The concept of a defect and its types
Papules appear due to a malfunction of the immune system
The process begins with clogging of the skin pores with sebum, which continues to flow and stretches them, promoting the formation of peculiar cysts. The process ends with their rupture, followed by penetration of the pore contents into the upper layer of the skin. The immune system receives a signal of a violation and reacts, resulting in papules appearing on the epidermis.
These formations can be inflammatory or non-inflammatory in nature.
The former are distinguished by a reddish tint and can dissolve on their own without leaving any traces.
The latter are characterized by excessive growth of the epidermis in the absence of an inflammatory process and require mandatory treatment.
In appearance and shape, papules are:
- oval;
- round;
- cone-shaped or miliary;
- flat or lenticular.
What does a papule look like?
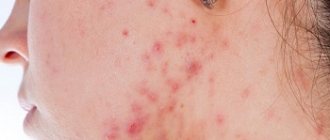
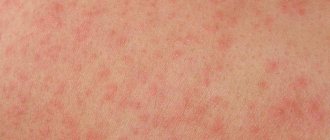
A papule is a type of pimple that looks a bit like little balls in the skin. They are dense nodules that may vary in color, size and depth of appearance. Red or pink papules are always accompanied by the formation of edema in the affected area of the skin and the addition of infection.
When pressing on the nodule it turns pale. If we compare this skin element with a pustule (vesicle), it does not have a characteristic white head. The latter is liquid pus that accumulates in the cavity of the vesicle. The process of formation of papules and pustules occurs in approximately the same way. However, in the first case, the activity of microorganisms in the skin leads to the formation of balls filled with pus. In the second, blockage of the sebaceous glands occurs with the accumulation of secretions in them. The progression of the inflammatory process leads to local edema and the appearance of a streakless formation.
Below are pictures to help you more clearly distinguish between papules and pustules. The photo shows the characteristic appearance of both skin elements. First, stripless nodules. Then characteristic formations with pus inside.
Causes of pathology
This skin condition is most often infectious in nature, provoked by the penetration of microbes and bacteria under the skin.
The disease begins as a result of exposure to the following factors:
- dysfunction of the sebaceous glands of the epidermis, occurring under unfavorable environmental conditions. Examples include environmental pollution and contact with hazardous toxic substances. Sometimes this condition can be caused by increased levels of cholesterol in cells;
- changes in the level of the body’s hormonal levels resulting from age-related changes in the body, under the influence of onset diseases or emotional instability;
- disruptions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract due to poor nutrition, existing pathologies affecting metabolic processes in the body;
- a stressful lifestyle with frequent nervous shocks, mental overload, prolonged depression and constant stress.
It is very difficult for a person without medical education to distinguish papules from ordinary acne. It is imperative to contact a dermatologist, who will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe a drug treatment regimen to successfully get rid of the defect that has arisen. Self-treatment can significantly complicate and worsen the course of the disease!
Pustular eruptions
The appearance of pustules on the body can be caused by many factors. A pustular rash on the face is most often a manifestation of acne (acne) and occurs as a result of not too scrupulous adherence to personal hygiene rules. The following may contribute to the appearance of acne:
- Lack of habit of washing hands, constant touching of fingers to the skin.
- Increased sweating.
- Metabolic problems.
- Not a very healthy lifestyle.
- Stress.
- General decrease in immunity.
With the development of acne, comedones (blackheads), pustules and papules may simultaneously be present on the patient’s skin.
There are also a number of serious infectious diseases that are accompanied by the appearance of a pustular rash. If many elements of rashes occur, severe itching, fever, symptoms of intoxication and other alarming symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.
Diseases accompanied by the appearance of papules on the face
Such formations on the skin can serve as a factor accompanying the course of many diseases, namely:
- horny eczema, which occurs with the appearance of painful papules on the skin. This pathology usually occurs in people who are constantly in contact with chemically aggressive environments and can become chronic;
- amyloidosis, which is characterized by rashes concentrated near the mouth, eyes and in skin folds;
- syphilis associated with the formation of papules in the mouth and tonsils, causing severe pain in the throat with possible loss of voice. This type of formation is difficult to treat;
- psoriasis, characterized by the formation of a papular rash with white scales that easily separate from the surface and are most often located in the wrist area, on the backs of the feet, in the elbows and knee joints. If left untreated, they merge with each other, forming plaques that can cover the entire body;
- lichen spines, the development of which can be caused by a hereditary factor, vitamin deficiency, as well as a weakened immune system. This type of pathology is characterized by the appearance of small and rough papules when touched, having different shapes.
Pointed types of papules, constantly increasing in size, are considered the most dangerous, since they can degenerate into oncological tumors and become quite large tumors, so timely consultation with a dermatologist in this case is mandatory!
For each patient, the dermatologist prescribes his own treatment package depending on the stages of the papules.
Difference between papules and pustules
You can recognize the formations yourself by reading the list of their external manifestations. By contacting a specialist, you will be able to correctly identify the nature of the rash and assess your health status. The doctor determines the difference between a papule and a pustule by the location of the formations, signs of development, and appearance.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
To prescribe therapy, minimize the likelihood of worsening the situation due to self-medication, and prevent undesirable consequences, become familiar with the characteristic signs of nodules and the symptoms of pustules.
Appearance
The papule resembles a small round, oval or cone-shaped nodule with clear boundaries. The size of the defect, like pustules, varies from a few mm to 3 centimeters in diameter. The formations may rise above the skin or remain flat and inconspicuous. The attributes have a dense, elastic structure.
The color of the papules varies depending on the disease that caused it, and can range from pearly white to pronounced red. The main difference from a pustule is the absence of purulent contents. When you press on the formation, it turns pale, the manipulation does not cause pain. Sometimes swelling of the skin is observed, and when the attributes merge, plaques form.
Pustules are pimples ranging in size from a pin to a pea with a pronounced head with purulent contents, unlike papules. When the shell breaks through, the mass comes out, and the resulting wound becomes covered with a crust. If the formation is single, there are no associated ailments, the problem area of the skin is quickly restored. When multiple foci of inflammation are observed, the attributes can merge, leading to an extensive pathological process that provokes scarring on the skin.
Pustules and papules are often confused with vesicles - small bubbles with exudate.
Reasons for education
The appearance of pustules is promoted by unfavorable external and internal factors. They are often the result of blockage of the sebaceous ducts with the contents spreading under the skin. Papules are provoked by infectious diseases affecting the body (molluscum contagiosum, syphilis, herpes, HPV, phthiriasis).
With acne, pustules, vesicles, and comedones are found on the face.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of rashes. The development of skin nodules is influenced by unfavorable environmental factors and internal changes accompanied by infectious invasions. The main causes of damage to the epidermis by pustules and papules:
- The introduction of a bacterial pathogen through microtrauma from the use of contaminated razors, touching the skin with unwashed hands, and the use of other people's hygiene products.
- Excessive sweating, causing microscopic damage to the surface.
- Problems with metabolic processes can cause pustules. Disruption of the systems responsible for metabolism contributes to the development of papules.
- Hormonal imbalances that often affect women. The occurrence of acne is observed during menstruation, puberty in adolescents, pregnancy, when the body undergoes restructuring.
- Taking medications. Drugs that affect the functioning of the endocrine system can trigger the formation of pustules on the skin.
- Immune suppression. Diseases accompanied by a decrease in the body's defense mechanisms lead to the appearance of papules and activation of viral processes.
To determine the cause of the appearance of tumors, diagnostics are carried out at a medical center.
Localization
Papules can appear on any part of the skin, depending on the disease that caused the rash. Pustules appear on the face, trunk, and limbs.
When the body is affected by molluscum contagiosum, nodules cover the scalp, abdomen, limbs, and genitals. Pearlescent pimples are located around the head of the penis. Formations caused by syphilis affect the torso, anogenital area, and oral cavity. Wart formations, which are often confused with papules and pustules, appear on the backs of the palms and fingers.
Based on the severity of the damage to the epidermal layer, formations are divided into superficial and deep.
For pustules, the typical location is the skin where the hair is located. The follicles become a cavity for the accumulation of purulent mass; often abscesses form on the chin, forehead, neck, armpits, groin area, in place of the papule.
With pustular psoriasis, there are attributes on the heels and palms. Based on the depth of penetration into the skin, ulcers are divided into dermal and epidermal.
Signs
The occurrence of formations is accompanied by characteristic signs and symptoms that help to recognize the nature of the element and prescribe treatment for pustules or papules.
When nodules occur without an inflammatory process, the skin does not change its original appearance. An element of dense consistency is formed on the surface, hardly noticeable against the general background. Before a rash occurs, the epidermis acquires a red tint, becomes swollen, hot, causing itching. The presence of pain in the area affected by the papule depends on the disease that caused the appearance of the elements.
Pustules, like purulent formations, begin to develop with redness, thickening appears on the skin, accompanied by burning, itching, and swelling of the tissues. When the abscess matures, a white rod appears, tension in the skin in the area of the attribute, and discomfort are felt. Depending on the size and location, pain and symptoms of general intoxication may be present, in contrast to papular formations.
Treatment options
Only a doctor is able to prescribe competent and qualified treatment after conducting a comprehensive examination of the patient’s body and passing all the tests necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis. In some cases, it is possible to take scrapings from the surface of the papules for histological examination in the laboratory.
Treating only the external manifestations of the disease is not enough, since the disease can worsen and become chronic, which is especially difficult to eliminate.
Therapeutic methods for treating papules are selected strictly individually for each individual patient, depending on the cause of their occurrence, shape, depth, degree of growth and other factors.
For information: for minor rashes without the presence of a specific disease, the following are generally prescribed:
- local spot treatment of papules using special anti-inflammatory compounds;
- intravenous administration of medications;
- external treatment with antiseptic solutions, lotions, antibacterial creams;
- taking multivitamin preparations that increase the body's defenses.
Self-medication is dangerous for your health! Don’t take risks and immediately seek help from a specialist for an accurate diagnosis of the pathology!
Juvenile acne and other forms of acne
White and red papules appear in newborns in the first days of life as a reaction to the mother’s hormones remaining in the tiny body. This type of acne is called “infant acne” and does not require treatment.
The next stage of significant hormonal fluctuations is associated with puberty. In the body of a teenager, the gonads develop, and the ratio of steroid production characteristic of a man or woman is formed.
Papulopustular inflammatory acne is most common in the age group from 13 to 25 years, and in women over 30 years of age it occurs in the form of late acne. The appearance of acne in adults is associated with internal diseases, taking medications and dietary supplements, and poor-quality nutrition. Papules and pustules form at any age when exposed to chlorinated water, petroleum products or cosmetics.
Prevention measures
You can prevent the appearance of papules on the face with the following simple measures:
- frequent hand washing, especially after visiting public places;
- regular cleansing of the facial skin to remove contaminants, bacteria and fatty secretions accumulated on its surface, which can cause clogged pores;
- proper, nutritious, balanced nutrition with a sufficient supply of vitamins and microelements that increase the overall protection of the body;
- daily walks in the fresh air, strengthening the local immunity of the skin.
Do not neglect timely medical consultation and get better!
Description of acne without signs of inflammation
Comedones, as is known, occur due to blockage of the mouths of the hair follicles or the ducts of the sebaceous glands. This type of acne consists of thick sebum, dead cells and epithelial scales.
Differences between clean pores and clogged ones
If these congestions form on the outside of the pores, then open (black) comedones appear, often called blackheads. These pimples do not immediately turn black. When a blockage occurs, the sebaceous plug contains a clear or white fluid. Then the fat hardens and, turning into a lump, acquires a yellowish tint. Due to the fact that the pores are open, under the influence of oxygen, lumps of fat begin to oxidize, as a result of which they acquire a characteristic black color, which makes them look like dots. The size of black comedones varies around 0.1-2 mm. All blackheads have a central black dot, but their color can vary from light yellow to brown and dark gray. Often, open comedones do not cause any trouble. Meanwhile, the picture changes if an infection gets into the glands.
Blackheads – virtually every person encounters them
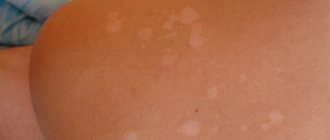
Closed comedones, also called whiteheads, whiteheads, wens and milia (whiteheads), form when oil becomes trapped internally at the bottom of the pores. In their structure, closed comedones resemble blood clots that do not reach the surface of the skin. In fact, they can be invisible to the eye and can only be felt by touch. Meanwhile, some whiteheads rise noticeably above the surface of the skin. Many people are familiar with such representatives of the type of closed comedones as millet. These pimples look like nodules that resemble millet grains, scientifically called milia.
Closed comedones are not always noticeable
Whiteheads most often form in the area of the cheeks, chin, forehead and cheekbones and are not particularly bothersome by their appearance - they do not hurt or become inflamed. Meanwhile, despite their relative harmlessness, closed comedones are still dangerous. The fact is that under the skin they tend to combine with neighboring inflammatory acne. As a result of such fusions, a large cavity is formed under the skin, which is gradually filled with pus. That is, in essence, a wen is a “time bomb”, which, when given a push, worsens the situation significantly.
We all remember the temporary problems of adolescence associated with the appearance of acne.