairline indicates problems with the gallbladder;
- pimples on the bridge of the nose - liver problems;
- ulcers on the temples - problems with the spleen;
- rashes above the lip - disruption of intestinal function;
- pimples on the nose - heart disease or endocrine disorders;
- rash on the chin - gynecological problems.
In the early stages of liver disease, they practically do not manifest themselves at all. The earliest symptom is specific skin rashes. They are caused by an increase in the amount of bile acid in the blood, which causes general intoxication of the body. The skin takes on a yellowish tint.
With cholestasis (blockage of the bile ducts), the rash is localized on the feet and palms, looking like marks from a burn. With cirrhosis, liver cells die and the whole body becomes covered with spots. Parasitic liver diseases cause rashes resembling hives. They are localized in the lumbar region and abdomen.
Also characteristic is a combination of rash and spider veins, which cause severe itching, which intensifies at night. Taking antihistamines (allergy medications) does not provide relief. Increased bilirubin gives the skin a yellowish tint.
If the contents of the intestines are poorly removed from the body, then some of the toxins will begin to penetrate into the blood. The body begins to get rid of poisons itself through the excretory system. Because of this, the condition of the skin worsens, and it becomes characteristic of:
- increased fat content
- dull complexion
- acne, not only on the face, but also on the back, stomach, chest
- noticeable “black dots” similar to volcanic craters
- skin becomes dry and dehydrated
- After acne heals, scars remain.
Source: https://xhockeypro.ru/syp/krasnaya-syp-na-tele-s-chernymi-tochkami/
Causes of subcutaneous problems on the face
A subcutaneous rash on the face is not just a cosmetic defect.
Its appearance is provoked by dermatological diseases and complex disorders in the body.
Among the decisive factors for the occurrence of such a rash on the face:
- Pathological disruptions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which are caused by exotic foods, abuse of sweets or fatty foods;
- Allergic reactions to cosmetics, food, solar radiation, detergents, etc.;
- Reactions to improper hygienic facial skin care, that is, using expired products, applying cream to uncleaned skin;
- Irritations caused by subcutaneous parasites - molluscs and demodicosis;
- Hormonal changes that are associated with age, pregnancy or menopause;
- Complex diseases of internal organs that cause the sudden appearance of a subcutaneous rash on the forehead and face require careful diagnosis and treatment.
Doctors emphasize that the rash on the face can be invisible, have a white tint, or, conversely, have an intense red color.
All therapy to eliminate subcutaneous rashes is carried out under the supervision of a specialist, only after undergoing an examination with mandatory scrapings from the affected areas.
Allergic rashes - their types, causes and mechanisms of occurrence
Contact allergy
A contact allergy (also called a contact allergy rash) is a rash on the skin, oral mucosa, or genitals caused by direct contact with an allergen. Adverse reactions that can also occur as a result of a rash, but are associated with the penetration of allergens through other routes (oral or respiratory), are not considered contact allergies. Contact allergies are further divided into two types: contact urticaria and contact dermatitis.
Meanwhile, allergic contact dermatitis is a type IV allergic reaction (not caused by IgE, slow), which occurs within a few hours or even days after contact with the allergen. The allergen, in contact with the skin, penetrates the upper layers and, if a person has an allergy, causes the accumulation of immune cells called T-lymphocytes at the site of contact. It is these cells that recognize the allergen as “unfamiliar”, the one that needs to be fought, and cause an inflammatory process on the skin.
What causes allergic contact dermatitis?
The culprits of allergic contact dermatitis are chemical substances that, being in pure form or in various products (creams, cosmetics, clothing), come into contact with the skin. Here is a list of allergens that most often cause allergic rashes:
- Metals: nickel, cobalt.
- Biocides used in the production of cosmetics.
- Potassium dichromate.
- Chemicals used in the processing of rubber products.
- Personal care products and some dermatological body creams.
- Substances found in tattoo inks and other inks.
However, only a consultation with an allergist and allergological studies can determine the real motive, which may not be mentioned in this list.
How can you tell if an allergic rash is caused by contact dermatitis?
Like most skin rashes, allergic contact dermatitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Redness of the skin;
- Swelling of the skin;
- Red, itchy rash on the body.
Ultimately, if contact with the allergen is not interrupted, symptoms intensify, swelling becomes pronounced, and a red, itchy rash on the body can turn into painful, open wounds. Thus, if this disease is not detected in time and an allergy test is not carried out, the situation becomes even more difficult.
So, how can you recognize that these are skin rashes caused by contact dermatitis? One of the most significant signs of allergic contact dermatitis is that the rash occurs exclusively at the site of contact with the allergen, such as under a ring or watch. If allergic contact dermatitis is caused by substances in creams, the allergic rash occurs only in the area where the cream is applied. What skin rashes caused by allergic contact dermatitis look like in photographs can be seen in Figures 1, 2 and 3:
Figures 1, 2, 3. Allergic contact dermatitis
How is allergic contact dermatitis diagnosed?
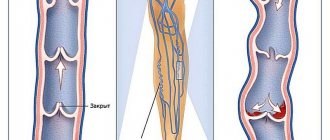
The diagnosis of allergic contact dermatitis is established and confirmed only during a consultation with an allergist-clinical immunologist. The rash is carefully examined by a doctor, and a patch test is performed for diagnosis. During the test, patches with special chambers are applied to healthy, intact skin (usually on the back). Each of the chambers is filled with various potential allergy triggers before being applied to the back. Patches with cameras and allergens are removed from the skin 2 days after application. This is when the initial assessment of the test result is carried out. If inflammation is observed in the area where the allergen was located (allergic acne, redness, swelling), the reaction is considered positive. If not, a secondary test evaluation is carried out 2 days later.
| Figure 4. Patch test | Figure 5. Allergic rash after a systemic reaction to a food allergen | Figure 6. Allergic rash following a slow-type reaction to a food allergen. |
How is allergic contact dermatitis treated?
The most important thing in managing allergic contact dermatitis is to identify the allergenic substance and avoid contact with it. Therefore, after research has allowed doctors to identify the main allergens, you should avoid contact with them. However, even knowing what substance causes this allergic rash, sometimes it is impossible to avoid contact. If this happens, don't worry:
- Immediately wash the area of contact with the allergen with warm water and soap.
- Avoid repeated contact. If this is not possible, use protective equipment (eg gloves).
- Follow your clinical immunologist's allergist's recommendations for treating your skin after accidental exposure to an allergen.
Rash caused by food allergen
Often when we suspect an allergic rash, we first blame foods. It's no secret that one of the symptoms associated with food allergies (usually food allergies cause gastrointestinal and/or systemic reactions) is red, itchy rashes on the body. Let us briefly discuss the types, mechanisms, principles of diagnosis and treatment of food allergies.
Our immune system is designed to protect the body from all biological and chemical factors that damage it (such as viruses, bacteria, single-celled or multicellular parasites). However, often, due to mechanisms that are not yet fully understood, the immune system perceives substances that are common and completely harmless to the body as a “foreign agent” that needs to be protected from, and creates a strong immune reaction. Here's how to describe any allergy. In the case of food allergy, a serological (IgE antibody) or cellular (T lymphocyte) immune response occurs upon consumption of the allergic food product. The most common food allergens are milk, eggs, ground and hazelnuts, fish and seafood, and wheat. All of these allergens can cause allergic reactions of both rapid and slow types.
Allergic reactions of the rapid type to food occur in the range from several minutes to several hours after ingestion. This type of allergy can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea.
- Systemic reactions (sudden and severe rashes all over the body, drop in blood pressure, anaphylaxis).
- Skin rashes.
- Atopic dermatitis or eczema.
Most allergic reactions to food occur in infants and children. The main causes are milk and eggs. Children usually outgrow these allergies before school age. However, if a child is diagnosed with a true allergy to nuts, soy, fish or seafood, the likelihood that the child will lose sensitivity to these products with age is low. Allergies to these foods usually last a lifetime and it is necessary that patients avoid allergic foods at all costs and always carry first aid medications with them. What an allergic rash looks like after a sudden reaction to an allergen can be seen in Figure 5.
How is an allergic reaction to food diagnosed?
One of the most accurate diagnostic algorithms for this type of allergy is a detailed blood test for specific IgE + confirmation of the diagnosis by an allergist-clinical immunologist during a consultation. In this case, it is very important not to make a mistake in choosing blood tests and choose those that can help you and your doctor distinguish true allergies from cross-reactions. Currently, the most accurate way to do this is to diagnose allergies at the molecular level (not just for allergen extracts, but also for the individual molecules that make up each allergen). Such molecular allergy tests at an affordable price in Vilnius are carried out at the Allergomedica clinic, but blood samples for testing can also be taken in clinics and laboratories cooperating with us. All you need to do is choose the most convenient location. Please note that these allergy tests are available for children and adults, so you can get a complete family screening.
How to treat rapid food allergic reactions?
Although there are currently some new ways to treat food allergies using specific immunotherapy, such treatments have not yet been validated or applied in clinical practice. Currently, once a true food allergy has been diagnosed, a strict elimination diet is recommended (patients are advised to avoid not only the food itself, but also any traces of it, and to cook and eat only from personal utensils, ensuring that they do not have the slightest contact with the allergen ). It is also recommended that such patients always carry an epinephrine auto-injector for first aid purposes.
Delayed allergic reactions to foods
This is a highly controversial topic in the allergy and clinical immunology community, but these reactions are still considered type IV hypersensitivity reactions (T-lymphocyte induced). They appear one or several days after consuming the allergen product and are less dangerous. Although, like fast-type food allergic reactions, they can cause digestive problems and allergic rashes - a systemic reaction that can endanger a person's life, slow-type allergic reactions do not cause. Most often, this allergy can manifest itself as diarrhea or constipation, bloating and/or pain, as well as nonspecific rashes on the body. As with fast-acting food allergies, delayed-onset food allergies often affect our little ones. With age, young patients successfully outgrow these allergies.
How are delayed-type allergic reactions diagnosed?
As with allergic contact dermatitis, the diagnosis of a delayed-type allergic reaction to food is established and confirmed exclusively by an allergist and clinical immunologist. A patch test is used for diagnosis, and fresh food products or products made from them are used as allergens (for example, milk or its powder, egg, soy powder, etc.). Often before a food allergen skin test, parents of patients are asked to think about what foods they think are causing the allergies and bring them to the allergist. Thus, for the patch test, not only potential allergens are accurately selected, but also those products (of the same brand, also processed) are used that will actually be eaten after the test is performed.
How to treat delayed allergic reactions to food? To treat these allergies, an elimination diet is also usually used for some time, but not as strict as in the case of rapid-onset food allergies.
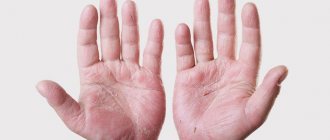
White type of rash
Doctors directly associate the appearance of a white rash on the skin with diseases of internal organs and systems. The most common of them are vitiligo, leucoderma, white and multi-colored lichen.
These changes in the skin can be provoked by constant stress, malfunctions of the immune system, problems with the liver or gastrointestinal tract, and poor nutrition.
Experts identify a certain group of diseases that cause white rashes on the body.
Idiopathic hypomelanosis in humans
It is characterized by a white rash that does not exceed 5 mm. It is smooth to the touch, but if not treated promptly it begins to peel off.
The risk group includes women and people with light skin tones. The development of the disease is associated with age-related changes after 40 years.
Pathogenesis of the development of pityriasis alba
Manifests itself in the form of white, uneven rashes of circular localization. Formed due to endocrine problems or pigmentation disorders. Less commonly, the main causes are nervous disorders and hereditary predisposition.
Pigmentless nevus on the skin
It can be mistaken for a wart. This pathology is much more dangerous; it can transform into a malignant tumor.
Drug therapy is complex and multi-stage.
Rashes with white nevus develop mainly in older people.
Treatment of white rashes of any nature occurs by restoring the structure of the skin with the help of medications and cosmetic procedures. It is important to start therapy after the first signs of manifestation and use an integrated approach.
Rash with blackheads
The skin is the largest human organ and it is not surprising that in the process of diseases occurring inside the body, side effects in the form of various kinds of rashes appear on the skin.
Any symptom requires careful consideration; in this article about skin rashes in adults, we analyze the causes with photos, help you identify the culprit of the rashes, and also consider diseases, the early symptoms of which are often skin manifestations.
Since skin rashes are the first sign of many diseases, this signal cannot be ignored; any suspicious rash that suddenly appears should be examined by a qualified doctor (dermatologist, allergist or therapist), since the disease in a weakened form can manifest itself as skin changes, without additional symptoms.
A rash may indicate:
- Immune system problems.
- Gastrointestinal diseases.
- Allergic reactions.
- Problems with the nervous system caused by stress.
So what is a skin rash?
It is generally accepted that a rash is caused by changes in the skin and (or) mucous membranes. Changes may include primarily changes in color, texture of the skin surface, peeling, itching in the red area and pain.
The rash can be localized in completely different places on the body, for different types of rash there are typical places of appearance, for example, rashes associated with allergic reactions most often manifest themselves on the hands and face, while manifestations on the surface of the body are more often associated with infectious diseases.
Remember, scratching the rash is unacceptable in any case, this will lead to even greater skin irritation and the possible formation of ulcers.
Types of rash
Primary - occur in areas of healthy skin or mucous membranes due to pathological processes in the body.
Secondary - occurs in place of the primary for certain reasons (for example, lack of treatment)
By far the most favorable from the point of view of diagnostic possibilities and subsequent successful therapy are primary protrusions. All protrusions differ in external characteristics such as size, shape, content, degree of color, grouping, etc.
Let's look at the main types of performances
Spot – Manifested by a change in shade or redness of the skin. It occurs in diseases such as syphilitic roseola, vitiligo, dermatitis, and birthmarks and freckles are also included in this type of manifestation.
| Spot on the skin |
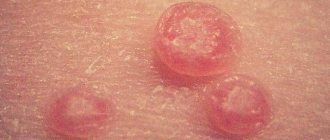
Blister - Located in the thickness of the skin, inside it is filled with hemorrhagic fluid, measuring from 2 to 6 mm, usually occurs with eczema, herpes, allergic dermatitis.
| Blisters on the skin |
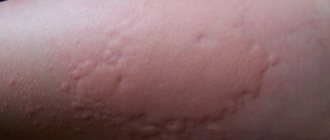
Blister - Swollen redness with smooth edges, can be of regular or irregular shape, common causes of appearance: urticaria, insect bites, toxicoderma, usually does not require special treatment.
| Blister on the skin |
An abscess is a pus-filled formation in the layers of the epidermis, divided by type into superficial and deep. Accompanying diseases such as acne, impetigo, furunculosis, ulcerative pyoderma.
| Pustule on the skin |
A bubble is a greatly enlarged bubble that can reach a size of 100 mm.
| Blister on the skin |
Nodule - can be found in all layers of the skin, externally it looks like a change in the surface of the epidermis with redness and a difference in density from the surrounding tissues, usually ranging in size from 1 to 10 mm. Typical manifestations of the nodule are caused by: psoriasis, several types of lichen, eczema, papillomas, various warts.
| Nodule on the skin |
Allergy rash
The cause of constant skin itching and visible rashes on the skin is often an allergy; this is a fairly common occurrence in our time, about 70 percent of people are somehow susceptible or have experienced allergic reactions.
What is an allergy? This is an aggravated reaction of the human immune system to an allergen that has entered the body, while in the process of getting rid of the presence of the allergen, the person’s blood vessels dilate, histamine is produced in large quantities, and redness, inflammation, swelling, and skin itching are almost always added to the above symptoms.
Attention! In the event of an acute allergic reaction with the formation of edema, the patient should immediately call an ambulance!
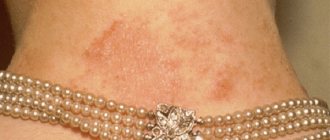
Allergic dermatitis also often manifests itself - when exposed to an allergen, a rash area forms at the point of contact, for example, when reacting to clothing - rashes in the waist, back and those places on the body where clothing fits most tightly to the skin, or when reacting to perfume or deodorant – in the area of greatest contact with the substance (often under the arms)
| Allergic dermatitis |
In a mild form of an allergic reaction, the symptoms resemble those of a cold: runny nose, possibly increased saliva and watery eyes.
If you experience symptoms such as dizziness, tachycardia, convulsions and nausea, this may indicate a severe allergic reaction in which there is a risk of developing anaphylactic shock, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Allergies can be caused by:
- Pet hair
- Plant pollen in summer or autumn
- Medications
- Food products (chocolate, milk, citrus fruits, etc.)
- Various nutritional supplements
- Substances contained in perfumes or household chemicals
- Substances that make up wardrobe items (fabric, metals, dyes)
Rash due to infectious diseases
Rashes in infectious diseases are often characterized by stages of appearance, first it appears in one place, then in another, also for each infection there are typical places for rashes, a specific shape and size, it is important to remember all the details and, when interviewing, report all this information to the doctor.
Below we look at rashes associated with various infectious diseases:
Rubella - in the initial period of the disease, a small rash appears on the face and neck, then within 2 to 6 hours the rash spreads throughout the body. Usually appears as round or oval redness ranging from 2 to 10 mm in size. Remains on the skin for up to 72 hours, then disappears without visible traces.
If you find yourself with a similar rash, you need to consult and examine a doctor, since similar rashes are symptoms of many infectious diseases. We also recall that rubella poses a particular danger to pregnant women, since if the mother is ill, the infection can harm the fetus.
Measles – the disease measles usually manifests itself with catarrhal manifestations. The rash appears after 2-7 days.
The primary places of protrusion are on the skin of the nose and behind the ears, then within 24 hours it spreads to the skin of the chest, face, then the arms and neck also become covered with rashes.
After 72 hours, the rash also covers the legs; the rash is most often intense and confluent. After the active phase of the disease, the rash changes color and forms something like pigment spots.
Chicken pox - at the onset of the disease it manifests itself as red spots, then bubbles with a red ring and liquid inside appear, similar in appearance to dewdrops. After two days, the outer surface of the bubble collapses and becomes less elastic. Subsequently, the blisters become coarser, crust over and disappear within seven days without leaving any visible traces.
Scarlet fever - Rashes with scarlet fever appear 24 hours after infection, the areas of active manifestations are the back, groin, elbow and knee bends, and armpit skin. Then inflammation appears on the skin, sometimes there is a slight blue discoloration in the places where roseola forms. The face with scarlet fever is usually not affected by a rash.
Source: https://womaninred.ru/syp-s-chernymi-tochkami/
Skin pathology in the form of small spots
A small skin rash is one of the symptoms of serious diseases. Most of them can appear at any age. The rashes are localized on any part of the body, on the face and mucous membranes.
Rashes develop based on several directions:
- Allergic reactions that are provoked by food, household chemicals, cosmetics, medications, pollen, direct sunlight and more;
- Infectious diseases of a bacterial or viral nature, manifested by a rash as the main symptom;
- Fungal pathologies, thrush, lichen, provoke the appearance of a small rash;
- Infection with parasites, scabies mites, and lice leads to irritation;
- Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus, cause this rash.
To eliminate this type of rash, you need to cure the underlying disease, then it will go away on its own. It is important to undergo a complete examination, especially of the stomach and intestines.
Diagnostics using ultrasound of internal organs will help to exclude complex pathologies. Effective in the treatment of ointments with antibacterial and antiallergic effects.
The prescription of drugs for external treatment and for oral administration is carried out after examining scrapings and smears.
Rashes similar to goose bumps in adults
Rashes similar in appearance to goose bumps are medically called follicular hyperkeratosis. The disease is not life-threatening pathological in nature, but in exceptional cases it is harmful to health.
The formation of small pimples protruding above the skin is often a consequence of hypothermia, overexcitation or other strong emotional experiences. This is not considered an anomaly.
Goose bumps appear suddenly and go away quickly. Goosebumps that do not go away for a long time are considered diseases requiring medical correction.
The most common causes of their occurrence:
- Serious vitamin deficiency. It is based on a deficiency of vitamins A, C, E. The formation of goose bumps is characterized by a constant course.
- Genetic predisposition. The ability of the skin to form goosebumps can be inherited.
- Excessive dryness will cause permanent goose bumps. The easily peeled upper stratum corneum clogs the pores, and unpleasant pimples appear.
- Impaired metabolism provokes the development of goosebumps on the skin.
- Insufficient use of hygienic procedures for cleansing the skin. Hyperkeratosis can occur when the follicular ducts are blocked.
- If you regularly use scrubs, creams or peeling, the surface of the skin will become even and smooth.
- To improve metabolism, it is necessary to draw up treatment principles together with your doctor.
- Use multivitamin complexes in treatment with an emphasis on vitamins A, C, E.
- It is necessary to accustom the body to bath procedures with cleaning and moisturizing.
The doctor will choose acceptable and effective methods to eliminate the rash and its consequences.
Definition of rashes
A rash is an irritated, noticeably changed (color or texture) area of the skin. Irritated skin may be red, swollen, itchy, or even painful. Although a skin rash is usually accompanied by changes in skin texture, such as small bumps on the surface of the skin, purulent or watery blisters, this is not always the case.
It is these subtle differences between the rash and the circumstances in which it occurs that are the most important factors in determining the true cause of the problem.
Although more than 50% of rash sufferers attribute their condition to allergies, we would like to emphasize that allergic rashes are only a small part of all skin rashes.
Pathology accompanied by fever
The appearance of a skin rash in an adult, which is accompanied by elevated body temperature, indicates the presence of an acute systemic disease.
This condition requires going to the hospital or calling an ambulance. The irreversible process is accompanied by a body temperature above 38 degrees.
There is evidence from medical practice that pathological simultaneous manifestations of high body temperature and skin rash will be life-threatening.
Doctors consider the most dangerous reasons to be:
- Toxic shock syndrome, which is caused by a bacterial infection;
- Epidermal necrolysis of a toxic course, developing on the basis of taking certain medications;
- Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, which occurs against the background of a bacterial infection;
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever, caused by a tick bite;
- Meningococcemia caused due to damage to the body by a bacterial infection;
- Fulminant purpura, the cause of which will be thrombotic disorders;
- Acute toxic shock syndrome due to bacterial infection.
These diseases belong to the group of rare ones. Diagnosis is complicated by the poorly expressed clinical picture of development. Calling an ambulance will help not only start treatment quickly, but also save the patient’s life.
Toxic shock after surgery or severe trauma causes mortality in almost 10% of patients. It is important for specialists to respond quickly and... A medical error can cost a patient his life.
The basic principle of treating diseases manifested by rash and high fever is based on intensive therapy in a hospital setting.
Emergency treatment consists of intravenous administration of plasma to restore lost volume.
Antibiotics are prescribed to eliminate the infection, and measures are taken to stop the underlying disease. The constant principle in such treatment is constant monitoring of the patient’s condition.
Non-allergic rashes
As mentioned in this article , allergies are just one of many causes of skin rashes. The table shows photographs of other common types of skin rashes and their distinctive features.
| Diaper rash. These rashes, common in children, are caused by prolonged contact with a wet diaper. Distinctive features: the rash occurs only in the place where contact with a wet diaper is possible, the skin looks reddened, and the skin feels warm to the touch. | |
| Flea bites. Fleas that usually attack our beloved four-legged animals can also bite us. Flea bites are not a rash, but they look very similar, so they are often mistaken for a rash. Just like the chicken pox rash, flea bites are small, red, itchy bumps. For this reason, parents often confuse flea bites with chickenpox, but it's worth noting a couple of important differences: Unlike chickenpox, flea bite rashes typically occur on the legs and feet. In addition, the skin at the site of pressure on the pimple turns white, unlike the case with chickenpox. | |
| Lyme disease rashes are caused by Borellia bacteria, transmitted by tick bites. The distinguishing features are a red spot surrounded by a red “halo,” otherwise known as a “bullseye.” The stain may feel warm to the touch, but it doesn't have to be. Without treatment, this spot spreads quite quickly and can reach the size of a brush. Lyme disease rashes are not painful or itchy. | |
| Chickenpox is caused by the Varicella zoster virus. It appears as small red itchy pimples that do not turn white when pressed. This illness is usually accompanied by fever and common cold symptoms (sore throat, stuffy or runny nose). | |
| Disease of the hands, feet and mouth . Several different viruses cause an illness in the hands, feet, and mouth that is similar to the chickenpox rash, but this time the rash is confined to the patient's extremities and around the mouth. The rash is small, painful, itchy. Most often, common cold symptoms and fever appear along with the rash. |
Author of the article: medical biologist Monika Miskinyte
Read more interesting and useful things in the Health Library
Literature:
- European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology “Global atlas of allergy”; The underlying mechanisms in allergy.
- European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology “Global atlas of allergy”; Allergic contact dermatitis.
- College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. "Food allergy" Prieiga per internetą: https://acaai.org/allergies/types/food-allergy
- European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology “Contact allergy”; prieiga per internetą: https://www.eaaci.org/patients/allergic-and-immunologic-diseases-and-causes/allergic-conditions/contact-allergy/about-contact-allergy.html
- European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology “Contact allergy”; prieiga per internetą: https://www.eaaci.org/patients/allergic-and-immunologic-diseases-and-causes/allergic-conditions/contact-allergy/about-contact-allergy.html
- Medical news today. „What is causing my rash?“ https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/317999.php
How to overcome unbearable itching
Skin rashes and itching can occur with many diseases. It is important to visit a dermatologist or call him at home.
Examination of skin scrapings may be necessary if the doctor suspects scabies or another infectious disease. The patient should be isolated in a separate room.
Bedding, clothing and dishes need to be treated. It is recommended to do this after each use if the diagnosis of scabies, measles or chicken pox is confirmed.
Doctors prescribe antihistamines when allergies occur. At home, you need to treat the affected areas with a cloth soaked in vodka or alcohol.
If the affected area has pronounced and extensive rashes, you can apply alcohol compresses. One tablet of Diazolin will help speed up the effect of external ointments. Doctors prescribe the use of various sedatives.
Effective treatment methods
Painful sensations are usually accompanied by atopic dermatitis, which develops based on genetic background. Inflammation develops even with low doses of exposure to the irritant.
Severe itching, accompanied by pain, causes physical and emotional discomfort.
Doctors advise contacting a dermatologist in the early stages of pathology.
An important stage in treatment is anti-inflammatory measures. An important emphasis is placed on eliminating direct exposure to irritants.
After identifying allergens using diagnostic tests, the dermatologist recommends individual treatment. Medicines should help relieve itching and restore the epithelial layer.
The most effective ointment and folk recipe
In long-term basic therapy, drugs for external use of the 2nd generation are used.
Treatment of rashes of various origins requires the use of specific ointments:
- To eliminate the symptoms of scabies and pediculosis, Benzyl benzoate is prescribed.
- The use of Levocetirizine and Desloratadine is indicated for the relief of allergic reactions and atopic dermatitis.
- Bepanten and Bepanten-plus are effective, well-known drugs for eliminating skin diseases. They have a wide range of effects, providing antifungal, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and combined results.
- To treat scaly lichen in folk medicine, a mixture of bee honey and table salt is used.
- Eczema is wiped with a tincture of alcohol, ginger, galangal, and nutmeg.
- Compresses or rubs made from lingonberry juice are effective in treating scabies.
- Purified kerosene in combination with celandine, in proportions of 1 to 2, eliminates fungal skin infections.
Chamomile and St. John's wort have a unique healing effect on skin rashes. These plants are recognized as universal antibacterial, anti-inflammatory natural remedies.
To relieve itching, use a mixture of kerosene and castor oil in equal parts. Doctors warn patients against using any folk remedies to treat skin rashes. There is a risk of further aggravating the problem with such self-medication.
Doctor: Olga Shishkina ✓ Article checked by doctor