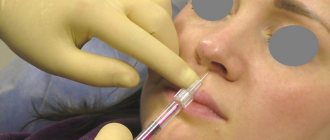
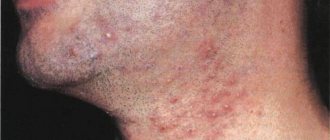
A lump appeared under the skin on the nose
It must be said right away that cones are different. They differ in color, size, location. Most often, small, painless, flesh-colored bumps occur. They are located on any part of the nose and can go away on their own, without treatment. Another category of neoplasms are painful flesh-colored or pink lumps, most often with purulent contents inside.
Such formations are dangerous, since the nose is equipped with a branched capillary network, and the infection can enter the bloodstream. There are neoplasms that appear due to overgrown bone or cartilage tissue. These bumps are shapeless, hard, and sometimes painful to the touch. A bump may appear on the bridge of the nose near the piercing.
Usually such formations go away on their own within a couple of months. They do not hurt, do not bleed, and they do not contain purulent contents. Separately, it is necessary to mention the formations that appear inside the nose. They are painful and sometimes bleed. Such formations look like bluish or red seals with a pronounced capillary network.
Wart on the nose - how to get rid of a lump
Lumps and bumps that cause discomfort and redness of the skin are the result of an infection entering the body. The main reasons causing the formation of compactions and tubercles include the following diseases:
- Lipoma is characterized by the presence of a soft tubercle with clear boundaries, without discoloration.
- Hygroma is an accumulation of fluid in the form of a lump that does not cause discomfort. The tubercle does not cause harm to health, but causes cosmetic inconvenience.
- Cellulitis is fatty tissue located under the surface of the epithelium that becomes inflamed with the formation of pus.
- Atheroma is a ball filled with sebum, caused by a blockage of the gland duct.
- Warts and papillomas come in different shapes and colors. Caused by viruses, injuries, hormonal disorders.
- Inflammation occurs due to the staphylococcus bacteria, causing the formation of bumps and pain.
- Erysipelas spreads rapidly and covers large areas.
- A furuncle is a ball formed when the sebaceous glands and hair follicles are damaged.
- Malignant tumors are characterized by the identification of compaction, which gradually increases in size.
In real life, warts on the nose cause trouble for many people, regardless of their nature.
Viral tumors are localized on the skin of the nose or the mucous membrane lining the inside of the nose. Three types of warts may appear on the nose:
- Ordinary (has the shape of a nodule);
- Flat (rises flat above the surface of the skin of the nose);
- Thread-like (the growths have the appearance of a thread or, in case of multiple accumulations, they are compared to the comb of a rooster).
Warts on the nose rarely cause pain in patients; the main complaint is a cosmetic defect and the inconvenience of facial care.
Reasons for appearance
The causative agent that causes the appearance of warts on the nose is the human papillomavirus, transmitted by contact and through household objects. This virus has many varieties, some appear in the form of papillomas of different structures and in different parts of the human body.
More than two-thirds of the population is infected with the human papillomavirus, but not everyone is aware of this, since concomitant factors are necessary for the symptoms of the disease to occur.
The main reason for the activation of HPV is a decrease in general or local immunity. This occurs during adolescence, against the background of significant hormonal changes (pregnancy), after infectious diseases, or in the presence of severe chronic diseases (metabolic disorders, AIDS).
The face is a vulnerable place - it is exposed to atmospheric phenomena (sun, frost, wind); high-quality cosmetics are not always used to care for facial skin.
These factors reduce local protective properties, provoking the occurrence of neoplasms in people infected with the human papillomavirus.
Advice from E. Malysheva...
You don’t need pills to make warts and papillomas disappear from the roots! Write down a simple but effective recipe that will help you get rid of such an unpleasant diagnosis once and for all. You just need to rub in the usual...
Which doctor should I contact?
If a ball, lump, or bump appears on the skin that does not go away and causes discomfort, you should consult a doctor:
- A dermatologist will help you get rid of a wart or papilloma;
- The surgeon will remove the abscess or benign neoplasm;
- The oncologist will identify the cancer manifestation.
The absence of bumps and bumps on the skin depends on the quality of body care procedures. You can reduce the likelihood of unpleasant formations on the surface of the skin by quitting smoking, drinking coffee and alcoholic beverages, and carefully performing hygiene procedures.
Neoplasms are treated by different specialists. Before contacting a specialist doctor, it is better to visit a therapist. This doctor will tell you who is best to contact. Most often, neoplasms on the face are treated by maxillofacial surgeons. But not all localities have specialized branches. Therefore, such patients can be treated by surgeons, otorhinolaryngologists, oncologists, and orthopedists.
What can't you do?
Many people believe that a lump can be treated at home. Some people are so carried away by the process that they have to correct the consequences in a hospital setting. Traditional healers offer many, according to them, effective recipes. Some of them are simply terrifying. So, what not to do:
- Heat. It is strictly forbidden to heat any new growths. If this is a purulent focus, then bacteria in warm conditions begin to multiply at double speed. If it turns out to be a malignant tumor, then the cancer cells will divide rapidly. In both cases, this will create a great threat to health and life.
- Squeeze. The nasolabial triangle contains a large number of blood vessels. If pus enters the bloodstream, the infection quickly reaches the brain. Inflammation of brain tissue may occur.
- Open at home (this happens too!!). Some “craftsmen” take it upon themselves to open the tumor at home. This can result in bleeding, blood poisoning, and damage to nearby tissues. It’s even scary to imagine what else could happen.
https://www..com/watch?v=K84x0erBgZs
A lump on the nose is not a case where the development of the disease can be overlooked. Therefore, when the first signs appear, it is better to visit a doctor.
Source: https://makeuphit.ru/shishka-nosu-cheloveka/
Prognosis and possible complications
The most dangerous complication of the progression of growths in the nose is the occurrence of a malignant tumor.
However, other problems are possible:
Nosebleed
- Brain injury and hearing and vision impairment as a result;
- Constant and heavy nosebleeds;
- Recurrences after surgical removal;
- Defects, atrophy and deformation of tissues of cartilage and nasal mucosa (including after treatment).
In such cases, treatment can be significantly complicated. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor promptly if you experience nasal discomfort.
In these situations, as a rule, treatment is accompanied by favorable prognosis and in most cases the patient makes a complete recovery.
Lump on the nose
A bump on the nose is a neoplasm that greatly impairs the aesthetic appearance and can cause discomfort and inconvenience in everyday life. If the bump on the nose is large enough, surgical removal is usually recommended .
Red bumps on the nose and their causes
Important! Most often, these formations are painless and are caused by various reasons.
Lipoma
Near the nose there is a large accumulation of sebaceous glands, and a so-called lipoma may appear there - this is a benign neoplasm, which is a dense accumulation of fatty tissue under the skin . The color of the skin does not change, there is no pain .
Keratosis, warts or papillomas
Most often, solid neoplasms are the above-mentioned keratosis, warts or papillomas.
The latter tend to grow strongly and are very unpleasant in that, being viral in nature , after removal they can appear again in the same or another place.
Note! The human papillomavirus is contagious. Infection can occur through microcracks in the skin, through contact and household contact.
Cyst
The intradermal cyst is dense to the touch . It can become inflamed with purulent contents coming out.
Other diseases that cause a bump on the nose
- Chondroma - affects the nasal septum, then gradually grows into the soft tissues, making breathing difficult.
- Congenital bump on the nose - nasal glioma . It is benign, usually does not cause discomfort, but sometimes, due to an unfortunate location, it can interfere with breathing.
- Fibroma is a tumor of the connective tissue of the nose. Soft to the touch, sometimes has a leg, benign. It does not cause discomfort, and if it grows, it grows very slowly, so it is quite safe.
- Nevi, or moles , are flat formations, usually congenital, containing a large amount of melanin pigment.
- Melanoma is a malignant tumor characterized by jagged edges and uneven color. It can spread very aggressively throughout the skin and quickly metastasize, so it requires immediate removal.
- Basalioma is a malignant formation that initially looks like an ulcer or a small wound-tumor, then develops into a mushroom-shaped growth. It is formed from cells of the basal layer of the epidermis and, as a rule, affects the wings of the nose. This type of cancer is not very aggressive, but still requires immediate treatment.
- Actinic keratoma is similar to ordinary keratosis, but appears exclusively in older people. It has an unpleasant appearance and dark color. If compactions appear in the keratome, it means that it is degenerating into malignant and requires immediate removal.
What to do
When a lump appears on the nose, it is necessary to undergo a full diagnosis: computed tomography, x-ray, rhinoscopy, pharyngoscopy.
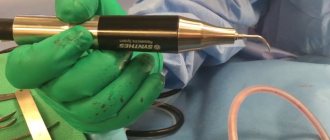
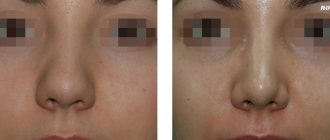
Photo 2: Removal is performed after diagnosis. It can be surgical, endoscopic, using laser or radiation therapy, as well as chemotherapy if the formation is malignant. Source: flickr (Gevorg Yeghiazaryan).
Homeopathic remedies for bumps on the nose
DrugsPurpose
| Thuja | For warts, polyps of various types, angiomas, lipomas and other types of growths. |
| Arnica | For bumps that appear as a result of injuries. |
| Argentum Nitricum | For warts located on the nasal mucosa. |
| Causticum | Treats large soft warts and bumps that often bleed. |
| Malavit | For all types of warts. |
| Barium carbonicum | In the treatment of wen on the nose (lipomas), atheromas. |
| Acidum Nitricum | For soft warts that have a stalk. |
| Arsenicum album | For senile warts that dry out, accompanied by itching and burning. |
| Silicea | For fibromas, hemangiomas. |
Source: https://www.gomeo-patiya.ru/simptomy/shishka-na-nosu-295.html
Atheroma
Atheroma is often confused with lipoma, also called a wen. In fact, it is a cyst, that is, a stretched sebaceous gland in which the excretory duct is blocked. The contents of the atheroma, sebum, gradually accumulates, stretching the capsule of the gland.
To the touch it is a dense, round formation with clear boundaries. The skin over the atheroma cannot be folded; sometimes the surface of the skin takes on a bluish color and you can see a point on it - a blocked duct. Atheroma can become inflamed and fester. If necessary, it can be removed by a surgeon.
Nasal basalioma: photo, features, appearance, similar skin diseases
Basalioma of the skin of the nose is the most common; this page presents its characteristic features; main types, their photos; treatment methods; externally similar skin diseases, their photos.
Features of nasal basal cell carcinoma
The nose is the most prominent part of the face; visible damage (including basal cell carcinoma) on the skin of the nose is often noticed by patients themselves at the very beginning of the disease. Due to its protruding position, it is most exposed to sunlight. For this reason, skin basalioma most often affects the nose.
The skin in the area of the cartilaginous part of the nose (tip and wings) is very thin and contains virtually no fatty tissue underneath. As a result, nasal basal cell cartilage penetrates relatively quickly into the cartilage; getting it out of the cartilage is only possible with great difficulty and is associated with disfiguring surgical interventions (see photo below).
Basalioma of the nose on its lateral surface at the border with the inner edge of the eye is also very dangerous - here there is a risk of penetration into the periorbital tissue.
If you have already had basal cell carcinoma before, the nose requires the greatest protection and attention, because after treatment, 30-40% will develop the disease again, but in a different place.
Tanning is contraindicated, and in the summer, in addition to a hat, a good sunscreen is needed.
Basalioma of the nose. Main types, their photos
Regarding the main types of nasal basal cell carcinoma, one should first of all expect nodular and ulcerative forms, since the anatomical features of the skin predispose them to them. The growth rate is relatively faster than other areas. The photo shows nasal basal cell carcinoma of the main varieties.
Nasal basalioma of the nodular type with the earliest manifestations. A small pearly plaque (marked with a large arrow) on the wing of the nose and an even smaller one (marked with a small arrow) in the nasolabial fold. These are very early stages of basal cell carcinoma. The gray arrow marks the intradermal nevus.
Further stage of development of nodular basal cell carcinoma. A single shiny nodule of nasal wing basal cell carcinoma with a large number of dilated vessels.
The photo shows a nodular basal cell carcinoma of the nose. A large, hard reddish shiny nodule with small ulcerations on the skin of the wing of the nose.
In the photo, pigmented basalioma of the nose on the left is of the pigmented variety; an ulcer appears in the central part.
Ulcerative basalioma of the nose under a scab. Periodically, part of the scab may come off, and the tumor then begins to bleed. In some people, the skin is completely covered with keratomas, which is why a basal cell carcinoma of this type may be perceived for some time as just another keratoma.
The photo shows a nasal basalioma of the ulcerative variety. A large round ulcer on the tip of the nose with ridge-like borders.
Large nasal basal cell carcinoma extending to the inner corner of the eye. Treatment of such a disease is not an easy task; usually a flap of skin is taken from another area and transplanted instead of the removed tissue; cryodestruction is also possible.
The photo shows a basal cell carcinoma of the nose in the dorsal and lateral areas. Closer to the center of the nose, basalioma appears as a recessed area, resembles a scar, and belongs to the sclerosing variety. Along the edge of the tumor on the right, basal cell carcinoma transforms into a nodule with ridge-like edges, taking on the appearance of a nodular variety.
Fibrosing basal cell carcinoma of the nose looks like scar plaques in the photo. To the touch it turned out that the tumor was spreading beyond the visible boundaries.
The photo shows the remaining healthy tissue after removal of nasal basal cell carcinoma. The disease was treated surgically with step-by-step examination under a microscope (Mohs method). The study showed that the tumor penetrates very deeply, even growing into the cartilage.
As for the treatment of nasal basal cell carcinoma, the differences relate mainly to the execution of the surgical method; other treatment methods do not undergo any changes, you will read about them in other sections of the site. In general, they ensure that the scar after removal of nasal basal cell carcinoma runs along natural folds and irregularities, becoming less noticeable.
Repositionable nasal flap. Wound after removal of basal cell carcinoma of the lateral surface of the nose with outlines of the flap moving along the wing.
Nasal basal cell carcinoma removed. To move the flap, the skin is peeled away from the underlying fatty tissue and cartilage. Final closure of the postoperative wound after treatment.
Rotational spiral flap. A small round wound remains after removal of nasal basal cell carcinoma.
In the photo, the basal cell carcinoma of the nasal wing has been removed and additional incisions have been made. The edges of the wound are connected in a Z shape.
This is what the scar looks like 3 months after surgical treatment of nasal basal cell carcinoma. The scar runs along the fold of the wing.
The following are photos of externally similar skin diseases characteristic of the nose area.
Rhinophyma, differences from nasal basal cell carcinoma
Rhinophyma is a slow-growing, often disfiguring tumor of the nose that most often affects men between the ages of fifty and seventy. It is characterized by a gradual increase in the size of the nose in the area of the wings and tip, then can move to other areas of the nose and cheek. Rhinophyma is most often referred to as stage 4 of the development of rosacea (rosacea).
This means that severe manifestations of rosacea will sooner or later lead to rhinophyma. The presence of rosacea makes it difficult to diagnose when there is a nasal basal cell carcinoma, because rosacea can be in close proximity to the basal cell carcinoma, and the basal cell carcinoma itself can be perceived as part of the inflamed skin of the nose.
The cause of rhinophyma is the excessive development of the sebaceous glands, the appearance of microbes that feed on sebaceous secretions, the development of chronic inflammation in the area of the sebaceous glands, and the proliferation of scar tissue and blood vessels in the area of chronic inflammation. In the past, rhinophyma was often associated with alcoholism, but new studies have not confirmed the connection.
It differs from basal cell carcinoma in its more extensive distribution, the presence of rosacea, and the absence of ridge-like edges. Rhinophyma is treated surgically
Rhinophyma. It can be mistaken for basalioma only in the initial stage. A mass of tissue on the surface of the nose with a lobular structure, with superficial dilatation of skin vessels. In this photo, the lesion extends to the cheeks; however, the swelling may be limited solely to the nose.
Kaposi's sarcoma presents as multiple pink-violet rashes. Unlike cutaneous basal cell carcinoma, Kaposi's sarcoma can occur anywhere on the skin or mucous membranes of the body, including internal organs.
Most often the lower extremities (especially the soles of the feet), head, and neck are affected. Kaposi's sarcoma usually occurs in people with HIV infection and is associated with immunodeficiency. Kaposi's sarcoma is treated with radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
The multiplicity of lesions, the connection with HIV infection, the absence of ridge-like edges are the main differences from skin basal cell carcinoma of the nose.
Kaposi's sarcoma. A characteristic purple plaque on the wings and tip of the nose in an HIV-positive patient. Nasal basalioma will differ in its edges; you should also pay attention to the edges of the tumor and the multiplicity of lesions in Kaposi's sarcoma.
In common parlance, spider veins. It is represented by a central arteriole that forms a nodule and capillaries diverging from the arteriole. Unlike nasal basal cell carcinoma, pressure on the spider vein causes it to turn pale. Pallor quickly disappears if you stop pressing, due to filling from the central arteriole.
Spider veins most often affect the face and upper body, often appear in young people and disappear on their own. If there is liver disease, then spider-like hemangiomas are multiple.
Unlike basalioma, they do not have the characteristic raised edges and waxy sheen; in older people they are often multiple.
Nevus Araneus (spider hemangioma, spider vein). At the center of the red lesion is a small (1 mm) red papule surrounded by a radiating network of blood vessels. Nasal basalioma will be distinguished by a raised edge, as well as a waxy sheen in the area of dilated vessels.
Spider vein on the lateral surface of the nose. In this case, there is a denser vascular network around the central papule; individual vessels are difficult to distinguish. All together makes the disease look like a small basal cell carcinoma.
Eosinophilic granulomas arise from chronic inflammation of the skin on the nose, chin, forehead, temples and cheeks. They appear as round or oval brown-red spots and raised plaques with enlarged pores, which makes them look like the peel of an orange.
Allergies and infection with worms contribute to the appearance of such plaques. Eosinophilic granuloma is treated with glucocorticoid injections.
Basalioma of the skin of the nose differs primarily in that it does not have enlarged pores; you can also rely on the classic signs of basalioma (raised edges and dilated vessels).
The photo shows an eosinophilic granuloma of the skin of the nose. An elevated red-brown nodule, similar to nasal basal cell carcinoma, but with enlarged pores and no dilated vessels.
Fibrous papules develop at a young age on the nose, less often elsewhere on the face. This dome-shaped, shiny lesion is 2-6 mm in diameter, sometimes has hair in the center, and is most often found on the wings and tip of the nose.
Although fibrous papules are very similar to flesh-colored intradermal nevi, they are denser to the touch. They are a type of angiofibroma. Fibrous papules are harmless, but do not disappear throughout life.
Surgical treatment is indicated solely for cosmetic purposes, since such tumors are not dangerous to health. Nasal basal cell carcinoma differs from fibrous papule in having raised edges and a more fragile surface that bleeds when touched.
Sometimes a biopsy may be necessary if the fibrous papule has the “pearly” appearance characteristic of nasal basal cell carcinoma.
A fibrous nasal papule is a benign tumor that is very firm to the touch. Nasal basal cell carcinoma is distinguished by raised edges and a more fragile surface that bleeds on contact.
Source: https://skinoncology.ru/skin-basalioma/nose-basalioma
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis is based on a cytological and histological study of material taken in the initial stages of the disease by scraping or biopsy (cutting out a piece of tissue) from the tumor area. If the basal cell carcinoma has already turned into an ulcerative form, then a smear-imprint is taken from the bottom of the ulcer or erosion for examination.
Dermatoscopy using a special device, a dermatoscope, is highly informative, allowing one to examine the tumor in great detail. It is especially necessary in cases where it is necessary to differentiate basal cell carcinoma from melanoma.
To make a diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma, the doctor may also examine the patient's skin under a Wood's lamp. For this procedure, a special cream is applied to the affected area, then an examination is performed in a dark room.
Photo gallery: devices for diagnosing basal cell carcinomas
Dermatoscope is a necessary device for diagnosing basal cell carcinoma.
Wood's lamp - a device for diagnosing skin diseases
In the light of a Wood's lamp, diseased areas of the skin change color
Ultrasound examination is also very important for diagnosis, as it allows one to accurately determine the boundaries, size and depth of growth of the tumor. This is very important for choosing a treatment method and deciding on the extent of surgical intervention.
The final diagnosis can be made only after a thorough study of the data obtained from all the studies described above. As a rule, diagnosing basal cell carcinoma of the nasal skin does not cause difficulties for a qualified specialist.
The main difference between basal cell carcinoma and other malignant skin processes is its slow growth and the almost complete absence of distant metastases.
Lump in the nose
Often a person is bothered by a bump on the nose, which is characterized by a benign formation that appears on the skin.
In most cases, the tumor does not change structurally, but is capable of growing rapidly. Bumps can be observed on the nose or inside.
It is impossible to get rid of the problem on your own; you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Self-medication threatens with dangerous consequences and suppuration of the lump.
A lump growing on the nose brings discomfort and hassle in choosing an effective method for its elimination.
Types of bumps on the nose
When a lump appears on the bridge of the nose, on top or inside the nasal cavity, you should seek medical help and determine the type of formation.
All bumps that appear in the nose are divided into malignant and benign formations. The latter are characterized by a painless course, during which benign cells grow.
Typically, this process occurs inside the nose and does not affect other areas. There are the following types of nasal cones:
- Papilloma is extremely rare. It can occur in men and women over 50 years of age.
- Angiogranuloma appears on the nasal septum and often provokes bleeding. This pathology is often observed in pregnant or breastfeeding women.
- Vascular tumors located inside the nose. These include hemangioma, lymphangioma and other formations. They are characterized by slow development in the area of the lower nasal concha or in the internal cavity.
- With chondromas, the nasal septum is damaged. The cone can grow to the orbit and maxillary sinuses.
- Osteomas damage bone tissue and progress slowly. They often form in the frontal sinuses and damage an area of the ethmoid bone or maxillary sinuses.
Bumps on the nose can occur for a number of reasons, including pathologies of internal organs.
You should take benign lumps seriously and remove them promptly, as they can develop into a malignant tumor. Malignant formations of the nasal cavity are divided into the following types:
- connective tissue formations (sarcomas);
- epithelial neoplasms;
- neurogenic cones.
The prognosis for malignant nasal cones is difficult to provide because many factors must be taken into account.
Main reasons
Before prescribing treatment, you should find out the reason why the subcutaneous lump came out. The main sources causing the problem are:
- inflammation of the nasal mucosa, which occurs in a chronic form;
- presence of adenoids;
- weakening of the immune system;
- the use of contaminated water for hygiene procedures, which penetrates into the nasal cavity;
- frequent picking of the nasal cavity with dirty hands.
An abscess that appears in a nostril or other part of the nose poses a health hazard. As a result, purulent inflammation develops, which affects the soft tissues of the head.
If you remove the lump on your own, secondary infection is possible, which can lead to blood poisoning and other dangerous consequences.
You should not try to squeeze out the boil or treat it yourself, but rather consult a doctor.
Symptoms
Bumps on the nose can make breathing difficult, cause bleeding and discharge of pus.
A tumor on the nose usually affects the inner wall.
The first characteristic sign of the formation of a boil in the nasal cavity is pain. The person complains that the resulting formation hurts and pus accumulates in it.
Given the small size of the formation and its benign nature, treatment is not difficult. Malignant lumps manifest themselves with more pronounced symptoms.
When a lump forms under the skin, a person experiences the following symptoms:
- breathing becomes difficult as the formation grows and closes the nasal cavity;
- pus is discharged from the nose;
- the mucous membrane is damaged by ulcers;
- blood often flows from the nose for no reason;
- Possible inflammation of the middle ear.
Over time, the lump thickens and becomes hard. If you do not pay attention to the above symptoms in time, complications will soon arise. In this case, pain and heaviness in the head will be added to the main symptoms.
If a malignant formation is detected, then in the later stages it leads to a change in the shape of the nose, and part of the patient’s face droops. The pathology is accompanied by hearing loss and tinnitus.
The latest signs indicate that the lump is malignant.
Diagnostics
If you notice a bulge in the nose area, you should contact a medical facility and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. It is important to determine the nature of education, its nature and type. The patient must first see an otolaryngologist, who will examine the area of concern and then prescribe the following diagnostic procedures:
- rhinoscopy, in which the nose is examined using special mirrors;
- olfactometry, which reveals whether the acuity of smell is impaired by special instruments;
- radiography of the paranasal sinuses;
- computed tomography and radiography of the skull;
- pharyngoscopy, during which the nasopharynx is examined.
If the patient begins to see poorly, then a consultation with an ophthalmologist is indicated, who checks visual acuity. The specialist performs exophthalmometry and determines the field of vision, and examines the fundus of the eye using ophthalmoscopy. If there is a suspicion that the resulting boil is infectious, a swab is taken from the patient’s mouth and pharynx.
What to do: treatment methods
A neoplasm that has arisen in the nasal cavity should be eliminated only after a diagnosis has been made.
If the lump is benign, then it is necessary to have an operation to remove it, after which the problem will disappear.
If the formation is small, it can be removed using radiation therapy, which has recently become especially popular. The described method is optimal and painless.
Bleeding nasal lesions are often removed endoscopically. After the procedure, the base of the tumor is cauterized to reduce the risk of relapse. Cauterization is possible using cryotreatment or electrocoagulation. Large formations are removed using a scalpel or radio wave knife. If the growth is malignant in nature, then chemotherapy is performed.
Malignant or benign lumps that have grown into the bone walls, or structures that are located near the nose, must be removed in parts.
In this case, doctors resort to external surgery, during which they dissect the bone structures and perform resection of a large amount of facial tissue.
After such surgical treatment, the patient requires reconstruction using plastic surgery.
Source: https://StopRodinkam.ru/shishki/v-nosu.html
Stages of formation
Bumps inside the nose form for various reasons and continue to develop in several stages at once. To avoid possible negative effects, it is important to begin timely and effective treatment. A lump in the nose on the septum forms at the initial stage of the disease. In total, experts distinguish three main stages:
- in the first, the formation is localized in the upper region of the septum;
- in the second stage, the growth spreads over most of the septum;
- the third stage is characterized by complete closure of the base of the nasal cavity.
If the necessary treatment is not provided, then in its advanced form, a lump in the nasal cavity leads to serious problems, since at this time the sense of smell is lost, and the openings of the paranasal sinuses are blocked. As a result, such a pathology can lead to a lack of air entering the body, as well as to the spread of infection.
What to do if a bump appears on your nose?
The nose is one of the most noticeable parts of the face, so those around you immediately pay attention to any changes in this area. A bump on the nose is very unsightly and is a reason for ridicule. In order not to experience psychological problems, you need to find out the cause of this trouble and get rid of it.
Clinical picture
It must be said right away that cones are different. They differ in color, size, location. Most often, small, painless, flesh-colored bumps occur. They are located on any part of the nose and can go away on their own, without treatment.
Another category of neoplasms are painful flesh-colored or pink lumps, most often with purulent contents inside. Such formations are dangerous, since the nose is equipped with a branched capillary network, and the infection can enter the bloodstream. There are neoplasms that appear due to overgrown bone or cartilage tissue.
These bumps are shapeless, hard, and sometimes painful to the touch. A bump may appear on the bridge of the nose near the piercing. Usually such formations go away on their own within a couple of months. They do not hurt, do not bleed, and they do not contain purulent contents. Separately, it is necessary to mention the formations that appear inside the nose. They are painful and sometimes bleed.
Such formations look like bluish or red seals with a pronounced capillary network.
Hernia
It feels like a soft protrusion under the skin, which can appear during exercise and disappear completely when lying down or at rest. A hernia forms in the navel, postoperative scar on the abdomen, in the groin, on the inner surface of the thigh. The hernia may be painful when palpated. Sometimes you can push it back in with your fingers.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the benefits of argan oil - properties, application for skin and hair
A hernia is formed by the internal organs of the abdomen, which are squeezed out through weak spots in the abdominal wall during an increase in intra-abdominal pressure: when coughing, lifting heavy objects, etc. Find out whether a hernia can be cured using traditional methods, and why it is dangerous.
Malignant tumors
Compared to other skin lesions, malignant tumors are very rare. As a rule, at first a focus of compaction or a nodule appears in the thickness of the skin, which gradually grows. Usually the tumor does not hurt or itch. The surface of the skin may be normal, flaky, crusty, or dark in color.
Signs of malignancy are:
- uneven and unclear boundaries of the tumor;
- enlargement of nearby lymph nodes;
- rapid growth in education;
- adhesion to the surface of the skin, inactivity when palpating;
- bleeding and ulceration on the surface of the lesion.
A tumor can develop at the site of a mole, like melanoma. It can be located under the skin, like a sarcoma, or at the site of a lymph node - lymphoma. If you suspect a malignant skin tumor, you should contact an oncologist as soon as possible.