What is hypertrichosis and how does it develop?
Hypertrichosis is a disease characteristic of both men and women, but it is the stronger sex that is most susceptible to increased ear hairiness. Very often it is confused with hirsutism, although there are specific differences, for example, hirsutism occurs only in women, and hypertrichosis of the auricle is predominantly a male disease.
Hypertrichosis is believed to be inherited when a mutation in the gene responsible for hair growth occurs in the fetus. In the future, this gene is inherited and mainly through the male line.
The mechanism of development of acquired hair growth is diverse. It depends on the reason for the increase in the level of androgenic hormones in the body or the increase in the sensitivity of the ear tissues to their effects.
Typically, excess hair only brings aesthetic inconvenience. But, in exceptional cases, it is a symptom of malignant tumors, endocrine diseases and metabolic disorders.
Hypertrichosis of some parts of the body
This type of disease is divided, in turn, into subtypes:
- Lumbar hypertrichosis in women and men. Soft, long and dark hair grows in the lumbar region. Along with this, neurological signs and spinal bifurcation (spinal dysraphism) can often be observed.
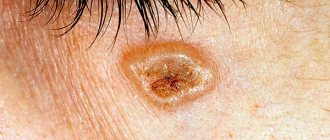
- Birth defects are nevi, abundantly covered with hairs. Such birthmarks can be light or black, reach different contours and sizes. There is a concept of Becker melanosis, and this disease manifests itself in the form of a nevus of huge volumes. The malaise is characterized by damage to the skin of an unchanged shape, which becomes pigmented even in old age.
- Prothoracic (presternal hypertrichosis) - hair growth in the chest area.
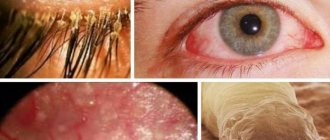
Hypertrichosis of the auricle and its causes
It is not always possible to say with certainty what can trigger a gene mutation that causes excess hair in the outer ear.
The main causes of congenital hypertrichosis are identified:
- infections suffered by the mother during pregnancy: rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes, influenza and others;
- abnormalities of the central nervous system and skeletal system;
- intoxication with alcohol, medications;
- maternal smoking and drug use during pregnancy;
- maternal malnutrition;
- severe pregnancy.
If a gene mutates under the influence of these factors, the epithelial cells degenerate and take the form of epidermal cells. This is fixed in the genome and is inherited, and can be transmitted through several generations.
Provoking factors:
- traumatic brain injuries and head surgeries;
- encephalopathy of any origin;
- severe and chronic infectious diseases;
- endocrine diseases and tumors of the glands: ovaries, pituitary gland, adrenal glands, thyroid and pancreas;
- porphyria, dermatomyositis;
- metabolic disorders, diabetes.
Hair growth can be caused by long-term use and overdose of local and systemic hormonal drugs (anabolic steroids, oral contraceptives, glucocorticosteroids). Drugs based on cyclosporine and minoxidil are dangerous.
The acquired causes of hypertrichosis of the auricle are varied, and it is not always possible to say with certainty what exactly triggered the increased hairiness. Any mechanical damage to the skin (injuries, cuts, surgeries) can lead to the formation of an increased number of hair follicles in the scar area. The same process starts if you shave or pluck vellus hairs - this stimulates the awakening of dormant follicles.
Hypertrichosis of the auricle can be caused by the following procedures:
- cryotherapy;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- depilation;
- puva therapy.
Hypertrichosis may occur during pregnancy due to hormonal changes in the body. Often this is temporary and goes away as soon as hormonal levels normalize. Also, if a woman experiences the development of male secondary sexual characteristics - virilism, then hair growth in the ear or other parts of the body is observed in 95% of cases.
What are the causes of the disease?
First of all, you need to take into account that the ailment is acquired at different periods of life or congenital. You can consider the main prerequisites for the formation of the disease:
- Hypertrichosis in children and adults as an indicator of cancer. There have been cases where a patient, several years before the discovery of a malignant tumor, had excess hair growth in certain areas of the body. This expression is associated with the mechanism of “revival” of hair follicles under the influence of various changes in the body.
- Genetic factor. During fetal development, viral and bacterial infections may appear, which provoke genetic mutations. The structure of epithelial red blood cells changes - they are transformed into cells with hair follicles. A simple gene is replaced by a mutated one, and as a result, hypertrichosis begins in women. The photo below demonstrates this disease.
- Exposure to certain medications. It is believed that this disease can be caused by taking penicillins, cephalosporins, corticosteroids and streptomycins. The disease develops as a side effect of the drug. In addition, under the influence of various substances used for medicinal purposes and increasing blood flow to the skin (medicinal mud, mustard plasters, hormonal ointments, paraffin), skin injuries appear.
- Hypertrichosis - what is it, and what other causes exist? It can also be a sign of other ailments: anorexia nervosa, mental disorders, fetal alcohol syndrome, porphyria, a consequence of traumatic brain injury, dermatomyositis, defects in the development of the skeletal system (disintegration of the vertebral arch).
- Excessive hair growth can be detected due to injuries to various areas of the body or constant thermal, mechanical irritation of the skin. In particular, the disease can form as a result of various burns, shaving, cryotherapy, at the site of scars, depilation, and others. There is even a concept of traumatic hypertrichosis, which appears in some areas of the skin, while in other places there are no symptoms of excessive hair growth.
Classification of hypertrichosis
Hypertrichosis occurs not only on the ears, but also on other parts of the body, so you should consider the general classification in order to have a better understanding of the pathology. It is classified according to the location of increased hair growth, forms and causes. First of all, the origin is distinguished: congenital or acquired.
Types of hypertrichosis of congenital origin are divided into universal and germinal. In the first case, it is transmitted to the child from one of the parents (hereditary), in the second case, a healthy gene mutates during an unfavorable pregnancy.
Forms of hypertrichosis of acquired origin:
- symptomatic - occurs as a symptom of various diseases: tumors, infections, diabetes, encephalopathies;
- medicinal - develops when using medications
- post-traumatic - hairiness forms in areas of injured and scarred skin;
- vellus - occurs with malignant tumors, characterized by covering the face and body with many vellus hairs;
- neurogenic - develops with damage to peripheral nerves, tissues of the brain and spinal cord.
By localization they distinguish:
- local hypertrichosis - hair growth is observed on one part of the body. This includes several subtypes: hypertrichosis of the auricles, lumbar, prothoracic, nevus. May affect certain parts of the face, genitals, limbs;
- general – excess hair growth spreads throughout the body or in several areas at the same time.
This classification proves that hypertrichosis of the external ear is a congenital and mostly inherited or acquired localized disease that occurs for a variety of reasons.
Types of disease
Hypertrichosis – what is it really? This is a very unpleasant disease, which also has its own varieties. Depending on the symptoms, degree and areas of hair growth, this disease can be divided into 2 main types:
- continuous hairiness or general hypertrichosis;
- disease of certain areas of the body or local hypertrichosis.
Symptoms and signs of hypertrichosis
The symptoms of hypertrichosis of the auricle are so specific that even with a visual examination, a preliminary diagnosis can be made. But increased ear hairiness does not always indicate hypertrichosis - small hairs, almost imperceptible, especially in men, are considered normal.
Classic signs:
- the ear canal is covered with hard hairs;
- vellus hair on the auricle becomes significantly thicker and darker;
- increase in area of hair growth;
- discomfort in the ear area associated with the awakening of the follicles.
Symptoms of hypertrichosis can be detected in newborns when a large number of soft and white or, less commonly, black and coarse hairs are visible on the ear. Sometimes this is considered a normal condition and they fall out on their own a few months after birth. If this does not happen or hair growth intensifies and covers surrounding areas, then consultation with a specialist is necessary.
With congenital pathology, excess hair growth usually begins to manifest itself in adolescence - in girls when the menstrual cycle is established, and in young people, symptoms of hypertrichosis of the auricle appear when, after puberty, a large amount of androgenic hormones are detected in the blood.
Symptoms of hypertrichosis of the auricle in middle-aged men manifest themselves not only in excess ear hair, but also in scalp baldness, which is caused by increased testosterone levels.
Hair growth in the ear area in women is often accompanied by signs of virilism: the voice changes, the mammary glands become smaller, the menstrual cycle stops and the physique changes.
Hypertrichosis in men
Excessive body hair in men appears during infancy or puberty (10–14 years). Society is tolerant of hairiness in men, and lush hair on the chest, back, legs and arms does not always give grounds to talk about hypertrichosis in men requiring treatment. However, if the hairline is combined with the developmental defects described above, then medical help cannot be avoided. In cases where the problem is only aesthetic in nature, you can get rid of hair by resorting to the services of a cosmetologist.
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of hypertrichosis of the auricle includes an external examination, medical history, laboratory tests and consultations with specialists in specialized fields. If congenital hypertrichosis is not confirmed, it is necessary to undergo examination by a dermatologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist or andrologist. Consultation with these specialists will help confirm or refute the development of hypertrichosis for reasons related to their specialization.
The patient is referred to an oncologist and for tests during which it is necessary to donate blood for tumor markers in order to exclude the presence of malignant processes before starting treatment. An examination by an otolaryngologist is necessary to exclude ENT diseases, and consultation with a traumatologist is necessary to exclude injuries to the brain and spine.
Diagnosis of hypertrichosis of the auricle includes:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- determination of hormone levels;
- tumor marker studies;
- blood for hidden infections, including sexually transmitted ones.
Additional examinations such as x-rays, computed tomography, MRI and ultrasound can exclude diseases of the internal organs and the development of malignant processes. When the diagnosis of hypertrichosis of the auricle is confirmed, the patient is prescribed special treatment, which should eliminate the cause of the disease.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, you must consult a dermatologist. At the first stage, he must examine the patient, carefully collect an anamnesis of the disease and differentiate hypertrichosis from hirsutism. To do this, he will prescribe some laboratory tests (determining the concentration of male sex hormones, analyzing the activity of the adrenal glands, studying gonadotropins).
In addition, a consultation with an endocrinologist, gynecologist, and other specialized specialists who can help determine the cause of the development of hypertrichosis is required. Only by eliminating it can positive results be achieved.
Treatment methods for hypertrichosis
Treatment of hypertrichosis of the auricle is carried out with medication and cosmetic methods. Drug therapy is effective only for acquired hairiness and is aimed at eliminating the provoking factor.
The drugs are prescribed by the doctor whose specialty is the cause of the pathology. If hypertrichosis of the auricle is caused by an increase in androgenic hormones, then medications are prescribed that reduce their levels.
List of drugs:
- Cyproterone.
- Abarelix.
- Dexamethasone.
- Diana is 35.
- Digoxin.
- Metipred.
If the disease is not caused by hormonal imbalance, treatment directly depends on the provoking factors. For tumors, surgery is necessary, and chemotherapy or radiation therapy may be needed. If inflammatory processes are present in the body, then antibacterial therapy is prescribed: Azithromycin, Amoxicillin, Flemoklav and others. Drug-induced hypertrichosis rarely requires treatment, usually after some time after stopping the medication, the level of hairiness decreases and disappears completely.
Treatment of hypertrichosis of the auricle does not always give results, so the only effective ways to get rid of excess hair are cosmetic procedures. You should not engage in hair removal on your own, especially plucking, so as not to provoke even more hair growth.
Which procedures are suitable:
- photoepilation.
- laser removal.
- electrocoagulation.
Children with congenital hypertrichosis are not treated until adulthood. All therapeutic actions are aimed at lightening the hairs. The most effective and efficient method is treating hair with 3% hydrogen peroxide.
Hypertrichosis in children
Congenital hypertrichosis usually appears at an early age; sometimes (extremely rarely) the body of a newly born child is already covered with dark, thick hair. Unfortunately, such conditions are symptoms of mental disorders and abnormalities in the structure of the skull . According to statistics, every sixth child with hypertrichosis is born to women suffering from alcoholism, while both girls and boys are equally likely to have problems with skeletal formation and mental retardation.
Attention! Hypertrichosis is a rare disease that is a manifestation of serious internal pathologies. Much more often you have to deal with relatively harmless increased hairiness, provoked by hormonal imbalance, the use of certain medications or mechanical irritation. Before you start fighting excess hair, you should consult a specialist!
Complications and prognosis of hypertrichosis
Complications of hypertrichosis include the spread of the pathological process. If the acquired causes are not eliminated, hairs may appear on the face, neck and any other parts of the body.
The consequences can lead to psychological problems - patients, especially women, begin to feel embarrassed about the defect and avoid people. Various areas of life suffer from this: relationships with family, friends, employees.
The prognosis of hypertrichosis of the auricle is in most cases unfavorable. It has been proven that most patients suffer from a congenital form of pathology, which cannot be eliminated. But among women there are very few patients with this diagnosis, and men try not to pay attention to excess hair.
Hypertrichosis: signs
This disease develops in stages, that is, the manifestations progress progressively. The patient begins to notice that intensive growth of vellus hairs dominates, and they grow over the entire surface of the body.
However, there are also other symptoms that significantly reduce the quality of life. With inherited hypertrichosis, the ailment is considered incurable, and it begins to develop immediately after birth. Increased hairiness in the baby spreads in the lumbar area, and tufts of long hair can be seen along the entire spinal ridge.
Even in children, hypertrichosis is inherited as a sign of irritability, nervousness, appetite disorder, restless sleep and bad mood. Caring parents need to pay special attention to such changes in the child’s behavior by immediately making an appointment with a local pediatrician.
The acquired nature of this disease also has its own manifestations, which make themselves felt by increased hair growth in the sternum, nasolabial folds, on the limbs and pubis. In addition, hair also grows on birthmarks, moles, representing a clear cosmetic defect. If you remove such “vegetation” yourself, the signs of the disease may only worsen. So neither the use of wax, nor laser hair removal, nor other cosmetic measures without prior therapy is indicated and even contraindicated.
Prevention of hypertrichosis
The diagnosis is difficult to prevent; many people do not know that they are a carrier of the mutating gene, unless their immediate relatives have had signs of increased hairiness.
But, if a person knows that he is at risk, he must adhere to the following preventive measures:
- do not injure the ear;
- avoid chemical and thermal exposure;
- take hormonal drugs with caution;
- undergo medical examination in a timely manner;
- treat infections promptly.
It is not recommended to use products that mechanically injure the skin: scrubs, peelings, aggressive masks. But, you should know that if the patient is hereditarily prone to hypertrichosis, then even preventive measures are not always able to prevent ear hair growth.
Be healthy!
General characteristics of normal hair growth
In the fetus, hair is embryonic, covering almost the entire surface of the skin; by the time of birth, as a rule, it disappears and is then gradually replaced by vellus and terminal hair. The former grow all over the body in children and adults, and even on the face of women. They are light, soft and have an average length of 1.5 mm.
Terminal hair is permanent. Unlike vellus, they are long, tough and dark in color. Their growth depends on the effect on the bulbs of androgens (male sex hormones - testosterone, etc.), which in men are synthesized in the testicles, and in women - in the ovaries and the adrenal cortex. In the cells of the hair follicles, under the influence of the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, testosterone is converted into highly active dihydrotestosterone, which, acting on target cells, regulates hair growth and loss.
However, hair follicles in different zones react differently to it. Cells of the follicles of vellus hair growth, as well as eyelashes and eyebrows, are insensitive to the influence of androgens. But in the pubic and axillary areas, follicles show high sensitivity even to low concentrations. Therefore, during puberty, at approximately the same rate in boys and girls (under the influence of adrenal androgens), active replacement of delicate vellus hair with coarse terminal hair occurs in these zones.
For the latter to grow in other areas (face, ears, back, chest), greater concentrations of androgens are required, which appear in older men. On the scalp, high levels of male sex hormones contribute to hair loss.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of congenital hypertrichosis, the expectant mother is recommended to give up all bad habits, spend more time in the fresh air, regularly visit doctors and follow all their instructions.
As for preventing the acquired form of the disease, it is very important to promptly consult a specialist for diagnosis and treatment of hormonal imbalances or any other disease that can lead to increased hair growth in certain areas of the body.
Hypertrichosis is not a death sentence, but it is a rather unpleasant problem, so the sooner you start looking for its causes and solutions, the better it will be for you.
Watch a video about congenital hypertrichosis
Treatment prognosis and possible complications
In most cases, the prognosis of therapy for hypertrichosis is favorable, but it greatly depends on the timeliness of treatment and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations. The disease is of a congenital nature and cannot be treated and it is only possible to eliminate excessive hair using various cosmetic methods.
If abnormal hair growth was associated with any pathologies, then patients may experience all sorts of complications. If tumor processes are detected, there is a high risk of death.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine can also help get rid of excessive vegetation. In treatment, decoctions of raspberries, walnuts, and white acacia root are used.
- A tincture of raspberry leaves helps to cope with hair growth. Plant raw materials are poured with vodka and left for a week in a dark place. Then take 10 drops of the product before meals. It is also beneficial to eat raspberries daily. The plant contains copper, which actively fights unwanted hair.
- To get rid of hypertrichosis, you need to drink a decoction of Datura root every day. The herb is brewed and infused for several hours. The product is used externally. To do this, use a cotton swab soaked in a herbal decoction. Store the medicine in the refrigerator.
- You can also lubricate hairy areas with green walnut juice. Some healers recommend using ash from nut shells in treatment. It is rubbed into problem areas. First, the ash is mixed with a small amount of water. Using lemon will solve the problem. Its juice is lubricated on the hair areas. Acid destroys the hair follicle and thins the hair structure.
In order not to aggravate the condition and provoke the progression of the disease, patients with hypertrichosis should not use massage procedures, paraffin masks, or skin peeling. It is necessary to protect the skin from any mechanical irritation that activates the hair follicles. It is important to limit the impact of nourishing cosmetics on the skin of problem areas. It is better not to use any cosmetic products.
Treatment Basics
As soon as it is possible to determine the true cause of increased body hair growth, you can proceed to directly eliminating the problem. Depending on the results of all examinations completed and tests taken, there will be two options for solving the problem: either drug therapy to solve the root cause (for example, problems with the thyroid gland), or cosmetic procedures.
Drug therapy
A gynecologist, endocrinologist or the same dermatologist, when studying the patient’s condition and the characteristics of the course of the disease, must select the most adequate treatment. So, if a person has been diagnosed with a disease of an endocrine nature, then all prescribed medications should be aimed at eliminating any endocrine disorders.
Corrective drug therapy is selected individually for each patient, because cosmetic procedures alone will not bring the desired effect. The same applies to gynecological problems, for example, polycystic ovary syndrome.
Depending on the severity and characteristics of the course of a particular disease, its treatment can be quite extended over time, so you need to be patient and set yourself up only for a positive outcome.
Important!
If there is a gynecological or endocrine underlying cause of hypertrichosis, shaving, hair removal or other methods of removing unwanted hair will most likely worsen the problem: the hair will grow back coarser and thicker.
Cosmetology procedures
This option for combating increased body hair is used as a symptomatic solution to the problem.
If, after all the diagnostic procedures that have been completed, the real cause of hypertrichosis has not been discovered, then all that remains is to get rid of the irritating vegetation in the old and proven way - hair removal.
In this case, the most optimal solution to the problem would be electrical hair removal, and, based on a person’s pain sensitivity threshold, it can take place both without the use of anesthesia and with local anesthesia.
The essence of the procedure is as follows: a special needle is inserted into the follicle of each hair in a selected area of the body, after which the device delivers an electric discharge, destroying the bulb. A hair that has nothing else to feed on falls out on its own.
On average, one such hair removal session takes up to half an hour, but more specific time costs are determined by the area of impact and the characteristics of the hair structure.
This method can completely rid a person of all visible manifestations of hypertrichosis, and among the disadvantages we can only highlight the comparative pain of the procedure performed and the duration of treatment. For example, to completely get rid of the manifestations of hypertrichosis in the chin area, you will have to undergo at least 60 sessions over the course of a year.
If we are talking about children and adolescents suffering from increased body hair, then electric hair removal is completely contraindicated for them. In this case, the hair is removed by using special creams (chemical depilation), and to make it less noticeable, peroxide bleaching can be used.
Prevention of hairiness
Unfortunately, congenital hypertrichosis cannot be prevented in any way; you just have to live with it and adapt.
The acquired form of hairiness can be prevented by eliminating the negative impact on risk factors that provoke the development of pathology. For example, you need to periodically check your hormonal status and learn to respond adequately to stress. By eliminating exposure to bad habits (alcohol, for example), monitoring your health, and choosing medications wisely, you can minimize the risk of developing hairiness.
As can be seen from the above, it is really difficult to live with hypertrichosis, both psychologically and socially. Therefore, it remains to advise those who do not have a genetic factor for the development of pathology to take care of their health. Contact your doctor promptly if you notice any changes in your hormonal levels or see the growth of excess hair. Hairiness detected in time is easier to treat.
Tell me, did you know about hypertrichosis, maybe you had it and were cured? Share your thoughts with readers in the comments and bookmark the article if it is useful and interesting to you.
Causes of the problem
Hypertrichosis of newborns can have the following causes:
The cause may also be a child’s illness:
- brain injuries, tumors;
- epidermolysis bullosa;
- local hair growth can be caused by trauma to a certain area of the body;
- dermatomycosis (fungal skin infection);
- anorexia, disorders of the central nervous system, epilepsy;
- endocrine pathologies.
It is believed that the sudden appearance of excessive hair is a harbinger of the development of a malignant tumor, especially if the cause of the disease has not been identified.
Causes
One case report reported that the patient was otherwise healthy, but no follow-up data were published.
With the exception of these unconvincing observations, all other described patients with acquired vellus hypertrichosis suffered from one of the malignant neoplasms. The age of the patients ranged from 19 to 79 years, and there were 3 times more women than men. Endocrinological studies carried out in some cases did not reveal any obvious changes.
Treatment
Treatment is effective if the underlying cause of abnormal hair growth can be identified and eliminated. If the functions of the endocrine glands are impaired, treatment by an endocrinologist is indicated. They also examine the neuropsychiatric status and identify functional disorders of the endocrine system as possible causes of hypertrichosis. If possible, stop local procedures and other influences that stimulate increased hair growth.
Congenital hypertrichosis has no cure.
For limited hypertrichosis, physiotherapeutic methods are used (hair is removed using electrolysis); various depilatories are also used for hair removal (the effect is short-term, hair can grow more intensively after using depilatory compounds; dermatitis is often present as a side effect of their use). If the hair is shaved with a safety or electric razor, there are no side effects of this kind. Hair is bleached using products containing a solution of hydrogen peroxide.
Famous people with hypertrichosis
- Saint Christopher is the Christian patron of bachelors, travelers and epileptics;
- Aceves, Jesus - Mexican actor
- Stefan Bibrowski is a Polish actor known as "The Lion Man"
- The Gonsalvus family is the first known case of hypertrichosis
- Fedor Adrianovich Evtikhiev - Russian showman
- Annie Jones - American showwoman
- Julia Pastrana - bearded woman from Mexico
- Sazufan Supatra - a girl with facial hair[1]
Hypertrichosis
Hypertrichosis is excessive local or general growth of dark and long hair on any part of the body.
The disease can be congenital or acquired. The Tenth International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) classifies hirsutism as hypertrichosis. These two diseases are manifested by pathological hair growth and often arise under the influence of the same factors. However, there are certain differences between them, which allows us to consider each of them as an independent nosological form.
Hirsutism is observed only in women. Pathological hair growth is observed in androgen-dependent areas of the body (on the face, chest, back, buttocks), that is, it follows the male pattern. Hypertrichosis affects people of both sexes and any age, and hair growth is observed on absolutely any part of the body.
Forms of the disease
So, there are 3 forms of the disease
Congenital universal - when the child is born completely covered with long vellus hair, it can also initially manifest itself only by the connection of the eyebrows with the scalp and further progression of hair growth covering all parts of the body (excluding the soles and palms)
Congenital local - local manifestation of hair growth. Often in combination with nevus - hyperpigmentation of individual areas
Acquired - due to the influence of external and internal factors.
Clinical hypertrichosis manifests itself in the form of hair growth up to 10 cm long or vellus hair.
Hair can grow everywhere or in limited areas of the body. For example, fusion of eyebrows, excessive hair on the legs, back and face are also signs of hypertrichosis with hair unusual for the nation (southerners are hairier than northern peoples).
At the same time, it is necessary to differentiate in case of excess hair growth:
hypergonadism, when it appears at 8-10 years of age;- tuberculosis;
- diabetes;
- alcoholism;
- alcoholic or vascular encephalopathy.
The covering of the entire body of a newborn baby with fluff is also hypertrichosis. This is how hypertrichosis manifests itself in the form of atavism.
What it is
The term “hypertrichosis” refers to excessive hair growth on any part of the human body, in particular, even in those places where the appearance of hair is not predicted by the action of male sex hormones - androgens.
All regrown hairs are usually dark and thick, and although men are more likely to suffer from their massive appearance (the disease is associated specifically with the Y chromosome), this problem often occurs in females, so this problem can be considered common.