Types of disease
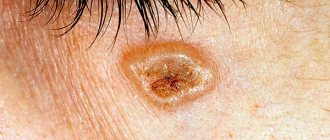
Streptoderma on the face in adults - photo:
There are several classifications of streptoderma on the face. They are based on certain characteristics of the disease.
according to its symptoms :
- acute - the signs are pronounced, and if treated in a timely manner, a rapid recovery occurs;
- chronic - symptoms are sluggish, stages of remission are replaced by periodic exacerbations. This form of the disease is almost impossible to completely cure.
Depending on the nature of the disease, there are the following forms of the disease:
- non-bullous - mild damage to the epidermis. Small ulcers (pustules) with a small fluid content in them form. After the ulcer ruptures, a crust forms on it;
- bullous is the most severe. Bubbles filled with liquid appear on a large surface of the skin. The diameter of the rash is up to 1 cm.
Depending on the depth of the lesion , it can be:
- superficial streptoderma - the infection is concentrated only on the surface of the skin and does not penetrate into the body;
- deep streptoderma - bacteria enter the body through the epidermis and cause various complications.
According to the nature of its occurrence, the disease can be primary - direct damage to the skin by streptococcal infection, secondary - manifest as a symptom of another disease.
How does the disease progress?
The incubation period of the disease lasts from 7 to 10 days. After this, the first signs begin to appear in the form of pink spots with irregular outlines. After a few days, purulent, vesicular lesions of the skin begin to appear in place of the spots.
It has already been noted that, apart from external manifestations, the skin disease has no signs. In some cases, only slight itching and dry skin are noted.
If the disease occurs in a deep form, instead of spots, ulcerative elements with a dense crust appear. When they heal, they leave scars on the surface. Streptoderma occurs on the face as well, but most often it affects the lower extremities. When the diffuse nature of the disease appears, the lesions begin to spread throughout the patient’s body.
In the chronic form, large lesions will appear, up to 10 cm in diameter. They have uneven edges and exfoliating stratum corneum at the periphery.
Initially, the disease is localized. When basic rules of personal hygiene are not followed and treatment is neglected, the infection will begin to spread. Therefore, it is important to know what streptoderma is and how to treat it so that it does not lead to advanced forms and complications of the disease.
Causes
The source of the disease can be both environmental factors and internal causes.
The development of pathogenic microflora on the face can be caused by:
- poor skin care (lack of cleansing, prolonged wearing of cosmetics, etc.);
- disturbance of local blood circulation;
- exposure to very high or low temperatures on the skin;
- facial injuries (cuts, abrasions, bites);
- metabolic disease;
- stress, overwork;
- chronic diseases, etc.
Today, streptoderma in adults is often a consequence of poor ecology and inappropriate working conditions.
Routes of infection
What is this disease transmitted from? Infection with this disease occurs through household contact, through direct contact with an infected person. It can also be transmitted through common objects. Children most often become infected in schools and kindergartens, that is, in groups where children communicate closely with each other and share toys.
Failure to comply with basic hygiene rules sometimes leads to a real epidemic among children. Streptoderma appears in adults through contact with a sick child or when using common objects with him.
Symptoms
The main symptom of streptoderma on the face is impetigo . These are formations (papules) that rise slightly above the surface of the skin. First, hyperemia suddenly appears on the skin.
, a bubble with a yellowish exudate inside appears . The extent of skin damage depends on the form of the disease.
Gradually, the formation grows to 1-2 cm. After opening the bubbles, yellow-brown crusts form in their place. Subsequently they disappear. During an exacerbation of streptoderma, the patient may experience itching.
The whole process lasts about 3-7 days.
If the affected areas are scratched, the infection can spread even further and cause a number of complications .
If adequate treatment is not undertaken, the localized form of the disease will become widespread.
Prevention methods
Following these recommendations will help prevent the development of the disease:
- wash your hands and face regularly,
- Before going to bed, carefully remove any remaining cosmetics from the skin,
- take care of increasing immunity,
- use only personal means and hygiene items,
- eat right,
- avoid hypothermia and thermal burns,
- get rid of bad habits,
- avoid stressful situations,
- treat skin wounds with antiseptic drugs.
Streptoderma on the face is an infectious skin disease that can occur in both acute and chronic forms. This pathology should be treated promptly, as it is fraught with complications in the form of a secondary infection and the formation of scars on the skin.
Diagnostics
The disease can be diagnosed by characteristic symptoms, as well as using laboratory tests. To confirm the diagnosis, you need to contact a dermatologist .
He will conduct a thorough examination of the patient. Determines primary and secondary signs of infection.
A bacterial culture of the fluid from the blisters may be prescribed to identify the causative agent of streptoderma.
In the chronic form of the disease, additional diagnostic measures are used:
- Ultrasound of internal organs.
- Coprogram, stool test for worms.
- Advanced blood test.
- Examination of the gastrointestinal tract using an endoscope.
Differential diagnosis
To confirm the diagnosis, diagnostic measures are prescribed:
- visual inspection of the skin,
- bacteriological culture of the contents of the vesicle,
- clinical blood test, as well as blood testing for hormone and sugar levels,
- stool analysis to identify worms,
- examination of the abdominal organs.
After identifying the disease, the specialist determines the course of treatment.
Treatment options
How to treat streptoderma on the face in adults? The main task of therapy for streptoderma is to localize the lesion and prevent the infection from spreading further. For single lesions of the skin, local treatment is limited.
In case of severe cases, a complex of external and systemic medications and procedures is prescribed to relieve streptoderma.
Local
How to treat skin? To prevent the spread of infection, local treatment of foci of infection is imperative.
with antiseptics 2-3 times a day :
- Boric or salicylic alcohol;
- Fukortsin;
- Miramistin;
- Hydrogen peroxide.
When the skin dries after the antiseptic, you can apply an ointment that contains an antibiotic:
- Neomycin;
- Erythromycin ointment;
- Chloramphenicol;
- Bacitracin;
- Levomikol;
- Methyluracil;
- Supinracin, etc.
It is better to apply the ointment on a gauze bandage and apply it to the affected skin for several hours.
In case of extensive foci of infection, hormonal ointments may be prescribed. But you can use them for a short time.
Otherwise, they can cause increased skin vulnerability, thinning, and aggravate the course of the disease.
- Lorinden;
- Kanizon;
- Betaderm;
- Akriderm.
For severe itching, antihistamines :
- Claritin;
- Fenistil;
- Telfast et al.
Systemic
If the infectious process is widespread, systemic antibiotics are indicated. Mainly used are cephalosporins, macrolides or penicillins .
- Augmentin;
- Flemoxin Solutab;
- Cefuroxime;
- Suprax;
- Erythromycin;
- Sumamed.
In parallel with antibiotics, a course of probiotics to restore the intestinal microflora (Linex, Acidolac, Bifinorm).
To strengthen the immune system and maintain the patient’s vitality, you need to take multivitamins :
- Multitabs;
- Kvadevit;
- Suprastin;
- Centrum.
After the removal of acute inflammatory phenomena, a course of ultraviolet irradiation in suberythemal doses is prescribed to the affected areas of the skin.
Immunomodulators:
- Neovir;
- Pyrogenal;
- Lycopid.
Physiotherapy:
- Laser therapy;
- UHF;
- UV irradiation.
Folk remedies
Is it possible to cure it with folk remedies? To dry the skin, you can use gauze dressings with herbal decoctions:
- chamomile;
- oak bark.
To prepare the decoction 1 tbsp. pour 200 ml of water over a spoonful of raw materials and simmer for 5 minutes over low heat.
For internal use , prepare an infusion of hazel bark (1 part bark, 10 parts water).
Keep in a water bath for half an hour. Cool and take 1 spoon every 2 hours.
Folk remedies can only be used as an adjuvant therapy. They cannot replace drug treatment.
Treatment of the disease
Therapeutic measures are prescribed depending on the age category, advanced stage of the disease and the presence of concomitant pathological processes. A diet that limits the consumption of sweet, spicy, fatty foods and potential allergens is also very important. Do not wet the affected areas. Wipe clean skin with antiseptic solutions based on chamomile, calendula and string. A sick person should use individual utensils and towels. Be sure to wash bed linen separately.
Pharmacy products
Treatment of the affected areas is carried out using the following antiseptic solutions: fucorcin, miramistin, chlorhexidine or boric acid. After the applied product has dried, treat the skin with the following medications: erythromycin ointment, tetracycline, ichthyol ointment, levomikol, salicylic-zinc paste, hyoxysone, baneocin. If there are blisters on the oral mucosa, you will additionally need to rinse with stomatidine and apply Metrogil-dent.
Also, the doctor often prescribes antibacterial drugs to suppress the activity of the pathogen (amoxiclav, augmentin cefazolin, erythromycin, sumamed, clarithromycin, doxycycline). All drugs and dosages are prescribed only by a doctor.
To eliminate itching, antihistamines are used: diazolin, suprastin, claritin. To restore normal microflora, the drugs Linex, Acipol, Lactiale are prescribed. To strengthen the immune system, it is advisable to use multivitamin complexes: Vitrum, Complivit, Supradin, as well as immunostimulants.
Treatment with traditional methods
Non-traditional treatments can only be used as auxiliary ones. Disinfection can be carried out using decoctions of sage, chamomile, oak bark, and string.
To increase the body's resistance to infections, you can take echinacea extract, cranberry juice, honey and garlic.
Contraindications and precautions
Streptoderma is a contagious disease. It can be transmitted by contact. Therefore, the patient must be isolated for 10 days until he ceases to be a source of infection for others.
During an exacerbation of the disease, the face should not be washed with water, so as not to spread the infection. The patient must have individual hygiene items and utensils. All cutlery must be thoroughly sanitized after use.
If the symptoms of streptoderma do not disappear during treatment, you should be further examined. This may be a signal of a disruption in the functioning of other organs and systems.
Complications of infection may include:
- dermatitis;
- eczema;
- diseases of internal organs;
- tissue abscess;
- autoimmune diseases;
- blood poisoning.
You can learn how to treat facial skin psoriasis from our article.
Treatment of the disease
If the foci of the disease are single in nature, the general condition of the patient does not suffer, and children have a normal immune status, then only local therapy is prescribed. In other cases, the treatment is supplemented with the administration of vitamins, restorative drugs, therapeutic UV irradiation, etc.
For the entire period of treatment, the patient must completely exclude contact with water. Healthy areas of the skin should be wiped with swabs previously soaked in water or chamomile decoction. Clothing made from synthetic fabrics provokes increased sweating. During the treatment period, you need to monitor the temperature and, if possible, wear only clothes made from natural fabrics.
If a child is diagnosed with dry streptoderma, he is isolated and quarantine begins for all persons who came into contact with him 10 days before the first signs appeared, this is the incubation period. A hypoallergenic diet is prescribed, everything fatty, spicy, and sweet is excluded from the diet.
Throughout the course of treatment, it is necessary to treat the skin in the affected areas. The blisters will be carefully opened at the very base using sterile needles. These areas need to be treated with a special compound several times a day. Then a dry bandage is applied to the affected areas, into which a special ointment is placed for disinfection. Crusts, which appear quite often when a patient has dry streptoderma, need to be lubricated with salicylic petroleum jelly. After a maximum of 20 hours, they can be removed painlessly.
If spots appear on the face, then jams may form that will go away for a long time. They should be lubricated with a special agent for speedy healing. Only a doctor can prescribe medications. If dry streptoderma lasts a long time and is rather sluggish, antibacterial drugs are prescribed, which should be taken for a week.
Preventive measures
In order to prevent dry streptoderma from appearing, it is important to carry out prevention. The following actions will help reduce the risk of infection:
- Healthy and fulfilling lifestyle. This helps strengthen the immune system.
- Immediate treatment of any damage to the skin, including bites, scratches, cuts, etc.
- Timely treatment of diseases occurring in acute and chronic form.
- Proper, balanced nutrition;
- Regular adherence to personal hygiene rules.
- Strengthening the immune system with vitamins and beneficial elements.
By following these simple recommendations, you significantly reduce the risk of this infectious disease.