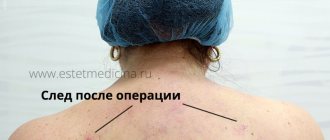
Reasons for plastic surgery
The problem regarding the appearance of the toes is their excessive length and discrepancy in size relative to each other. More often, girls with “Greek” feet go to the doctor. With this feature, the second finger becomes too prominent compared to the others. Excessive length also occurs in any of its neighbors.
And although the feet are not the most visible part of the body, patients tend to undergo shortening surgery more often for aesthetic reasons. There are other reasons to contact a surgeon with a problem:
- inability to wear high-heeled, open-toed or narrow-toed shoes due to physical discomfort;
- constant injury to the finger from any shoes;
- congenital anomalies of phalanges, bones, soft tissues;
- deformities of the fingers (hammertoe, valgus), arising for various reasons.
Devices and clamps for toes
To correct some deficiencies, it is not necessary to undergo surgery immediately. After consulting with a doctor, it is worth trying conservative methods, that is, wearing special devices. They are suitable for those with a tendency to develop hallux valgus and at its initial stage. But their main purpose is to protect the foot from injury during the recovery period after surgery.
| Toe braces | Short description | Photo |
| Silicone retainers | They consist of a bridge between the thumb and second finger, as well as protection of the first from the outside. | |
| Hinge devices | All parts of the foot are fixed in the correct position, limiting movements. The devices are indicated for wearing after surgery. | |
| Hard clamps | They have a dense frame, so they firmly limit the movement of the fingers. They can be used after surgery on either one. |
In some cases, not external, but internal devices are needed - titanium screws, biodegradable materials. They are almost always used during thumb surgery.
How is plastic reduction performed?
In most cases, the operation is performed under local anesthesia. General anesthesia or epidural can be used, it depends on the scale of the intervention. There are several ways to do it:
- Osteotomy of the metatarsal bone. It is dissected, gaining access through an incision in the skin, and then part of the tissue is removed. After connecting the bones with a screw, the wound is sutured.
- Osteotomy of the phalanx. In this case, only this section is shortened.
- Combined operation. It corrects the metatarsal bone and phalanx of the finger.
- Arthrodesis of the interphalangeal joint. Not only its capsule is affected, but also tendons and soft tissues. Sometimes arthrodesis must be combined with osteotomy of the phalanx.
To learn how surgery is performed to reduce the length of the second toe, watch this video:
Methods for solving the problem
The defect can only be eliminated through surgery. To do this, it is necessary to determine the nature of the splice. There are two types. In the first case there is a bone adhesion, in the second there is a soft tissue form (membranous or skin). The classification also depends on the length of the fusion and the number of fused phalanges.
After the collected hardware examination data, the doctor prescribes a planned operation, if possible. In case of fusion of the phalanges of the foot, surgical manipulations are not performed. Only the fingers can be separated. Many patients do not need medical intervention, since the defect does not affect gait or cause pain. If, nevertheless, the doctor decided to carry out the separation, then the best age would be 4 - 5 years from birth. If terminal syndactyly has been diagnosed, then the operation is performed within six months. Early intervention prevents the curved development of the phalanges. After the operation, a plaster splint is applied for 3 to 4 months.
In most cases, doctors recommend separating the phalanges to prevent negative development of the feet as they grow older.
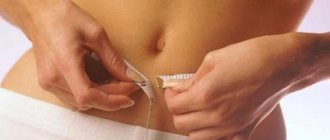
Rehabilitation after toe plastic surgery
Upon completion of the operation, the patient will have a recovery period:
- 3 days you need to lie more with your legs elevated;
- you will have to take painkillers for some time;
- For 2 weeks you can move only with crutches, limiting the duration of walking;
- seams should be treated with antiseptics;
- they are removed after 10 - 15 days;
- be sure to use clamps;
- after a month you can step on your feet, but wear orthopedic shoes;
- after 8 weeks it is permissible to wear regular shoes, but without high heels;
- Dress shoes are allowed to be worn after 3 - 4 months.
Toe shortening: price, postoperative period, reviews, complications, surgical technique
Toe shortening is not such a rare operation in plastic surgery. Often called the Cinderella operation, it allows you to correct the shape of your toes and reduce the size of your feet. The procedure has its own characteristics that must be taken into account before going under the knife.
What is toe shortening
Toe shortening is a procedure in which it is possible to eliminate excess length or abnormal structure of this area. The operation involves eliminating the defect and restoring the functionality of the department.
Concept
This procedure is most often of an aesthetic nature, although sometimes it is prescribed for medical reasons, for example, with constant friction, pain in the fingers, overgrowth of cartilage and bone tissue. Most often, people with “Greek foot” turn to it, in which the second toe protrudes too much compared to the rest, but such a defect can also appear on neighboring ones, or even on several.
In addition to aesthetic reasons, they may also apply due to:
- Inability to wear high-heeled shoes;
- Feeling of discomfort with any type of shoes;
- Congenital or acquired after injury anomalies of the phalanges;
- Deformation of fingers under the influence of internal and external causes.
Based on this, the type of operation is selected. However, the impact may differ.
Kinds
In the process of reducing toes, use any of the following methods. Depends on the severity of the defect and the specific finger. This is how it is used:
- Osteotomy of the metatarsal bone with abnormal length;
- Osteotomy of the phalanx with a pronounced length of the whole part;
- Osteotomy of the phalanx and metatarsal bone, if there is a painful corn and hammertoe deformity (most often with severe transverse flatfoot);
- Arthrodesis of the proximal interphalangeal joint for severe hammertoe finger deformity with accompanying stiffness. It is also used if the patient wishes to wear only dress shoes.
Indications
Indications for use are factors such as:
- Aesthetic requirements for the appearance of the foot and toes;
- Congenital defects in the structure of the fingers;
- Acquired defects in the structure of the fingers;
- Deformations caused by diseases or other reasons;
- Permanent finger injury;
- Desire to wear open high-heeled shoes.
Contraindications
Contraindications for which surgery is not performed:
- Blood clotting disorder;
- Infectious pathologies in the area of intervention;
- Diabetes;
- Oncological pathologies;
- Disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system (including CHF, AHF);
- Obesity;
- Epilepsy;
- Impaired blood circulation during innervation of the foot;
- Hypersensitivity to the composition of anesthesia and other drugs;
- Thrombophlebitis.
Combined procedure to lengthen the third and fourth toes and reduce the size of the second (before and after photos)
Comparison with similar techniques
If we talk about such methods, then an analogue is the use of conservative methods, for example, the use of special accessories such as silicone or rigid clamps, hinge devices. They can reduce the manifestations of a number of defects, but they cannot completely eliminate or make the fingers much shorter.
Carrying out
The procedure requires some preparation. This is especially true in cases where there are contraindications that are revealed during the examination. In such cases, you need to first undergo therapy for the underlying disease, and then agree on surgery.
Necessary tests and measures
A general diagnosis is carried out, which consists of:
Anticoagulants and other medications that affect blood composition are stopped approximately two weeks before surgery. During the same period, quit smoking and alcohol.
Be sure to follow a gentle diet.
The operation itself takes about an hour.
Many patients compared it to going to the dentist, as local anesthesia is administered, during which the patient remains conscious and hears everything the doctor does. No pain is felt.
Work on one finger takes about half an hour. If several elements need to be processed, manipulations may take longer.
It is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- General anesthesia or epidural is used;
- An incision is made in the area of manipulation;
- Excess tissue is removed through access;
- The bones are connected with a screw;
- The skin is sewn together.
In the case of correction of hallux valgus deformity, the procedure may differ. An incision is made at the base of the big toe on the sole side. The joint is cleared of growth, and a section of wedge-shaped bone near the middle phalanx is removed. Next, the finger is moved to its normal position and secured with a screw.
Possibility of combination with other types of plastics
Any of the types of this operation can be combined depending on the indications. Thus, osteotomy can be performed simultaneously on the metatarsal bone and phalanges. Arthrodesis of the interphalangeal joint affects not only the joint capsule, but also tendons and soft tissues.
During the operation, part of the skin may also be removed if there is excess skin. Pins must be installed to set the right direction for the bone healing process.
To restore the correct axis of the finger, it is necessary to change the tendon system in the area of manipulation.
In the case of hallux valgus, there is a risk of relapse, but as practice shows, symptoms after surgery are less pronounced.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is carried out in stages:
- For the first three days, it is advisable to walk as little as possible. It is better to take a lying position with your legs raised up on an elevated surface.
- For 2 weeks, movement is carried out with the help of crutches.
- The sutures are treated with antiseptics before the sutures are removed in 10-15 days and after until the wound surface is completely healed.
- Special fasteners are used.
- After a month, you can step on the treated areas, but only if you wear orthopedic shoes.
After 2 months, you can wear regular shoes, but without high heels, and dress shoes are allowed to be worn after 3-4 months.
Complications most often develop due to non-compliance with the rehabilitation regime, but in rare cases they can also occur due to poorly performed surgery. They usually appear in the form of:
- Bleeding;
- Tissue infection;
- Hematomas;
- Slow fusion of bone tissue;
- Chronic pain syndrome;
- Loss of sensitivity in the operated area;
- Displacement of bone joints;
- Unsatisfactory aesthetic appearance of fingers.
Reviews about this procedure
Most often, reviews of the procedure are positive, as the foot acquires an aesthetically pleasing appearance. It is possible to get rid of congenital and acquired anomalies, as well as joint deformities. In this case, in the end, patients could wear beautiful open shoes. The seams, as a rule, became discolored and became hardly noticeable.
Negative feedback concerned cases where the aesthetic appearance of the toes and feet did not coincide with expectations. There have been cases where a patient's operated fingers could not touch the floor while standing. In such cases, additional correction was required.
Average prices
The price depends on the severity of the defect. On average, the cost for processing one finger varies between 25-30 thousand rubles.
Often, when correcting several areas at once, clinics can discount several thousand for each finger.
The procedure can be done in clinics such as “Ortomed”, “GSclinic”, MDC “Olympus”, “Da Vinci”, City Clinical Hospital No. 29 named after. N. E. Bauman and other plastic surgery clinics.
Can it be done at home?
At home, you can try to correct the shape of your fingers using special clamps and other devices. They are also used during the rehabilitation period after surgery.
They allow you to keep the joints in a normal position, due to which the ligamentous apparatus and soft tissues correct their shape and force the joints to be in a normal position. But with severe deformations, such an effect will be ineffective and insignificant.
In this video with Elena Malysheva you will learn about the treatment of hallux valgus:
Source: https://gidmed.com/plasticheskaya-hirurgiya/vidy/esteticheskaya/nogi/ukorachivanie-paltsev.html
Possible complications
An operation to shorten fingers or eliminate their deformation can also cause problems:
- bleeding;
- development of infection in soft tissues;
- delayed bone healing;
- chronic pain syndrome or, on the contrary, loss of sensitivity due to nerve damage;
- displacement of bone areas;
- unsatisfactory aesthetic effect.
Complications arise more often due to the patient’s fault when he violates the conditions of rehabilitation. They may be caused by the unique characteristics of the body, or by doctor errors.
Possible complications: swelling, scars and others
If events develop negatively after surgery, there are problems:
- pronounced swelling,
- healing with the formation of a rough scar,
- wound infection,
- finger necrosis,
- rejection of the transplanted skin flap,
- finger deformities (one of the consequences of scars),
- changing the shape of the nail,
- movement of the interdigital commissure, forcing a new intervention to separate the fingers.
Most complications arise due to mistakes made during plastic surgery.
Frequently asked questions from patients
Plastic surgery of toes, if not the elimination of hallux valgus, is done relatively recently. Therefore, it raises many questions.
How to prepare for surgery?
It is necessary to undergo general clinical tests, have an ECG, fluorography and x-ray of the feet. Taking blood thinning medications should be stopped 2 weeks before surgery, and it would be a good idea to stop smoking.
Will the effect last a lifetime?
If this is a purely aesthetic intervention, the result will remain unchanged forever. Once the hallux valgus is corrected, the problem may return. But even in this case, the signs of pathology will not be as pronounced as initially.
How much does the operation cost?
If you need to correct 1 finger, it will cost 30,000 rubles. and more . Anesthesia and dressings are paid separately.
An intervention to correct the toes by an experienced doctor will last less than 1 hour. However, it is difficult and traumatic. Therefore, if you want to have surgery, you should think carefully first.
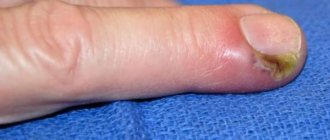
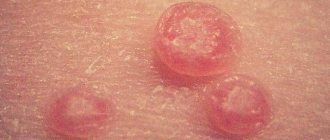
The appearance of a callus on the little toe is quite common, which is explained by excessive friction in this area. The formation is quite painful and unpleasant, which requires timely treatment.
Types of calluses on the little toe
Various types of calluses can appear on the little toes. The most common symptoms observed in people are:
- Wet calluses. It is a fairly common type of formation caused by excessively tight shoes. A callus appears on the top or side where the skin rubs against the shoe. This is a bubble containing a cloudy liquid.
- Dry formations. Appear when choosing the wrong shoes. The formation is a hard thickening of the skin. The callus has a round shape and is characterized by a lack of pain.
- Bone formations. The occurrence is observed if pressure is constantly applied to the bone. Pathology also occurs when bones do not heal properly after a fracture.
- Corns. These formations are located in the upper layers of the epidermis. In most cases, they are observed on the lateral surface of the little finger.
- Ingrown calluses. They appear with constant and intense friction on a certain area of the skin. The formation is characterized by severe pain, which causes discomfort while walking. This callus is characterized by the presence of a rod inside.
In order to prescribe rational treatment to a patient, it is necessary to determine the type of formation.
Reasons for appearance
The appearance of formations on the little toes is observed when wearing uncomfortable or excessively tight shoes. If low-quality materials are used for its production, this causes the appearance of calluses.
First aid
If a person finds a callus on his little finger, then he must provide himself with first aid, which will eliminate the possibility of aggravating the situation. Initially, you need to stop wearing excessively tight shoes.
Otherwise, it will continue to rub the callus. If the formation is wet, this can lead to a breakthrough of the film and the development of an infectious process.
To avoid complications, the patient must be prescribed rational treatment. That is why he must go to the medical center.
Treatment
Callus therapy can be carried out in various ways. The choice of a particular one directly depends on the type of calluses. To treat calluses, traditional medicines as well as traditional medicine can be used.
Regardless of the treatment method used, the patient is recommended to undergo steaming baths.
With their help, the affected skin on the little finger is softened. After they are carried out, the removal of the little finger is ensured as painlessly as possible. After the baths, it is recommended to cover the callus with a band-aid.
Folk remedies
To treat small calluses, you can use drugs offered by traditional medicine. They not only have high effectiveness, but also safety, which makes it possible for absolutely all patients to use them.
- Aloe. With the help of this indoor flower, a variety of diseases are treated. For the treatment of calluses, the use of old fleshy leaves is recommended. A piece of leaf is cut from one of them, which is twice the size of the formation. You need to remove the skin from the back side. The pulp of the leaf is applied to the formation and fixed with a bandage.
Traditional medicines are safe and effective in the fight against calluses. But, patients need to consult a specialist before using them.
Traditional medicine
Treatment is carried out using pharmaceutical preparations, which are produced in the form of gels and ointments and have a local effect.
Doctors recommend using ointments whose main component is salicylic acid.
The use of special patches is also recommended. They are developed on the basis of universal components, with the help of which softening of the callus is ensured, as well as its removal.
How to get rid of a callus on the little toe, watch this video:
Traditional medications for calluses should only be prescribed by a doctor, who first determines the type of formation.
Contacting the doctor
If an ordinary wet callus forms in the area of the little finger, you can treat it yourself. But, if suppuration appears, the patient is advised to consult a doctor.
If the formation is excessively large, the patient should consult a doctor. A person should know that timely seeking help from a specialist will eliminate the development of undesirable effects.
What is forbidden to do
When a wet callus forms, it is necessary to adhere to certain rules in treatment. It is strictly forbidden to pierce a callus at home, as this can lead to the development of an infectious process and the appearance of more serious complications.
If the callus has burst, it is forbidden to remove the skin, as it protects the wound from infection.
Treatment of a burst callus
Quite often it happens that the callus on the little finger bursts on its own. In this case, it is necessary to carry out its treatment. First of all, it is recommended to steam the formation. If dirt has accumulated under the skin, it must be removed.
The formation must be treated with hydrogen peroxide. After this, an ointment is applied to the callus, which has antiseptic and disinfectant properties. In order to eliminate the possibility of infection, a patch or sterile bandage is applied to the callus.
How to Identify and Treat a Dislocated Hip (Hip)
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for Joint Treatment: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your joints by taking every day...
Read more "
It is not for nothing that hip dislocation is considered one of the most difficult types of injuries. A person cannot walk for a long time, and the treatment and rehabilitation period are characterized by increased complexity. Why does this happen, how to determine the presence of such a problem and what to do?
Anatomy
Normally, all parts of the hip joint (i.e., the femoral head, acetabulum, acetabular labrum, external ligaments and internal ligament of the femoral head) give it high strength, thanks to which it can withstand the fairly large loads that fall on the lower extremities.
The hip joint is surrounded on all sides by muscles that further strengthen it. The gluteal muscles are the most developed.
Causes
Taking into account the peculiarities of the anatomy of the hip joint, it is easy to understand that in order to dislocate it, a fairly significant force will be required, applied at a considerable speed. Most often these are road accidents, falls from heights and sports injuries. But such a dislocation is not always an acquired condition and can also be congenital or a consequence of developmental pathology.
By the way, pathological conditions are often observed in children and are better known as “hip dysplasia.” If we are still talking not about congenital, but about traumatic hip dislocations, then they are often accompanied by damage to soft tissues, ligaments and fractures of the femur.
During a dislocation, the mechanism of action on the joint is characterized by a sharp inward rotation with simultaneous adduction of the hip.
Hip dislocation according to the ICD 10 code is listed as S73.0.
Symptoms of injury: how to distinguish from a fracture
The presence of the described problem can be judged by the following signs:
- severe pain in the pelvic area;
- inability to stand on a leg (injured);
- deformed appearance of the limb, which depends on the characteristics of the dislocation (for example, with the posterior type of injury, the leg will be bent, turned inward and slightly shorter than the other, while the anterior dislocation implies an extended or bent position of the injured limb and its lengthening).
Moreover, if nerve damage occurs during injury, the patient will have no sensation in the foot and ankle joint area.
It will be possible to make a final diagnosis of a hip dislocation based on the existing symptoms only after analyzing the position of the injured limb and a number of other diagnostic procedures (for example, if a fracture of the pelvic bones is suspected, doctors take an X-ray).
Classification
There are four types of the described problem, and their classification is based on the direction of the head of the femur. These include:
- posterosuperior (the head will be placed behind the wing of the ilium);
- posteroinferior (the head is located near the ischium);
- anterosuperior (the head is located in front of the wing of the ilium);
- anteroinferior (the head is located next to the pubic bone).
Posterior types of hip dislocations are more common, approximately 3-5 times more common than the anterior ones.
First aid
Of course, at the slightest suspicion of such a complex injury, you must immediately consult a doctor by calling an ambulance. After hospitalization under anesthesia, the doctor will perform a reduction of the dislocation.
In no case should you try to cope with this problem on your own, since one careless action can significantly aggravate the situation or even cause disability, but you need to provide help before the doctors arrive:
The same banned issue for which Ernst fired Malakhov!
Joints and cartilage will be cured in 14 days with the help of ordinary...
- If you accidentally find yourself with an injured person, then before the specialists arrive, you can give him an anesthetic (if possible intramuscularly) and fix the injured limb in a motionless position. You can use available materials in the form of sticks or reinforcement, pre-wrapped with a bandage.
- As an alternative fixation option, you can tape the injured leg to the healthy one. The main thing is that during immobilization it is in the same position as immediately after the injury.
- You can also alleviate the victim’s condition with the help of a cold compress applied to the hip joint area. An ice pack or a regular cloth soaked in cold water can be used as a cooler.
- Having completed these manipulations, all that remains is to wait for the ambulance to arrive, because transporting the victim in a passenger car that is not equipped with everything necessary is extremely undesirable.
Diagnostics
The victim will undergo a diagnostic stage, which consists of:
- examination by a traumatologist (a specialist examines and feels the damaged joint),
- radiography, which is mandatory (pictures are usually taken in two projections: side and front),
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging.
The latter diagnostic procedures are not always prescribed, but only in cases where X-ray examination is not enough to make a final diagnosis.
In most cases, hip dislocation is not difficult to diagnose, but it is important to learn about its features and correctly identify the problem.
Treatment
A victim with a dislocated hip can expect the head of the bone to be reduced to its natural position. For this, doctors use several methods: Kefer-Kocher, Janelidze-Collen, Depres-Bigelow. Since this procedure is quite painful, most often it is performed under local anesthesia, although in particularly difficult cases general anesthesia can also be used.
To assess the correctness of the reduction, it is necessary to take a repeat radiograph of the hip or computed tomography.
After the procedure, a plaster cast is applied to the injured limb (from the lower back to the very toes) so that it fixes three joints at once: ankle, knee and hip. In some situations, it may be necessary to apply skeletal traction for a period of 3-4 weeks.
You can also learn by watching this video how the procedure for reducing hip dislocation using the Kocher method is performed.
The procedure involves passing a metal wire through the tibia and hanging a weight from it. During this entire time, the patient is prescribed bed rest, and after a month, another 8-10 weeks are prohibited from putting any weight on the injured limb (you can only walk with the use of crutches). Most often, full recovery occurs only after three months.
If the reduction of the hip dislocation occurred immediately after the injury, that is, you quickly figured out what to do, then the further prognosis is quite favorable.
Rehabilitation period
A hip dislocation is a fairly serious injury, which means that both the treatment and the subsequent rehabilitation period have some peculiarities and require strict adherence to all doctor’s instructions.
The speed of your recovery after an injury largely depends on the timeliness and correctness of all rehabilitation measures:
- Massage is the first type of rehabilitation measures. The main goal of a course of such procedures is to normalize blood flow in the affected limb, reduce pain, accelerate the process of resorption of swelling, increase muscle tone and quickly restore movements.
- Physical therapy begins during the period when the patient is still prescribed bed rest and consists of three main stages:
- first, the simplest exercises are performed and in a minimal amount, aimed at restoring blood flow in the leg;
- then, simple movements begin to be performed more intensely and are aimed at restoring mobility in the hip joint;
- The third stage involves performing a set of exercises, after which it will be possible to put full loads on the injured leg.
- Physiotherapy is a course of exercises that is selected taking into account the characteristics of each patient’s injury and depends on its severity, type of treatment and clinic capabilities. The main methods of physiotherapy during the rehabilitation period after treatment of hip dislocation include UHF, diadynamic currents, magnetic therapy and various thermal procedures.
- Sanatorium-resort treatment involves the use of thermal waters, therapeutic mud and other facilities specially designated for this purpose - specialized resorts and sanatoriums.
Prevention
In order to prevent calluses from appearing on the little toes, a person must constantly adhere to certain rules of prevention:
- When choosing shoes, it is recommended to ensure that they completely match your foot size.
- It is best to give preference to shoes that are made from natural fabric.
- Before putting on your shoes for the first time, it is recommended to use an antibacterial patch. It is applied to places where formations may appear.
- A fairly effective preventive remedy is a pencil, the action of which is aimed at combating calluses.
- If the patient's skin is unprotected, then it is not recommended for him to wear closed shoes.
- The choice of socks and tights must be approached responsibly. They must exactly match your foot size.
- If you have a tendency to sweaty feet, it is recommended to constantly combat this pathological condition. In this case, talc is used, as well as various powders.
- Women are advised to regularly change shoes with high heels and thin soles.
- A person should constantly take care of their feet. For this purpose, hygiene procedures are regularly carried out, and special creams are used.
- If your feet are frequently injured, it is recommended to use special orthopedic shoes.
This video will tell you how to cure calluses on your little finger at home:
Timely and proper prevention of calluses will eliminate the possibility of their formation.
Calluses in the area of the little toes appear quite often. A person can develop various types of formations in this place. In order to ensure proper treatment, it is necessary to determine the type of callus. For the purpose of treating formations, folk recipes or pharmaceutical preparations are used.
Author: Averina Olesya Valerievna, candidate of medical sciences, pathologist, teacher of the department of pathological anatomy and pathological physiology
Most of us find it difficult to imagine solving ordinary everyday problems and professional activities without fingers. On the legs they are needed for support and proper walking; on the hands, fine motor skills allow not only the necessary self-care skills, but also provide writing.
Unfortunately, there are situations in life when the feet and hands undergo irreversible changes, in which all organ-preserving treatment methods cannot ensure tissue preservation, so there is a need for amputation of the finger.
Due to the traumatic nature and persistent unsatisfactory results, amputations are carried out only in cases where the possibilities of more gentle treatment have been exhausted or it is not feasible due to the extent of the lesion. In other words, such an operation will be performed when saving the finger is simply impossible:
- Traumatic injuries, finger avulsions, severe crushing of soft tissues;
- Severe degrees of burns and frostbite;
- Necrosis of the fingers due to vascular disorders (diabetes mellitus, primarily thrombosis and embolism of the blood vessels of the hands and feet);
- Acute infectious complications of injuries - sepsis, abscess, anaerobic gangrene;
- Trophic ulcers, chronic osteomyelitis of finger bones;
- Malignant tumors;
- Congenital malformations of the osteoarticular system of the fingers, including amputation of the toes for the purpose of transplanting them to the hand.
After the removal of fingers and toes, the patient becomes disabled, his life changes significantly, so the question of the need for such intervention is decided by a council of doctors. Of course, surgeons will try to the last to use all available methods of preserving the fingers and toes.
If treatment is necessary for health reasons, the patient’s consent is not required. It happens that the patient does not agree to the operation and there are no absolute indications for it, but leaving the sore finger can cause serious complications, including death, so doctors try to explain to the patient and his relatives the need to remove the fingers and obtain consent as quickly as possible.
Shortening of limbs
Shortening of limbs
- this is a decrease in the length of one limb relative to the other or a decrease in the length of both limbs, which disrupts the proportions of the human body. Minor shortening (1–2 cm) is common and has no clinical significance.
Significant shortening of the lower extremities, especially unilateral, is manifested by disturbances in support and walking, and can provoke a number of diseases of the joints and spine. The diagnosis is made after special measurements.
Correction is possible with insoles and orthopedic shoes; in case of severe shortening, the limb is lengthened using the Ilizarov apparatus.
Limb shortening is a widespread phenomenon. A slight difference in the length of the lower limbs is detected in 90% of people.
Among the reasons are the dominance of one of the cerebral hemispheres, poor posture and incorrect muscle patterns that influence the formation of the body during the growth of the child.
A difference in leg length of up to 1-2 cm is imperceptible even to the patient himself and is discovered only during special studies. Shortening one limb by more than 3-5 cm causes a noticeable distortion of the pelvis and causes discomfort to a person when walking.
Shortening of limbs
Shortening of the limbs can be unilateral or bilateral.
Symmetrical bilateral shortening is detected in achondroplasia and some other genetically determined diseases and is manifested by a discrepancy in the proportions of the torso and limbs.
Asymmetrical bilateral shortening is observed with developmental anomalies of the upper and lower extremities. The cause of unilateral shortening may be traumatic injury, tumor, infectious process or developmental defect.
In traumatology and orthopedics, the following types of unilateral shortening are distinguished:
- True
. Formed due to organic damage to the bone. It is detected by segment-by-segment measurement of limb length. The sum of the lengths of the thigh and lower leg on one side is less than on the other. Occurs as a result of improperly healed fractures, malformations, tumors and some infectious diseases (tuberculosis, syphilis). - Relative
. Formed when there is a violation of the relationships between the segments of the limb. Subjectively, one limb looks shorter than the other, but upon measurement it is discovered that the lengths of the legs and thighs are the same. It occurs due to displacement of the articular ends of the bone due to intra-articular fractures and congenital dislocations. - Apparent
. Formed due to forced flexion. As in the previous case, the length of the legs subjectively appears different, but measurements confirm that the length of the segments is the same. The cause of the apparent shortening may be arthritis, arthrosis, swelling of the articular ends of the bone or post-traumatic contracture.
If one patient has several types of limb shortening (for example, a decrease in the length of the femur due to an improperly healed fracture of the femur in combination with a flexion contracture of the knee joint), they speak of a total shortening. The total shortening is determined by placing planks of varying thickness under the foot until the anterior superior pelvic spines are at the same level.
A decrease in limb length by more than 5 cm is usually accompanied by lameness and is clearly noticeable even without special measurements.
A less pronounced difference in leg length is sometimes not visually determined, since it is compensated by the tilt of the pelvis and the curvature of the spine. Lameness may be absent.
The difference in the level of location of the popliteal fossa, the upper poles of the patellas, the greater trochanters, and the anterior and posterior superior iliac spines should cause caution.
Even a slight shortening of the limbs cannot be considered a harmless phenomenon, since it leads to a disruption of the normal anatomical relationships between parts of the body when standing and walking.
The alignment of the joints is disrupted, the torso and limbs are somewhat displaced and twisted to ensure a normal vertical position of the body, so-called compensatory deformations occur.
The load on one leg increases, the pelvis warps.
The spine, when one limb is shortened to 1.3 cm, forms a C-shaped bend; when shortened by more than 1.3 cm, it forms an S-shaped bend. Over time, poor posture becomes fixed and scoliosis may develop. Muscles are constantly in a state of increased tension.
Pain in the back, joints and muscles, fatigue, heaviness in the feet and legs after walking appear. Blood flow worsens, the lymphatic system suffers.
With the long-term existence of the pathology, the development of osteochondrosis, coxarthrosis and gonarthrosis, as well as worsening of flat feet, is possible.
To clarify the severity and nature of the shortening, measure the absolute and relative length of the limb and the length of each segment, using visible bony protrusions (anklebones, upper pole of the patella, articular space of the knee joint, greater trochanter and superior anterior iliac spine) as landmarks. Measurements are taken with the legs fully extended, with alternate flexion of the hip and knee joints and with simultaneous flexion of the large joints of the limb. To identify relative and apparent shortening, special tests are used.
The list of additional studies depends on the location and presumed cause of the shortening. For old fractures, tumor processes and infections, radiography of the lower leg or radiography of the thigh is prescribed.
For arthrosis, an X-ray of the knee joint, an X-ray of the hip joint or arthroscopy of the knee joint is performed. If soft tissue damage is suspected, MRI data is used.
According to indications, patients are referred for consultations to an oncologist, phthisiatrician, venereologist, infectious disease specialist, rheumatologist and other specialists.
Treatment of this pathology is carried out by orthopedists-traumatologists. For small shortenings, conservative correction is usually carried out - special insoles or orthopedic shoes are used to eliminate the difference in leg length.
In case of significant shortenings, the tactics are determined individually and depend on the reason for the change in limb length, the patient’s age, his state of health and other factors.
The most popular and effective method of surgical treatment of shortenings is limb lengthening using the Ilizarov apparatus.
The Ilizarov apparatus allows you to lengthen the tibia by 8-10 cm, and the thigh by 5-6 cm. It should be borne in mind that the increase in the length of the segment is carried out gradually and can last up to six months or more.
Installation of the device on the lower leg is relatively easy for patients to tolerate, since it allows them to maintain sufficient mobility and does little to interfere with movements in the joints of the limb, etc. Installation of the device on the thigh is more difficult to tolerate, since it significantly limits movement and self-care.
During the entire treatment period, patients perform special exercises aimed at preventing muscle atrophy and maintaining joint mobility. Functional results are good.
Source: https://www.KrasotaiMedicina.ru/diseases/traumatology/limb-shortening
Preparing for surgery
Preparation for surgery depends on the indications for it and the patient’s condition. During planned interventions, the usual list of tests and studies is required (blood, urine, fluorography, cardiogram, tests for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis, coagulogram), and to clarify the nature of the lesion and the expected level of amputation, radiography of the hands and feet, ultrasound examination, and determination of the sufficiency of work are performed vascular system.
If there is a need for urgent surgery, and the severity of the condition is determined by the presence of inflammation, infectious complications and necrosis, then during preparation, antibacterial agents and infusion therapy will be prescribed to reduce the symptoms of intoxication.
In all cases when surgery on the hands and feet is planned, blood thinners (aspirin, warfarin) are discontinued, and the attending physician must be informed about taking drugs from other groups.
Anesthesia for amputation of fingers is often local, which is safer, especially in the case of a serious patient’s condition, but is quite effective, because no pain will be felt.
In the process of preparing for amputation or disarticulation of fingers, the patient is warned about its result; it may be necessary to consult a psychologist or psychotherapist, who can help reduce preoperative anxiety and prevent severe depression after treatment.
Amputation of fingers
The main indication for amputation of the fingers is considered to be trauma with complete or partial separation. When avulsion occurs, the surgeon is faced with the task of closing the skin defect and preventing scar formation. In the case of severe crushing of soft tissues with their infection, there may be no opportunity to restore adequate blood flow, and then amputation is the only treatment option. It is also carried out in case of necrosis of soft tissues and elements of the finger joints.
If during the injury several fractures occur, bone fragments are displaced, and the result of organ-preserving treatment is a motionless, crooked finger, then surgery is also necessary. In such cases, the absence of a finger causes much less discomfort when using the brush than its presence. This indication does not apply to the thumb.
Another reason for amputation of fingers can be damage to tendons and joints, in which preservation of the finger is fraught with its complete immobility, disrupting the functioning of the remaining fingers and the hand as a whole.
Distribution of finger and hand amputations by prevalence
The choice of amputation height depends on the level of damage. Always take into account the fact that a stationary or deformed stump or a dense scar interfere with hand work much more than the absence of an entire finger or a separate phalanx. When amputating the phalanges of long fingers, an operation that is too gentle is often performed.
When forming a stump, it is important to ensure its mobility and painlessness; the skin at the end of the stump should be mobile and not cause pain, and the stump itself should not be thickened in a flask shape. If it is technically not possible to recreate such a stump, then the level of amputation may be higher than the edge of the finger injury.
When performing operations on the fingers, the location of the lesion, the profession of the patient, and his age are important, so there are a number of nuances that surgeons know and must take into account:
- When amputating a thumb, they try to preserve as long a stump as possible; even short stumps are preserved on the ring and middle fingers to stabilize the entire hand during movements;
- The inability to leave the optimal length of the finger stump requires its complete removal;
- It is important to maintain the integrity of the heads of the metacarpal bones and the skin of the spaces between the fingers;
- They try to keep the little finger and thumb as intact as possible, otherwise the support function of the hand may be impaired;
- The need to amputate several fingers at once requires plastic surgery;
- If the wound is heavily contaminated, there is a risk of infectious lesions and gangrene, plastic and gentle operations can be dangerous, so complete amputation is performed;
- The patient's profession affects the level of amputation (for people with mental work and those who perform delicate work with their hands, it is important to perform plastic surgery and maximum preservation of the length of the fingers; for those who are engaged in physical labor, amputation to the maximum extent can be carried out for speedy rehabilitation);
- The cosmetic result is important for all patients, and in some categories of patients (women, people in public professions) it becomes crucial when planning the type of intervention.
Disarticulation is the removal of fragments or the entire finger at the joint level. For pain relief, an anesthetic is injected into the soft tissues of the corresponding joint or into the area of the base of the finger, then the healthy fingers are bent and protected, and the person being operated on bends as much as possible, and a skin incision is made on the back side above the joint. When removing the nail phalanx, the incision is made 2 mm towards the end of the finger, the middle - 4 mm and the entire finger - 8 mm.
After dissection of the soft tissues, the ligaments of the lateral surfaces are intersected, the scalpel enters the joint, the phalanx, which is to be removed, is brought out into the incision, and the remaining tissues are intersected with a scalpel. The wound after amputation is covered with skin flaps cut from the palmar surface, and the sutures are necessarily placed on the non-working side - the back.
Maximum tissue savings, the formation of a flap from the skin of the palmar surface and the location of the suture on the outside are the basic principles of all methods of amputation of the phalanges of the fingers.
Classification of finger syndactyly
The anomaly has different types and forms, degrees of development. Therefore, by type it is divided into:
- Soft fabric. The fingers are connected by a thin ligament or skin bridge.
- Bone. Bone tissue is present at varying lengths of the fusion.
Syndactyly can be complete or incomplete. The first case is diagnosed when the fusion reaches the tips of the fingers and nails. With incomplete syndactyly, it reaches the joints. A simple pathology consists of fused normally formed fingers. When complex, they have abnormalities of ligaments, tendons, bones and joints.
Pathology is divided into genetic types:
- 1st (zygodactyly) is a soft tissue connection of the 3rd and 4th fingers, 1st and 2nd - feet,
- 2nd (synpolydactyly) occurs with fusion of the 3rd and 4th fingers, supplemented by doubling of the little finger, the same features of the 4th and 5th toes with an appendage at the last one,
- The 3rd is diagnosed with complete bilateral fusion of the 4th and 5th fingers, shortened little finger,
- 4th (Gaza syndactyly) is characterized by a complete bilateral soft tissue connection of the fingers, which is why the hand looks like a spoon,
- The 5th is characterized by a fusion that connects the metacarpal and metatarsal bones in most cases of cutaneous syndactyly of the 3rd and 4th fingers, 2nd and 3rd toes.
The anomaly is often unilateral and develops on the arms.
Toe amputation
Unlike the fingers, which are most often subject to traumatic injuries that lead to a surgeon, on the foot and its fingers the need for surgery arises for a number of diseases - diabetes mellitus, endarteritis, atherosclerosis with gangrene of the distal parts of the legs.
Toe amputation due to diabetes mellitus is performed quite often in general surgery departments. Violation of trophism leads to severe ischemia, trophic ulcers and, ultimately, to gangrene (necrosis). It is impossible to save the finger, and surgeons are deciding whether to amputate it.
It is worth noting that with diabetes it is not always possible to limit yourself to the removal of one finger, because nutrition is impaired, and, therefore, one can only hope for adequate regeneration in the scar area. Due to significant disorders of the blood supply to soft tissues in various angiopathies, surgeons often resort to more traumatic operations - disarticulation of all fingers, removal of part of the foot, the entire foot with a section of the lower leg, etc.
When amputating toes, the basic principles of such interventions must be observed:
- Maximum possible preservation of leather on the sole side;
- Preservation of the work of flexors, extensors and other structures involved in multidirectional movements of the feet, in order to ensure further uniform load on the stump;
- Ensuring mobility of the joint apparatus of the feet.
For small lesions (frostbite of the distal phalanges, for example), it is possible to amputate the distal and middle phalanx without significantly impairing the functionality of the foot, with the exception of the big toe, which provides a supporting function, so if necessary, its removal is done as sparingly as possible.
When amputating the second finger, at least some part of it must be left, if this is possible due to the circumstances of the injury or disease, since complete amputation will subsequently result in deformation of the thumb.
Amputations on the feet are usually performed along the line of the joints (disarticulation). In other cases, there is a need to cut the bone, which is fraught with osteomyelitis (inflammation). It is also important to preserve the periosteum and attach the extensor and flexor tendons to it.
In all cases of injuries, avulsions, crushing, frostbite of the toes and other lesions, the surgeon proceeds from the possibility of maximally preserving the function of support and walking. In some cases, the doctor takes a certain risk and does not completely excise non-viable tissue, but this approach allows you to maintain the maximum length of the fingers and avoid resection of the heads of the metatarsal bones, without which normal walking is impossible.
Toe disarticulation technique:
- The skin incision begins along the fold between the toes and the metatarsus on the plantar side of the foot in such a way that the remaining skin flap is as long as possible, the longest in the area of the future stump of the first toe, since the largest metatarsal bone is located there;
- After the skin incision, the fingers are bent as much as possible, the surgeon opens the joint cavities, cuts the tendons, nerves and ties the blood vessels of the fingers;
- The resulting defect is covered with skin flaps, placing the sutures on the back side.
If the cause of amputation of the fingers was an injury with contamination of the wound surface, a purulent process during gangrene, then the wound is not tightly sutured, leaving drainage in it to prevent further purulent-inflammatory process. In other cases, a blind suture may be applied.
Healing after amputation of toes requires the administration of painkillers, timely treatment of sutures and changing bandages. In case of a purulent process, antibiotics are required; infusion therapy is carried out according to indications. The sutures are removed after 7-10 days. If healing is favorable after the initial operation, the patient may be offered reconstruction and plastic surgery, as well as prosthetics to facilitate work, walking, and support on the foot.
Recovering from toe removal requires physical therapy exercises to develop muscles as well as new skills for using the rest of the foot.
Plastic surgery of the legs: indications and contraindications
In the modern world there are a lot of girls, and, perhaps, men, who have high demands on their appearance. Much attention is paid to the appearance of the legs.
But it’s not often that a woman can boast of the grace of her legs, and a man – the strength and beautiful relief. The reasons for the presence of leg defects can be different, for example, heredity or some kind of injury.
Plastic surgery of the legs involves the correction of external defects of various origins. Excessively thin legs or the presence of leg asymmetry can be easily corrected with the help of plastic surgery.
Leg correction surgery is available for women and men of all ages. The only exception is those under 18 years of age.
The most common problem that surgical leg surgery solves is the presence of curvature. As a rule, there are two types of curvature.
- an “o” shape by the leg bones , in this case the knees point in different directions and the calves are turned out.
- The second type is a curved “x” shape . In this case, the knees are close and the calves are directed to the sides.
Plastic surgery of the legs can correct crooked legs by correcting the soft tissues and contour of the legs. The result of plastic surgery is beautiful and graceful legs.
Indications for leg plastic surgery include the following:
- Thin legs without characteristic relief. In this case, the patient’s pelvis can be wide, narrow, or medium in size.
- Asymmetrical leg defects.
- Characteristic curvature in silhouette shapes.
It should also be remembered that plastic surgery of the legs can be carried out under certain conditions on the part of the patient.
Contraindications to surgical plastic surgery include:
- diseases of the internal organs of the body;
- oncological diseases;
- poor blood clotting;
- poor blood circulation in the patient’s lower extremities;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- age up to 18 years.
Leg plastic surgery is carried out through the introduction of silicone implants. With the help of implants, the contour of the legs becomes ideal.
At the first consultation with a doctor, the type of plastic surgery of the legs required for the patient is determined.
Leg plastic surgery involves a preliminary examination of patients, which includes an x-ray and the necessary tests. Before surgery, you should not smoke or drink alcohol , or take certain medications.
The doctor may also prescribe special anti-inflammatory drugs before surgery.
Leg correction is performed through an incision under the knee, after which a silicone implant is placed. The main rule for this procedure is the correct placement of the implant so that there are no extraneous sensations during contact. The operation is performed under general anesthesia and takes a couple of hours.
After plastic surgery of the legs, you need to wear special compression garments for a month or a little more. The sutures are removed after two weeks from the moment of plastic surgery.
After the operation, the patient remains in the clinic for some time. Doctors recommend not to bother with physical activity or stressful situations for about two months after leg surgery.
Leg plastic surgery is an effective and very effective option for correcting leg imperfections. In addition, the results after surgery last for the rest of your life.
Traumatic amputation
Traumatic amputation is the partial or complete separation of fingers or sections of them as a result of injury. Surgical treatment for such injuries has some features:
- The operation is performed only when the patient’s condition is stable (after recovery from shock, normalization of the heart and lungs);
- If it is impossible to sew back the torn part, the finger is completely removed;
- In case of severe contamination and risk of infection, primary wound treatment is required, when non-viable tissue is removed, the vessels are ligated, and sutures are applied later or repeated amputation is performed.
If amputated fingers are delivered with the patient, the surgeon takes into account their shelf life and tissue viability. At a temperature of +4 degrees, fingers can be stored for up to 16 hours, if it is higher - no more than 8 hours. A storage temperature of less than 4 degrees is dangerous due to frostbite of the tissue, and then sewing the finger in place will become impossible.
No matter how carefully the operation to amputate fingers and toes is performed, it is impossible to completely eliminate the consequences. The most common of them are purulent complications in the case of traumatic amputations, progression of the necrotic process in vascular diseases, diabetes, formation of a dense scar, deformation and immobility of the fingers, which is especially noticeable on the hands.
To prevent complications, it is important to carefully adhere to the amputation technique and the correct choice of its level; in the postoperative period, recovery with the use of physiotherapeutic methods and physical therapy is mandatory.
Treatment of arthritis of the fingers - diet + folk remedies
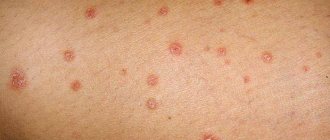
We often see elderly people with disfigured joints of their hands. “The reason for this is old age,” it seems so at first. But, alas, this is far from the case. Young people also suffer from this disease. Arthritis of the fingers is a fairly common disease.
The inflammatory process can occur in absolutely any joint. Most often it affects the small joints of the fingers. Arthritis of the finger joints causes great inconvenience and unbearable pain. During the illness, severe pain is accompanied by local changes in the skin (redness, swelling), and the appearance of fever in the patient.
Types of disease
Arthritis, which affects the fingers, is a rather insidious disease. It happens that, against the background of relative health, it suddenly bursts into a person’s life, and immediately in an acute form. Experts classify the disease as infectious, rheumatoid and metabolic arthritis.
- Infectious arthritis on the fingers appears due to infection. In this situation, it is necessary to eliminate pain. Manifestations of arthritis can be seen in the photo.
- Metabolic arthritis occurs as a result of the accumulation of purine in the blood, which is found in large quantities in meat. An excess of this substance disrupts the metabolic balance. This, in turn, causes a concentration of uric acid in the blood, which in the future can lead to a more serious disease - gout. With this type of arthritis, patients experience severe pain in the phalanges of the fingers, and lumps form on them.
- Rheumatoid most often appears in old age, less often in children. The main reasons are considered to be hypothermia, heredity, trauma, infectious diseases, and age. As a rule, this type of arthritis of the fingers and toes appears after prolonged physical activity. There is a feeling of discomfort in the fingers, the skin turns red, and swelling appears.
Symptoms of the disease
To know what to deal with, it is necessary to clearly understand the symptoms of arthritis of the joints of the fingers in order to timely seek qualified help. The disease is quite insidious; it chooses its victims even among the young. According to doctors, the disease becomes younger every year.
- The very first and most alarming symptom is an increase in temperature. A person may seem absolutely healthy, and a sharp jump in the mark on the thermometer will lead to complete confusion.
- I suffer from chills for several days, and sometimes fever.
- The added lethargy and complete powerlessness aggravate the already unpleasant situation.
- In addition, dizziness appears and appetite disappears.
- To this is immediately added the following symptom - severe pain and aching in the joints of the hands. The pain can be very different: from sluggish, aching to cutting and sharp.
- Next, we carefully examine the appearance of the hand. Swelling and redness around the joint is a clear sign. And if at the same time you feel severe stiffness, then it is clear that these are symptoms of arthritis of the joints of the fingers, which will now only intensify with every minute.
Most often, arthritis of the thumb begins, and if the disease is not treated, it spreads to the other fingers.
The disease is developing quite rapidly. At the first suspicion, you should immediately contact specialists for diagnosis and treatment. If the moment of onset of the disease is missed and the disease is already progressing, many unpleasant surprises await you:
- the joint capsule becomes inflamed, releasing excess lubricant;
- cartilage destruction occurs;
- the joint begins to deform;
- fingers lose mobility and curl.
Causes of the disease
The reasons can be very different, there are about 150 of them. Here are just a few of them:
- bruises, injuries, joint surgeries;
- metabolic disease;
- malfunction of the endocrine glands;
- infectious diseases, viruses;
- professional, sports loads;
- poor nutrition;
- hypothermia;
- bad habits;
- ecology;
- heredity.
Very important: if you experience a feeling of stiffness, persistent and recurring pain or swelling when waking up in the morning, seek a qualified diagnosis. After all, the causes inherent in the disease of arthritis of the joints of the fingers may be unexpected.
Treatment
The disease has been studied in detail. Special medications have been developed that help fight the disease. If treatment is started in a timely and comprehensive manner, it can be quite successful. If you consult a doctor at the first symptoms, you can not only save the patient from severe pain, but also disability.
How to treat arthritis so that therapy is effective?
- It is important to diagnose and begin treatment at the earliest stages.
- For infectious arthritis, corticosteroids, vaccines and antibiotics are prescribed.
- Analgesics are used to relieve severe pain and inflammation.
- To stop the degenerative process, chondroprotectors will be used to restore cartilage tissue. If the expected positive effect does not occur, specialists prescribe stronger antirheumatic drugs.
A patient with arthritis often experiences feelings of irritation, tearfulness, and sleep function is impaired. To improve the condition, sedatives and sleeping pills are prescribed. Often, various anti-inflammatory and analgesic rubs, infusions, creams or ointments are used for illness. It would be a good idea to take vitamins, preferably in the form of injections. This will not only reduce the symptoms of pain, but also improve the condition of the nervous system.
Treatment of arthritis of the fingers gives a positive result if used in combination with physiotherapy (electrophoresis, diadynamic therapy, UHF, ultrasound, magnetic therapy). In the remission stage, the patient can be offered mud applications and hydrotherapy. Each patient must have an individual approach.
How to treat arthritis with folk remedies
Not only drug therapy can give positive dynamics. When it comes to treating with folk remedies, I usually use ointments and compresses with mustard, mumiyo, and blue clay. We should also not forget about decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs. In any case, any treatment should begin only after diagnosis and consultation with specialists. For example, using an ointment made from the yolk of one egg and a teaspoon of turpentine and apple cider vinegar has a good effect. All this is mixed until smooth and rubbed into the skin until completely absorbed.
How to alleviate the course of the disease
There are several rules that must be followed during illness to make it easier to bear:
- the load on the finger joints should be kept to a minimum;
- Perform daily stretching exercises with moderate intensity;
- doctor’s orders must be followed unquestioningly;
- ensure a good night's rest;
- in acute conditions of arthritis, the diet should be strict.
In particular, the diet contains the following recommendations: you need to consume a certain amount of foods from each group daily:
| Group | Number of servings (minimum) |
| Fruits and vegetables | 2 / 3 |
| Cereals and bread | 6 |
| Milk and dairy products | 2 |
| Lean meat, fish, legumes, nuts, eggs | 1 |
Dishes should be prepared with a minimum amount of fat and salt. You should also drink enough fluids and drink alcohol in moderation.
No one can tell you whether you will be completely cured of the disease or not, but following preventive procedures and doctor’s orders will greatly help alleviate the condition and continue to live a full life.