Peeling of the skin represents an accelerated process of necrosis of body surface cells with their exfoliation, which significantly worsens the appearance of the skin, disrupting the natural balance of tissue regeneration. Due to the influence of many reasons, such changes are observed, contributing to excessive drying of the surface and active rejection of epithelial cells.
The visual characteristics of peeling represent the presence of small scales of the epidermis in certain areas of the skin, which manifests itself regardless of the type of skin, be it oily or combination. But most often people with dry skin suffer from such symptoms, when the root cause of peeling is genetically determined.
Make an appointment with a dermatologist by phone or by filling out the online form
| Select a clinic | Rash on back | Rash on cheeks | Rash on elbows |
Allergy
Dry skin can occur as a result of exposure to an allergen. Such a substance can be:
- Food - chocolate, red vegetables and fruits, milk, eggs, almost any product can cause food allergies
- Laundry detergents - stain removers, powders, conditioners, rinse aids
- Cosmetics - cream, powder, eye shadow, soap, shower gel, hair styling products, etc. (see list of harmful substances in cosmetics, creams).
- Household chemicals - any cleaning products for dishes, sinks, toilets (see the impact of household chemicals on health, how to make safe products yourself)
- Metals - jewelry, buckles, rivets, buttons, zipper
- Insect bites (mosquitoes, midges, bees)
- Medications.
Two types of allergic reactions may occur:
- contact dermatitis - in this case, a skin reaction appears after prolonged exposure to an irritating substance (not immediately). First, the skin turns red, itching and peeling appear (possibly the formation of bubbles with liquid). Later, the affected area of the body becomes covered with a dry crust.
- urticaria - in this case, the reaction occurs instantly after the action of the allergen - hyperemia, swelling at the site of exposure, and a strong desire to scratch immediately appear.
More often, a predisposition to allergies is determined at an early age, especially in children whose relatives suffer from hypersensitivity to any substance. At an early age, the most common occurrence is the appearance of redness and peeling in the area of the cheeks, buttocks, and natural folds (see diathesis in a child).
What diet is necessary for peeling skin?
Balanced hypoallergenic diets will help fight the disease. First of all, you need to identify those products that cause painful reactions. Eliminate chocolate candies and bars from your daily diet. Citrus fruits, raspberries, strawberries, pomegranate, melon, black currants can also cause dryness. Honey, fish, nuts, mushrooms, cocoa, caviar are included in the list of such products.
Salads seasoned with vegetable oil have a healing effect. You should include porridge, eggs, dairy products, carrots, tomatoes, liver, and seeds. These products help increase the level of vitamins A and E. The lack of vitamin B can be compensated by unrefined cereals, green vegetables, avocados, bananas, carrots, walnuts, and cod fish liver.
Application of moisturizing creams
Moisturizers are excellent products that restore the skin's moisture balance, but only when used correctly. They create a “water buffer” on the surface of the skin. Under conditions of normal air humidity, the cream binds moisture from the air and transfers it to the skin, but when the moisture content in the environment is low, the opposite process occurs: water from the skin is released into the environment and the skin begins to peel off. This feature must be taken into account when using moisturizing cosmetics.
Symptoms
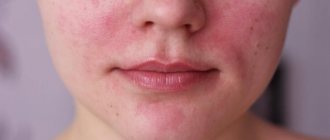
Clinical manifestations are: excessive peeling against the background of dry skin, roughening ( lichenification )/thinning of the skin, the appearance of small cracks, decreased skin turgor and elasticity due to lack of water and lipids. Patients may be bothered by mild itching, burning, a feeling of tightness and increased irritability of the skin. In cases of various dermatological, endocrine diseases and pathologies of internal organs, dry skin and excessive peeling may be just one of the symptoms among the various manifestations of the disease.
There are several stages of clinical manifestation:
- First degree. Dry skin is not constant, there may be slight flaking and a slight feeling of skin tightness. Typically, these symptoms quickly disappear with the use of moisturizers.
- Second degree. A constant feeling of dryness and tightness of the skin, visually noticeable fine-plate peeling, small wrinkles appear. The skin becomes sensitive, irritation and peeling may appear even with mild exposure to physical/chemical irritants or under the influence of minor negative environmental factors. Using cream does not completely solve the problem.
- Third degree. Severe dry skin, the presence of large-plate peeling, possible itching and erythema, with deepening cracks in the skin. Wrinkles. Emollients/moisturizers are not very effective.
- Fourth degree. Severe large-plate peeling, accompanied by degenerative changes in the epidermis/dermis.
Lack of vitamins
There are many vitamins and microelements, the lack of which can negatively affect the health of the skin and its appearance. Such substances are necessary in minimal quantities, but their contribution to the metabolic processes of the whole organism cannot be overestimated. For vitamin deficiencies, moisturizing the skin with cosmetics does not have any effect. The skin most often peels off on the face, knees and elbows (on the extensor side). Most often, the lack of the following vitamins affects the skin condition:
- Vitamin A (if there is a deficiency, there is a deterioration in the condition of hair and nails, and visual disturbances are possible, especially at night).
- Vitamin K (if there is a deficiency, there is increased bleeding and a long period of healing of minor skin lesions).
- Vitamin C (with a deficiency, wrinkles appear, the skin becomes pale, sleep patterns are disrupted, and gums bleed).
- B vitamins: B2, B3, B7, B12 (with insufficient intake, sleep disturbances, hair loss, bleeding gums, fatigue, dandruff, depression, nervousness are observed).
- Vitamin E (deficiency is manifested by the premature appearance of wrinkles, hyperpigmentation of the skin, and a long period of healing of skin injuries).
Hypovitaminosis can be caused by poor nutrition or disturbances in the absorption of foods (see vitamins in tablets - dispelling myths). But it should be borne in mind that an excess of some vitamins is also manifested by a deterioration in the condition of the skin, nails and hair (see why nails peel and crumble).
What diseases cause skin peeling?
There are many reasons that cause peeling skin. These include both ordinary allergies and more complex skin diseases. Dermatological diseases can be infectious or non-infectious. These include:
- Hereditary disease ichthyosis;
- Diseases of internal organs;
- Psoriasis;
- Dermatitis manifested in seborrhea;
- Lupus erythematosus;
- Fungal diseases of an infectious nature;
- Syphilis in secondary manifestations;
- Pityriasis rosea;
- Scarlet fever;
- Dry erytherma;
- Mycosis and xerosis.
With ichthyosis, the skin has a characteristic grayish tint. Its surface is covered with small scales. The patient experiences discomfort. His skin is peeling and itching. For this disease, no chemicals should be used. Even regular soap causes redness and irritation.
The main causes are sunburn, infections, HIV problems, dry skin in psoriasis, and skin injuries. Medicines play an important role. Seborrheic dermatitis occurs as a consequence of changes in the functioning of the skin. Sebum will be released in large quantities. This leads to progression of the disease.
Pityriasis rosea appears due to low levels of the body's immunity. This may be hypothermia of the dermis, insufficient nutrients. A cold or flu also worsens the condition of the body. It begins to react sensitively to external irritants in the form of soap, lotions, and other cosmetics. Cold wind, frost or hot weather increase pain.
Secondary syphilis appears as a skin rash. These invisible spots cause general malaise. The patient has a headache and a fever. Lymph nodes become larger. Peeling occurs suddenly. The deep layers need moisture. No amount of cosmetics can correct the situation. Treatment measures will give results if we find out the exact cause.
Dysbacteriosis
In newborns, peeling skin can be caused by dysbiosis. In this case, the baby may experience constant underweight, loss of body weight, pale skin, tummy problems (frequent regurgitation, flatulence, bowel irregularities). In adults, skin problems can also be associated with intestinal dysfunction. Patients often complain of a metallic taste in the mouth, alternating constipation and diarrhea, an insatiable desire to eat, rumbling in the stomach, flatulence, bloating, dry mucous membranes, headaches (see symptoms of dysbiosis).
A lack of bacteria in the intestines leads to disturbances in the process of digestion of food. Even with a complete diet (sufficient supply of nutrients, vitamins and microelements, optimal ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates), a person is not able to absorb them effectively, and the likelihood of developing vitamin deficiencies increases (see how to treat dysbacteriosis).
Classification
Based on etiopathogenetic characteristics, several groups of dry skin accompanied by excessive peeling are distinguished:
- Acquired. Associated with the impact of harmful environmental factors on the surface layers of the skin.
- Constitutional. At the same time, dryness and flaking of the skin are caused by genetic mutations leading to functional/structural disorders in the surface layers of the epidermis. For example, mutations of the FLG gene, which is responsible for the synthesis of filaggrin (filament-aggregating protein). Its deficiency leads to a disruption in the structure of the natural moisturizing factor (NMF), respectively, to transepidermal water loss from the skin.
- Dry skin and flaking due to age-related changes. There are several such periods: from the first day of a newborn and for 15-30 days after the birth of a child (in infants), which is due to the removal of caseous lubricant and a decrease in swelling of the skin. The second period (in a child from 4 to 8 years old), since during this period there is minimal activity of sex hormones ( cortisol , estrogen , testosterone , progesterone ), which is accompanied by a decrease in the production of sebum by the sebaceous glands. And the third period is old age (after 70 years), which is explained by involutional dystrophic processes in the skin and a reduced content of sex hormones, which leads to a decrease in the function of the sebaceous glands.
Hormonal changes
In the human body, the amount of estrogen produced directly affects the condition of the skin. This hormone controls the production of sebum, which is a natural moisturizer for the skin. Changes in estrogen levels can be observed in diseases of the endocrine system and problems in the functioning of the following organs:
- Thyroid gland
- Ovarian
- Adrenal glands (read about adrenal insufficiency), etc.
Hormonal changes await women during menopause (about 50 years). At this time, there is a natural decrease in estrogen levels (not associated with diseases of the endocrine system), which leads to skin aging, aging, loss of moisture and dryness. The skin begins to peel off, and the woman almost never leaves the feeling of tightness.
Call a dermatologist at home for peeling skin
Calling a doctor to your home will solve many problems. The patient does not have to make an appointment. He will be able to invite a specialist at a convenient time. In a home environment, it will be easier to talk about your problems. A dermatologist will be able to find out all the reasons related to the patient’s lifestyle. Draw up a treatment regimen after identifying all causative factors. In a confidential conversation, it would be better to offer recommendations on the use of cosmetics.
Helminthiasis
When infected with helminths (worms), in some cases, skin reactions may occur, including peeling and rashes. Along with such manifestations, there are problems with the intestines, increased body temperature, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, and signs of intoxication (poisoning by waste products of worms). Some parasites enter the human body through the skin, and an allergic reaction often occurs in these places. Some individuals parasitize muscle tissue, which can also cause skin manifestations (see signs of worms in humans).
Prevention measures
Diseases that cause scaly spots on the body in an adult or child can be prevented by the following preventive measures:
- daily hygiene procedures for the whole body, including the face and head;
- using only high-quality cosmetics and hygiene products, without adding carcinogens and allergens;
- eliminating contact with allergens that cause red spots on the hands and other areas of the body to itch and peel;
- use of medications only after a doctor’s prescription, in strict dosages;
- avoid exposure to open sunlight for patients prone to the formation of dermatitis, eczema and other skin pathologies;
- eliminate low-quality cosmetics, which can lead to the formation of red spots on the eyelids that will peel and itch;
- avoid contact with patients infected with viruses and infectious diseases;
- use ointments for peeling skin in a timely manner to prevent the pathogen from spreading throughout the body;
- daily proper nutrition, taking multivitamins as recommended by a doctor;
- periodic visits to a therapist with laboratory tests.
Many people do not understand why the skin on the face, chin, chest, legs, and wrists peels. To eliminate the process, it is recommended not to carry out treatment yourself. This can lead to a deterioration in the patient's well-being. This is especially true when a child has peeling skin all over his face. Without contacting a pediatrician, you may miss the early development of autoimmune diseases, allergies and dermatological abnormalities.
Demodicosis (parasitization of eyelash mites)
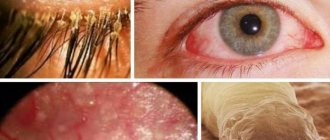
The tick often chooses the human face as its habitat, in particular the eyelids, eyebrows, chin area, nasolabial triangle, forehead or ear canals. At the injection site, peeling (in the form of scales or crusts), swelling, and the formation of swollen and reddened areas are noted.
If the parasite settles on the eyelids, then the person may experience rapid eye fatigue, local loss of eyelashes, difficulty opening the eyes in the morning (a sticky liquid is formed that prevents the eyelids from opening). When using cosmetics and detergents, the skin affected by the mite becomes very itchy and swollen. If the eye itself (its mucous membrane) is affected, then dryness, photophobia, and protrusion of capillaries on the surface are observed.
Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus may be one of the causes of peeling skin. A rather insidious disease, in the initial stages and during latent course it manifests itself only in the form of itching of the skin and its dryness. Subsequently, dryness of the mucous membranes of the mouth and genitals appears. Thirst and frequent urination are often observed, deterioration in mood, rapid fatigue, weight loss (there may be a sharp jump in the scales up or down), and depression are often observed.
When the concentration of glucose in the circulating blood is constantly high, the human body tries to reduce it, mainly through excretion in the urine. For these purposes, the lion's share of the free fluid found in the human body is used. It is the lack of moisture that leads to dry skin.
Erythema fissures (dry or asteatotic eczema)
The disease is chronic, with relapses occurring in the cold season. Severe peeling of the skin on the arms and legs is most often observed, but the disease can affect the entire surface of the body.
Along with peeling, there is general dryness and redness of the skin, a clear highlighting of all physiological lines (skin pattern) and the presence of linearly cracked areas (escoriations). Often the process is accompanied by inflammation, which gradually progresses (often with advanced fissured erythema, weeping and exudate are observed). The affected areas of the body hurt (see symptoms and types of eczema).
Treatment
What to do if your skin is peeling? Therapeutic measures should always be aimed at the main cause of the process (physiological or organic), only then will the necessary effect of therapy be achieved. In any case, only a doctor can determine the exact nature of the disease, so never delay visiting him.
However, whatever the reason, it is important to properly care for flaky skin and lead a healthy lifestyle.
General recommendations for lifestyle changes:
- always try to wear underwear and clothes only made from natural fabrics, this will allow the skin to “breathe” and speed up the recovery process of the affected areas of the skin;
- do not forget to take courses of vitamins and immunostimulating drugs;
- choose cosmetics with the least amount of chemical components;
- try to eat more fresh vegetables and fruits, eliminate processed foods and fried foods from your diet.
These measures will help cope with peeling skin if it is caused by natural factors. You should not neglect them if your skin problems are caused by any disease. But in this case, treatment of the disease manifested by peeling should still come first.
Etiological treatment includes taking medications intended to treat the disease that caused the peeling (antibiotics, antimicrobial or antifungal agents), as well as the correction of all chronic processes.
Symptomatic remedies to help alleviate the patient’s condition:
- ointments that accelerate healing;
- antipruritic agents;
- drugs containing a glucocorticoid component that reduce local inflammation and tissue swelling;
- if the cause of peeling lies in intestinal problems, then sorbents are widely prescribed.
Ichthyosis
The flaky areas of the human body with ichthyosis resemble fish scales (have a quadrangular shape), the disease itself is a pathology of keratinization of the skin and is inherited (manifests in early childhood). Often the scales are pigmented (hyperkeratosis). The disease has several forms.
Ichthyosis vulgaris
Ichthyosis vulgaris is the most common form, affecting people of different sexes with equal frequency. It appears on the entire surface of the body, except for flexion surfaces (armpits, neck, groin, articular cavities, etc.). Most often, scales are observed on the elbows and knees (on the outer extensor surface) and have different colors (from whitish to gray-black). In a child, the disease practically does not manifest itself on the face; in an adult, areas of dryness and peeling may occur on the forehead or cheeks. On the palms and skin of the feet there is flour-like peeling with a pronounced network-like pattern; nails are rough, brittle and deformed; hair thinning and hair loss are noted; teeth are highly susceptible to caries. Patients with ichthyosis have a hereditary predisposition to eye diseases (myopia), and relapses of retinitis and conjunctivitis often occur. Cardiovascular or liver failure may be diagnosed.
Recessive ichthyosis
Inherited only by men (on the X chromosome). The scales are shaped like black-brown scutes (reminiscent of crocodile skin) and have a fairly dense structure. Often the disease is accompanied by a child's developmental delay, disturbances in the formation of the skeleton, cataracts, epilepsy or hypogonadism (insufficient testicular function).
Congenital ichthyosis
The disease begins its development in utero (at 16-20 weeks of pregnancy). In a newborn, the scales can reach a centimeter in thickness, have different shapes, be completely smooth or slightly jagged, and the skin between them is deeply cracked. In infants, there is deformation of the mouth, ears, eyelid skin and skeleton. There may be bridges on the fingers and toes and missing nail plates. Most babies are stillborn or die a few days after birth.
Epidermolytic ichthyosis
One of the forms of congenital ichthyosis. The skin of a newborn has a bright red color (as with a thermal burn); the areas of the feet and palms are covered with a thick layer of white epidermis. The scales are torn off at the slightest touch, hemorrhages into the mucous membranes and skin are possible - such children do not live long. Over time, there are fewer flaky areas, but relapses of the disease occur quite often. In the areas of natural folds of the skin, by the 4-5th year of life, thick scales with a dirty gray color are formed. Subsequently, children are diagnosed with endocrine and nervous system disorders (paralysis, mental retardation, polyneuropathy, infantilism, etc.).
Lupus erythematosus (SLE)
A systemic autoimmune disease (own immunity destroys normal body cells, the decomposition products of which cause general intoxication of the body and multiple damage to internal organs). Women are more often affected by the disease.
Not all patients with lupus experience peeling skin. Most often, red papules (rash) appear on the nose and cheeks (shaped like a butterfly); hyperemic, dry areas may appear on the torso and arms. Often symptoms appear in the genital area and mucous membranes of the nose and mouth - there are multiple ulcers. The hair and nails of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus are prone to brittleness, and patches of hair loss occur.
Possible manifestations of the disease include:
- Joints (their symmetrical deformation occurs, pain increases).
- Blood (neutrophil leukocytes have fragments of nuclei from other cells, anemia).
- Cardiovascular system (endocarditis, pericarditis, myocarditis, atherosclerotic vascular lesions)
- Kidney (nephritis, blood and protein are found in the urine, the outflow of fluid from the body is disrupted, swelling progresses).
- Nervous system (convulsions, psychosis, peresthesia, encephalopathy, cerebrovasculitis).
- Gastrointestinal tract (stool disorders).
Patients may experience a sharp rise in body temperature, rapid fatigue, and frequent headache attacks.
Pityriasis rosea
With the disease, both itching and peeling are observed at the same time, progression is noted in the autumn or spring months, when the body is weakened by seasonal colds.
The first signs of pityriasis rosea can be confused with symptoms of a respiratory infection: the temperature rises, there is general malaise, fatigue, general weakness, and enlarged lymph nodes. Later, peeling spots are observed on the skin; they have symmetrical outlines and are localized in the torso and thighs. Initially, one large spot appears (up to 4 cm in diameter), its surface slightly rises above the surface of the rest of the skin, the color can vary from bright pink to yellow-pink.
Later, over the course of 2-3 weeks, the formation of small spots is observed, flaking at the edges, their size does not exceed 2 cm. Gradually, the plaques disappear, and in their place a pale mark forms, which disappears after some time. Pityriasis rosea is rarely the cause of peeling skin on the face. Itching may be absent or pronounced, often intensifying from the patient’s neuro-emotional stress.
Types of skin peeling
With skin disorders, different types of peeling may occur:
- Pityriasis;
- Lamellar;
- Large-plate.
The characteristic features of the first type are small scales. But they cover the entire surface, forming different shades. It all depends on the presence of certain disorders within the body. Silvery-white scales occur with psoriasis. Yellowish - a consequence of seborrhea. Dark ones are formed when the disease is ichthyosis.
Lamellar peeling is accompanied by the formation of larger scales. In the large-lamellar form, rejection of the stratum corneum in entire layers is observed.
Psoriasis
There are several forms of psoriasis, each of which has individual symptoms. The disease occurs as a result of activation of lymphocytes and an increase in the intensity of the growth of a network of small capillaries in the upper layers of the skin. There is the formation of a flaky, dry area of skin that itches, and severe tightness is also noted (see how to treat psoriasis).
Simple psoriasis
Inflamed areas of the skin are covered with plaques that rise above the rest of the surface; they are thickened and prone to stratification. The skin becomes thinner, and bleeding occurs at the slightest pressure. The disease is spreading quickly. Peeling can be observed on the scalp (the scalp).
Inverse psoriasis
Areas of dry, smooth, inflamed skin appear, which also protrude slightly upward. They are localized in the flexion zones of the arms and legs, as well as in the natural folds of the skin (groin area). Often such plaques are injured mechanically (by clothing, for example) and infection penetrates into the resulting wounds.
Guttate psoriasis
The patient's skin becomes covered with small areas of inflammation, their shape resembles dots or drops, and their color varies from pale pink to bright purple. The onset of the disease often coincides with viral diseases.
Pustular psoriasis
Many pustules (blisters with liquid) appear on a person's skin. Often they become infected with bacteria, and the fluid resembles pus. The skin under the foci of inflammation exfoliates, and the blisters themselves merge. Peeling of the skin is localized on the legs, arms and forearms.
There are possible summer and winter variants of the course of psoriasis. In the first case, under the influence of sunlight, the symptoms worsen; in the second, on the contrary, long-term remission is achieved.
Scarlet fever
The disease is of an infectious nature, caused by streptococci. The patient has signs of general intoxication, body temperature rises, chills begin, headache, and aches throughout the body. After some time, the skin becomes covered with small rashes in the form of dots, they have a bright pink color, the skin becomes pink. Scarlet fever is also indicated by a strong difference in the color of the skin on the face: the nasolabial triangle is pale, without a rash, and the cheeks “burn”, become bright red, and have a rash on them.
Often, a doctor diagnoses a sore throat during the initial examination; the lymph nodes become significantly denser and are painful on palpation. The tongue becomes covered with a brownish coating, which gradually disappears on its own. Its mucous membrane becomes bright crimson, and the shiny papillae are clearly visible.
About a week after the onset of scarlet fever, the rash disappears, leaving no traces or pigmented or depigmented areas. After a couple of weeks, peeling appears, first on the delicate skin of the neck, natural folds, and then throughout the body. The skin comes off in layers, starting from the last phalanx of the fingers, gradually spreading to the surface of the hands and soles.
Causes of roughness
Rough skin can occur in both adults and children. To understand how easily these skin manifestations can be eliminated, you should analyze the reasons for the changes that have occurred.
Firstly, skin type is determined genetically. The role of heredity in the appearance of rough skin is undeniable if such qualities are inherent in the skin from the very birth of a person. Love your face, because modern cosmetology methods allow you to eliminate unevenness and roughness.
It is possible to predict possible skin reactions to external procedures and cosmetics by compiling a so-called genetic skin passport.
Secondly, roughness and dryness of the skin in open areas can occur due to forced deprivation of moisture from the skin, for example:
- Under extreme weather environmental conditions. Low-temperature frosty weather, sharp winds, and scorching rays of the sun contribute to the drying out of the top layer of skin, causing dryness and flaking, which becomes a problem on our face.
- In case of improper skin care. Inadequate skin care, as well as excessive, too frequent use of cleansing cosmetics, can deprive the dermis of natural protection and cause roughness and peeling. A cosmetologist will tell you what to do in this case.
- When using low-quality cosmetics. The skin on your face may react with irritation and an allergic reaction to poor-quality chemical components of a cosmetic product for your skin type. Therefore, the selection of caring cosmetics must be treated with great attention.
Thirdly, the cause may be damage to the integrity of the skin. Even the most minor damage can cause not only roughness, but also death of the dermis. The skin, especially the face, should be carefully looked after. It is recommended to use a soft towel, and after washing, lightly pat your face, avoiding vigorous drying.
Fourthly, alcohol and smoking abuse. The face is a mirror of health, and changes caused by alcohol are difficult to compensate for with cosmetics. Alcoholic drinks have a diuretic effect, as the body, through increased work of the liver and kidneys, strives to quickly remove toxic waste products.
The liquid first leaves the subcutaneous tissue, so rough, flaky skin always accompanies a drinker. The barrier function of the epidermis is further reduced taking into account such an aggressive irritating factor as tobacco smoke.
Seborrheic dermatitis
The disease occurs as a result of the active activity of microbes in natural human secretions (sebum). Most often, the disease manifests itself in the scalp, facial skin, ears, chest, and back of the body (see seborrheic dermatitis on the face). Dandruff is a mild form of seborrheic dermatitis.
Irritation, redness and well-defined dry plaques (flaking) appear on the affected area of the body. The scales themselves are quite fatty and are formed as a result of the connection of neighboring nodules that have a yellowish tint. When dermatitis is localized in the area of natural folds (the area under the breasts, behind the ears, in the groin area), weeping may appear, subsequently the skin cracks and may fester. The progression of the disease is quite slow, but the involvement of significant areas of the body in the process requires immediate medical attention, especially in children (if additional symptoms are present: growth retardation, diarrhea).
Blepharitis
The disease manifests itself on the skin of the eyelids. The edge of the upper or lower eyelid thickens, turns red, and multiple scales (a mixture of epithelial cells and sebum) form on it.
The disease is accompanied by itching of the eyes, the eyelids become significantly heavier (it is difficult to open the eyes in the morning). With prolonged exercise, rapid fatigue is observed, the eye reacts painfully to bright light (photophobia), and tearing from the wind is often observed. Eyelashes can grow deformed, fall out profusely, and stick together. In some forms of blepharitis, ulcers or ulcers form along the edges of the eyelid.
Prevention for peeling skin
Preventive measures for this disease are the first steps. You should pay close attention to your diet. After washing in the bath or shower, you need to use cosmetics that soften the skin. In cold weather it is necessary to protect yourself from wind and frost.
If you cannot solve the problems yourself, then seek the help of a specialist.
Methods for diagnosing skin diseases:
- Diagnosis of skin diseases
- Diagnosis of skin diseases at home
- Diagnosis of allergic skin diseases
- Diagnosis of bacterial skin diseases
- Diagnosis of viral skin diseases
- Diagnosis of hair diseases
- Diagnosis of nail diseases
- Diagnosis of skin tumors
- Blisters on the skin
- Dermatoscopy
- Demodex tests
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections
- Mushroom tests
- Skin scraping
Secondary syphilis
With secondary syphilis, skin lesions rarely peel off, but if this happens, dryness is noted only at the edges of the rash. They themselves never merge, have a dark red color, are quite dense, round in outline, and are flush with the skin. Patients do not experience pain or itching. The lesions disappear on their own, leaving no depigmented areas of skin or scars. The formations are distributed over the entire surface of the body, including areas of the feet and palms.
It happens that the rash with secondary syphilis has the form of papules, then it protrudes slightly above the main level of the skin and is prone to fusion of nodular areas. Papules may affect the mucous membranes of the mouth, genitals, and larynx. When they are localized in natural folds, weeping is observed, later erosion is formed, from which liquid is constantly released. A papular and pink rash may occur simultaneously.
Additional signs of secondary syphilis may be baldness. Its lesions can be small or reach large sizes. In women, syphilis can provoke the formation of depigmented areas on the skin of the neck, front armpits, décolleté, back, abdomen or lower back. The areas do not peel, do not cause discomfort (pain, itching), and are surrounded by hyperpigmented cells. In men, the voice becomes hoarse, this indicates damage to the vocal apparatus by the causative agent of syphilis.
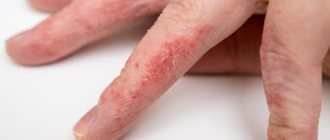
Peeling on the arms and legs
Considering the abnormally large number of dying epidermal cells on the upper extremities, one will have to study a long list of their focal localization.
Most often, inflamed areas are found on:
- brushes;
- fingertips or fingertips;
- bends near the elbow joints;
- forearms;
- wrists.
Occasionally, the inflammation progresses so much that it even reaches the armpits, gradually descending down to the abdomen.
Whatever rashes on the shoulders puzzle the victim, the first step is to eliminate aggressive chemicals from daily use. These can be either powders that leave marks even on the back, or cleaning products. Some particularly sensitive patients suffer even from simply drinking water that contains heavy particles.
But in this case, peeling will be observed not only on the nails and hands, but also near the thighs, on the chest, in the intimate area, because the whole body is washed with the same water. That is why doctors recommend not trying to mask peeling using foundation, and not looking for how to relieve a syndrome whose name they do not know on their own.
It is likely that the source of the skin disease prone to dryness was:
- eczema;
- psoriasis;
- dermatitis of various origins.
When a patient’s attack begins suddenly, accompanied by itching and burning, then with a high degree of probability the diagnosis will include a mention of some kind of dermatitis. Not only local lotions, but also medications will help cure it. A specialist will explain the algorithm for how to clean lamellar peeling with various tablets.
All the same things can be diagnosed for people who are faced with problematic irritation of the heels, entire sole, and calves.
But if only the lower extremities are affected, the likelihood of a number of other diagnoses increases:
- fungal infection;
- diabetes;
- hyperhidrosis;
- fluid deficiency.
For each individual case there are own recipes. Almost all courses of treatment for feet with peeling include mandatory intake of vitamins to support the functioning of the liver and blood vessels.
In rare cases, psychosomatics or cancer cannot be excluded. Oncological neoplasms of benign and malignant types are even found near the nipples, testicles, on the labia, buttocks, scrotum, penis, and around the anus. Therefore, if you find strange peeling in the perineum along with itching, you should immediately consult a doctor. There is no need to try to look for what an oncological lesion of the foreskin looks like, or to find out how herpes on the pubic part differs from mycosis.
Diagnostics should be entrusted to professionals who will conduct a thorough, in-depth analysis in order to then determine how to cure the pathology.
Fungal skin infection
Fungal infections can also cause flaking of the skin. In each area of the body, mycosis can manifest itself with different symptoms.
Feet and palms
In most cases, fungi settle between the toes or in the plantar and palmar parts of the extremities (see foot fungus). Peeling is mild, and slight inflammation may occur. The skin between the fingers bursts, the cracks are quite painful and do not heal for a long time. On the plantar and palmar parts, the skin thickens, becomes rough, and a whitish coating (floury peeling) may appear in the grooves. Blisters may appear on the foot and palm; they tend to merge and subsequently crack and form erosions.
Smooth skin areas
In such areas, fungi form a round-shaped lesion with slight peeling; the color can vary from whitish to brown. The growth of the spot occurs along the periphery, the entire zone rises slightly above the skin level. There is no inflammation.
Groin area
Fungi affect skin folds, the upper inner thigh, lower abdomen, and buttock area. The lesions are bright pink or red in color, very flaky and inflamed. Clear boundaries of the spots are observed.
Hairy area of the head
Scalp fungus is more often diagnosed in children. The lesions have clear outlines and are devoid of hair (at the first stages, their weakening, breaking off and loss are noted). The spot has the shape of a tubercle and may acquire a yellowish color with scales and crusts (sometimes with the presence of blood).
Onychomycosis
Often, nail fungus affects surrounding tissues. In this case, the skin at the edge of the nail plate peels off, and its stratum corneum thickens.
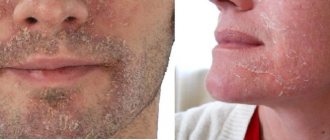
Face
The area below the lips (chin, neck) is most susceptible to infection with fungus. The nodes have a lumpy, scaly surface with a red or purple hue. When a bacterial infection occurs, the pustules acquire a yellowish tint.
More often, dry skin and flaking are caused by age-related changes, an allergic reaction or improper care. Low air humidity, use of medications, chlorinated water, hot bath, adherence to a strict diet, vitamin deficiency can also cause dryness. In this case, special treatment for skin peeling is not required.
Possible causes of peeling skin on the neck
Atopic dermatitis
Rough skin on the neck can occur for various reasons, including the result of illness.
Allergic reactions
Allergy is a chronic disease in which an inadequate, unwanted, unexpected reaction of the immune system to substances that do not usually cause negative consequences occurs.
Allergens can be:
- medicines: retinoids, diuretics;
- products: citrus fruits, eggs, milk, seafood, honey;
- plant pollen;
- household chemicals;
- low-quality jewelry;
- cosmetical tools;
- personal hygiene products;
- fabrics.
Atopic dermatitis is often observed, the first symptoms of which in infants are called diathesis. The affected areas become red and begin to itch. A rash, hardening, and swelling appears. The child's sleep is disturbed.
In childhood and adolescence, the elbows, cheeks, chin, and area under the knees are affected; in adults, the neck, palms, and fingers are affected.
Atopy develops in the presence of provoking factors:
- genetic predisposition;
- dysfunction of the epidermal barrier;
- immunological mechanisms;
- environmental triggers.
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic disease. Periods of exacerbation are followed by remission.
Stressful situations
Stress, anxiety, constant worry, fears are the cause of changes in the condition of the skin.
The dermis contains nerve endings, which, when the psychological state is disturbed, begin to send random nerve impulses. This leads to disruption of blood circulation, cell function, sebum secretion, allergic reactions, loss of moisture, etc. Peeling and redness of the skin are possible.
Demodicosis
Demodicosis
Demodicosis is a parasitic disease. Its causative agent is an opportunistic microscopic mite of the genus Demodex.
The causes of demodicosis are not clear. Experts believe that deeper penetration into the skin from the hair follicle and active reproduction of mites are facilitated by:
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- hot climate;
- constant nervous tension;
- disruptions in the functioning of the endocrine system, liver, and gastrointestinal tract;
- exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
The appearance of a demodectic lesion leads to the destruction of epithelial cells and disruption of the epithelial barrier. As a result, the waste products of the parasites enter the surrounding tissues and cause dryness, peeling, redness, itching, and rashes.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic disease characterized by an accelerated life cycle of epithelial cells. This leads to their accumulation on the surface, the formation of clearly defined red plaques, and pronounced silvery peeling.
The neck, mainly the back, scalp, nails, joints, and hands are affected.
It is believed that the cause of psoriasis is a genetic predisposition.
Parasites
The waste products of parasites are dangerous allergens. Therefore, allergic reactions are often the result of helminthic infestations.
The presence of parasites in the body leads to an increase in atopic dermatitis and other allergic diseases.
The allergy is resistant to traditional treatment and may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Insects and arachnids
Insect and arachnid bites sometimes cause peeling, itching, redness, swelling, and pain.
In severe cases, joint pain, chills, nausea, vomiting, headaches, suffocation, and anaphylactic shock are possible.
Infections
Herpes occurs with reduced immunity
Skin infections are diseases caused by pathogens (viruses, bacteria). These include:
- scabies;
- chickenpox, measles, scarlet fever;
- herpes;
- lichen;
- fungal infections
The diseases have different symptoms, but all have rashes and peeling.
Avitaminosis
Long-term poor nutrition causes vitamin deficiency. A person feels chronic fatigue, constantly wants to sleep, gets tired quickly, becomes irritable, and is susceptible to viral infections.
The skin becomes dry and rough, cracks and rashes appear. With a lack of iron in the body, the epidermis becomes pale and dry.
Peeling means a lack of unsaturated fatty acids omega-3, vitamins A, D. Vitamin E deficiency is manifested by brown pigment spots.
Hormonal imbalance
Hormones directly affect the condition of the skin. Dryness and flaking of the neck at the front cause problems with the thyroid gland.
Hormonal imbalance is observed:
- in pregnant women;
- in adolescence;
- during menopause.
Endocrine diseases provoke metabolic disorders and cell dehydration, which affects the epidermis. Treatment should be prescribed by a specialized specialist.
Diagnostics
If there is a suspicion of the presence of a disease, it is necessary to carefully examine the questionable foci. It is important to determine:
- The nature of the spots (tubercle-shaped, merging, single, weeping, etc.)
- Outlines (clear, blurry).
- Color of formation (whitish, pink, red, brown, purple, brown, black, etc.)
- Sensations (itching, pain, pinching).
- Associated phenomena (general weakness, fever, headache, vomiting, blood in the urine, joint pain, etc.)
To identify and cure the disease, you must consult a doctor. Self-medication is unacceptable. It is quite difficult to make a diagnosis at home; it is often necessary to undergo several tests, study scrapings in the laboratory, some cases require mandatory examination of the material for malignant formations, and analysis for syphilis. It is necessary to perform a full range of studies. Only after this will the doctor tell you how to get rid of peeling skin forever, and whether this is even possible.
| Cause | Character of peeling | Localization location | Presence of a rash | Additional signs |
| Cracked erytherma | smooth, does not protrude above the surface of the skin | legs, arms, entire body | No | there are linear cracking of the skin, pain syndrome |
| Ichthyosis | smooth, shaped like fish scales | does not affect flexion zones (armpits, popliteal area, inner elbow area, groin) | No | pigmented scales, nails and hair brittle, thin |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | tubercles present | nose, cheeks, rarely: arms, torso | nose, cheeks, rarely: arms, torso | there are signs of damage to the joints, hematopoietic, nervous system, gastrointestinal tract and other organs |
| Pityriasis rosea | lumpy surface | torso, thighs | No | foci of peeling have the form of spots, the initial spot is up to 4 cm in diameter |
| Psoriasis | areas raised above the surface of the skin | natural folds of skin, scalp, legs, arms, forearms | No | the skin itches, feels tight, increased bleeding, possible formation of pustules with fluid |
| Scarlet fever | skin peels off in layers | whole body | yes, in the initial stages of the disease | there are symptoms of general malaise in the initial stages of the disease |
| Seborrheic dermatitis | plaques have clear outlines, pinkish or yellowish color | face, ears, back, scalp | No | plaques feel greasy to the touch |
| Blepharitis | scales have a yellowish tint | eyelid skin | No | eyelids swell |
| Secondary syphilis | only the edges of the spot peel off | skin and mucous membranes | papular or pink (possibly both at once) | papules grow together and are located mainly on the mucous membranes; the pink rash does not grow together. |
| Fungus | peeling in layers or rounded areas of skin | entire body surface | No | predominantly rounded outlines of the focus of fungal infection |
| Helminthiasis | varied | any area of the body | may be present | digestive disorders, symptoms of intoxication |
| Demodicosis | yellow records | face (rims of eyelids, eyebrows, nasolabial triangle, chin) | No | severe itching, swelling, hyperemia |
| Allergy | varied | any area of the body | may be present | hyperemia is observed, itching may be present, blisters form, a reaction occurs after exposure to an allergen |
| Lack of vitamins | dry skin | any area of the body | No | In parallel, there is a deterioration in the condition of hair and nails, increased fatigue, weakness, bleeding gums, the appearance of wrinkles, and aging skin. |
| Dysbacteriosis | dry skin | any area of the body | No | indigestion, weight loss, hunger |
| Hormonal changes | dry skin | any area of the body | No | coincides with the onset of menopause, estrogen levels decrease, skin tightness is noted |
| Diabetes | dry skin | any area of the body | No | the skin itches, urination increases, and symptoms of depression are present |
| Climate change | dry skin | exposed areas of the body | No | the frequency of appearance coincides with the change of seasons |
| Using moisturizers | dry skin | areas exposed to cosmetics | No | occurs after using a cosmetic product |
Author:
Selezneva Valentina Anatolyevna physician-therapist
Causes of very dry neck skin
The neck is not only a very crooked part of our body, glorified by artists and poets. It is also an object of close attention due to its increased sensitivity.
Medical reasons ↑
Quite often, many women and men experience certain unhealthy manifestations on the neck: peeling, spots, rashes, premature formation of wrinkles, redness and dryness. Let's try to analyze in detail the causes and possible solutions to just such a problem as redness and dryness of the skin on the neck: erythema, lichen, ichthyosis, dermatitis, fungal infections, eczema, diabetes.
This is a short list of diseases, one of the symptoms of which may be redness and even itching. However, there are a number of other reasons and factors that lead to similar phenomena on the neck and face.
To accurately weed out serious health problems and focus on cosmetic techniques and medications that will relieve symptoms and bring your skin into complete order, you will most likely have to visit specialists such as an allergist, dermatologist, infectious disease specialist, neurologist, who will find out the causes and They will prescribe treatment or send you to a beauty salon.
Other common reasons ↑
Peeling of the skin is the accumulation of excess dead skin cells, which occurs due to a violation of the mechanism of keratinization and exfoliation of the upper layers of the epidermis. If the skin peels and turns red, you can easily eliminate this if you get rid of some of your bad habits and acquire new ones that benefit not only your appearance, but also the body as a whole, namely:
Avoid swimming in hot water.
Perhaps you are taking baths too often and for too long?
Most likely, your skin is dry and simply does not receive a sufficient dose of hydration.
You are not properly caring for the largest organ of our body - the skin. In particular - on the neck.
Frequent visits to a swimming pool with highly chlorinated water.
Try to dress according to the weather: in the cold season, be sure to cover your neck with a fashionable, stylish scarf made of natural fabric.
Choose high-quality caring cosmetics. If necessary, use the services of a cosmetologist. Any redness is a reason to consult a specialist and find out why this is happening.
To restore a healthy, young, well-groomed appearance to your hair, nails, and skin, your body should not lack vitamin A and other important microelements.
Eat sensibly. The cause may be an unhealthy diet.
Drink at least 2 liters of clean water per day (not counting coffee, tea, compote, cocktails).
Quit smoking, reduce the consumption of alcoholic beverages to a minimum or also give up.
Do neck exercises regularly. This will allow the skin to be more elastic, firm, and normalize its balance.
In parallel with using other methods to eliminate redness, peeling and dry skin (we mean proper care, masks and peeling), eliminate as many of the above factors as possible, which have an extremely negative impact on the condition of the skin in the neck, face and décolleté.
Moisturizing masks ↑
Peeling and dry skin can be visually removed with the help of active moisturizing, which the problem area really needs. To do this, first of all, use home remedies that your body is accustomed to.
Take half a peach or apricot and half a banana, add a quarter glass of warm milk. Beat everything with a blender and apply this composition in a thick layer to the cleansed neck and décolleté. Leave for 20 minutes.
Add a spoonful of sour cream or cream to 2 tablespoons of cucumber pulp.
Essential and base oils perfectly moisturize the skin. The neck is very fond of olive, almond, tea rose, coconut, primrose oil, sea buckthorn, and cocoa.
Here's how to use them correctly: combine 3 drops of essential oil with a base oil (olive or almond) heated to 40 degrees, add a little honey, oatmeal and mix everything thoroughly.
You can apply this composition for longer than 20 minutes, including on the face.
The simplest option may be this: add any essential oil to the moisturizing day cream for the neck and face in a ratio of 1 to 10. Stir the product thoroughly with a clean orange stick and use as usual.
Once a week, you can simply wipe flaky and red skin with a pad soaked in extra virgin olive oil.
Each of these masks should be done once a week. Wash it off with water at room temperature. If you feel tightness on your skin, apply a nourishing cream.
Nourishing masks ↑
Along with moisturizing, you need to regularly nourish your skin. An excellent option would be to apply a moisturizing mask and a nourishing one a few days later. Before carrying out the latter, gently peel the skin with fruit (citrus fruits, apples, strawberries), vegetable (tomatoes) or berry gruel, semolina with a spoon of cream, oatmeal and even just oatmeal. Don't forget about your cleavage.
Nourishing mask with a whitening effect: add half a teaspoon of parsley juice, a tablespoon of cream and warm honey to the banana pulp. Leave the product on the cleansed skin of the neck and décolleté for 15 minutes. Parsley, citrus juice, clay, and fermented milk products perfectly whiten redness and age spots.
Mix a small piece of melted butter with oatmeal and a spoonful of honey. If the consistency is too thick, add milk or fruit juice.
To additionally nourish the skin, you can use the following ingredients in different proportions: egg yolk, cottage cheese, full-fat kefir or natural yogurt, cosmetic clay (especially white), honey, wax, fruit.
Natural oils have powerful nutritional properties. For a nourishing mask, you can use the following esters: castor, coconut, peach, apricot and grape seeds, wheat germ, flaxseed oil.
You can combine components, change proportions, remove unsuitable ones and add other useful substances. Make sure you don't have allergies. Don't forget about basic care: cleansing, toning, moisturizing (in the morning), nutrition (in the evening).
Give your skin care, take care of it, apply substances to your neck and chest that will help maintain youth, elasticity, and most importantly, health. You will definitely see the result.
Did you like the article? Save it to your social network page!
Dry skin on the neck
answers from doctors for free
- Articles
- Peeling skin on the neck
Peeling caused by dry skin is medically known as xeroderma. Most often it is caused by unfavorable environmental factors, but it can also be caused by the development of the disease. Peeling skin on the neck is also accompanied by irritation, redness, sagging and painful cracks.
Causes of peeling skin
Dryness is caused by an excess amount of dead skin cells in the epidermis. Peeling skin on the neck appears for the following reasons:
- Side effects from taking certain medications (retinoids, antihistamines, diuretics);
- Diet with low nutritional value, lack of vitamins and microelements;
- External natural conditions;
- Pityriasis rosea;
- Psoriasis;
- Atopic dermatitis;
- Scarlet fever;
- Fungal infection;
- Hypothyroidism;
- Eczema
In addition to diseases, other factors can influence the appearance of unpleasant symptoms. Such as frequent washing in hot water, aggressive effects of household chemicals, chlorinated water and others.
Diagnosis of peeling
Finding out why the skin on your neck has become dry and irritated may require some research. Independent preliminary diagnosis of peeling is available on our website. But only an experienced specialist can reliably establish the cause. First of all, consult a dermatologist.
It is possible to determine exactly what caused peeling in individual areas of the neck using laboratory tests. Usually carried out:
Which doctor treats peeling skin on the neck?
If you feel peeling skin on your neck, you should consult a doctor of the following specialty:
After the examination, the doctor will prescribe the necessary diagnostics in your case. Some diseases are difficult to diagnose, as they say “by eye”. Therefore, you need to trust your doctor when prescribing tests. After all the tests, the doctor will be able to formulate the correct course of treatment. Remember: accurate diagnosis and correct diagnosis are already 50% of success in treatment!
Treatment of peeling on the neck
The main enemy of irritated skin is dehydration. Soaps and other cleaning products should be used with extreme caution. Do not use lotions and creams containing alcohol and lanolin.
If peeling is caused by climatic factors, it is recommended to pay special attention to skin protection. It is necessary to make masks with vegetable oils, lactic acid products and vitamins.
They perfectly soften and moisturize the skin.
If peeling is caused by a lack of vitamins, you need to change your diet. You should definitely include fish and seafood, liver, cottage cheese, whole grain bread, nuts, cereals, and colored vegetables in your menu.
In addition, there are vitamin complexes that will help restore the required amount of nutrients in the body in the shortest possible time.
And yet, doctors strongly do not recommend self-medication, and at the first symptoms, consult a specialist.
The key problem in the treatment of arthrosis is to slow down the development of arthrosis.
Skin rashes on the head in men can appear at any age. Sometimes that's enough.
Despite the fact that not a single doctor would call tanning a beneficial thing, every year the majority do.
Peeling of the skin of the palms is a rather unpleasant symptom that is not so rare. .
We advise you to read: Soft bandages for the head, neck, torso, limbs
Materials from the portal can be used only with the consent of the copyright holder. 16+
The project was created jointly with the publishing house