At different stages of life, representatives of the fair sex note changes in breast size, and their reduction is especially distressing. This is a cause for concern, which is quite justified: the problem may not only be of an aesthetic nature.
To fully reveal the reasons for such phenomena, let us consider the structure of the female breast.
General information
The aesthetic role of the female breast is far from the most important. Its main component is the mammary gland, which is designed to provide nutrition to the born child. It consists of lobes, between which connective tissue septa pass. Those, in turn, branch into smaller segments. And the latter are formed by alveoli and efferent ducts, which, uniting, flow into the milky sinuses and ultimately open on the nipple.
The function of glandular tissue depends entirely on hormonal influences. Three biological substances play a key role in the regulatory process: estadiol, progesterone and prolactin. The breasts have receptors for each of the hormones. Estrogens promote the development of the milk ducts and stromal elements, progesterone stimulates the growth and increase in the number of lobules, provokes retention of intercellular fluid, and prolactin helps to increase sensitivity to the first two and is responsible for the production of a specific secretion - human milk. Therefore, during periods when hormonal changes occur in the body, the breasts are subject to the greatest changes.
Causes and mechanisms
Only a doctor can understand why breasts become a source of discomfort. A specialist with the necessary qualifications and experience will examine the woman and indicate the origin of the problem. In most cases, worries are in vain, because everything is determined by physiological changes. Most often, breast engorgement and tenderness is a normal phenomenon observed during various periods:
- The onset of puberty in girls.
- In the second phase of the menstrual cycle.
- During pregnancy.
- After childbirth.
This effect is primarily due to increased progesterone and growing prolactin. The latter is especially actively produced by the pituitary gland in the last trimester of pregnancy and after the birth of a child. Similar processes are observed during an abortion, but to a much lesser extent. In addition, pain may occur due to the individual characteristics of the body and the increased sensitivity of the nervous system.
In addition to conditions that can be explained from a physiological standpoint, pathological processes, both general and local, become causes of obvious discomfort in the chest. Most often we are talking about endocrine disorders, inflammatory and tumor disorders. Therefore, doctors may suspect:
- Premenstrual syndrome.
- Mastopathy.
- Mastitis.
- Breast cancer.
Hormonal disorders, which often underlie the symptoms that arise, can occur against the background of the influence of unfavorable factors, which include physical fatigue, poor nutrition, emotional stress, infections and intoxications, bad habits, and gynecological diseases. This is something that can disrupt the natural regulatory balance in the female body and cause breast problems. But each case requires individual consideration and differential diagnosis.
When faced with chest discomfort, you should immediately consult a doctor to find out the nature of the changes.
Symptoms
Any condition, including physiological, is manifested by certain symptoms. And when identifying pathology, the clinical picture is extremely important. At the stage of the initial examination, the doctor analyzes and details the complaints, conducts an examination and evaluates objective signs. In a situation with pain and swelling of the chest, you need to determine the main parameters of the symptoms:
- Expressiveness.
- Duration.
- Preferential localization.
- Dependence on external factors, menstrual cycle, etc.
Other signs accompanying the main ones are also revealed. Sometimes they provide equally important information about pathology. This way, an almost complete picture of what is happening is formed and the main reasons why the breasts can become enlarged are determined, causing some concern.
Premenstrual syndrome
For more than half of women, the approach of menstruation will be marked by a complex of vegetative-vascular, emotional and psychosomatic disorders, united under the concept of premenstrual syndrome. Appearing in the second phase of the cycle, they completely disappear with the onset of discharge. One of the manifestations of this condition is considered to be severe breast engorgement, which is accompanied by a feeling of fullness and even pain. But besides this, there will be other signs:
- Irritability and anxiety.
- Headaches, cardialgia.
- Swelling of soft tissues.
- Aches in the joints.
- Numb hands.
- Bloating.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Diarrhea or constipation.
- Increased heart rate.
The severity and number of symptoms vary within different limits, which allows us to talk about the severity of premenstrual tension and its forms: neuropsychic, edematous, crisis, cephalgic.
Mastopathy
Mastopathy is considered a common condition among women of reproductive age. It is based on benign growth of gland tissue. Therefore, those whose breasts are enlarged and painful should think about this possibility. Symptoms of mastopathy may include:
- The appearance of compactions (nodules).
- Chest pain before the onset of menstruation (mastalgia).
- Clear discharge from the nipples.
Depending on the morphological changes in the gland, three forms of mastopathy are distinguished: diffuse, nodular and mixed. Sometimes pain is provoked by even a light touch to the chest or can radiate to neighboring areas: the armpit or shoulder. And although the process is benign in nature, it can increase the risk of malignant degeneration. Therefore, women should not allow mastopathy to be taken lightly.
Mastopathy is a common disease in modern women. It is benign in nature, but can also become the initial stage of oncology.
Mastitis
If the breast hurts and has increased in volume, then inflammatory diseases – mastitis – cannot be ruled out. They are observed during the development of infection or are provoked by congestion in the gland (lactostasis). The breast turns red and swells, the skin over it is hot to the touch, purulent contents may be discharged from the nipple, and palpation is characterized by severe pain. The woman’s general condition also suffers: malaise appears and the temperature rises. The inflammatory process can acquire an encysted character, i.e., proceed like an abscess. Then your health deteriorates even more.
Breast cancer
The greatest danger among breast problems is a malignant process in the glandular tissue - cancer. The tumor is initially completely asymptomatic and is often detected only during a preventive examination. And among the clinical symptoms that develop later, the following should be alert:
- The appearance of a dense, painless node, fused to the surrounding tissues, the size of which does not depend on the phases of the menstrual cycle.
- Skin changes: redness or marbling, lemon peel, ulcer.
- Retraction of the nipple area.
- Bloody issues.
- Breast deformity.
- Enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
Cancer can take on an infiltrative-edematous form when the breast in a certain area becomes rude with tissue compaction. But pain does not appear immediately, but in the long term, when the tumor grows into neighboring tissues.
Before this, the breasts are practically not bothered, which is the reason for the late application of some women.
Treatment
The choice of treatment method depends on the cause that provoked the pathology. Most often, therapy is medications that can relieve symptoms. Hormonal drugs containing prolactin or progesterone are prescribed.
Note that self-medication can significantly worsen a woman’s condition. Specific medications have contraindications. During menopause, estrogen synthesis inhibitors will be prescribed. The symptoms go away, but migraines, nausea, and weakness appear.
The method of treating gynecomastia depends on the cause of it. If the enlargement of the mammary gland occurs as a result of taking any drug, then stopping it will be sufficient for recovery.
In case of severe growth that creates problems for the patient, surgical intervention is recommended.
There are a number of indications for surgical treatment:
- heavy load on the muscles of the back and spine;
- problems with the cardiovascular system caused by excess weight;
- psychological discomfort of the patient.
Operation description
False gynecomastia is the most treatable. In this case, liposuction is performed with further correction of the shape of the mammary gland through a lift. The surgeon makes an incision (approximately 3-4 millimeters), through which a tube is inserted, with its help the fat is pumped out.
True gynecomastia is treated with surgery, during which excess glandular tissue is removed, and the shape of the areolas can be corrected (if necessary).
The operation takes from an hour to several hours, depending on the complexity, and can be performed under either local or general anesthesia. The procedure is carried out only in a hospital setting. The patient remains there for another day after surgery.
There are a number of rules that a woman must follow during the recovery period:
- wear shapewear for two weeks;
- refrain from smoking and alcohol until the stitches heal;
- avoid exposure to direct sunlight;
- exclude sports activities for a month.
Full recovery takes about 6 weeks.
Like any surgical intervention, this operation has some consequences:
- the appearance of hematomas;
- swelling of the breast.
However, they all go away within 2-3 weeks.
Complications
Complications from surgery associated with this disease are rare. They may be as follows:
- incomplete removal of excess glandular tissue;
- decreased nipple sensitivity;
- uneven breast contour.
As an alternative to surgery, some women try to use various diets and special exercises, but all these methods are useless, since it is impossible to reduce breasts without removing the cause of their growth. With exercise you can get rid of fat, but excess skin, and especially overgrown glandular tissue, will not disappear. Based on this, women suffering from a similar illness should definitely visit a doctor who will prescribe appropriate treatment for them.
Gynecomastia is certainly a very unpleasant disease, so when its first symptoms appear, you should seek advice from a specialist. An advanced disease causes both physical and psychological problems for the patient; in addition, one should not forget about the possibility of the disease degenerating into breast cancer. Timely and adequate treatment will return the patient’s self-confidence and her breasts back to beauty and health.
Additional diagnostics
Any preliminary diagnosis requires further verification using additional methods. It is possible to say exactly why your breasts are enlarged and painful only after a comprehensive examination, including laboratory tests and instrumental procedures. Based on the clinical situation, the doctor recommends that the woman undergo:
- General blood and urine tests.
- Blood biochemistry (hormonal spectrum, tumor markers, inflammation indicators, antibodies, etc.).
- Analysis of nipple discharge (microscopy, bacteriology, for atypical cells).
- Mammography.
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands.
- Tomography.
- Biopsy with histological examination of the material.
Based on the research results, the doctor makes a final conclusion and plans treatment measures. And the effect of any therapy will be better the earlier the disease is detected. Therefore, women should always be careful about their breasts, and if alarming symptoms appear, immediately seek medical help. Even the most dangerous diseases can be successfully treated while they have just begun to develop.
Perhaps almost all women have encountered such a phenomenon as. Most often, this happens regularly and is associated with a certain period of the menstrual cycle, in particular with the onset of ovulation. But any representative of the fair sex is recommended to know all the reasons why breasts may become enlarged, since this metamorphosis is not always harmless. How to recognize the true factors that influenced changes in breast volume? And what to do if swollen glands cause discomfort and make a woman anxious?
Before discussing the possible reasons why breasts may become enlarged, it is necessary to understand all the intricacies of its structure. - a complex formation that includes three types of tissues:
- Glandular
- Connective
- Fat
The glandular tissue is precisely the part of the breast in which the milk ducts leading to the nipple pass. It can be called the main tissue, since it and only it is responsible for the formation and secretion of milk during lactation. The shape and size of the bust is given by adipose tissue - the more it is, the larger the size. That is why, with a sudden weight loss, a woman’s breasts also drop significantly. Connective tissue becomes a kind of layer between glandular tissue and adipose tissue.
In addition to tissues, the glands also contain numerous blood vessels and nerve endings. During puberty, a girl’s body begins to actively produce female hormones that affect the condition of the breasts. The glands begin to swell, become sensitive and painful. This process continues until about age 20 and is finally completed by age 25.
Changes in breast size can be caused both by natural causes associated with hormonal changes during certain periods of life, and by various pathological phenomena, both in the mammary glands themselves and in the body as a whole.
How do women's breasts work?
The female breast is an organ that consists of two hemispheres located symmetrically. The basis of the breast is gland, or glandular tissue, formed by 15-20 glandular lobes. In turn, the lobes consist of small spheres - alveoli, which produce milk during lactation.
The glandular tissue is surrounded on all sides by adipose tissue, which is also located between the lobes.
The gland is attached to the pectoral muscles by connective tissue. In the chest itself, contrary to a well-known misconception, there are no muscles. From the inside it is permeated with ligaments intertwined with each other. This is a kind of frame that supports the breasts and prevents sagging.
The ratio of glandular and adipose tissue, as well as the amount of connective tissue present, is individual for each woman.
Natural causes
The condition of the female breast is closely related to the reproductive system of the body. Any hormonal fluctuations immediately affect the mammary glands, most often leading to their enlargement and increased sensitivity. In some cases, swelling of the glands in women, pain, high sensitivity of the nipples and other symptoms are associated with two natural and safe causes. They are:
- Ovulation
In the middle of the menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs: a mature egg breaks out of the follicle and begins its journey through the fallopian tube. This process is accompanied by a sharp jump in female hormones in the woman’s body, which are necessary to prepare the uterus to receive a fertilized egg.
One of these hormones is estrogen, which has a powerful effect on breast fat and increases it. As a result, the nerve fibers are under pressure from the rapidly expanding tissue - therefore, breast enlargement is accompanied by pain and swelling. When menstruation occurs, pain and tension in the glands subside, and by the end of it all symptoms disappear completely.
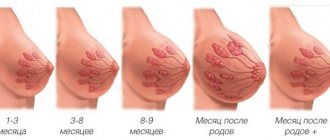
If pregnancy occurs, it can become one of the earliest signals for a woman. The condition of the mammary glands is influenced by the same hormones - estrogens and prolactin. The first maintains the uterus in the desired condition, while the second is responsible for preparing the glands for the upcoming feeding of the baby. During pregnancy, the breasts can increase by 1-2 sizes during the first trimester, and along with it the nipple and the areola noticeably enlarge and darken. Vessels and veins also appear on the chest, which is associated with increased blood flow in this part of the body.
If the above conditions are the cause of painful enlargement of the mammary glands, there is no need to worry. Breast swelling before menstruation is one of the manifestations of PMS, which is a consequence of a slight hormonal imbalance. By consulting with a gynecologist, you can adjust your hormonal levels and get rid of the symptoms of premenstrual syndrome. When it comes to pregnancy, the situation is somewhat different: the process of bust enlargement is not only normal, but also mandatory - this is how the glands prepare for feeding.
Causes of hypomastia
In addition to estrogen and progesterone, thyroid hormones produced by the thyroid gland take an active, albeit indirect, part in the formation of mammary glands. The mechanism of action on female breast growth for these hormones is not direct. Long-term stress during adolescence can be an inhibitory factor for breast growth. At least from tense relationships in the family.
Constant nervous stress affects the production of thyroid hormones, but they are responsible for the overall growth of the entire body during puberty! That is, on the growth of muscle and bone tissue, the growth and normal formation of the lymphatic and nervous systems, and even - attention! - on intelligence. And mental instability, increased nervous excitability in a dysfunctional family due to a lack of the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine and trioxine, after it affects the intellect, will not allow a teenage girl to correctly comprehend the changes happening to her, which can drive her consciousness into a new round of depression.
And this is no joke - the number of suicides among girls due to dissatisfaction with their appearance (including small, underdeveloped breasts) is very high.
In addition to the connective tissue that forms the breast, its volume also depends on the condition of the vascular system. The muscle tissue located deep under the mammary gland as such has minimal influence on its size: girls who are actively involved in fitness, “pumping iron” can increase their breasts by a maximum of half a size. A “pumped up” pectoral muscle is more likely to slightly lift the chest. However, this is already a lot.
The most severe cases of underdevelopment of the mammary glands occur when trauma, inflammation, or the influence of hormonal deficiency interfere with their formation at the earliest stages. Injuries to the chest or surgical operations on it. Inflammatory diseases of the hypothalamus and thyroid gland. Iodine deficiency - in areas where water and soil are poor in iodine.
Finally, the formation of breasts in girls also largely depends on the fat layer (here proper, balanced nutrition is of great importance).
Fashion. Public opinion. Standards accepted in youth subcultures. These factors sometimes turn girls with a completely normal figure for their age into experimenters with their own bodies. As a tool for changing it, they begin to use killer diets that lead to an extreme degree of exhaustion - anorexia, after which the mammary glands will never return to normal and will remain forever underdeveloped. The social environment from which girls come can be very varied: from well-to-do children from the middle class to people from poor or dysfunctional families.
Then, if in the period from 16 to 19 years old, a girl wants to buy a fashion model standard 90 x 60 x 90, nothing will work with the “upper” 90. Urbi et orbi, a flat-chested woman will appear, who can only be helped by “push-up” or silicone implants.
In addition to the above cases, the cause of hypomastia may be a genetic predisposition to it. And heredity - flat-chested mothers and grandmothers will have a granddaughter/daughter with a “zero” size.
“Who is to blame” has been sorted out. Now, as is customary,
Alert
Unfortunately, enlarged mammary glands often signal the development of some disease. Moreover, the disease is not always associated with the glands themselves: the cause may also lie in pathologies of the genitourinary or endocrine systems. A particularly alarming sign is the disproportionately noticeable enlargement of only one breast in women - such a symptom requires immediate contact with a mammologist, since it often indicates the presence of both benign and malignant formations in the breast.
In general, all pathological causes of breast enlargement outside the menstrual cycle are as follows:
- The presence of a severe hormonal imbalance, due to which the norms of female hormones in the blood are exceeded.
- Disorders of the endocrine system - for example, diseases of the adrenal glands or thyroid gland.
- The presence of various diseases of the mammary gland: mastitis, mastopathy, cyst formation, cancer.
- Development of diseases of the genitourinary system: gynecological diseases of an infectious and inflammatory nature.
- If an uncharacteristic phase of the cycle has begun, or previously no changes in the gland were observed, but the breasts have enlarged, it is better not to delay with the thought “it will go away on its own” or, even worse, to self-medicate - you need to contact a mammologist.
- When the cause lies in hormonal imbalance or endocrine system disorders, timely hormonal therapy can restore balance and return the breast to its normal state. If any breast disease is detected, treatment will depend on the stage of the disease: in the initial stages, conservative treatment is effective, but in advanced cases, surgical intervention may be required.
- And finally, gynecological diseases of various types are cured with individual methods and medications, after which the bust usually restores its previous shape.
Pathological causes
Pains of a pathological nature are sensations that are not considered natural and normal manifestations. They only indicate the appearance of some kind of disease, which may be associated with the reproductive system or with other parts.
Pain of a pathological nature is provoked by various diseases. If we talk about breast diseases, then we can talk about:
- Mastopathy. A common disease of modern women, in which connective tissue grows. The pain is frequent and prolonged. The shape and size of the nipples often change. You will not be able to get rid of the disease on your own. Only drug treatment will help in this case.
- Abortion. Since the body was set up for the further development of pregnancy, it does not immediately stop producing hormones. After an abortion, your breasts may hurt for a week to 9 days. This gradually stops the production of hormones that were involved in preparing the mammary gland for feeding the baby. If your chest does not stop hurting for a longer time, then you should consult a doctor.
- Miscarriage. Often, a miscarriage is not natural unless the body has performed improper fertilization beforehand. This is accompanied not only by chest pain, but also by prolonged bleeding in the form of menstruation, which may last longer than usual (usually 2-4 days longer than normal menstruation).
Severe discomfort, noticeable breast enlargement is a signal from the body about the development of diseases:
- Mastopathy - manifests itself both during menopause and at any age. Signs - after the next menstruation, the breasts become full, sore, and there is a feeling of heaviness. The diagnosis can be cystic, fibrous, diffuse or focal mastopathy.
- Fibroadenoma (during pregnancy). It is associated with the appearance of benign tumors. Causes pain and swelling of the glands. The pathology cannot be treated during pregnancy, since medications cannot be taken.
- Oncology - a disease of a malignant or benign nature causes breast swelling.
It does not matter whether the swelling of the glands is caused by physiology or pathology. You should not ignore the symptoms, but consult a doctor for a correct diagnosis.
Other factors
Breasts can increase not only due to any internal hormonal or pathological changes, but also under the influence of other factors.
We are talking, first of all, about weight gain: when a woman begins to gain weight, her stomach and chest are the first to become rounded - those areas that represent a strategic reserve of fatty tissue. Therefore, before you panic about your suddenly enlarged bust, you should make sure you haven’t gained a couple of extra pounds over the last month? In this case, a light diet will allow you to return to your previous size.
Experts also recommend that a woman evaluate her diet. Perhaps, recently it contains quite a lot of products containing so-called phytoestrogens - substances similar in their properties to natural estrogen produced in the body. These products include:
- soybeans and various soy products
- legumes (beans, peas, lentils)
- white cabbage, cauliflower and Brussels sprouts
- many seasonings (ginger, turmeric, sage, anise, cloves, thyme)
Usually, adding these products to the diet in adequate quantities will not only slightly correct the shape of the bust, but will also have a beneficial effect on its condition.
Physical training
And finally, another reason is physical activity. More precisely, active sports. With regular training, the pectoral muscles are effectively strengthened, which much better support the entire breast (there are no muscles in the structure of the gland itself).
A woman may not pay attention or not notice changes in this area for a long time - especially if the goal of the training was at a different point. It should also be clarified that the breasts do not so much become larger as they are tightened and take on a natural and more beautiful shape. By combining physical activity with proper massage, you can achieve incredible results.
Every woman dreams of beautiful, lush and firm breasts. An unexpected and sharp enlargement of the mammary glands, alas, does not at all seem like a dream come true - rather, on the contrary, it causes great anxiety.
There are many reasons for this phenomenon. Some of them are associated with natural states of the body, such as ovulation, pregnancy or the postpartum period. Other reasons may indicate serious hormonal imbalances, the presence of gynecological diseases or breast diseases. The condition and shape of the breasts can be affected by diet, exercise, or fluctuations in body weight. In any case, if enlarged breasts cause concern, you should immediately consult a doctor in order to avoid more serious consequences in time.
Today, almost every woman has had to deal with chest pain, as well as enlarged mammary glands. Perhaps the fair half of the population most often turns to gynecologists with such problems. If your breasts hurt or are enlarged, this does not necessarily mean that the woman is susceptible to a serious illness.
In some situations, chest pain and enlargement of the mammary glands are absolutely natural processes, because the condition of the female breast directly depends on the direction and development of its hormonal levels. It is for this reason that chest pain can be divided into physiological and pathological.
In order to understand what is within the norm and what you need to be wary of, let’s take a closer look at each of the options.
Why are breasts shrinking?
Anatomically, a reduction in the size of a woman’s breasts can result from a reduction in the amount of fatty or glandular tissue that forms it.
This is facilitated by reasons that can be divided into two groups.
- Reasons of a physiological nature: cyclical hormonal fluctuations, pregnancy and lactation, weight loss, sports, age-related changes.
- Pathological causes associated with diseases of internal organs (including cancer), endocrine and hormonal disorders.
The female breast is a target organ that is affected by many factors, including lifestyle, general condition of the body and the action of various hormones. Bust reduction is an indicator reflecting these processes.
Physiological pain
Physiological chest pain is normal in nature, so there is no need to worry in this case. It has long been known that changes regularly occur in the soft tissues of the female breast, which primarily depend on the production of the following types of hormones:
- Estrogen or estradiol. Responsible for the development and functioning of the thoracic ducts. If estradiol is produced in excess, the risk of breast atrophy and an increase in the amount of fat deposits in soft tissues increases.
- Progesterone. Thanks to him, a woman is capable of lactation. Progesterone is responsible for the development and functioning of the alveolar lobes. With its deficiency, the development of pathological abnormalities in the chest is possible.
- Prolactin and oxytocin. These two types of hormone play a very important role in the functioning of the female body. The first one favors the production of milk, and the second one is responsible for its release.
Menstrual syndrome
The causes of pain and enlargement of the mammary glands in women are associated with the amount in which one or another type of hormone is released in a certain period of time. So, before women begin menstruation, the breasts may increase in volume and become slightly sore. At the end of this period, unpleasant symptoms disappear on their own. If no alarming manifestations arise, then such a manifestation can be considered normal!
In women, such manifestations of chest pain are called mastodynia. The causes of pain with mastodynia are sometimes quite difficult to distinguish from mastopathy.
The main distinguishing feature of mastodynia is its frequency. That is, the chest does not always hurt. And as soon as menstrual syndrome sets in, all discomfort in women stops. If mastopathy develops, the chest hurts for a long period of time. Unpleasant sensations may continue even after menstrual bleeding has ended.
Pregnancy and lactation
The mammary gland enlarges and hurts during pregnancy in women. These symptoms are especially pronounced in the first three months of the term. Why is this happening? It is during this time period that women produce a large amount of the hormone progesterone, which in turn has a strong effect on the mammary glands. This type of hormone allows you to maintain pregnancy for all 9 months. And if during this period women’s breasts and nipples become enlarged, then such a symptom is normal.
By producing prolactin and oxytocin, women produce milk, which she can use to feed her baby.
The causes of pain, which are due to menstruation and pregnancy, are physiological. They do not pose a danger to women's health, and therefore do not require drug treatment.
Hormonal imbalances
With a sharp change in hormonal levels, other diseases may arise that will relate to a non-gynecological profile. Among such ailments, hepatitis, cirrhosis of the liver and frequent nervous tension and stress are particularly dangerous.
Diagnosis of cancer cannot always be made in its initial stages. However, without yet knowing about the presence of a serious illness, unpleasant sensations may appear in the mammary glands, and the nipples may begin to swell and increase in size. In the initial stages of cancer, pain may resemble symptoms of mastopathy. Therefore, it is very important to pay attention to any unusual discomfort in the chest.
The presence of a malignant neoplasm can be suspected if the lump is very closely fused to the breast and touches the nipples; also, discharge mixed with blood or pus may indicate cancer.
Why is it important to carry out regular independent palpation of the glands? According to gynecologists and mammologists, this procedure will prevent the development of serious abnormalities in the functioning of the mammary glands. This will also make it possible to start timely treatment and avoid possible complications of the disease. In any case, chest pain is not a simple phenomenon, which sometimes requires special attention and control!
Preventive measures
If the tumor appears suddenly, it hurts and feels hard, but there is no discharge when squeezed, then a fibroma may develop. Adenoma, unlike the previous disease, has elastic contours that affect only the glandular tissue in the milk lobes.
Mastitis is not just a lump, but a disease that occurs only during breastfeeding. If lactation does not return to normal, and this is observed in the first 3 months after birth, then compactions, increased temperature, and hard lobes are possible. During this period of time, one milk lobe may become larger than the other.
If a woman has contraindications to medications, and her temperature continues to remain at 38 or above, immediately call an ambulance. With this disease, regardless of the temperature (38 or 40), feeding is prohibited, as the milk may burn out.
In any case, if a woman discovers a knot or lump of any size, if previously one of the breasts did not bother, but now hurts or aches, then this is a reason to consult a doctor. You do not need to take any ointments on your own. Depending on the examination of the milk lobes, you may be referred for an ultrasound and blood donation.
The physiological processes that occur in the mammary glands are embedded in the genetic code. Therefore, prevention of tissue edema is impossible. Moderate exercise helps normalize carbohydrate metabolism. This is a guarantee that hormonal imbalance will not occur. It is worth limiting your use of:
- soy;
- potatoes;
- flax;
- asparagus;
- wheat;
- dates.
These products pose a threat to normal metabolism.