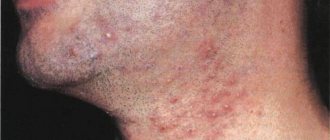
Hirsutism often acts as a symptom of a number of diseases. The condition is excessive hair growth in androgen-dependent areas in women of the masculine (male) type, provided that secondary sexual characteristics are preserved. These areas include: face, chest, linea alba, sacrum, buttocks, inner thighs, and excessive hair growth throughout the outer arms. At the same time, the new hair does not look like the vellus hair common to the female body - the new hairs are hard, dark and long.
There is also a change in pubic hair in the form of a cone-shaped narrowing upward. In addition to the appearance of hair in places unusual for the female body, androgenetic alopecia, acne vulgaris, low (not typical for women) timbre of voice, slight increase in muscle mass, increase in the size of the genital organs, increased sexual desire, menstrual dysfunction up to amenorrhea, may be observed. changes in character. Additional manifestations are not a necessary component of hirsutism. It is worth mentioning that such a condition can only be discussed in relation to women. These changes are based on an endocrine imbalance between female and male sex hormones with a predominance of androgens. It happens that male pattern hair growth is observed in pregnant women and women during menopause.
Hirsutism: what is this disease?
If a woman experiences malfunctions in the endocrine system, then her body hair begins to grow rapidly - the stomach, chest, back, ears, nipple areolas, and face are the most affected.
This happens because the woman’s body begins to produce more hormones, which should predominate in the male half of humanity, but female hormones become scarce, and in this case, the hair follicles begin to function very actively.
Hirsutism in the fair sex is not a common occurrence. According to medical statistics, the disease occurs in approximately 5% of the female population of the planet.
Ladies have to deal with unpleasant manifestations all their lives, taking medications, using all kinds of expensive cosmetic products and even turning to surgeons.
Men cannot have this disease. In relation to representatives of the stronger half of humanity, it is applicable to use the word hypertrichosis, and not hirsutism.
Hypertrichosis is a disease in which a woman experiences excess hair growth in different parts of the body, including those where hair growth does not depend on the amount of androgen secreted by the body.
This disease can develop in both representatives of the stronger half of humanity and women, and hirsutism is an exclusively female pathology.
If hirsutism has developed to a very severe stage, then the woman, in addition to hair on the skin, also has other external signs of a male body:
- the voice becomes rougher;
- hair falls out on the head;
- breasts begin to shrink;
- and the clitoris, on the contrary, increases;
- acne appears on the face.
Next, we will describe in more detail why a woman can develop hirsutism, how it will manifest itself and how to treat it.
IDIOPATHIC HIRSUTISM: SYMPTOMS
It should immediately be noted that there are several types of hair on the human body. As many people know, the entire skin is dotted with the finest non-pigmented hairs or fluff. If, for some reason, instead of fluff, hard pigmented processes begin to appear on the back and stomach - this is a sure signal of an increase in testosterone in the body.
A woman with hair growing on her face
First of all, male-type hair appears in young girls in the form of thickets on the face. The temporal processes begin to lengthen, and the line of the antennae becomes more noticeable. It is noteworthy that this hair is not “female”: it is short and does not curl, has a dense structure and resembles overgrown stubble.
Symptoms of the first signs of hirsutism:
- Changing skin type. Excessive production of testosterone by the ovaries provokes hyperactivation of the sebaceous glands. They begin to produce more oil and sweat, which can result in the formation of blackheads and pimples;
- Hair growth in the nipple area, inner thighs, stomach, back, buttocks;
- Increased hair growth on the arms and shoulders.
Symptoms of this condition indicate the effects of increased androgens on hormone-dependent organs. The main sign is the appearance of male-type vegetation.
For diagnostic purposes, the degree of hair growth in 11 areas of the body is assessed. The severity of the property in each zone is assessed on a scale from 0 to 4.
Then the numbers are summed up and the so-called hirsut number is obtained, a value of up to 7 indicates normal, 8-12 points indicates a borderline condition. And only a score above 12 points will indicate hirsutism.
An increased content of androgens activates the sebaceous glands in the following way: it increases secretion production and disrupts the process of cell desquamation.
We recommend you find out: What does it mean when antibodies to thyroid peroxidase are very elevated
The condition of the skin worsens: the hair ducts are blocked, a bacterial infection occurs, and acne appears.
Treatment of skin manifestations by a cosmetologist does not bring relief. Prescribing drugs with antiandrogenic effects improves skin condition.
Obesity
Uneven fat deposition when hormones are imbalanced also occurs in the male pattern: in the abdomen, neck, and arms.
It is important to discover the cause of terminal hair growth before starting therapy.
The situation is worsened by the fact that adipose tissue is a depot of sex hormones. To effectively treat increased hairiness, such women are recommended to follow a therapeutic diet and sufficient physical activity to bring their body weight back to normal.
Dysmenorrhea
The cycle changes are as follows:
- heavy menstruation;
- tendency to mark bleeding;
- irregular cycle;
- amenorrhea (lack of menstruation).
However, not all female hairiness is accompanied by such problems. At
In familial hirsutism, the cycle and ability to conceive are not affected.
Pregnancy with increased hair growth is possible if the content of female sex hormones is not disturbed, the menstrual cycle is preserved and ovulation occurs.
If the growth of androgens interferes with the normal functioning of the ovaries, we can talk about motherhood only after treatment.
The main symptom of idiopathic hirsutism in girls is excessive growth of terminal hair in androgen-sensitive areas. However, menstruation (and ovulation) and circulating androgen levels remain normal. Moreover, studies on the idiopathic type of hirsutism have found altered functioning of androgen receptors and disruption of their metabolism.
| HIRSUTISM | The primary symptoms of idiopathic hirsutism are excess terminal hair growth in androgen-sensitive areas. The average Ferryman-Gallway score is around 1-9 (usually above 6). |
| MENSES | Typically, periods are regular with normal ovulation. This means that women with idiopathic hirsutism are not infertile. |
| MALE HORMONES | The content of androgens circulating in the blood remains unchanged (normal). |
| SKIN SENSITIVITY | Increased local activity of 5a-reductase. Experts believe that there may be a genetic change in the function of androgen receptors and 5a-reductase, which can influence the manifestation of hirsutism. |
Diagnosis of women with idiopathic hirsutism should be carried out using the following medical tests:
- daily measurement of basal body temperature (diagram),
- blood tests for progesterone in the luteal phase, as well as DHEA (DHEA sulfate, DHEAS), testosterone;
- tests for levels of 17-OH progesterone (follicular phase), cortisol, ACTH.
The diagnosis of “idiopathic hirsutism” is also often made in women by exclusion, in cases where serum androgen levels and the ovulatory process appear normal.
Ferriman-Gallwey scale and hirsut number
To correctly identify the type of hirsutism, it is very important to evaluate the Ferriman-Gallwey scale.
The Ferriman Index was originally developed for anthropological research and clinical assessment of hair growth in women (1961) in four different degrees of severity on 11 parts of the body: face (lip, chin), chest, upper and lower back, upper and lower abdomen, arms and forearms, legs.
Although more objective tools are available, they are complex, expensive, or difficult to use. The ease of use and low cost of the Ferriman-Gallway system make it a potentially attractive tool for widespread use by gynecologist-endocrinologists.
If you want to check your level of hirsutism (hirsutism number):
- Look at the image and select the distribution of hair growth in all 9 body parts shown.
- Choose the appropriate score from each picture.
- Add up all the points. The total resulting amount will be your index, or hirsut number on the Ferriman-Gallwey scale.
Results: transcript
| From 1 to 9 | Idiopathic hirsutism. A medical examination is not required. It is recommended to avoid excessive sun exposure and tanning. |
| 10-16 | Transitional stage. Further observation and evaluation of body hair growth over a period of 3-6 months is required. If growth is noted, consult a doctor. |
| 17-25 | Hirsutism (symptom of diseases). It is highly recommended to conduct hormonal tests to identify the underlying cause of hirsutism and prescribe treatment. |
| 26-36 | Severe hirsutism (possible swelling). Visit your doctor immediately. Some tumors (for example, adrenal glands) can provoke a severe form of hirsutism. |
Excessive hair growth becomes a problem for many women. A change in appearance has a negative impact on the psycho-emotional state and disrupts the usual way of life. After a thorough examination and identification of the cause, it turns out that hirsutism is to blame.
Hirsutism is a disease characterized by excess hair growth in women. With this disorder, hair growth on the face, chest, and abdomen, which is unusual for females, is observed. Excessive hair may also appear in the nipple area. All this negatively affects a woman’s psyche, often causing stress and anxiety.
It is worth distinguishing between two definitions: hirsutism and hypertrichosis. The latter refers to an increase in body hair volume. At the same time, they are located in the usual places: the armpits, the pubic area, the front of the legs. The appearance of male pattern hair is a sign of a disorder and requires additional examination of patients.
Initially, the signs of hirsutism are subtle. Many women do not attach importance to them, fighting “extra” hairs in various ways.
However, in the case of a severe disorder that leads to a change in appearance, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Among the possible signs accompanying hirsutism in women (photos of the manifestations of the disease are given below), experts highlight:
- Excessive hair growth on the chin, upper lip, abdomen, back, chest, buttocks and inner thighs.
- Body changes according to the male type - wide, massive shoulders, narrow pelvis.
- Changing the timbre of your voice.
The reasons for the development of pathology are different, so doctors often combine them into groups. The first includes factors associated with ovarian dysfunction. Hormonal imbalance provokes a malfunction of the endocrine system, including the ovaries.
Upon examination, it often turns out that hirsutism has developed due to progesterone. An increase in the concentration of this hormone leads to a decrease in the content of female hormones - estrogens - in the blood.
Improper functioning of the adrenal glands can also be considered as a cause of increased hair growth. Excessive production of steroid hormones by these glands leads to the formation of a male-type appearance. At the same time, there are also disturbances in the functioning of the pituitary gland, which begins to excessively produce cortisol, which is a steroid.
The next group of reasons is associated with a disorder in the genetic apparatus. It has been established that hirsutism is hereditary.
Taking this into account, we can say with a high degree of probability that the presence of pathology in parents or close relatives will lead to the development of hirsutism in children. There is no way to influence this.
Hirsutism - causes, diagnosis and solutions
Hirsutism is excessive growth of coarse pigmented hair in women on the face and body according to the male pattern.
The appearance of coarse shaft hair in certain areas - above the upper lip, chin (like a mustache and beard), on the back, abdomen, hips and other androgen-dependent areas that are highly sensitive to male sex hormones, causes cosmetic problems, accompanied by development in women psychological complexes. Hirsutism occurs in 5-10% of women of childbearing age. Its severity is sometimes so great that patients resort to mechanical removal of excess hair. Hirsutism is not a problem of an exclusively cosmetic nature; on the contrary, it is often a sign of serious diseases of the endocrine system, and therefore requires careful examination, monitoring and correction by a gynecologist and endocrinologist.
It is necessary to differentiate hirsutism from hypertrichosis, which develops against the background of a number of diseases (hypothyroidism, anorexia, reaction to taking a number of medications, etc.) and is characterized by total excess hair growth, not limited to androgen-dependent areas.
Difference between hirsutism and hypertrichosis of excess hair growth
The causes of hirsutism in women can be different, from predisposition to taking oral contraceptives or special medications. The main factors for the appearance of this disease can be divided into external and internal.
- External are the effects of medications. For example, oral contraceptives, which affect the production of antiandrogenic hormones, are “fire” contraceptives. This also includes various types of corticosteroids, fat burners, dietary supplements for building muscle mass;
- Internal. The organs that are responsible for the normal amount of androgens in the body are the adrenal glands. Accordingly, with any disruption of their work, the hormonal levels immediately change. Likewise, if testosterone is not normal, then the ovaries need to be checked. Their function is the production of hormones with antiandrogenic properties (estrogen and others).
There is another type of signs. This is an idiopathic syndrome. The signs of this type of hirsutism are similar to the previous ones, but the causes have not been studied. But doctors believe that this particular type of disease is the most insidious. There are no primary noticeable symptoms: the cycle is not disrupted, there are no signals of virilization. This makes it difficult to detect in its early stages and ensure effective treatment.
HIRSUTISM: SYMPTOMS
The main symptom of hirsutism in women is the growth of unwanted hair on the face, chest, and back. This thick, dark hair is different from the normal, fine hair that is normally found on any healthy woman's body.
Other signs of hirsutism may include:
- acne, pimples,
- menstrual irregularities,
- the girl has a rough voice,
- muscle or weight gain,
- reduction in breast size.
Excess hair on a woman's face and/or body not only spoils her appearance, but is often a symptom of a serious disorder. There are several main causes of hirsutism.
Heredity plays an important role, and hirsutism often becomes a “family disease” that is inherited.
Ethnicity
Women of Middle Eastern, South Asian and Mediterranean origin are most likely to suffer from increased hairiness. This condition can be considered normal.
High levels of male hormones (androgens) lead not only to male pattern baldness, but also to hirsutism.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
PCOS occurs when there is an imbalance of hormones in a woman's body and causes the formation of cysts in the ovaries, as well as other symptoms.
A disorder in which the production of the stress hormone cortisol increases, which affects the entire hormonal balance of a woman.
Neoplasms of the ovaries, adrenal glands or brain disrupt the proper production of hormones and can lead to polycystic disease, hyperprolactinemia and other endocrine disorders.
Taking certain medications affects hair growth and can provoke symptoms of hirsutism. Such medications include hormones, anabolic steroids, drugs for the treatment of endometriosis, Minoxidil (which can lead to hypertrichosis), and hormonal allergy medications.
In some women, the hair follicles on the skin of the body are overly sensitive to even normal levels of male hormones. This provokes increased hairiness without any hormonal disturbances.
When is hirsutism diagnosed?
To find out the cause of increased hair growth, you need to consult an endocrinologist or gynecologist-endocrinologist. He will prescribe an ultrasound of the thyroid gland and ovaries, blood tests for insulin, testosterone and other sex hormones. The specialist will also conduct an external visual examination and assessment using the Ferriman-Gallwey scale.
Sometimes a woman cannot be diagnosed with any health problems. In this case, the cause of excessive hair growth on the body and face remains unclear, and the condition itself is classified as idiopathic hirsutism.
Is it possible to prevent or avoid the development of hirsutism?
There is no prevention. You cannot change genetics and congenital predisposition. If hirsutism is caused by heredity, it cannot be cured. However, you can try to avoid certain conditions that lead to increased hair growth in women (such as obesity and insulin resistance), and not unnecessarily take medications that lead to increased hair growth.
The main methods of treating hirsutism include medications (primarily antiandrogens for elevated male hormones), removal of unwanted hair by various methods for a short or long term, means to slow down its growth, as well as natural herbal supplements, which in some cases can help.
The most common drugs in this group are spironolactone and finasteride. They block the production of male hormones, which reduces the amount of new hair on the body. However, they will not get rid of the hair that is already there. The effect of taking antiandrogens becomes noticeable after an average of 3–6 months.
Birth control pills
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7-oeAOzJCdQ
Oral contraceptives (OCs, COCs) containing cyproterone acetate (for example, Diane-35) also suppress the growth of unwanted hair and can be prescribed as a treatment for hirsutism.
If a woman is diagnosed with insulin resistance, which provokes PCOS and hirsutism, she may be prescribed a drug with metformin (Siofor or Glucophage). With a decrease in insulin, testosterone will decrease, and along with it, excessive hairiness will go away.
For problems with the adrenal glands, treatment with glucocorticoid drugs (synthetic steroids) is prescribed.
Products to slow hair growth
The most popular prescription creams Vaniqa and Eflora, which slow down hair growth, contain the substance eflornithine. It is used on small areas of the face. The effect becomes noticeable after 4–8 weeks of use. Side effects include irritation, rash, and burning.
In combination with taking medications, it is recommended to remove unwanted hair using short-term or longer-term methods, which include:
- shaving,
- wax,
- plucking,
- hair lightening,
- depilatory creams,
- sugaring,
- epilators,
- electrolysis,
- photoepilation,
- laser hair removal.
Treating hirsutism with home remedies
Some vitamins and herbal extracts can replace medications for mild hirsutism and reduce symptoms. First of all, such natural and safe remedies that have proven their effectiveness include:
- inositol is a pseudovitamin that reduces testosterone by lowering elevated insulin;
- flax - regular consumption of 40 g of flax seed for at least 3-4 months reduces the male hormone testosterone;
- mint - drinking mint tea 2 times a day for a month reduces testosterone;
- cinnamon - like inositol, this remedy can replace metformin for insulin resistance.
In addition to these methods, women who suffer from hirsutism due to obesity and insulin insensitivity can help reduce the growth of unwanted body hair with proper nutrition, exercise and weight loss.
Hirsutism in women can occur due to various reasons. Among them:
- proliferation of connective tissue in the ovaries (Frenkel syndrome);
- hypofunction of the thyroid gland;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- hypercortisolism syndrome;
- side effects of medications;
- tumors of the endocrine glands (adrenal glands, ovaries, pituitary gland);
- idiopathic hirsutism.
The incidence of excess hair growth in women is up to 10%.
With hirsutism, male pattern hair growth occurs. What does this mean? If you compare a man and a woman, you will notice that representatives of the stronger half have a greater percentage of muscle mass, a rough voice and pronounced hair growth.
These features are associated with the influence of the male sex hormone. The action of testosterone leads to the appearance of hair on the face, body, arms and legs.
For a man, this state is natural. Different types of hair grow on the body, each of them has its own localization and time of appearance.
Long hair is localized on the head, in the axillary regions, on the genitals, and in men, also on the chin.
Bristly hairs form the eyebrows and eyelashes. They are hard and pigmented.
Vellus hair. Soft, short, colorless. They appear in the baby's womb, cover the entire body and after birth begin to be replaced by intermediate hairs. This species is long and pigmented.
In adults, the intermediate cover is replaced by the appearance of darker and denser vegetation on the body. This is the so-called terminal hair.
Testosterone in women is produced by the adrenal cortex and ovaries.
Normally, it does not have a strong effect on overall hormonal levels and appearance due to its low content in the blood.
When the functioning of the endocrine glands changes, the balance of hormones is disrupted. Thus, an increase in the activity of the pituitary gland leads to the production of large amounts of adrenocorticotropic (ACTH) and gonatotropic hormones.
ACTH stimulates the production of testosterone by the adrenal glands, and gonadotropic hormone stimulates the secretion of sex hormones by the ovaries.
Increased testosterone affects the bulbs in androgen-sensitive areas. This leads to the growth of terminal and long hair. This is how excess male-type hair growth occurs in women.
Hirsutism before puberty and in adolescents is extremely rare. Typically, hairiness in girls is associated with congenital pathology of the gonads.
We recommend you find out: How dangerous is hypercortisolism syndrome, how to diagnose and treat it?
In some cases, puberty is accompanied by the appearance of polycystic ovaries.
The appearance of vegetation in unexpected places is accompanied by acne, weight gain and causes significant psychological problems.
Teenagers may not pay attention to the irregularity of menstruation, since their appearance worries them more than the development of reproductive function.
In some cases, increased hair growth is the “calling card” of women in a family. In this case, they talk about hereditary (or familial) hirsutism.
Most often this occurs in Mediterranean and Eastern women. Then they talk about excessive hairiness as a variant of the norm.
The problem is purely cosmetic in nature, so drug correction is not required.
Idiopathic
Causes and mechanism of development of hirsutism
There are 3 types of hair:
1. Original fluff
- thin, delicate hairs on the body that appear and disappear during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus. They can only be seen in newborns born prematurely.
2. Vellus hair
- thin blond hair, the length of which does not exceed one or two centimeters.
3. Terminal hair
- hard shaft hair with pronounced pigmentation. Short, coarse hair forms eyelashes and eyebrows, and long hair grows on the head, in the armpits and external genitalia, and in men also on the face, chin, back, and abdomen.
Vellus hair is transformed into shaft hair due to the influence of male sex hormones. In girls and adult women, androgen-dependent hair growth in the pubic and armpit areas is considered natural. Hair growth on the legs and forearms is not associated with the influence of androgens. The quantity and quality of hair on a woman’s body depends on a number of factors, such as ethnicity, levels of sex hormones, and the degree of skin resistance to androgens.
Being the direct precursor of estrogens - female sex hormones, androgens in the female body are produced in the ovaries and adrenal glands, and determine the level of development of sexual desire, hair growth of the external genitalia, muscle mass, bone growth in adolescence and the closure of growth zones. In order for the ovaries to function normally, the level of androgens plays a very important role.
Peripheral tissues are influenced by testosterone and dihydrotestosterone. It is these hormones that promote the growth of coarse pigmented hair. Androgens, in turn, lengthen the activity phase of the hair follicle, increase its size and hair diameter, and also increase the production of secretion by the sebaceous glands of the scalp and face. As a result of this influence of androgens, zonal changes in hair growth are observed, namely, hair falls out from the scalp, and in androgen-dependent areas of the body, their number increases sharply.
Increased androgen production
may be observed with:
— functional disorders of the female reproductive glands
- polycystic ovary syndrome, tumor processes in the ovaries, amenorrhea of hypothalamic nature, etc. In this case, there is a disruption in the frequency of menstrual flow, infertility and enlarged ovaries. This is the most common cause of hirsutism;
— functional disorders of the adrenal glands
as a result of congenital or acquired pathology of the cortex, or as a result of an adrenal tumor;
— functional disorders of the pituitary function
, which is observed in acromegaly, prolactinoma, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome.
Hyperandrogenism in women can develop as a result of taking a certain group of medications (corticosteroids, anabolics, interferon, streptomycin, androgens, etc.)
Hirsutism can also be hereditary, and it is more often detected in representatives of the Mediterranean and Caucasian ethnic groups, and less often in Asian and European women.
If the cause of hirsutism is not identified, they speak of idiopathic androgen excess syndrome
, which is characterized by increased sensitivity of skin and hair follicle receptors to it. This form of hirsutism is also one of the most common, occurring in a quarter of all hirsutism presentations. At the same time, the ovulatory function does not suffer, the menstrual cycle and reproductive function are preserved.
Hirsutism in adolescents
Hirsutism in girls can appear as early as age six (often due to an early increase in ovarian volume). You should know that the appearance of body hair in maturing girls and boys is a natural process that gives no reason to suspect the development of hypertrichosis or hirsutism. However, you need to control the situation and immediately contact an endocrinologist if the girl has a “moustache” above her upper lip, and also has coarse dark hairs around the nipple and on her stomach (along the white line). Unlike girls, boys do not suffer from hirsutism.
Hirsutism in women - causes of excess hair
Hirsutism is mainly caused by the following reasons:
- Cushing's syndrome;
- adrenal pathology;
- androstendinoma (adrenal tumor);
- congenital adrenal hyperplasia;
- ovarian pathology (polycystic);
- taking hormonal drugs (anabolic steroids, COCs, androgens);
- familial hirsutism (not a cause for concern and occurs only as a genetic feature, often found in representatives of certain nationalities);
- idiopathic hirsutism (also does not have an organic basis, it occurs due to increased sensitivity of the hair follicles to the normal content of androgens or due to the hyperactivity of a number of enzymes).
Treatment methods for hirsutism
If a woman is overweight, her doctor will likely suggest losing it first, since obesity affects how the body produces hormones. Maintaining a healthy body weight can bring androgen levels back to normal without the use of medications.
However, a girl may need medical treatment if excessive hair growth is a symptom of PCOS or adrenal disease. Birth control pills and anti-androgen medications can help balance hormonal levels.
- Antiandrogen drugs
Antiandrogens can block androgen receptors and reduce the production of male hormones from the adrenal glands and ovaries. The most commonly used drugs that block the effect of testosterone on hair follicles are Spironolactone and Finasteride (blocks 5-alpha reductase).
- Combined contraceptive pills, oral contraceptives
Pills (OCs) that contain estrogen and progesterone can help reduce cysts that occur due to PCOS. Estrogen can also reduce the amount of excess hair. These drugs are prescribed as long-term therapy for hirsutism. Improvements occur no earlier than three to six months.
Vaniqa® (Vanica, eflornithine) is used to reduce excess facial hair in women. It is applied 2 times a day and works by slowing down the growth of hair follicles and increasing the intervals between hair removal treatments. Vaniqa cream can be combined with other medications. Typically, facial hair growth in girls slows down after 1–2 months. Side effects of eflornithine include skin rash and irritation.
Hair removal is a non-medical way to deal with unwanted hair. These are the same methods that many women use to remove hair from their legs, underarms, and bikini area.
- Waxing, shaving and depilatories
Removing excess hair with wax, using depilatory creams, razors or sugaring is an effective, accessible and inexpensive method. These products are easy to use, the results are visible immediately, but they don’t last long. In addition, girls with hirsutism tend to have unwanted hair that is thick and coarse. Because of this, after removal the skin becomes very sensitive and susceptible to irritation and ingrown hairs.
Laser hair removal occurs due to damage to the follicles by light rays. Damaged hair follicles cannot produce hair, and the hair that is already present falls out. When completing the full course and proper treatment, laser hair removal can provide a stable positive result.
This is hair removal using electric current. He treats each hair follicle individually, so sessions may take longer. Like laser hair removal, electrolysis is an expensive, time-consuming procedure that requires multiple sessions to achieve the desired results. Some women find these procedures uncomfortable or painful.
Treatment of increased facial and body hair in girls is a long-term task. Most women diagnosed with hormonal imbalance respond well to therapy, but hair may resume growth if hormones return to baseline levels and become abnormal after treatment is stopped.
Depending on the underlying cause and choice of therapy, treatment for hirsutism can be lifelong. Laser hair removal or electrolysis can provide more permanent results than shaving, waxing, sugaring or depilatories. If the cause of increased hairiness is PCOS or problems with the adrenal glands, the girl may require lifelong treatment.
Taking care of your emotional state
Hair growth associated with hirsutism can be a serious psychological challenge for some women. If you are worried about excessive hair growth, if you feel that your self-esteem is low and your sense of femininity is being lost, then in such a situation you need to seek help from a doctor. A specialist will not only recommend effective treatments that suit your lifestyle, but will also help you overcome the emotional problems that accompany hirsutism.
You can combat the psychological effects of hirsutism with the following tips.
- Physical activity. Physical activity helps combat hormonal imbalances, promote a healthy weight, and improve your chances of pregnancy. But in addition to all of the above, exercise also reduces symptoms of depression and anxiety. If a woman feels that she is in good physical shape and, observing herself in the mirror, notes her athletic figure, then her self-esteem will be at the appropriate level.
- Talk to someone. If you suffer from hirsutism, there is a high chance that someone in your family also has the condition. Talk to this woman. Find out how it counteracts hirsutism. Let her share with you tips on managing hair growth and dealing with the stress it causes. If there are no such women in your family, you can find them among your friends or talk about the problem with a psychologist. You should also share your feelings with your loved one. If your hair growth is forcing you to avoid physical contact, then it is important to communicate the reason why you are trying to distance yourself.
- Create a comfortable home environment. If you make your home a sanctuary, you will have at least one place where you won't have to worry about hirsutism. Try aromatherapy, abdominal massage with lavender and bergamot oils, regularly go to bed at the same time of day, stop watching TV and using electronic devices before bed, and keep your bedroom completely dark. You can also relax by taking warm baths, reading books, trying new recipes to cook, watching comedies, listening to your favorite music and chatting with friends on social networks.
- Manage depression naturally. To do this, spend time in nature, use essential oils of lavender and Roman chamomile for calm and good sleep. Additionally, consider taking the following supplements:
- St. John's wort;
- B-complex vitamins;
- probiotics;
- vitamin D3;
- fish oil.