Seborrhea (seborrheic dermatitis) is a skin pathology that is expressed by dysfunction of the sebaceous glands. In addition to physical discomfort, the disease spoils a person’s overall aesthetics and also provokes the development of psychological complexes. More often, the chest, back and head areas are involved in the pathological process, but seborrhea on the face causes particular discomfort.
Statistics indicate impressive figures - facial seborrhea affects 6 to 8% of the planet's population. What is the reason for such a spread of pathology, what symptoms indicate it and what kind of therapy can it be treated?
Reasons for the development of seborrhea on the face
The human body has a huge number of exocrine glands, which perform an important function: through the production of sebum (sebum), the glands nourish, moisturize, protect and soften the skin. Features of the localization of such glands, in particular on the face, provoke the progression of seborrhea:
- in the frontal region;
- on the eyebrows;
- nasolabial “triangle”;
- scalp.
When a malfunction occurs in the body, sebum is produced in excess and “works against a person” - it becomes a favorable environment for the development of fungal and infectious diseases. More often, facial seborrhea is accompanied by excessive activity of the secretion organs.
But in medical practice, there are cases of dry seborrhea of the face, when, under the influence of various factors, the function of the glands is inhibited. The third type of pathology is mixed, when both manifestations of seborrheic dermatitis occur.
In each case, the chemical composition of sebum changes, which disrupts the oxygen exchange of the skin, reduces the protective functions of the epithelium and provokes irritation.
The sebaceous glands in the body of a healthy person produce up to 20 g of sebum per day, in a patient - 1.5-2 times more.
The main “provocateur” of the development of seborrhea is the opportunistic yeast-like fungus Pityrosporum (pityrosporum), which parasitizes the hair follicles, as well as the exocrine glands.
Normally, pityrosporum is found on the surface of the skin in 90% of people, but in the presence of a favorable environment, it begins to actively multiply and acquire pathogenic properties.
The reasons for the appearance of seborrhea on the face and the activation of the fungus are caused by the following factors:
- genetic predisposition;
- hypovitaminosis, weakening of the body's protective functions;
- pathologies of the endocrine system, including hormonal imbalance (increased testosterone), diabetes mellitus;
- stress, overwork, violation of work and rest schedules;
- disruption of the central nervous system;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver;
- insufficient facial skin care, lack of proper hygiene.
Men are more susceptible to oily seborrhea of the facial skin. This fact is due to an excess of testosterone in the male population, the peak of which activity occurs during puberty (from 12 to 20 years). But in some cases, pathology manifests itself regardless of gender and age.
What can be used from traditional medicine?
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis with folk remedies is aimed at eliminating the unpleasant signs of the disease.
Traditional methods are good for treating the symptoms of dermatitis: itching, burning, swelling. The natural power of medicinal herbs perfectly restores the immune system and helps the body fight pathogenic microflora on the face.
Healers use complex ointments as a natural antiseptic: take 1 tbsp. l baby cream, olive oil, golden mustache juice and mixed with a teaspoon of valerian tincture. The resulting composition is applied in a thin layer to the inflamed areas of the face.
To strengthen the body's protective function, take orally:
- decoction of oak bark;
black currant tea;- herbal mixture of burdock, elecampane and St. John's wort;
- herbal tea made from calendula flowers, chamomile and plantain leaves;
- collection of immortelle flowers, corn silk, string and tansy
- decoction of sage leaves.
Such treatment with folk remedies stimulates general and local human immunity. Lotions of medicinal tinctures made at home are great help. It is important to know that different bases are used for oily and dry types of seborrheic dermatitis. For oily types, an oil base is prohibited, and for dry ones, it is advisable to use castor or olive oil as the base for a homemade tincture.
For oily seborrheic dermatitis, a tincture of St. John's wort is suitable: 3 tbsp. l of raw material is poured with two glasses of alcohol and left for a week. Before use, the tincture is diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio.
When dry, a tincture of calendula with castor oil gives a good effect on the skin.
An alcoholic tincture of this plant is mixed with castor oil in equal proportions. Before application, the liquid must be shaken and applied with a cotton swab to the affected areas of the face.
Therapy for seborrheic dermatitis should be carried out in a complex manner. This is not just a temporary restriction in food and a single course of medication. If the patient does not adhere to proper nutrition after the end of treatment and is frivolous in the choice of facial cosmetics, seborrheic dermatitis will return again.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic skin lesion that occurs due to disruption of the sebaceous glands. Pathological processes are accompanied by the formation of red plaques and rashes, unbearable itching and pain in inflamed areas. And when the skin in visible areas of the body becomes inflamed, psychological discomfort is added to the physical one. The treatment of the disease is based on the use of special local remedies - lotions, ointments or creams. Ointment for seborrheic dermatitis helps relieve inflammation and get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of the pathology.
Symptoms
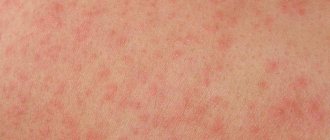
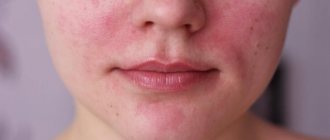
The most common is oily seborrhea of the face, which is often accompanied by a secondary infection of infectious or fungal origin. Symptomatically, the pathology manifests itself as:
- increased sweating;
- enlarged pores on the face;
- inflammatory processes that provoke redness of the epithelium;
- foci of suppuration;
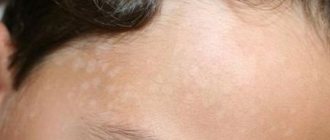
Dry seborrhea is characterized by:
- the appearance of dry, flaky skin;
- fine dandruff appears on the hair and face;
- hair loss occurs;
- changes in the skin are accompanied by itching and burning;
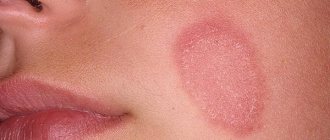
- Pinkish and red spots of thin epithelium appear on the skin.
The mixed type of disease combines the symptomatic manifestations of the two varieties described above.
Reasons for appearance
The formation of dry crusts on the scalp and face is called seborrhea or seborrheic dermatitis. And this is not such a harmless phenomenon. Many attribute seborrheic manifestations to seasonal drying of the skin, inappropriate cleansers, and lack of vitamins. But such problems are quite easy to fix.
If, after the measures taken, dandruff does not disappear, then the reasons are more serious: perhaps the metabolic process has failed, or the immune system has failed, chronic illnesses have worsened, and chronic illnesses have begun to progress. According to experts, flaky skin can appear due to the following reasons:
- eyebrow dye may be of poor quality or unsuitable for a particular skin, causing seborrheic manifestations;
- prolonged exposure of the facial skin to cold and wind, causing drying;
- a fungus that, in the absence of treatment procedures, has spread from the scalp to the face;
- stress, hypo- and avitaminosis, causing dryness, peeling, allergic manifestations;
- overwork due to lack or insufficient rest, significant excess of workloads;
- hormonal disorders;
- a sharp change in regime, lifestyle;
- significant changes in diet, a large proportion of fatty, spicy foods and dishes, preservatives;
These factors can be combined or be the only cause of seborrhea on the eyebrows.
In addition, experts have identified other reasons that can provoke such manifestations:
- change of seasons, climate zone, sudden onset of extreme cold;
- neurological diseases in old age;
- HIV and AIDS diseases;
- dandruff-causing fungus Malassezia , even leading to seborrheic and atopic dermatitis;
- specific individual reactions of the body (for example, to ultraviolet radiation, to medications);
- exacerbation of chronic ailments;
- genetic predisposition.
Attention! Not in every case it is possible to establish the exact cause, but it has been proven that seborrhea on the eyebrows is not a consequence of infection, it is not contagious, and in itself is not dangerous.
So, what can you do to get rid of this unpleasant phenomenon and make your eyebrows look healthy and well-groomed again?
Appearance from photo
Externally, oily facial seborrhea is characterized by the following manifestations:
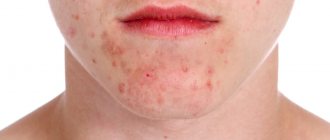
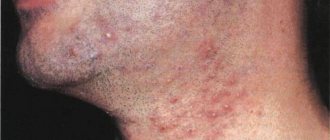
- acne;
- comedones;
- milia;
- scars on the skin as a result of acne;
- increased oiliness of hair and skin.
With the dry type of the disease, dry skin, cracks, peeling and scales appear. The hair of patients with dry seborrhea is brittle, and the head is covered with fine dandruff. Dry seborrhea is more common in children.
Mixed seborrheic dermatitis is easily confused with the manifestation of atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and lichen. Therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, a doctor’s examination is necessary.
Nature of the disease
Under the influence of various provoking factors (primarily due to dysfunction of the sebaceous glands), the proliferation of the fungus Malassezia furfur gets out of control, resulting in symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis. The scalp (face and hair growth area) is affected, as well as other areas of the body, with the exception of the palms and soles.
Often the disease becomes chronic; in addition to damage to the skin, the condition of the hair also deteriorates significantly.
Seborrhea often causes diffuse alopecia. Seborrheic dermatitis is most susceptible to people between the ages of 20 and 50, but the disease can develop at any age. At the same time, seborrhea is much less common in women.
Treatment of seborrhea on the face
The standard therapeutic regimen for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis includes:
- means to enhance the body's immune function;
- multivitamin complexes;
- external agents (creams and ointments);
- sedatives;
- physiotherapy (ozone therapy, cryotherapy, Darsonval microcurrents, UV and gamma radiation).
If secondary infection develops, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and NSAIDs. Also, in the treatment of dry and oily seborrhea on the face, external agents (usually corticosteroid ointments) are actively used to relieve foci of inflammation.
Use of external preparations
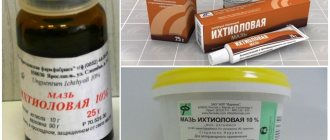
Among the variety of external remedies for the treatment of oily and dry seborrhea on the face, the following creams and ointments are popular:
- Flucinar is an antiseptic that relieves itching and redness of the skin;
- Advantan is an effective hormonal remedy against itching and inflammation;
- Skin cap. The ointment is based on zinc, which eliminates allergic rashes, reduces itching and irritation;
- Belosalik (Russian analogue of Akriderm). Effective in the treatment of dry seborrheic dermatitis.
Ketoconazole, Lamisil, sulfur-salicylic and naphthalene ointments are also used for medicinal purposes.
Treatment of acute inflammatory response
An acute inflammatory reaction with seborrhea on the face requires rapid relief of unpleasant symptoms, so the course of treatment includes:
- antiallergic drugs, such as Loratadine;
- NSAIDs, such as Indomethacin;
- corticosteroids such as Dexamethasone and Akriderm;
- in some cases - antibiotics.
Complete elimination of the disease is possible only with comprehensive treatment and adherence to a gentle diet. At the discretion and with the permission of the attending physician, therapy is supplemented with traditional medicine and physiotherapy (after the symptoms have subsided).
Traditional recipes for seborrhea on the face
Traditional recipes for the treatment of seborrhea on the face and scalp are designed to normalize the secretory function of the sebaceous glands and restore the epithelium. The main components are often the following herbs:
- series;
- plantain;
- chamomile;
- St. John's wort;
- nettle;
- burdock;
- sea buckthorn;
- viburnum.
Also used in home remedies are sea salt, castor oil, kefir, whey, and apple cider vinegar. Here are a few recipes:
- Gauze wipes are moistened in whey and applied to the affected areas for 1 hour twice a day. After the procedure, the face is thoroughly washed. Kefir is used in the same way;
- Every morning, wipe the skin with the following mixture: add 150 g of vermouth and 100 g of crushed horseradish root to 300 g of vinegar. The infusion is kept for a week and stored in a cool place;
- Based on the above herbs, infusions are made at the rate of one tablespoon per glass of boiling water. Rinse hair with infusion or use it as a tonic and facial compress;
- Make a mask from one fresh cucumber and a tablespoon of honey. The mixture is kept on the face for 10-15 minutes, after which it is washed off;
- Sea salt is used as a scrub, which is used to massage the scalp and face. In this way, it is possible to gently exfoliate dead skin and “dry” excess sebum.
Home remedies cannot replace basic treatment, and independent “therapy” provokes the development of complications. Therefore, the use of traditional recipes must be agreed with a doctor.
Difference from other types of seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrhea on the skin is a pathological process of an inflammatory nature that develops due to a disorder of the nervous and neuroendocrine regulation of the functions of the sebaceous glands in the layers of the epidermis. Under the influence of provoking factors, a change in the composition of sebum occurs, which causes disruption in the process of skin respiration and a decrease in infection resistance.
The table shows how dry seborrhea on the face differs from other types of this disease.
| Dry form | Bold form | Mixed form |
| Insufficient sebum production | Increased work of the sebaceous glands | Symptoms of dry and oily seborrhea at the same time are characteristic. More often the scalp has decreased secretion of the sebaceous glands, and areas on the face have increased secretion. |
| Dry, cracked skin | Skin has an oily sheen | |
| White and yellowish scales on the forehead, nose and chin | Widespread rash (white head pimples) |
Dry skin does not always lead to dermatitis. In order for an inflammatory process to form, it is necessary to create a favorable environment for the disease on the skin of the face.
Diet
The condition of the skin directly depends on the diet. Therefore, another step on the path to recovery is to follow a diet plan that includes:
- refusal of “fast” carbohydrates;
- minimizing salted, smoked, fried foods in the diet;
- refusal of spices, spices, alcohol.
In the treatment of skin diseases, including seborrhea on the face, it is important to normalize digestive function, as well as daily bowel movements to effectively cleanse the body of toxins.
For seborrheic dermatitis, emphasis is placed on the use of:
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- soups;
- vegetables;
- steamed fish, lean meat;
- foods rich in fiber;
- rye bread.
Doctors also recommend eating small meals and having “fasting” days once a week. "Fasting" does not mean fasting. As an alternative, mono-diets, “unloading” on kefir, fruits or vegetables, are recommended.
It is very important to follow a hypoallergenic diet even after facial seborrhea has been cured.
Prevention
Compliance with simple rules prevents the primary development of pathology and also reduces the possibility of relapse to a minimum:
- first of all, eliminate the factors that provoked the disease (treat pathologies of internal organs, avoid stressful situations);
- strictly follow a hypoallergenic diet;
- pay attention to skin care cosmetics;
- carefully observe the hygiene of the face and other “seborrheic” areas;
- observe a work and rest schedule in which walks and sea air are recommended.
The main thing in the treatment of facial seborrhea is to identify the primary source of the pathology. Only in this case will the doctor be able to draw up the correct therapeutic regimen to effectively solve the problem in a relatively short time.