Injuries to the facial bones of the skull are quite common, with injuries to the nose occupying the leading position. Statistics show that about 40 percent of facial injuries occur due to a complex fracture of the nose. Such an injury occurs when someone falls on their face, for example, as a result of an accident or a fight.
After an injury, the patient must be examined by a surgeon. In most cases, such injuries result in bone fracture or cartilage damage, which is visible to the naked eye. To assist patients, repositioning of the nasal bones is indicated.
Author of the article / Site experts Shulepin Ivan Vladimirovich, traumatologist-orthopedist, highest qualification category
Total work experience over 25 years. In 1994 he graduated from the Moscow Institute of Medical and Social Rehabilitation, in 1997 he completed a residency in the specialty “Traumatology and Orthopedics” at the Central Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics named after. N.N. Prifova.
Repositioning of the nasal bones
Repositioning of the nose will be required in one of three cases of damage in the area of the nasal skeleton:
- with a closed injury to the nose, when the skin surface is externally intact or slightly damaged (bruising, swelling, minor scratches), but an x-ray shows a violation of the integrity of the nasal bone;
- with an open fracture of the nose, as a result of which there is a rupture of soft tissues, bleeding of various types, bones may be exposed from the wound, and fragments are visible;
- in case of a displaced injury, when the incorrect position of the bones is externally visible.
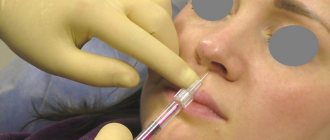
The nose is realigned by a maxillofacial surgeon or traumatologist. Patients with such injuries must be hospitalized as quickly as possible, since nasal injuries can interfere with normal breathing, and it is also very important to take an x-ray to obtain information about possible associated injuries (injuries to the eye sockets, frontal bone, etc.). Considering that 70% of nasal fractures are accompanied by a concussion, one can imagine the scale of the injury that the victim received.
With a closed fracture
First aid for a closed fracture should be provided at the site of injury. This can be done by others, or by the victim himself, if he remains conscious and can provide himself with basic help. So, immediately after receiving a closed injury, you need to apply ice to your nose - this will help narrow the blood vessels, stop the spreading bruise and swelling of the nose.
When admitted to a hospital, the patient is given an x-ray to see which bone is broken. Retraction of the nasal bridge, as well as displaced nasal fractures, are common. It is very important that with a closed fracture the integrity of the nasal septum is preserved - then repositioning is much easier.
Complex fractures are repaired surgically, but without cutting tissue. To do this, a Volkov elevator is used - the instrument is inserted to the required depth, after which part of the bone is lifted and restored in the right place. All interventions are performed under local anesthesia. After reposition, turundas with a medicinal substance are placed in the nose, which will help to initially support the tissue near the nasal septum until the formation of callus begins. Seven to ten days after surgery, a second consultation with a doctor is indicated.
In case of a displaced nasal fracture, the instrumental-finger method can be used, when the doctor either with his fingers or with the help of fingers and instruments sets the nasal bones to their normal position.
With an open fracture
If an open injury occurs, surgery is performed to realign the nose under endotracheal anesthesia. In some cases, doctors may use other methods of inducing a patient into a narcotic sleep. Typically, open fractures are more complex - this is primarily due to the fact that:
- blood loss occurs;
- there is a high risk of infection in the blood;
- Such injuries mostly contain fragments and may have atypical inclusions (glass, metal particles) that must be removed during surgery.
Surgery takes quite a long time depending on the extent of the lesion. Doctors restore the structure of the nasal bone and treat soft tissues. The fragments are being realigned. The tampons will hold the bones in position until the healing process begins. Usually, a few days are enough for the bones to “set.” After the operation, the skin is sutured and a sterile bandage is applied.
After injury
After nasal repositioning, recovery is extremely important. Therefore, during the rehabilitation process, some restrictions are imposed on patients:
- Patients should not go to the bathhouse or sauna for several weeks, as this can cause extensive nosebleeds.
- You should not wear glasses so as not to create pressure on the nasal septum.
- Avoid situations that could result in the person getting hurt again.
- If you have breathing problems, it is recommended to use vasoconstrictor drops.
All rules must be followed in full. This is very important to avoid the negative consequences of a fracture.
The child has
Nasal fractures in children occur during a fall, playing with peers, or as a result of traumatic situations in physical education lessons. Children have a peculiarity of injury - due to the elasticity of the nasal septum, there are no immediate consequences, as in adults. The child may not even remember that he hit his nose - severe pain will go away over time, but after a few days the symptoms of injury will begin to increase - the nose will become swollen, a characteristic nasal voice will appear, congestion, the child may complain of a headache. If such symptoms appear, you must contact the clinic, where the baby will have an x-ray and a diagnosis will be made. It is quite possible that this will not be a fracture, but a subluxation of the quadrangular cartilage, which the doctor can easily correct.
Symptoms of a fracture
In case of a fracture, you should promptly seek medical help. This is especially important if a child has been injured, because a deformed nose is fraught not only with an aesthetic defect, but also with the cause of frequent ENT diseases.
Symptoms characteristic of a fracture:
- bleeding (can be both scanty and heavy);
- state of shock, possible loss of consciousness;
- formation of swelling in the nose and eyes;
- the appearance of bloody streaks in the eyes;
- difficulty breathing, frequent desire to blow your nose;
- skin damage (with an open fracture, pieces of bone are visible);
- strong pain;
- hematomas at the site of impact and under the eyes.
The situation may be complicated by increased temperature, hyperemia at the site of injury, and softening of tissues. Such signs, which appear several days after the impact, indicate the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the wounds.
The deformation also depends on how the impact occurred. A blow inflicted from the front leads to a fracture of both nasal bones; to this may be added fractures of the frontal processes of the upper jaw and retraction of fragments.
During a side impact, the back of the nose shifts to the side, and bony protrusions are formed.
A strong blow can cause the outer part of the nose to completely flatten.
Indications and contraindications
The indication for surgery is direct bone damage caused by trauma. It is best to perform the operation in the first few hours after the injury. The maximum for such interventions is seven days. Otherwise, callus will begin to form and it will not be so easy to restore the integrity of the bones.
Contraindications to immediate bone reduction are:
- problems with blood clotting;
- herpes;
- severe damage to internal organs resulting from trauma;
- inflammatory processes in the nasal sinuses;
- patient's state of shock.
Contraindications to the operation do not mean that it will not be performed at all. The intervention is postponed for some time until the patient’s condition returns to normal and the pathologies that interfere with surgical intervention are eliminated.
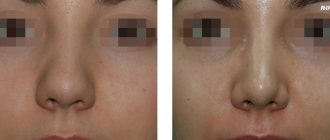
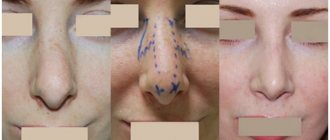
Rhinoplasty without surgery
Girls do not dare to undergo nose reduction surgery because of an overwhelming fear of it. Therefore, for most people who want to reduce their nose, the non-surgical method is considered the best option. Many cosmetology clinics offer many different non-surgical procedures. Among others, rhinoplasty without surgery is offered.
Correcting the shape of a woman's nose without surgical intervention became possible after the appearance of special degradable and non-degradable gel preparations in the cosmetology field.
Degradable gels, after they are administered, dissolve within a couple of months, while non-degradable gels remain in the human body for life.
Surgeons specializing in plastic surgery have great doubts about non-degradable gels. This is because such gels never remain in the place where they were injected, they can migrate throughout the body. This property is especially noticeable when non-surgical nose correction is carried out: this gel can only be placed on the basis of cartilage or bones, and no methods have yet been invented to secure it. The problem is complicated by the fact that the gel is a semi-liquid substance, and there are no special cavities on the nose that can hold the unknown material. Even if this procedure is performed by the best plastic surgeon, he will not be able to predict how the non-degradable gel will behave.
Degradable gels can be eliminated from the human body in about six months or a year. For this reason, the use of such correction of individual facial imperfections or the shape of the nose is not so dangerous. After all, after a while the facial features will return to their original appearance. We must not forget that this method will not help solve the problem forever, but only for a while.
The main disadvantages of such gels are short-term or temporary results. The thing is that with any plastic surgery, new tissue is added. After all, no matter what the nose correction is, without surgical intervention it still makes it bigger.
When a patient wants to straighten his nose, during plastic surgery the surgeon will grind down the unnecessary hump, but with non-surgical rhinoplasty he will straighten it with the help of a gel, which he will place on the back of the nose. This means that the entire nose will visually increase in size.
There is no need to be completely categorical. Undoubtedly, gels of a degrading nature can exist and be used in non-surgical interventions. They are also used by highly qualified plastic surgeons who have extensive experience in the field.
They use nose contouring only when correction of a certain defect in the shape itself is needed, but their own tissue is not enough.
Complications and consequences
If the patient does not follow the doctor’s recommendations, he may encounter negative consequences after a fracture, such as the formation of a hematoma that interferes with bone fusion, or malunion, which is accompanied by a pronounced defect. Also, problems during the recovery stage can lead to loss of smell, asthma, and migraines. In patients with improperly fused bones, nasal breathing is impaired, inflammatory processes occur in the nasal sinuses, and polyps may appear.
To prevent complications and serious consequences from appearing, bone repositioning must be carried out in a timely manner, immediately after injury. In Moscow, such an operation can be performed for an average of 7,000 rubles. The price depends on specific clinics, as well as the complexity of the intervention.
The recovery period after surgery takes about ten days; in complex cases, recovery can take up to three weeks.
Repositioning of the nasal bones is a mandatory procedure when a nasal injury occurs that damages the integrity of the bone tissue. It is necessary to do reposition as soon as possible, and after the injury, a consultation with a doctor is required to find out how severe the damage is. Timely intervention is the key to successful recovery of patients.
First aid
Qualified assistance will help alleviate the general condition and avoid loss of consciousness of the patient.
- Under no circumstances should the victim be kept in a lying position. You need to tilt your head slightly forward, this will help prevent bleeding into the esophagus.
- Apply something cold to the injury site. Particular care should be taken when doing this. Touching too hard can cause severe pain. Painkillers may be administered intravenously, if available.
- Treat the fracture site with iodine.
- Gauze swabs soaked in water are placed in the nasal passages.
You should not diagnose the consequences yourself. Only a doctor can accurately determine how serious the problem is.
Precautions to be taken:
- Do not touch a bruised nose.
- Under no circumstances should you adjust it yourself without medical assistance.
- You need to go to the first aid station in a sitting position.
The effectiveness of the treatment depends on the promptness of first aid.
The video provides information about possible fractures and first aid that should be provided to the victim.
First aid involves applying ice to the damaged area. This will reduce swelling and relieve some of the pain. Cold should be applied immediately after impact.
For high-intensity pain, you should take a pain reliever. The doctor will give it to you in the hospital, and if the patient took the drug on his own, this should be reported to the specialist so that there is no overdose.
If necessary, the patient is vaccinated against tetanus.
In some cases, hospitalization of the patient is required. It is relevant in the following situations:
- Significant external deformation.
- Heavy bleeding.
- Complicated fracture, accompanied by damage to nearby areas.
If the injury is recent, conservative treatment is sufficient. The specialist carries it out:
- By placing the bones in the correct position with your fingers or using a spreader. If they are displaced sideways or upwards, then a specialist’s hands are enough to realign them. In case of retraction, it is better to use an expander. This is a tool that is used to put displaced sections of bone back into place.
Similar services in other companies
- Selection of contact lenses ophthalmologist (ophthalmologist) initial appointment 0
b - Selection of simple and complex glasses by an ophthalmologist (ophthalmologist) without ordering 0 b
- Collecting smears and scrapings from patients 0 b
- Study tomography (tomogram) computer multislice (MSCT) non-contrast wrist joint (2 joints) 4,000 b
- Study tomography (tomogram) multislice computed tomography (MSCT) non-contrast of the lumbosacral spine 2,750 b
- Study tomography (tomogram) computer multislice (MSCT) non-contrast shoulder joint 2,800 b
- Computed multislice tomography (MSCT) examination, non-contrast, of the abdominal organs + retroperitoneal space (liver, pancreas, spleen, gallbladder, kidneys, adrenal glands, regional lymph nodes) 3,500 b
- Study tomography (tomogram) multislice computed tomography (MSCT) non-contrast thoracic spine 2,750 b
- Study tomography (tomogram) computer multislice (MSCT) non-contrast knee joint (2 joints) 4,000 b
- Study tomography (tomogram) computed multislice (MSCT) non-contrast wrist joint (1 joint) 2,800 b
- Study tomography (tomogram) computer multislice (MSCT) non-contrast brushes 2,800 b
- Study tomography (tomogram) multislice computed tomography (MSCT) non-contrast hands (2 limbs) 4,000 b
- Study tomography (tomogram) computer multislice (MSCT) non-contrast ankle joint (1 joint) 2,800 b
- Computed multislice tomography (MSCT) examination, non-contrast, of the pelvic organs (bladder, prostate, uterus, ovaries) 3,500 b
- Study tomography (tomogram) multislice computed tomography (MSCT) non-contrast cervical spine 2,750 b
- Study tomography (tomogram) computer multislice (MSCT) non-contrast of the abdominal cavity and pelvis 5 400 b
- Study tomography (tomogram) multislice computed tomography (MSCT) non-contrast foot (2 limbs) 4,000 b
- Taking a smear or scraping from the urogenital tract at the patient examination center 0 b
- Study tomography (tomogram) computer multislice (MSCT) non-contrast knee joint (1 joint) 2,800 b
- Study tomography (tomogram) computer multislice (MSCT) non-contrast ankle joint (2 joints) 4,000 b
If you did not find what you were looking for on the page or want to find additional information on your request, try using the search form or follow the links to the following sections:
- Medical services
- Surgical operations
- Surgical recovery
Mistake #1
Try to figure out for yourself whether it is a bruise or a fracture. You should not probe a swollen and bleeding nose or take other measures (for example, try to move it left or right, much less try to straighten it) - this can only cause even more harm. There is a danger of displacing bone fragments when palpated, and then a fracture without displacement will become a fracture with displacement. By the way, doing diagnostic research about the injury that occurred is not only dangerous, but also pointless. After all, as practice shows, a fracture is not always more dangerous than a bruise. After all, if the nose is broken without displacement of the bones, then no treatment will be needed - time will heal itself. Conversely, with a severe bruise, even if the bones remain intact, deformations of the external nose may occur, which must be corrected surgically. But only an ENT doctor can deal with this.