A little bit of history
The first method of pain relief was used by Avicenna; he cooled the limbs until they lost sensitivity. Amroise Paré compressed blood vessels and nerves. In Ancient Egypt, they used sleepy tubes that were soaked in narcotic herbs.
The real anesthetic began to be used at the end of the nineteenth century, it was cocaine hydrochloride. But the drug was very toxic and led to high mortality; its use was abandoned.
They were made to faint by bleeding. This method was cruel and was not developed. During the period of hostilities, they even used alcohol until they were in a strong state of intoxication.
General principles of pain-relieving procedures
In order for local anesthesia in dentistry to bring the expected effect and not become a source of complications, it is important for the doctor to follow certain principles of its implementation:
- You should first assess the patient’s condition and find out if there are any allergic reactions to painkillers.
- The correct choice of anesthetic drug and place for its administration.
- The use of exclusively sterile preparations that are compatible with oral tissues.
- The temperature of the solution for administration should be close to normal human body temperature.
- The rate of drug administration should be minimal, and the patient should not experience any unpleasant sensations (burning, itching, pain) during the process.
- Only sharp needles should be used to avoid tissue injury.
- The area of the upcoming injection must be pre-treated with an antiseptic.
- The injection should not be unexpected: the patient must be prepared for local anesthesia.
Anesthesia and its effects
Anesthesia is a state of artificial memory loss that is reversible. It blocks the feeling of pain during surgical operations. Special anesthetics are used, which are selected by the anesthesiologist. He calculates the optimal dosage of the drug and combines it with other drugs. In this case, the individual characteristics of the patient are taken into account.
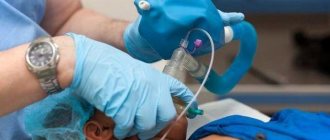
There are two types of anesthesia: general and local. General anesthesia is used to block pain. Such anesthesia leads to immobility, and the patient cannot control the body. Two methods are used: administering the drug through a vein and supplying gaseous anesthetic through a mask.
Local anesthesia involves injecting a painkiller into the area where surgery will be performed. For example, to remove a tooth, an injection is made in the oral cavity in the gum. This place begins to go numb and cannot be touched. Is local anesthetic dangerous? The patient is fully conscious, pain is blocked locally. Such manipulations do not cause any particular concern.
The effects of the common drug have been studied for a long time. But it is known that the anesthetic acts on the subcortical formation of the brain, which is supplied with energy. A common drug inhibits this function, it gradually fades away, the brain ceases to be active and falls asleep. We can say that the patient is in artificial sleep.
During anesthesia, reflex functions to stimuli such as injections or touch may be preserved. Doctors consider this normal.
There are no absolute contraindications
Now that professionally trained specialists have appeared, as well as high-tech equipment and modern medications, anesthesia has really become one of the safest things in our lives. For those who are best convinced by numbers, we can give the following example: in a relatively healthy person (it is clear that a 100% healthy person usually does not need surgery), the probability of severe complications from the use of anesthesia is 1 case in 200 thousand operations. That is, the risk of dying on the way to the hospital (for example, having an accident or being hit in the head by a brick or icicle from a roof) is 25 times higher than the risk of dying as a result of general anesthesia.
| By the way | |
| Before surgery, you must tell the anesthesiologist about all medications you are taking. This is necessary because many drugs, in addition to their main effects, also have side effects. In addition, when used together, drugs may change their activity and duration of action. For example, taking regular aspirin affects blood clotting; sleeping pills and sedatives can change the body's response to the administration of painkillers. | |
Some patients may experience such unpleasant consequences of anesthesia as nausea, dizziness, temporary memory loss, sore throat, hoarseness, etc. But these sensations, as a rule, pass quickly and do not harm the body. But with competent work of the anesthesiologist and an individual approach to the patient, such phenomena do not happen at all.
The point of view that several anesthesia taken over a short period of time is especially harmful to health has no basis in reality. For example, it is known that patients with severe burns receive general anesthesia often and for a long time (after all, they require regular dressings, as well as skin grafts and plastic surgery), and there is no reliable statistical evidence that anesthesia causes serious complications in them.
Someone was probably confused by the words about a “relatively healthy patient.” It is clear that among those who are routinely placed on the operating table, young and ideally healthy people are not so common. Concomitant diseases - hypertension, angina pectoris, bronchial asthma, etc. - can complicate the work of the anesthesiologist. But this is also the professionalism of an anesthesiologist. After all, this specialist should, before the operation, receive not a formal piece of paper from a neurologist, cardiologist or therapist with the inscription “anesthesia is indicated” or “anesthesia is contraindicated”, but objective information about the person’s state of health.
There are no absolute contraindications to the use of anesthesia, but with some concomitant diseases a certain degree of risk remains, which can and should be minimized. If the anesthesiologist determines that the patient's current health condition is not optimal for anesthesia, he will refer the patient to the appropriate specialist to correct the situation (for example, stabilize his blood pressure).
Why are people afraid of general anesthesia?
People are afraid not of the surgery itself, but of the effects of anesthesia, because each person reacts individually to the anesthetic.
History has many facts where the body did not succumb to the influence of drugs, and an additional dose led to death.
The famous Russian commander of the Red Army M.V. Frunze died under the influence of an anesthetic. But this is just one version. The legendary personality was given general anesthesia during the operation using ether; he could not sleep for a long time. Then the anesthesiologist added a dose of chloroform. After this, cardiac arrest occurred.
The second reason for fear of such drugs is the body's immunity. A person can receive an anesthetic but not be put into artificial sleep. So he can be immobilized, but feel physical pain. This can lead to death from pain or a feeling of terrible pain. Such cases are extremely rare and out of 1000 people there may be two such patients.
How to prevent and eliminate consequences
To avoid problems from surgery with general anesthesia, you should eliminate all bad habits, especially smoking and alcohol. It is advisable to start following a special diet and walking in the fresh air within a couple of weeks. This will strengthen the body before a serious test, but does not guarantee that there will be no consequences.
Some complications are not critical and go away on their own in a short time. If this does not happen after a month, then you need to consult a doctor. After all, each individual complication needs to be treated differently. If we are talking about postoperative cognitive dysfunction, then sometimes special drugs are needed - neuroprotectors, nootropics, antioxidants, as well as intellectual training for the brain. When it comes to hypertensive patients, they are necessarily prescribed strengthening cardiovascular therapy. Almost every patient is prescribed a diet that promotes rapid recovery of the body. That is, in each individual case the doctor will prescribe his own treatment.
The effect of anesthetics on the body
The question of whether general anesthesia is harmful to humans will not be disputed by any physician. So why is general anesthesia dangerous?
The effect of anesthesia on the human body is primarily reflected in the activity of the brain. The most dangerous consequence is cognitive dysfunction leading to central nervous system disorders. Anesthesia has the following consequences for the body:
- loss of sleep or frequent awakenings at night,
- decreased ability to work and rapid fatigue,
- absent-mindedness and inability to concentrate,
- deterioration of memory and ability to memorize,
- disorientation in space,
- pain in the muscles and throat,
- slight clouding of consciousness,
- itching or irritation of the skin.
The causes of such symptoms are:
- A short-term loss of consciousness provokes a micro stroke due to a decrease in blood pressure.
- Death of brain neurons.
The following factors increase the risk of developing asthenic syndrome:
- chronic diseases,
- age category,
- high rate of anesthesia,
- low intellectual development.
The effects of anesthesia can manifest themselves for a long time in the form of:
- panic fear,
- local memory loss,
- changes in heart rate, increased blood pressure,
- changes in the functions of the liver gland and kidneys, the anesthetic is a strong toxin and has a negative effect on the body.
What are the dangers of general anesthesia for the cardiac and vascular system?
Heart parameters play a big role when using anesthesia.
If the patient suffers from ischemia, tachycardia, arrhythmia, then he is sent for diagnosis. Only then is it determined whether surgery with anesthetics is possible.
Consequences of general anesthesia after surgery in children
With children everything is much more complicated. Their body has not yet matured, it is only growing, the foundations are being laid in it. Surgeries with general anesthesia are very dangerous for young children. Most of these patients experience developmental delays of several years. The child becomes nervous, inhibited, has poor memory, and slow learning. Of course, in 90% of cases, the child subsequently catches up with his peers, but falling behind is still extremely unpleasant for both the child and the parents. That is why they try not to give children general anesthesia, only in the most urgent and severe cases.
Effect of anesthetic on women
The female body is special; it goes through several stages of development. The effect of anesthesia on a woman’s body depends on the periods of life: puberty, pregnancy, menopause and menstruation.
General anesthesia is harmful for pregnant women, as it will have negative consequences on the health of the unborn child.
Artificial birth or caesarean section using anesthetics has the following consequences for a woman:
- headache,
- disgust,
- vomit,
- impaired concentration,
- back muscle spasms.
Contraindications for use
Without pain relief, it is impossible to perform even the simplest operation; the slightest surgical intervention causes unbearable pain. Therefore, from time immemorial, before anything was removed or corrected, people were rendered unconscious by stunning them with a blow to the head. Over time, drugs began to be used, which caused side effects.
The consequences of anesthetics may appear during surgery or much later; they are determined by the method of administration and composition. There are often side effects and complications that occur very rarely, but are critical, even fatal, which is why general anesthesia is dangerous.
Undesirable consequences after surgery can develop due to the presence of many contraindications in anesthetics. These include:
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- diseased kidneys and liver;
- nervous system disorders;
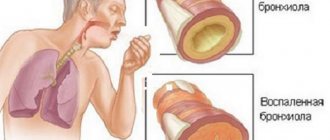
- diseases of the respiratory system: pneumonia, emphysema, atelectasis, obstructive bronchitis, exacerbation of bronchial asthma;
- diathesis;
- blood poisoning.
There are characteristic contraindications for children: recent surgery, rickets, any diseases caused by infection, recent vaccination.
Effect of anesthesia on children
Is anesthesia harmful for children? The effect of anesthesia on the child’s body is reflected in brain activity. Doctors believe that anesthesia for a child under two years of age affects his development. At such an early age, the child’s brain is in the formative stage and has the greatest likelihood of consequences such as neuronal destruction. As a result , children experience difficulties: their memory deteriorates, they find it difficult to concentrate, their activity decreases, and their ability to memorize decreases.
Anesthetics definitely have a negative effect on the body. But if you think about how many human lives have been saved by anesthesia, the risk is completely justified. The narcotic state makes it possible to perform complex operations that last for several hours. Science does not stand still, and anesthetics are being improved. The risk of dying from drugs exists, but it is much lower than being in a car accident.
Types of anesthesia
The harm of anesthesia depends on its type. Most often, a one-time use of painkillers does not pose a particular threat to humans.
Various drugs can put the patient into a state of sleep, including narcotic and non-narcotic analgesics, anesthetic drugs, and neuroleptics . There are several types of general anesthesia. Depending on the method of penetration into the human body, there are:
- Inhalation type - the entry of medicinal substances into the circulatory system through the lungs by inhaling gaseous agents. Used in dentistry.
- Non-inhalation method. Administration of drugs intramuscularly or intravenously is used less frequently than the first method. This method of pain relief can be divided into:
- classical injection of drugs - recofol, thiopetal, ketamine - into the venous blood, leading to deep sleep with preservation of respiratory ability and slight muscle relaxation;
- neuroleptanalgesia is carried out using droperidol, fentanyl. A superficial method of pain relief, causing drowsiness and lethargy;
- ataralgesia. Loss of pain with the tranquilizers diazepam and fentanyl;
- combined anesthesia. It represents a gradual intake of drugs from various pharmacological groups: anesthetics, narcotic analgesics, antipsychotics, inhalants together with relaxants ditilin, arduan. When used, these substances block neuromuscular impulses, which leads to a complete loss of respiratory ability . This condition poses a danger to children and adults.
Such anesthesia is carried out with tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation.