Why don't systemic antibiotics cure acne?
1. Hyperproduction of sebum.
The increase in the level of sex hormones, which is usually observed during rapid puberty, increases the secretion of sebum. 2. Pore blockage. Skin pores become filled with oil, bacteria, and dead skin cells. This can be seen in the form of unsightly white and black dots on the skin. 3. Growth of bacteria. Hundreds of species of bacteria live on our skin and interact with it all the time, starting from birth. Overproduction of sebum and other factors spur their growth. 4. Inflammation. Excessive growth of bacteria initiates an inflammatory process in the skin, which results in those terrible pimples that bring a teenager to the doctor's office.
“Systemic antibacterial drugs help us control the growth of bacteria, but we do not influence other factors, so acne cannot be cured with antibiotics alone. But we have a lot of potentially serious side effects associated with long-term antibiotic therapy,” explains Dr. Tamburro.
Reviews about the drugs
Reviews from patients about the treatment of facial acne with systemic medications are varied. For many, the pills helped them cope with the problem in a fairly short time. Some people, on the contrary, complain about their low effectiveness and a large number of side effects, such as dry mouth, chapped lips, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, depression, etc. Most of the dissatisfied patients mentioned that they themselves prescribed this or that medicine , which led to an undesirable result of therapy.
Acne - causes and mechanism of development
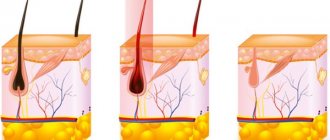
Under the surface of the skin there are many hair follicles, from which hair grows and penetrates the surface of the skin through its pores (Fig. 7a). At the base of each hair follicle there are many small sebaceous glands that produce sebum. This fat comes from the sebaceous glands through narrow channels, first into the lumen of the hair follicle, and then (along the hair shaft) it rushes out to the surface of the skin.
The development of acne is associated with two points:
- Strengthening the function of the sebaceous glands at the base of the hair follicles - increased sebum production is directly related to the increased production of androgens (male sex hormones) by the adrenal glands. These hormones are produced in both sexes, but to a lesser extent in women. This is why acne develops during puberty in teenagers.
- Epithelial keratosis within the follicle - the surface of each hair follicle is covered from the inside with layers of epithelial cells. An increase in the rate of exfoliation of epithelial cells from the inner surface of the follicle leads to an increase in the number of exfoliated dead cells in its lumen.
Increased sebum production and an increase in the number of desquamated cells lead to the formation of plugs that clog skin pores (Fig. 7b). It is these plugs that are called acne vulgaris. Blackheads may look: → in the form of white bumps, if the plug forms deep in the pore (Fig. 9), → in the form of black dots inside the pores, if the plug forms at the surface of the skin (Fig. 10).
The formation of plugs leads to the fact that the sebum constantly produced by the sebaceous glands cannot come out and accumulates in the lumen of the hair follicle (Fig. 7b). A closed space with a nutrient medium inside is an ideal place for the development of infection, and therefore bacteria that have entered the hair follicle from the surface of the skin begin to multiply intensively there.
This leads to the development of inflammation in and around the follicle. Inflammation can occur for a long time without the formation of pus; in this case, such a formation is called a papule (Fig. 10). A papule looks like a red, inflamed bump on the surface of the skin. Papules can disappear without a trace over time, but usually they transform into pustules. The pustule is already a classic pimple with pus inside (Fig. 11).
In addition, with more severe forms of acne, large inflammatory formations - nodules and cysts - can form. The nodules are large, dense, painful papules, which also have no pus inside (Fig. 12). Cysts, as a rule, arise when an attempt is made to squeeze out pimples located deep in the skin, as a result of which pus penetrates deeper into the tissue (Fig. 13).
Antibiotics for acne –
It is known that doctors’ commitment to prescribing a particular antibiotic depends on geographical, historical conditions, and information and educational programs. Thus, the choice of antibiotic and the principles of its prescription differ in the USA, Great Britain and continental European countries. Among systemic antibiotics for the treatment of acne, the group of tetracyclines (tetracycline, doxycycline and minocycline) and the group of macrolides (erythromycin) have the most evidence regarding clinical and microbiological effectiveness.
Tetracycline group drugs remain the priority among systemic antibiotics for the treatment of acne. Doxycycline is characterized by higher microbiological and clinical efficacy compared to tetracycline.
Currently, it is used less and less due to the increasing resistance of microflora and the high frequency of unwanted drug interactions.
The duration of systemic antibiotic therapy can reach 24 weeks or more with mandatory monitoring of results every 4 weeks. In clinical practice, it is advisable to combine oral antibiotics with external agents containing retinoids or benzoyl peroxide. If there is no dynamics of the process, alternative therapy with systemic retinoids (isotretinoin, Aknetin) should be prescribed.
SIDE EFFECTS - with antibiotic therapy with tetracyclines or macrolides, side effects from the gastrointestinal tract (colitis and diarrhea) occur in 5% of patients, candidiasis (vaginal) - in 6% of women. Other complications include onycholysis (doxycycline), ulcerative esophagitis (doxycycline), persistent exanthema (tetracycline and erythromycin), photosensitivity including porphyrin-like changes in the skin (long-term tetracycline therapy), phototoxic rash (doxycycline), liver dysfunction and changes in clinical analysis blood (tetracyclines and erythromycin).
Choosing the optimal effective antibacterial drug for the treatment of acne is a very difficult task. Often the choice is based on the personal preferences of the clinician, taking into account the brand name, the medicinal base of the drug, its form (solution, gel, cream, ointment), cost and effectiveness of treatment.
It should be remembered that the main problem of long-term use of antibiotics is the development of persistent microbial resistance, so the persistent prescription of more and more new antibiotics to patients with acne who do not show clinical improvement after antibiotic therapy is unjustified. To improve the effectiveness of acne therapy, information regarding the global/regional status of microbial resistance to that drug should, if possible, be used before prescribing a specific systemic antibacterial agent.
Currently, we know much more about acne than we did 5-10 years ago. Specialists have a number of effective medications from different groups in their arsenal, but, unfortunately, none of the modern treatment methods can guarantee the absence of relapses of the disease in the future. It is important to regularly adjust the prescribed treatment and dynamic follow-up monitoring of the patient even after achieving clinical remission.
A delicate issue for the fair half of humanity is the removal of facial hair, in particular in the area: neck, upper lip, as well as temples, eyebrows, forehead line, chin, cheeks - laser hair removal solves this problem once and for all.
Antibiotic anti-acne medications successfully cope with skin inflammation of any complexity. On the other hand, along with the pathogenic microflora, the beneficial microflora is destroyed, so immunity is reduced. For this reason, it is not recommended to self-medicate. Below are some reasons against using antibiotics:
- Most drugs negatively affect the functioning of the liver, as a result, a large amount of toxic substances accumulate in the body;
- Antibiotics can cause allergic manifestations (dysbacteriosis, candidiasis), the use of drugs is individual. The cause of allergies is the aggressive effect of antibiotics on pathogenic and beneficial microflora. In this regard, it is recommended to take antibiotics together with antifungal and prebiotic drugs;
- The drugs often cause dizziness, loss of balance while walking, discoloration of teeth, and sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation.
- It is important to choose the right dosage and duration of medication.
Drugs of this pharmacological group have the following effects on skin with inflamed acne:
- Bacteriostatic effect. This means stopping the further growth of pathogenic bacteria.
- Bactericidal effect. Medicines completely destroy bacteria.
- Reduces fatty acid levels. Their content is reduced by 2 times.
- Suppress the mobility of neutrophils during the inflammatory process.
There are 2 groups of antibiotics:
- External. They are applied either to the entire acne-affected skin, or locally to each pimple, depending on the preparation.
- System. They are taken orally, and the medicine acts entirely on the entire body. The tablets have an effect on the stomach, and when administered subcutaneously, intramuscularly or intravenously, the medicine bypasses the gastrointestinal tract.
Firstly, a course of treatment is prescribed only after a diagnosis is made. Secondly, many factors must be taken into account (the cause of the disease, the severity of the disease, etc.).
Despite the fact that ointments, creams and gels for acne are sold freely in pharmacies, they should also be prescribed by a doctor. The fact is that each of these drugs is aimed at combating a specific type of acne. Only a doctor can determine which type of bacteria has affected the patient’s skin and which bacteria is the causative agent of the disease. The most effective means are:
- Gel "Baziron". Aimed at treating acne caused by the bacteria Propionibakterium acnes or Staphylococcus epidermidis. The gel is applied exclusively to the pimple, as it can cause burns to healthy skin.
- Ointment "Zinerit". Contains erythromycin, which is considered the most effective component in the fight against acne. Girls love this ointment very much, because you can apply makeup on it.
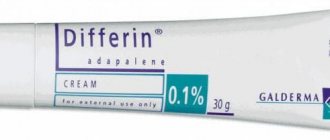
- Cream "Differin". It contains a retinoid, which is also effective against acne. This remedy is especially indicated for those who are predisposed to post-acne, that is, spots after acne. In addition, the cream also lightens existing marks. You only need to apply the cream at night.
- Gel or cream "Skinoren". Contains azelaic acid. A very effective remedy.
- Gel "Curiosin". Contains hyaluronic acid and zinc. The gel effectively fights acne, but does not dry out the skin and promotes its nutrition and regeneration.
Antibiotics for acne are most often used externally (as part of creams and gels), less often - in the form of tablets. Gels with antibiotics are prescribed for all forms of acne, except for the form when there is only acne without inflammation. And under no circumstances should you use ointment forms of antibiotics!
- Antibacterial creams and gels - usually contain antibiotics such as erythromycin and clindamycin. Usually prescribed for acne, mixed acne (acne with pimples). Examples of gels with clindamycin: “Clindovit”, “Dalacin”, “Clindatop”.
There are combination drugs where the antibiotic is combined with drugs from other groups. Such drugs are preferable and stronger, but before using them, you need to consult a dermatologist:→ “Duak-gel” – contains clindamycin and benzoyl peroxide, → “Deriva-S”, “Klenzit-S” – clindamycin and adapalene (retinoid), → “Isotrexin gel” – erythromycin and isotretinoin (retinoid). → the drug Zinerit is an effective combination drug based on erythromycin and zinc.
- Oral antibiotics – tableted antibacterial drugs should only be prescribed by a doctor. They are usually prescribed only for cystic acne. However, oral antibiotics may be prescribed for both acne and acne if standard topical therapy for the latter has not been successful.
Important rules for using drugs
It should be noted that the effect of systemic antibiotics is cumulative, and even after the end of the therapeutic course they continue to work. Providing a complex effect, they treat not only acne on the face, but also stop other inflammatory processes.
There are some rules for using these medications:
- therapy is prescribed exclusively by a doctor when grades 3 and 4 acne are detected;
- for moderate severity of pathology, use Tetracycline, Clindamycin, Erythromycin acne tablets;
- A severe form of dermatological disease requires complex treatment;
- The duration of therapy should not exceed the period of time recommended by the specialist.
Features of the use of antibiotics
The best results from taking antibiotics can be achieved by using benzoyl peroxide, hormones and adapalene. You need to combine medications with probiotics and do not start therapy without conducting a test aimed at detecting and identifying the causative agent of the disease.
Rules for the use of hormonal drugs
All hormonal and contraceptive medications for acne are taken at the same time, with a glass of plain water. Eating does not affect the effect of the medicine in any way. It is prohibited to increase or decrease the dosage without the knowledge of the doctor.
Like antibiotics, they have an impressive list of contraindications and can lead to:
- obesity;
- changes in blood sugar levels;
- diseases of the digestive system.
How to treat acne correctly -
If you are unable to maintain your facial skin in good condition on your own, be sure to consult a dermatologist. Treatment of acne in adults and adolescents is the same, with the exception of women in whom hormonal contraceptives can be used as additional therapy.
How to treat acne will depend primarily on what kind of inflammatory elements are on the skin of the face. Treatment will be different in situations where there is –
- when there are only acne,
- only pimples (papules and/or pustules),
- for mixed forms of acne (acne pimples),
- in the presence of nodules and cysts.
Below you can see a list and description of medications, as well as a diagram (Fig. 14), which shows what needs to be used for each form of acne.
Duration of treatment – in order to achieve any noticeable improvement in the condition of the facial skin, up to 4 weeks of treatment are necessary. The standard course of treatment is about 6 weeks. However, with persistent acne, treatment can take up to four months (and sometimes longer) to get good results and get rid of not only acne, but also post-inflammatory skin pigmentation.
Is it possible to choose the drug yourself?
Before choosing the necessary tablets for acne, acne and pimples on the face, you must:
- find out why they appeared. It may be necessary to use only an external agent with a drying and healing effect;
- determine the type of skin;
- If you have allergies, give preference to hypoallergenic drugs.
Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and hormonal tablets should only be taken under medical supervision, so you cannot prescribe them yourself. If we are talking about vitamins, dietary supplements, ointments, topical gels, then consultation with a specialist is advisable. He will definitely tell you which acne pills are better and more effective.
Treatment of acne in women -
Oral contraceptives may be used as an adjunct to primary treatment in adolescent girls and women. First of all, this treatment method is recommended for healthy women who also need contraception. Hormonal contraceptives are also prescribed to those women for whom traditional acne treatment methods (described above) do not give good results.
In addition to oral contraceptives, women can also use androgen blocking drugs, for example, Spironolactone. Read more about these treatment methods here.