Any surgical intervention is accompanied by the use of anesthesia. The introduction of potent drugs into the body, especially during deep anesthesia, often entails not the most pleasant manifestations for the body. However, there are situations when their use is contraindicated. This means that general anesthesia is performed only for emergency medical reasons or when the risk to the patient's life is justified by the risk of using anesthetics.
The professionalism of medical personnel is the key to the success of the operation
During the operation, the presence of an anesthesiologist is simply necessary
General anesthesia is one of the most difficult types of anesthesia and, if we are discussing which anesthesia is better to choose, preference should clearly not be given to it, especially for pregnant women. Complications of general anesthesia, manifested in loss of control over anesthesia by medical personnel, can pose a threat to the health and life of the person on the operating table.
There are three main components of general anesthesia:
- Medication sleep. During which the patient is forced to “calm down”;
- Analgesia. The person does not feel pain. The body’s automatic (vegetative) reactions to surgical trauma are suppressed. Such reactions may be, for example, tachycardia (increased heart rate), increased blood pressure;
- Muscle relaxation. It involves muscle relaxation, resulting in the provision of normal conditions for surgical interventions.
As you can see, the primary task set before the anesthesiologist is to eliminate pain. If it doesn’t exist, it means that physiological protective mechanisms will not turn on.
Main types of general anesthesia
Endotracheal anesthesia
- Intravenous;
- Inhalation:
- Endobronchial;
- Mask;
- Endotracheal.
- Combined.
What type of anesthesia will be better? The doctor decides based on the specifics of the operation and the individual physiological characteristics of the patient’s body.
Advice: the best option for short-term operations is intravenous anesthesia, so it is better to do it, for example, during gynecological curettage.
Stages of general anesthesia
There are four of them: analgesia, motor stimulation, surgical anesthesia and agonal stage. Analgesia, as mentioned earlier, is accompanied by the shutdown of pain sensitivity centers. The patient is in a state of “stunning”, while breathing is deep, the pulse quickens, but reflexes are still preserved.
The stage of motor excitation is characterized by the following phenomena:
- Increased skeletal muscle tone;
- Uncoordinated movements in space;
- Erratic contractions of the arms and legs;
- Trying to get up from the operating table;
- Pupil dilation;
- Frequent swallowing;
- Voluntary urination;
- Reflex cessation of breathing;
- Vomiting.
The stage of surgical anesthesia is divided into four levels. These are superficial, light, complete and ultra-deep anesthesia. With light anesthesia it is already possible to perform superficial operations.
Control of general anesthesia
Modern equipment will allow you not to miss even the slightest changes in the patient’s condition
Monitoring the patient's condition under anesthesia is mandatory, since one of the consequences of general anesthesia can be death. Doctors monitor the following vital signs of the human body: body surface temperature; color of mucous membranes; oxygen content in the blood; pulse; pupil reaction; blood pressure; continuous recording of ECG and so on.
Inhalation anesthesia can be controlled by anesthesia machines and anesthesia monitors.
Means for inhalation anesthesia
For inhalation anesthesia, special volatile liquids are used that easily turn into vapor. Gaseous substances are also in great demand. After the first inhalation, the components of the drug penetrate into the lungs and blood through diffusion. The degree of concentration of the drug in the body depends on how long the inhalation was used.
Of great importance is:
- tidal volume;
- permeability;
- general condition of the surface of the alveoli;
- hemodynamics;
- the degree of solubility of the drug in the bloodstream.
It is on all these characteristics that the intensity of the increase in the total concentration of the drug in the patient’s body depends, which affects the quality of anesthesia.
Almost all types of drugs are evenly distributed in tissues and bloodstream. Minor differences are associated only with the individual characteristics of the patient’s body and the principle of blood supply to internal organs. All components of medications are excreted from the body unchanged.
The intensity of elimination is influenced by the same factors as absorption. Gaseous agents are released the fastest. This category includes: Isoflurane, Ftorotan and Enflurane. Among gaseous agents, nitrous oxide is in great demand.
In isolated cases, the development of the following complications cannot be ruled out:
- Nausea.
- A sore throat.
- Weakness and muscle pain.
- Headache, dizziness.
- Liver disorders.
- Vomiting of central origin.
- Stopping breathing.
- Heart failure.
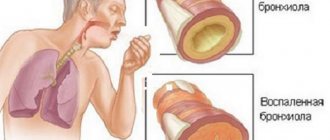
During anesthesia, there is a high probability of vagal reflexes that are dangerous to the patient’s health. For example, the development of bradycardia, bronchospasm, increased secretion of the tracheobronchial glands.
To reduce the likelihood of complications, an injection of M-anticholinergic drugs (for example, Scopolamine, Atropine) is administered before anesthesia.
For effective sedation, sleeping pills and broad-spectrum tranquilizers are used. To reduce the likelihood of a patient vomiting during surgery, anesthesiologists administer special centrally acting antiemetic medications.
Volatile liquids
Anesthesia drugs in pharmacology are constantly being improved, since in laboratory conditions specialists are actively working to ensure that anesthesia drugs have a minimum of adverse reactions.
The following drugs belong to the category of volatile liquids:
- Enflurane (medicine for general anesthesia during short-term surgical interventions).
- Ftorotan (synthetic medicine).
- Anesthetic ether (typical aliphatic ether).
- Isoflurane (halogen-containing drug).
Ftorotan, which is an effective fluorine-containing aliphatic compound, is in greatest demand among anesthesiologists. This drug is 4 times superior to ether, due to which it is highly active.
To induce a patient into a state of anesthesia, Ftorotan is used in a concentration of 4 vol.%. This type of anesthesia is easily manageable. After stopping inhalation of the medication, the patient wakes up after 15 minutes.
Halothane, which is a volatile, non-flammable liquid, is highly effective. The product is applied using a special evaporator. Anesthesia begins to take effect within 2-7 minutes. The stage of excitement does not take much time, there is no pronounced motor restlessness.
The drug does not have a negative effect on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. Halothane is often combined with narcotic analgesics, nitrous oxide and curare-like drugs, since its analgesia and muscle relaxation are much less pronounced than with ether anesthesia.
Possible adverse reactions include:
- Decreased blood pressure levels.
- Bradycardia.
- Decreased contractile activity and general myometrial tone.
- Malignant hyperthermia.
Sevoflurane is one of the new fluoride-containing drugs. The drug has high rates of effectiveness, does not irritate the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, and the degree of negative impact on the functioning of internal organs is insignificant. This drug is actively used in various areas of surgery.
Gaseous substances
Drugs in this category are most often administered intravenously. The patient enters a state of anesthesia almost instantly, since there is no arousal stage. Sodium thiopental is highly effective, sold in bottles in the form of a dry substance, which must be diluted before use.
The medication begins to act within 5-30 s. after introduction. The patient's awakening is replaced by post-anesthesia sleep. The use of sodium thiopental is relevant when it is necessary to relieve convulsive conditions. The drug is contraindicated in chronic pathologies of the liver and kidneys.
Adverse reactions include: allergic reactions, coughing attacks, arterial hypotension and laryngospasm.
The category of popular gaseous drugs for anesthesia includes:
- Hexobarbital.
- Methohexital.
- Propanidid.
- Ketamine.
Propofol, which is injected into a vein either dropwise or in small doses, is highly effective. The medication begins to act after 40 s.
The drug does not cause analgesia, which is why it is used together with opioid-type analgesics.
Propofol is used for induction of anesthesia when surgeons are about to perform a simple surgical procedure.
The most common consequences of general anesthesia
Recovery from anesthesia is an equally important stage, characterized by the restoration of reflexes and a return to normal functioning of the body. Anesthesiologists continue to monitor the patient after the operation, as various types of consequences of anesthesia may occur.
There are the following consequences associated with dysfunction of the cardiovascular system:
- Reduced pressure;
- Pulmonary edema;
- Increased pressure;
- Pulmonary embolism;
- Disturbance of normal heart rhythm.
There are consequences associated with breathing problems:
After anesthesia, headache and drowsiness may occur, which usually pass quickly.
- Spasm of the larynx and closure of the vocal cords;
- Carbon dioxide accumulation;
- Increased sputum production;
- Bronchial spasm.
Other consequences of general anesthesia:
- Allergic reactions;
- Hiccups;
- Acute adrenal insufficiency.
The most common effects, especially in children and pregnant women, are vomiting and nausea. A serious consequence of anesthesia for patients with epilepsy can be the development of convulsive syndrome.
Tip: For patients with epilepsy, the best type of anesthesia is spinal, which uses only four milliliters of local anesthetic. Such small doses of an anesthetic substance can cause an anticonvulsant effect.
Methods of administering inhaled anesthetics
Anesthesia agents are selected by anesthesiologists as carefully as possible, since all the nuances of the upcoming surgical intervention must be taken into account, as well as the patient’s condition and the principle of his body’s reaction to various drugs.
In pharmacology, there are a large number of different medications for anesthesia, the correct choice of which can reduce the likelihood of adverse reactions.
In traditional medicine, there are 4 ways to use inhalational anesthetics:
- Using Esmarch's mask. Anesthesiologists use special equipment to put a patient under anesthesia.
- The half-open method is similar to the open one, but in this case the components of the drug do not mix with air vapor. During this procedure, a small amount of carbon dioxide is produced.
- Semi-closed method. A pre-prepared drug mixture is fed into a special reservoir in small doses as the patient often inhales. This method is characterized by the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the reservoir, which the patient inhales repeatedly.
- The closed method requires complex equipment. Doctors use a special chemical to subsequently neutralize the carbon dioxide present in the inhaled mixture.
Only with the correct use of anesthesia can one achieve reverse inhibition of spinal reflexes, loss of consciousness and all types of sensitivity in the patient. Anesthesia drugs reduce the tone of skeletal muscles with the obligatory preservation of the activity of the vasomotor and respiratory centers.
Open method using Esmarch mask
General mask anesthesia is performed in an open manner using simple masks. This method of inducing a patient into a state of anesthesia is used extremely rarely, since specialists do not have the ability to accurately dose the anesthetic.
Possible complications include hypoxemia, hypercapnia, and other complications that are associated with the entry of saliva and gastric contents into the respiratory tract.
Inhalation anesthesia can be carried out either using a simple Esmarch, Schimmelbusch or Ombredan-Sadovenko mask, or thanks to complex equipment, thanks to which carbon dioxide or oxygen is removed along with narcotic drugs.
Semi-open method
If this type of anesthesia is used, then the patient gradually inhales a narcotic mixture, which is maximally isolated from the penetration of atmospheric air. In this case, the risk of hypercapnia is completely excluded, but hypocapnia may develop.
Semi-closed method
The drug mixture inhaled by the patient is isolated from the penetration of oxygen. The patient exhales partly into the apparatus, partly outside it.
For this case, the equipment is equipped with a special carbon dioxide absorber. This type of anesthesia is common.
Closed method
This type of anesthesia is characterized by the fact that the inhalation and exhalation of the medicinal mixture are maximally isolated from the environment. The closed method of anesthesia is economical for the drug involved, since after the release of carbon dioxide, the entire gas mixture necessarily enters the patient’s lungs in full.
A high mortality rate among surgical patients is associated with improper anesthesia technique. The situation is aggravated by insufficient preparation of the patient for surgery and anesthesia.
Contraindications to general anesthesia
Contraindications to such anesthesia may be the following:
- Acute alcohol intoxication;
- Taking drugs;
- Severe form of bronchial asthma;
- Neurological and mental disorders;
- The presence of hormone-dependent pathologies, etc.
Contraindications to anesthesia in children:
- Severe rickets;
- Purulent rashes on the skin;
- Infectious diseases;
- Gastrointestinal tract disorders.
The two-week period after vaccination can also be considered a contraindication for general anesthesia in children.
It should be noted that when it comes to saving the patient’s life, the question of contraindications to this type of anesthesia does not arise.
Advice: general anesthesia and operations during pregnancy are performed only for emergency reasons, when there is also a threat to the life of the mother. In all other cases, it is better to wait until the birth of the child. If an alternative is possible, then preference should be given to local anesthesia; it is an order of magnitude higher in terms of safety for the fetus and the maternal body than general anesthesia.
When discussing which anesthesia is best to choose so that fewer complications arise for the human body, general anesthesia, as you can see, should be last on the list. The development of medicine and pharmacology today has made it possible to use more gentle methods of pain relief, in which the patient remains conscious, and therefore adaptation after anesthesia will be much easier.
We recommend reading: pediatric dentistry under anesthesia
Safe anesthesia
For each patient, specialists at the International Andrology Center select the type of anesthesia that is right for him.
Often anesthesia scares people, sometimes even more than surgery. The biggest fear is the unknown and possible unpleasant sensations when falling asleep and waking up. Numerous conversations about how it is dangerous to health also do not set the mood for positivity. Parents become especially worried when the doctor talks about the need for general anesthesia during surgery.
Operations under anesthesia in children are carried out according to the same rules as in adults, taking into account age characteristics. In children, due to anatomical and physiological characteristics, critical conditions occur more often than in adults, from which resuscitation and intensive care are required. However, in modern medicine, exclusively gentle drugs are used that can put an adult and a child into artificially induced deep sleep, and all drugs are selected strictly individually not only by the child’s age, but also by weight, height, and other anatomical and physiological characteristics.
What is anesthesia for children? In simple terms, this is a temporary loss of consciousness caused by a set of special drugs. It can include many manipulations aimed at facilitating the process of falling asleep, surgical intervention, and awakening. Among the events carried out are:
· Placement of IVs.
· Installation of a monitoring system for blood loss compensation.
· Prevention of the consequences of surgery.
Parents should understand the essence and risk of anesthesia, the characteristics of types of anesthesia and contraindications to its use, and be sure to tell the doctor:
How did the pregnancy and childbirth go?
What type of feeding was it: breastfeeding (for how long) or artificial feeding;
What was the child's illness?
reactions to vaccinations;
· whether he and his immediate family have allergies.
All this is especially important for young children; you need to ask the anesthesiologist questions if something is unclear, and the final decision on what type of anesthesia to perform rests with the doctor!
In medical practice, there are several types of pain relief:
· Inhalation or hardware-mask - the patient receives a dose of painkillers in the form of an inhalation mixture. It is used for short, simple operations.
· Intramuscular anesthesia for children is practically not used today. Since the anesthesiologist cannot control the duration of sleep and many drugs for this type of anesthesia are not used in pediatric practice.
· Intravenous – has a multicomponent pharmacological effect on the body. Ventilation of the lungs is performed with a special apparatus. Anesthesia is used on its own for children extremely rarely, only in cases of urgent need; it is more often used in combination with hardware-mask.
Are there any contraindications?
Anesthesia for children can always be performed, with the exception of the patient or relatives refusing the procedure. However, before carrying out a planned operation, it is important to take into account all the nuances and features:
· The presence of pathologies of various nature that can negatively affect the state during sleep and recovery.
· If the patient has recently suffered from acute respiratory viral infection or another viral infection, the operation should be postponed for several weeks until the body has fully recovered.
· Allergy to drugs. The doctor studies the records in the chart in detail. If it becomes clear that there is an allergy to medications, he immediately changes his tactics.
· Health features – high fever, runny nose.
Before surgery, the anesthesiologist studies the patient's chart in detail, noting all the points that may affect the method of pain relief. In addition, a conversation is held with parents in which important points are clarified.
How to properly prepare a child for anesthesia?
According to modern concepts, any surgical interventions, painful procedures, diagnostic studies in children (especially young children) must be carried out under anesthesia or sedation! Young children simply do not know what is in store for them, and often no premedication (preliminary administration of drugs to eliminate anxiety and fear, preparation for general anesthesia) is necessary.
Regardless of what type of anesthesia the operation is planned under, the patient is first prepared for surgery. Groups of children by age: newborns, up to 6 months, 6-12 months, 1-3 years, 4-6 years, 7-9 years, 10-12 years, over 12 years.
The anesthesiologist takes an active part in preparing the child for surgery. For planned operations, all preparation can be divided into general medical and pre-anesthesia: psychological and pharmacological premedication. An obstetric history is important: how the pregnancy and childbirth went (on time or not), the child’s anthropometric data - the correspondence of body weight and height to his age, psychomotor development, visible disorders of the musculoskeletal system, behavioral reactions.
Psychological preparation: hospitalization for a child is a difficult moral test; he is frightened by separation from his mother, people in white coats, the environment, etc. The anesthesiologist, attending physician and ward nurse help and explain to the mother how to behave.
Doctors recommend not always telling your baby that general anesthesia is coming. The exception is cases when the illness interferes with him, and he wants to get rid of it. However, if the children are old enough, it is necessary to explain that a special children's anesthesia will be carried out, as a result of which they will fall asleep and wake up when everything is already done and not a trace remains of the previous illness.
It is advisable that the baby is calm and not afraid. It is necessary to provide rest, both emotional and physical. The main thing that parents need to remember is that the baby should wake up after anesthesia and see the people who are dearest and closest to him.
Much depends on the professionalism of the anesthesiologist, since it is he who selects the necessary dosage of drugs used during anesthesia. The result of the work of a good specialist is the child remaining in an unconscious state during the period necessary for surgical intervention, and a favorable recovery from this state after the operation.
In modern medical practice, drugs that have stood the test of time and long-term practice of use in adult patients are approved for use in children. Thus, drugs with a strictly defined duration of action were selected, devoid of serious side effects, which are quickly eliminated from the body. The child recovers from anesthesia very quickly (in 15-30 minutes), after which he can immediately move and eat.
It is rare that intolerance to drugs or their components occurs. It is possible to predict such a reaction only if the patient’s blood relatives had it. Now we will list the consequences that can arise as a result of drug intolerance, but we note once again that this is an extremely rare case (only 1-2% probability):
· anaphylactic shock;
· malignant hyperemia. A sharp increase in temperature to 42-43 degrees.
· cardiovascular failure;
· respiratory failure;
· aspiration. Release of stomach contents into the respiratory tract.
Some studies also suggest that anesthesia can damage neurons in a child's brain, leading to cognitive impairment. In this case, memory processes are disrupted: absent-mindedness, inattention, and deterioration in learning and mental development appear for some period after the operation. Such processes are opposed by a number of factors:
1. the likelihood of such consequences is highest with intramuscular anesthesia. Nowadays, this method and drug are practically not used for children.
2. Young children are at greater risk.
3. The validity of the conclusions that only some studies have made has not been conclusively proven.
4. These symptoms go away quite quickly, and operations are performed in connection with real problems with the child’s health. It turns out that the need for anesthesia exceeds the possible temporary consequences of it.
Parents must understand that the condition of their baby throughout the entire operation and for 2 hours after it is monitored by modern medical equipment and personnel. Even if some consequences arise, he will be provided with the necessary assistance in a timely manner.
Anesthesia is an ally that helps a child get rid of health problems in a painless way. Therefore, parents should not worry too much.
In modern medicine, pain relief is a gentle tactical means, the use of which during surgery is a necessity.
In our clinic, during operations, only a combined type of general anesthesia is used (a combination of inhalation anesthesia with intravenous and local anesthesia), where the dosage of drugs is carried out taking into account the weight, height, age of the child, and concomitant pathology. Monitoring the child’s condition before, during and after surgery is carried out using modern equipment (Germany), under the supervision of a highly qualified team of specialists led by an anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the highest category.
If you have any questions, we will be happy to answer them. Health to your children!
03.10.2020
Back forward