A hematoma or bruise on the face is an unaesthetic sight, accompanied by pain. No one is immune from trouble, since bruises remain not only after a fight, but also from accidental contact with furniture, door frames, or after a fall.
The last factor explains the bruises on the face and body of small children. Parents of children know exactly how to remove a hematoma on the face, since they are faced with such situations and keep the necessary means for treatment in the first aid kit. These can be medicinal ointments, compresses, you can use the advice of traditional medicine. The bruise will not go away immediately, but it is possible to speed up the resorption of the hematoma.
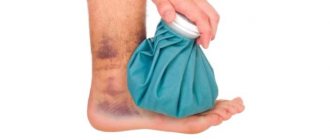
If there is a hematoma, apply ice
A subcutaneous hematoma itself is an accumulation of blood in soft tissues due to damage to blood vessels as a result of contact with a hard object. Depending on the severity of the bruise, a hematoma on the face may have varying degrees of manifestation. In total, doctors distinguish 3 degrees:
- light. Appears after a while, disappears after 3-4 days;
- average. It appears after a couple of hours in the form of swelling and pain;
- heavy. It appears after an hour, the pain is felt throughout the head, an examination is required for internal bleeding;
- very heavy. Paralysis of the damaged area, damage to the nose or eye, and fracture of the skull bones are observed.
Reasons for appearance
A hematoma, or bruise, is an accumulation of blood resulting from damage to blood vessels. It can be visually noticed by a local change in the color of the skin. Most often, bruises on the face and body appear as a result of injuries, bruises and other mechanical damage. Hematomas often form during dental treatment. They can also be caused by traumatic injuries to the oral cavity.
A significant reason to pay attention to your own health is a hematoma on the face that has formed for no apparent reason. In this case, the bruise may be a symptom of vascular disease or other pathological conditions. Hematomas on the face can form due to nutritional deficiency and long-term use of certain medications.
Main symptoms
The hematoma develops in several stages. With traumatic injuries, the first symptoms are pain and noticeable swelling. The skin tone in the affected area gradually changes. The bruise may be blue, cyanotic or purple in color. As the hematoma resolves, it again changes its color to yellowish and then disappears without a trace.
With serious bruises, the functions of the facial muscles may be impaired. In rare cases, a hematoma on the face may be accompanied by an increase in body temperature. Small and painless bruises can be treated independently at home. However, if the hematoma is extensive, appears after a serious injury, or for no reason, you should consult a doctor.
First aid for facial bruises
The size and color of the future bruise directly depend on what measures were taken immediately after the injury. It is necessary to begin treatment of a hematoma on the face with the use of a cooling compress. Use ice or any cold object. Be sure to wrap it in a clean cloth. A cold compress should be applied immediately after injury and should be kept in place for no more than 30 minutes. The effectiveness of this effect is explained simply: under the influence of cold, blood vessels narrow, thereby avoiding extensive subcutaneous hemorrhage.
If the hematoma on the face is large enough and painful, the use of medicinal painkillers is allowed. For injuries that result in bruising in combination with violations of the integrity of the skin, it is necessary to use antiseptics to wash abrasions and scratches.
Ointments for hematomas
Used to treat bruises with bruises and abrasions. External hematomas are treated with simple medicinal ointments and solutions for their speedy recovery.
If after an injury the victim feels pain and discomfort, then it is necessary to use an ointment with an analgesic effect.
Ointments for hematomas and bruises
If the cream is applied immediately after a bruise, a bruise will not appear at all.
If this is done after a few hours, the bruise will resolve within two days. If you use the cream every other day, everything will go away in three days.
Helps accelerate the resorption of bruises and the disappearance of bruises, reduces swelling. It has contraindications for hemophilia (blood clotting disorder).
Indovazin is a gel based on indomethacin and troxerutin.
Troxerutin strengthens the vascular wall, improves microcirculation, reduces fragility and permeability of capillaries.
Contraindicated in hemophilia (blood clotting disorder), ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, children under fourteen years of age and pregnant women.
Remedies for bruises based on Arnica
Arnica is a perennial medicinal plant that grows in the mountains.
Ointments based on it have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, regenerating and antibacterial effects.
Used for resorption of subcutaneous hematomas and bruises, muscle pain, abrasions, sprains, bruises.
Contraindications : during pregnancy, during lactation, with violations of the integrity of the skin, children under 18 years of age, with hypersensitivity, allergies. With prolonged use, blistering dermatitis may occur.
Heparin ointment
It also helps improve the absorption of heparin.
Benzocaine has an analgesic effect.
Heparin-based products are used for treatment from 5 to 15 days.
Contraindications: open wounds, ulcerative-necrotic processes, venous thrombosis, hypersensitivity.
Do not use simultaneously with antihistamines, NSAIDs and tetracyclines.
Allergic reactions may occur.
Troxevasin
Contraindications: hypersensitivity, allergic reactions (symptoms of dermatitis, urticaria).
Badyaga
Products based on this unique natural component have excellent absorption properties.
Badyaga is a freshwater sponge. Its skeleton consists of silica needles, which are interconnected by organic matter.
The effect of ointment with badyaga is to irritate areas of the skin with silicon needles.
This action leads to vasodilation and increased blood supply.
After applying the gel, the skin turns a little red and a slight warming effect occurs.
Treatment of hematomas on the face with medications
Today in any pharmacy you can find a wide range of products for healing bruises. The most popular ointments and gels among them are: “Indovazin”, “Rescuer”, “Badyaga”, “Ambulance”, “Troxevasin”, “Bruise-off”. They need to be applied directly to the affected area of the skin. “Troxevasin” contains troxerutin, a substance with anti-inflammatory properties, it excellently relieves swelling and restores capillaries. Gel "Indovazin" is another product that contains troxerutin, as well as indomethacin. This drug relieves pain, swelling and redness. There are restrictions on use: the product is not recommended for use during pregnancy and under the age of 14 years.
“Sinyak-off” is a drug based on leech extract, pentoxifylline and ethoxydiglycol. With timely use, this ointment can significantly speed up the process of hematoma resorption. When choosing a cream or gel to heal a bruise on the face, you must carefully study the instructions for use. Most medicines of this type are made from natural ingredients and are safe to use. But still, some of them have contraindications and limitations in use. If an allergic reaction occurs, further use of the selected drug should be discontinued.
Traditional methods
Not all methods of traditional medicine are effective and efficient. However, some of them are worth attention
- A solution of vinegar and iodine (1 tsp table vinegar and 5 drops of iodine). The mixture is applied to the bruise using a tampon and kept for no more than 20 minutes.
- A good remedy is iodine mesh.
- For the next recipe you will need 50 g of finely chopped parsley, which is poured with 250 ml of vodka. Use a cotton pad to moisten the affected area with the infusion.
- The washed aloe leaf is cut lengthwise and applied to the bruise, secured with a bandage or plaster.
- Arnica infusion (can be purchased at any pharmacy). Excellent helps fight swelling.
In addition, you can use other natural ingredients to remove bruises, such as plantain, burdock or coltsfoot leaves.
Folk remedies for quick healing of bruises
There are many traditional medicine recipes, invented by our ancestors, to combat hematomas. It is believed that a bruise will go away faster if, starting from the second day of its formation, a warm compress is periodically applied to the affected area.
How to get rid of a hematoma on the face using home remedies? Try applying a cabbage leaf to the affected area. Rinse it thoroughly first, dry it with a towel, and then beat it with a culinary hammer. This way the cabbage will give more juice, which has a healing effect. Compresses that stimulate the resorption of bruises are made from blue clay. The powder is dissolved in water to a creamy consistency. Then wrap it in cotton cloth and apply it to the hematoma for 40-60 minutes. There is also a known home remedy for hematomas, such as salt lotions. To prepare them, a strong brine is prepared from ordinary table salt. Gauze is soaked in the resulting liquid, applied to the sore spot and wrapped with a woolen scarf on top. Keep the lotion for 10-15 minutes.
Treatment without pharmaceutical drugs using lotions
Not everyone trusts pharmacy medications. Sometimes there is no money to purchase quality ointment. A remedy that helps to quickly cope with painful “decoration” of the face are compresses.
Vegetables, fruits and other products present in the kitchen are suitable for cooking. Let's look at the most effective recipes.
With apple cider vinegar, iodine and salt
Compresses based on apple cider vinegar are in demand, inexpensive to prepare and allow you to quickly forget about an unpleasant skin defect.
Prepare the following composition:
- Vinegar - 2 tbsp. L;
- Iodine – 0.5 tsp;
- Kitchen salt – 1 tbsp. l.
Soak a gauze swab in the solution and apply to the problem area for 15-20 minutes. Perform manipulations as often as possible, at least 3 times a day.
With beets and honey
Grate medium-sized beets and place in a colander to drain the juice. Add 1 tbsp to the remaining puree. Honey. The gruel is thoroughly mixed and applied to damaged skin.
If possible, place a cabbage leaf and a piece of polyethylene on top and secure with a bandage.
Leave the compress on for 20 minutes, during which time the bruised area will warm up well and be saturated with useful microelements that activate blood flow.
With starch
Potato starch helps quickly remove bruise marks. It is enough to prepare a starch-based compress: dilute a couple of tablespoons. Starch with a small amount of water. A dense paste should form at the exit.
The composition can be applied overnight. Just be sure to securely fasten the bandage.
With medicinal herbs
To prepare an herbal cocktail, take 2 tbsp. l. Wormwood, 3 tbsp. l. St. John's wort, 1 tbsp. l. Ledum and hop fruits. The ingredients must be dried and crushed. Pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave in a thermos for 3 hours.
Then soak a handkerchief or gauze swab in the infusion and apply it to the bruise. Keep the compress on your face until the cloth cools down.
When should you see a doctor to treat a bruise?
Hematomas appear from time to time on the body and face of almost every person living an active life. Most of us are accustomed to thinking of bruises as minor skin injuries. Often we do nothing at all to treat them. And yet, in some cases, a hematoma is indeed a reason to contact a specialist.
It is necessary to visit a doctor if bruises on the face appear for unknown reasons. Another reason for examination is an extensive hematoma on the face. What to do after serious injuries and how to properly treat a large bruise must be decided by the doctor. A visit to the hospital in this case is also necessary to exclude the possibility of a concussion and bone fractures. If the hematoma does not go away for a long time, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Causes and symptoms of bruises
The main causes of facial bruises: a fall from a height, a blow from a hard object, compression of facial tissue during road accidents or natural disasters.
The first sign of a facial injury is pain. This is a signal of damage or irritation of nerve fibers. The intensity of pain depends on the severity of the injury and the location of the affected area.
The most lasting pain occurs when the nerve trunks of the face are damaged. In this case, the injured person experiences sharp, burning and shooting pain. It intensifies with any movement of the facial muscles.
After exposure to a traumatic agent, the skin acquires a bright red tint. This is how the blood entering the interstitial space shines through the skin. Gradually its concentration increases, and the affected area changes color to blue-purple.
Gradually, the breakdown of hemoglobin begins in the hematoma. After 3-4 days, a breakdown product of blood cells, hemosiderin, is formed, which causes a green color, and on days 5-6 hematoidin, which is yellow in color.
This alternating change in the color of the hematoma is popularly called “blooming bruise.” In the absence of complications, the hematoma completely resolves within 14-16 days.
Reasons to immediately consult a doctor are the appearance of clear fluid from the ear, cyanosis (blue discoloration) of the area around the eyes, convulsions, loss of consciousness, nausea and vomiting. These are signs of a serious traumatic brain injury, requiring a detailed examination of the body and certain treatment tactics.
Classification of soft tissue bruises
In traumatology, bruises are classified according to severity.
This allows you to determine treatment tactics and assess the possible risk of complications. Bruises are characterized by minor damage to the subcutaneous fat. They do not cause concern, do not require contact with a specialist and resolve on their own within 5 days. There may be minor pain and blue discoloration of the damaged area.
Severe damage to subcutaneous fat. Bruises are accompanied by hematoma, swelling and acute pain. In this case, complex treatment with pharmacological drugs is necessary.
A severe bruise affecting the muscles and periosteum is often accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the skin. There is a high risk of bacterial infection. In these cases, a visit to a traumatologist is mandatory.
Rated as extremely severe. In this case, the functionality of the facial skeleton is impaired and the risk of complications from the brain is high. The condition of the injured person requires emergency medical attention.
Treatment of hematomas under medical supervision
There are several treatment options for complex and extensive hematomas. It is effective to administer medications by injection directly into the affected area. If there is a large accumulation of blood or the development of sepsis, the patient may be prescribed a puncture. During this procedure, the doctor inserts a needle under the skin and suctions out excess fluid. Some particularly serious and advanced cases (for example, if a hematoma on the face becomes inflamed after a blow) require surgical treatment.
The main goal of surgery is to remove the source of infection. After such an operation, a drainage is installed. To accelerate the resorption of hematomas, physiotherapy, ultraphonophoresis and cryotherapy are used.
What to do if the hematoma does not go away?
Sometimes the hematoma can spread to the scalp, neck and even chest.
Large hematomas take a very long time to resolve and may be accompanied by suppuration, which will subsequently lead to sepsis.
In such situations, the doctor performs a puncture - inserts a needle into the hematoma cavity and sucks out the fluid.
If suppuration begins, the source of infection is removed surgically. Then drainage is installed and antibiotics are prescribed.
In some cases, when the hematoma does not resolve for a long time, a repeat puncture with the administration of penicillin is required.
The patient experiences general malaise and fever. Often an infection is added to the inflammation, for example, due to diseased teeth.
A high temperature is a sign of an abscess, which may be accompanied by suppuration. The doctor cuts the hematoma and removes its contents.
Possible complications
Small bruises usually go away quickly and painlessly. But fairly large hematomas must be treated under the supervision of a doctor. If you receive serious injuries, going to the hospital is mandatory.
Treatment of a hematoma on the face should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist, since there is a high probability of developing inflammatory processes in the soft tissues of the body. With strong blows, a bruise can only be an external manifestation of the injury. Fractures of the skull bones and concussion without quality treatment can be accompanied by a wide variety of complications and pathologies.