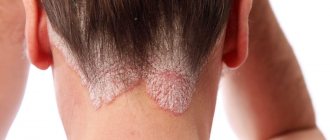
What is psoriasis?
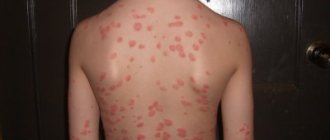
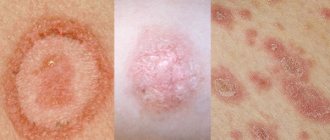
Psoriasis is a fairly widespread chronic skin disease, characterized by the presence of a monomorphic rash in the form of pink-red nodules with a loose silvery-white scaly surface. The disease lasts for years, alternating periods of relapses and remissions are observed.
Typically, this disease causes the appearance of dry, red spots raised above the skin surface, but some people with psoriasis do not have visible skin lesions. These spots, called psoriatic plaques, in most cases first form on places that are subject to pressure and friction - the buttocks, the surface of the knees and elbows.
However, they can also be located and occur on other areas of the skin, including the palmar surface of the hands, the scalp, the external genital organs, and the plantar surface of the feet. Psoriasis is a chronic disease, usually characterized by an undulating course. The patient may have both periods of improvement and remission (caused by therapeutic methods or unexpected), and periods of exacerbations or relapses (most often provoked by unfavorable external factors - stress, alcohol consumption).
The severity of the disease in different patients, or even in one patient during periods of exacerbation and remission, can vary widely - from local small damage to complete coverage of the body with psoriatic plaques. Often, over time, progression of the disease is observed (especially in the absence of treatment), an increase in the affected area with the involvement of new areas of the skin, exacerbations become more frequent and more severe. Some patients may experience a continuous course of the disease without unexpected remissions.
The fingernails or toenails are also often affected. Nail lesions can occur in the absence of skin lesions and be isolated.
Stages of the disease according to severity
In medical practice, psoriasis is also classified according to the severity of the disease and the area of affected skin:
| Stages of the disease | Characteristic |
| light | the skin is affected in several places, but the area of the rash is not critical; |
| average | psoriasis begins to progress, there are more lesions, and the affected area can cover up to 10% of the skin; |
| heavy | psoriasis reaches a critical level, the body surface is severely affected. |
The last stage of the disease, namely severe, is very dangerous for human health and life:
- Psoriasis not only affects the skin, but also the nail plate, which can lead to complete loss of nails. Some doctors mistakenly make a diagnosis, confusing the pathology with fungal diseases, and may prescribe the wrong course of medications.
- The disease distorts the joints, causing psoriatic arthritis. Psoriasis can deform the spine and tendon-ligamentous apparatus. These are the most dangerous pathologies that make a person incapacitated for the rest of his life.
- Against the background of the pathology, depression, increased fatigue, or exaggerated nervous excitability may develop, because people with this disease experience psychological discomfort and difficulties with socialization.
- In the severe stage, the patient requires disability and limitation of many types of work, as well as constant medical care and hospitalization.
In addition, a disease such as psoriasis can bring many psychological problems, especially in young patients. Psoriasis can appear at the age of 15, when the life values of a young person are formed. The disease interferes with normal life activities, causes discomfort, and disrupts sleep and rest patterns. People susceptible to this pathology experience serious difficulties in finding work and starting a family, as they are forced to hide their illness. Successful socialization in society is difficult.
Since psoriasis progresses slowly and is a chronic disease, it cannot be completely cured. However, with the help of competent comprehensive treatment, it is possible to maintain the remission stage longer.
Stages of psoriasis
One of the most important elements in the clinical picture and course of psoriasis is its division into stages. If for acute diseases this is less important, then in the case of chronic pathology, a clear identification of stages is extremely necessary. After all, in this way it is very easy to assess the course of the disease, determine its sensitivity to a specific treatment method and choose further tactics for managing patients with psoriasis.
The following stages of psoriatic skin lesions are distinguished:
- Progressive stage of psoriasis;
- Stationary stage of psoriasis;
- Regressive stage of psoriasis;
Progressive stage of psoriasisShe says that the disease is beginning its next exacerbation. After all, psoriasis is characterized by wave-like development. Clinically, the progression of the process can be recognized based on the following signs:
|
Stationary stage of psoriasisIt is an indicator of a reduction in inflammatory skin changes. These data indicate the effectiveness of the treatment and the need to change it to less aggressive methods. Clinical features of the stationary phase of psoriasis are:
|
Regressive stage of psoriasisThis is perhaps the most pleasant moment in the treatment of psoriasis, both for the patients themselves and for the attending physicians. She says that the exacerbation of the disease has been practically defeated and the main task for the near future will be to prevent further exacerbations. Signs of the regressing stage of psoriasis are:
The stage of psoriasis is based on the activity of the inflammatory process. The pattern of clinical manifestations is that the more pronounced the redness of the skin, the more active it is. |
Possible complications
Widespread psoriasis is a complication of ordinary organic damage and without the necessary treatment it can develop into more severe forms, such as:
- Psoriasis of the joints. This form is usually accompanied by inflammatory processes in the joints of the limbs, ankles, fingers and spinal column.
- Damage to internal organs - cardiovascular, endocrine and nervous systems.
- Arthritis mutilans. This form is a complication of joint psoriasis. It leaks, destroying bone tissue, resulting in curvature of the vessels, which causes their immobility.
Common psoriasis has three stages: progressive, stationary and regressive. The reasons for its development have not yet been precisely determined by medicine, but there are factors that provoke the occurrence of the disease. Without proper treatment, this type of psoriasis can develop into severe forms that are dangerous to health, especially in the progressive stage, which is why it is often treated in a hospital setting.
Symptoms of psoriasis
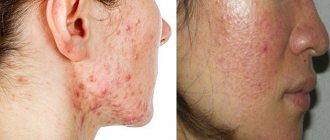
Classic symptoms of psoriasis include raised patches of skin that are red and covered with a silvery-colored flaky crust. They usually form on the elbows and knees. There are several types of psoriasis. Their symptoms can come in different combinations and vary in intensity. The most common symptoms of psoriasis are:
- Bright red psoriatic plaques, often covered with flaky crusts of a silvery hue. They can occur anywhere, but, as a rule, they are localized in the elbows, feet, lower back, knees, and hands. Approximately 90% of people with psoriasis have a similar symptom.
- Small bleeding areas located in places where the flaky skin completely peels off or breaks off.
- Nail problems are a very common symptom, especially in severe forms of the disease. Small dimples appear in the nails, the end of the nail separates from the nail bed, and the toenails or in some cases the fingernails become yellowish discolored.
- Itching, especially during spontaneous outbreaks of the disease or when the plaques are localized, for example, under the buttocks or breasts.
Symptoms of psoriasis may also include:
- Similar plaques located in the same places on both sides of the body.
- Outbreaks in which a large number of droplet-like plaques appear.
- Joint pain, sensitivity, swelling.
The course of this disease can be divided into several stages. The first stage begins with an exacerbation, when there is a constant increase in the number of fresh rashes. The second stage is the stationary stage, in which the pattern of rashes remains unchanged, they do not become smaller or larger.
Regression is the third stage, characterized by the absence of rashes. A person affected by psoriasis feels suffering not only from external manifestations - red papules and crumbling scales. Patients are forced to experience unpleasant sensations from itching, which appears periodically.
The general condition of the body with psoriasis remains unchanged, the disease does not affect the usual way of life, and does not require being in any specific conditions. But still, this is a serious, aesthetically unattractive skin disease, and if the process of its development is not controlled, it will entail a lot of inconvenience and restrictions, such as, for example, the inability to wear short sleeves or sunbathe on the beach.
There is also a danger of increased itching; when scratching, difficult-to-heal wounds are formed. If left unattended, psoriasis can spread to the joints, leading to psoriatic arthritis, in which the joints of the bones become painful or swollen.
Forms of the disease
Psoriasis can occur in the following forms:
Vulgar
Slowly progressive psoriasis, in which rashes merged with each other are visible on the skin, occupying most of the skin. With all this, the areas affected by the rash appear red, swell, and the skin begins to peel off, and quite severe itching is observed. This form of the disease can cause general weakness and cause enlarged lymph nodes, as well as other related problems.
Plaque
This form of psoriasis is quite painful.
Its characteristic features are as follows: the content of ESR and leukocytes in the blood significantly increases, general weakness and fever are observed, and small plaques appear at the site of redness, which are very itchy and painful.
teardrop-shaped
This form of the disease is one of the most difficult to tolerate due to the fact that it regularly worsens. Characteristic symptoms are: fever, severe itching and acute pain at the site of the skin lesion, and general weakness.
Articular
With this form of the disease, significant damage to joint tissue occurs. Visually, you can observe redness on the skin in places of inflammatory processes, as well as swelling. In addition, aching pain occurs in the affected joint area, which causes stiffness of movement.
With this form of psoriasis, the likelihood of the following diseases significantly increases: hypertension, myocardial ischemia, diabetes mellitus, cerebral circulatory disorders and others.
Causes of psoriasis
Psoriasis cannot be contracted through a handshake or through household and personal hygiene items. The disease appears between the ages of 18 and 25 years. It appears as large spots on the skin, located anywhere on the human body.
Stress is considered a fairly common cause of exacerbation, development or occurrence of the disease. Psoriasis can be triggered by varying degrees of emotional shock. To date, the reliable causes of psoriasis are not known.
Possible causes of psoriasis include disruption of the endocrine system, changes in immunity, severe shocks and hereditary predisposition, although this area has not been fully studied.
The only thing that can be identified for sure is the mechanism of the appearance of psoriatic rash. It is based on an immune imbalance. It is a disruption in the normal functioning of the immune system, in which the body's cells and antibodies begin to show aggression towards its own tissues. And since the skin is one of the mirror images of the general state of health, it is most often affected by any autoimmune reactions.
On the subject: the best foods that boost immunity
The following factors can lead to such a strong immune imbalance in the body:
- Genetic predisposition. The risk of developing psoriasis is much higher among immediate relatives, especially first-degree relatives;
- Severe stress or constant mental stress;
- Diseases of the endocrine system;
- Metabolic disorders, vitamins and microelements. In this regard, it is especially worth dwelling on silicon deficiency in the body;
- Intestinal parasites;
- Viral infections.
There is no need to dwell separately on all the listed reasons, since there is more than enough information of this kind in various sources. It is worth pointing out the new elements that scientists have established regarding the etiology of psoriasis.
Parasitic diseases
Numerous studies have revealed a direct connection between infection with parasites that live and multiply in the intestines and the incidence of psoriasis. It turned out that the number of carriers of parasitic infections is much higher among patients with psoriasis than on average among healthy people.
A special role among these pathogens belongs to roundworms, lamblia, whipworms, bovine and pork tapeworms. Their role in the development of the problem is explained by the fact that when they exist in the intestines for a long time, toxic products of their vital activity are constantly released into the blood. They have high allergenic abilities, which lead to immune imbalance. The result is psoriasis.
Silicon deficiency in the body
Another important point among the causes of this disease can be considered a deficiency of silicon in the body. This pattern was established on the basis of a spectral analysis of the blood of patients with psoriasis.
It turned out that this microelement plays a very important role in the body, in particular in the structure of the skin, blood vessels and connective tissue. Its deficiency can be caused by poor soil and impaired absorption from the intestines. Again, the main role in this case belongs to intestinal parasites, the growth of which consumes almost all the silicon that comes from the external environment.
Read more: Flint water - a remedy for 100 diseases
Causes and risk factors
Unfortunately, to date, medicine has not determined the exact prerequisites for the development of psoriasis, however, there are people who may be at risk for its occurrence.
The following factors lead to the disease:
- Constant stress and emotional turmoil.
- The presence of various infectious diseases, especially those caused by viruses.
- A fairly long course of therapy with potent medications (β-blockers, antimalarials, drugs based on lithium and arsenic, as well as combined oral contraceptives).
- Weakening of the immune system.
- Alcohol abuse and regular smoking.
- Various damage to the skin (cuts, injuries, etc.).
- Hereditary predisposition.
Hemoscanning as a diagnostic method
A new direction in the diagnosis of psoriasis, which is widely advertised almost everywhere, is hemoscanning of blood. Different sources provide the most contradictory data. The primary goal of this article is to critically analyze all possible options and draw constructive conclusions from the abundance of information. About everything and in order.
The essence of the hemoscanning method is a visual assessment of blood. This procedure requires a special electron microscope with a high degree of magnification, and only one fresh drop of blood from the person being examined. In this case, the assessment is made instantly, since the blood is placed under a microscope, and the resulting image is displayed on the monitor screen. In this way, you can examine the structure and relationship of the formed elements and plasma, and identify signs of changes characteristic of psoriasis. The patient can be present during this study, listening to the comments of the diagnostician. The method refers to diagnostic techniques of alternative medicine.
Based on the data described above, we can conclude that the method is simply ideal for diagnosing almost all diseases. After all, without unnecessary numerous studies, you can get detailed information about your health in a short time. This is the point that is alarming regarding its reliability. This is used by many scammers who, thanks to it, promote their drugs and dietary supplements. But we should not forget that the method actually has a fairly good scientific basis and really helps to roughly determine the supposed qualitative changes in the blood that are characteristic of many diseases. Psoriasis is included in their list.
Hemoscanning is a fairly good method for monitoring treatment and controlling the activity of the inflammatory process in psoriasis. It is unacceptable to use it as the only method. It must be complemented by various diagnostic methods of traditional medicine.
Classic diagnosis of psoriasis
Psoriasis is diagnosed by a dermatologist or therapist based on external signs. The disease is easily recognized by the characteristic location of the lesions on the body. Usually, a clinical examination is sufficient; the diagnosis is always unmistakable, since a patient with psoriasis has skin changes that are typical only for psoriasis. If the picture of the disease is unclear, especially at an early age, then additional studies may be required, namely a skin biopsy.
In this case, a small piece of skin is taken and the pathologist examines the tissue sample and gives a conclusion. There is no blood test for psoriasis, because the blood retains its physical properties. The exception is severe psoriasis, spreading over the entire surface of the body, contributing to dehydration and disruption of the water-salt balance of the blood.
If a patient has pain or swelling in their joints, they may be tested for psoriatic arthritis. Any specialist in diseases of the skeletal system, after an X-ray and a blood test, will prescribe the correct treatment, preferably this should be a timely measure
Suitability category “B” for psoriasis
To receive an exemption from the army for psoriasis, it is enough for the draft commission to approve your fitness category B. In accordance with Article 62 of the Schedule of Diseases, this category is assigned in two cases:
- For limited forms (less than three plaques on the skin),
- With common forms (the presence of three or more plaques on the skin of different anatomical areas).
To obtain category B for this pathology, you must provide the military registration and enlistment office with certificates and extracts from your medical record confirming the presence of the disease, undergo an additional medical examination according to an act from the military registration and enlistment office and receive a conclusion in the act confirming the diagnosis of psoriasis. You can learn more about how to obtain an exemption from military service for health reasons here.
Is psoriasis transmitted?
The question of the possibility of transmission of psoriasis from sick people to healthy people does not lose its relevance. This is due to the fact that patients with common forms of psoriasis look very noticeable against the background of the general mass. Not everyone understands that this disease is strictly individual and should not cause concern for others. This raises a lot of different types of questions:
- Is psoriasis contagious through contact? Numerous studies have found that psoriasis is not transmitted through direct contact under any circumstances.
- Is psoriasis transmitted sexually? Sexual relations with patients with psoriasis are absolutely safe, since this disease is a purely individual feature of the diseased organism.
- Is psoriasis transmitted to children during pregnancy? Pregnancy and childbirth are not directly related to the transmission of the disease from mother to child.
- Is psoriasis inherited? Genetic predisposition is one of the reasons for the development of psoriasis. The higher the risk, the closer your relatives have psoriasis.
Suitability categories and psoriasis
Depending on the form of the disease, a conscript may receive categories “B3”, “B”, “G” or “D”
| Suitability category | Category Description | Psoriasis grade |
| B-3 | Eligible with restrictions, subject to conscription | If there are no documents confirming the disease or the conscript has hidden the disease |
| IN | Limited use, transfer to reserve | For limited forms |
| G | Temporarily unsuitable, granting a deferment | When a disease is first detected, it is provided for treatment and examination |
| D | Unfit for service in the armed forces, decommissioned | Common form with complications |
How to treat psoriasis?
Treatment of the disease must be carried out by a qualified doctor and individually for each patient. Treatment depends on the patient’s age, general health, profession (the influence of occupational factors), gender and personal characteristics of the patient. The nature of the course of the disease and its stage are established, and provoking factors are eliminated (drinking alcohol, drug intolerance, allergic diseases).
Attention is paid to the general condition of the patient (psychological and physical). Normalization of the environment, rest, short hospitalization or change in work schedule can make changes in the course of the disease. If signs of psoriasis are detected, it is recommended to immediately seek medical help. It is the doctor who prescribes various drugs and other therapeutic methods.
One of the newest and most effective methods of treating psoriasis is genetically engineered biological drugs (GEBP), the second common name is biology.
The principle of action of these drugs is to act on various molecules that cause inflammation and contribute to the formation of plaques, damage to nails, and joints. The first GEBDs acted on the tumor necrosis factor, reduced the manifestations of psoriasis, but at the same time weakened the body's anti-infective (especially anti-tuberculosis) and anti-tumor immunity. Modern drugs block IL-17, which is responsible for the appearance of psoriatic plaques. The effect on interleukin IL-17a is targeted and only slightly affects the normal functioning of the body’s immune system. Such drugs are well tolerated by patients.
How to use genetically engineered biological drugs? GIBPs were developed quite recently, less than two decades have passed since their appearance. Unfortunately, psoriasis cannot be cured completely, but with the help of long-term constant use of biologically active drugs it can be brought into long-term remission. This is exactly the option when a person with psoriasis can lead a normal life without the presence of manifestations of the disease.
Treatment begins with several frequent injections (induction therapy), then only maintenance injections are required once at a certain period of time.
Often, an obstacle to the treatment of psoriasis with biologically active drugs is their high price. But now there are drugs available at affordable prices for independent purchase.
Therapeutic therapy can be depicted in the following table:
| Systemic therapy (indicated for severe cases or lack of effect from local treatment) | Local treatment (indicated in all cases of psoriasis alone or in combination with other methods) | Instrumental methods (Assigned differentiated and individually) |
|
|
|
On the subject: Treatment of psoriasis - a review of effective remedies
Essential minerals and vitamins for psoriasis
Silicon for psoriasis. In recent years, the issue of silicon deficiency as one of the causative mechanisms of psoriasis has been increasingly discussed. Therefore, it is advisable to include drugs based on it in the treatment complex at any stage of the disease. The mechanism of their action is in two directions. On the one hand, silicon, after absorption in the intestine, is transported to the affected skin, improving its structure, on the other hand, it acts as a sorbent, absorbing all antigenic complexes from the systemic bloodstream and removing them with feces.
Vitamin D for psoriasis. An extremely important trace element for the successful fight against psoriasis is calcium. But it is practically not absorbed without vitamin D. Therefore, preparations based on it are necessarily included in the treatment process. It is best to take them after the active phase of the disease has been transferred to stationary or remission. The role of calcium and vitamin D is that they stabilize cell membranes, reducing the release of inflammatory mediators into the blood. Before taking specific products, it is better to familiarize yourself with their composition, since most of them contain both of these components.
Fish oil for psoriasis. Any inflammation is accompanied by severe acidification of the environment and cell death. To better restore them and bring the immune system into balance, antioxidants are needed. Omega-3 acids found in fish oil are among the most powerful. Therefore, it is highly desirable to include them in the complex of treatment measures for psoriasis.
Lecithin for psoriasis. The result of psoriatic inflammation is massive death of epithelial cells. For their rapid restoration, phospholipids are needed, which act as the basic building material of all body tissues. One of the most powerful sources of these compounds is lecithin. By including drugs based on this substance, you can achieve faster relief of inflammatory manifestations and restoration of the skin (
Indications for hospitalization
Treatment at home is not always possible. In some cases, hospitalization is required. Indications for it are:
- manifestation of complications that appear during the course of the disease or as a result of treatment;
- rapid progression of the disease;
- the affected area is more than 25% of the skin;
- ineffective treatment at home;
- the need for procedures that can only be performed in a hospital (day or 24-hour);
- the presence of more complex diseases that require mandatory hospital stay;
- the need for constant supervision by specialists;
- a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition, with decreased performance, painful sensation.
Any of the above reasons can be a reason for admission to a day hospital or complete hospitalization for round-the-clock monitoring by specialists. With forced, but timely measures taken, the patient can be relieved of severe symptoms, which results in stable remission.
Drug treatment
The doctor selects a treatment regimen depending on the symptoms of the disease
The goal of treating the progressive stage of psoriasis is to stop the pathological process and achieve the transition of the disease to the stationary stage. This is done through drug therapy.
Progressive psoriasis, the treatment of which is chosen correctly, declines quite quickly. The following groups of drugs are used in therapy:
- glucocorticosteroids;
- indifferent ointments;
- cytostatics;
- immunosuppressants.
Glucocorticosteroids are the basis of drug treatment for the progressive stage of psoriasis. Prescribe medications for external use - various ointments and gels. Therapy can be carried out with betamethasone or hydrocortisone. Betamethasone is used for severe inflammation, hydrocortisone has a more gentle effect, therefore it is used for mild to moderate symptoms.
Indifferent ointments at a progressive stage are used to reduce inflammation. They are effective only at the early stage of the disease. Indifferent ointments cannot be combined with hormonal agents, so treatment is carried out in several stages.
To stop the pathological process, the doctor may prescribe an ointment based on a cytostatic agent, for example, Methotrexate or its analogues. This medicine stops the process of excessive cell division, which results in the formation of dense, scaly plaques.
Immunosuppressants are medications that come in the form of tablets or injections. They are necessary to reduce the autoimmune response as psoriasis progresses.
The exact treatment regimen depends on the severity and characteristics of the symptoms and is selected only by a doctor. It is not safe to treat psoriasis on your own with glucocorticosteroids or cytostatics.
Prevention
The main preventive measure for limited psoriasis is considered to be a healthy diet and a healthy lifestyle.
It is worth noting that this rule applies not only to relapses, but also to remissions. Periodically, you need to cleanse the body of accumulated toxins in order to eliminate overload of the skin. It is imperative to monitor the condition of the intestines, avoiding constipation and diarrhea.
You need to be especially careful when taking medications that are intended to combat other ailments.
In addition, you should cook food using sea salt, and also take relaxing baths with this trace element. The use of flaxseed oil, nettle and brewer's yeast will be beneficial.
It is also worth considering that if psoriasis recurs, you need to give up foods that contain milk and gluten.
Video on the topic
About the first signs of psoriasis in the video:
In conclusion, we can summarize that, despite the chronic form of this disease, the prognosis for patients with limited psoriasis is very favorable. With proper treatment and proper nutrition, long-term remission can be achieved, but this requires some effort.
It is pedantic adherence to all medical recommendations and a healthy lifestyle that will ultimately give a positive result. Modern alternative medicine promises such patients a complete cure, but the predisposition to psoriatic rashes will remain with them forever. The main thing is to follow the rules recommended by your doctor, because this is the only way to get rid of any ailments.