Skin grafting, or dermatoplasty, is a surgical procedure performed to recreate damaged areas of the skin. Skin grafting after a burn is used if the basal layer of the dermis is affected, there are noticeable scars and other deep defects. The method of surgical treatment depends on the extent and location of the wounds. For burns of 3B and 4 degrees, surgery is performed immediately after injury. More often, dermoplasty is prescribed after tissue restoration to eliminate scars.
Who is suitable for skin grafting?
Skin transplantation is a complex surgical operation, which is prescribed for deep lesions of soft tissues. The success of therapy depends on:
- surgeon qualifications;
- area of the wound surface;
- patient's immunity.
The main indication for surgery is a deep burn when other treatment methods are ineffective. Without the epidermis and dermis, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the body and heat exchange is disrupted. Burn injuries are fraught not only with cosmetic defects, but also with non-healing wounds and severe pain. Dermoplasty is necessary for extensive small-area burns, which are accompanied by total death of the skin down to the fatty tissue.
Skin transplantation after a burn in children and adults is advisable when all layers of the epidermis, dermis, fatty tissue, and muscles are damaged. Burns 3A, 3B, 4 degrees are the main indications for transplantation. In case of partial destruction of the basal layer, surgical treatment is prescribed after tissue healing to eliminate cosmetic defects - hypertrophic scars, burn scars.
How to do plastic surgery after a burn
In most cases, the operation is performed under general anesthesia. After it has taken effect, the process goes like this:
- Using a transparent film, the size and contours of the problem area are determined. Using the resulting pattern, the boundaries of the donor flap are drawn onto healthy skin.
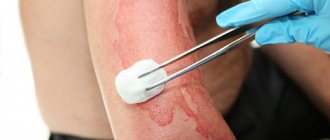
- A scalpel is used to excise the area of tissue that will be transplanted. The autograft is treated with a special compound and sent to a machine that separates the part of the required thickness.
- Bleeding is stopped on the donor surface. To do this, the wound is sutured or an antimicrobial healing composition is applied. A bandage is applied on top.
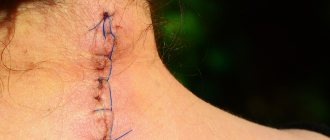
- The scar surface is wiped with an antiseptic and dried. The graft is placed in the desired location. Using synthetic threads, its edges are connected to the boundaries of the wound. A sterile bandage is applied on top.
To learn how plastic surgery is performed after a burn, watch this video:
Types and techniques of plastic surgery on the skin
Skin grafting surgery after a burn is carried out in several stages. The duration of the procedure depends on:
- type of transplanted material;
- area of the burn wound;
- surgeon experience.
In surgery, there are 2 types of dermatoplasty:
- primary – suturing fresh burn wounds;
- secondary – correction of defects after skin regeneration.
Two dermatoplasty techniques are used - free and non-free, each of which has its own characteristics.
Non-free plastic
The operation involves plastic surgery using partially rejected local tissues and pieces from other parts of the body. In the second case, a flap on a feeding pedicle is used - pieces of skin with a subcutaneous fat layer and blood vessels.
There are three groups of transplants:
- flat;
- insular;
- tubular.
Plastic surgery with local grafts is performed in different ways:
- replanting of partially rejected flaps;
- plastic surgery according to I. Dieffenbach with the application of loosening notches to the graft;
- operation according to Yu. K. Shimanovsky with the closure of square wounds with movable rectangular flaps.
For burns in the facial area, plastic surgery using adjacent triangles is used. They are cut out together with the subcutaneous fat so that their angles are 30, 45 or 60°. The first type of triangle is used for facial plastic surgery, the last two are used to cover burns near the joints.
Transplantation can quickly restore normal functioning of the skin, remove inflammation, and also prevent the occurrence of an infectious disease or infection.
When transplanting a donor flap from another part of the body, the operation is carried out in 2 stages:
- preparing the graft for transplantation;
- suturing a prepared piece of skin to the burn wound.
Remote dermatoplasty is used to correct defects on the face. In a direct transplant, the surgeon removes a flap containing subcutaneous tissue from the shoulder area and then performs a nose job.
In difficult cases, they resort to combined non-free plastic surgery with simultaneous sewing in of local burned tissues and pieces from other parts of the body.
Combined techniques are used for primary transplantations immediately after a burn. If successful, there is no need for secondary surgery to correct cosmetic defects.
Free plastic
Free dermatoplasty is conventionally divided into two types.
Vascularized
Transplantation of complex grafts with the formation of new vessels inside the graft. It is carried out with a microscopic instrument under a microscope. To take a piece of skin, use a sharp scalpel, through which a piece is removed along with subcutaneous fatty tissue and the vascular network. During surgery, the vessels quickly connect with the capillaries around the wound.
Nonvascularized
Transplantation of large areas of skin using a dermatome (an instrument that removes a layer of skin of the required thickness). During the operation, two types of grafts are used - split or layered. The former include all layers of the dermis, and the latter exclusively the outer layers of the epidermis.
To take a split flap, a medical instrument in the form of a plane is used. It is intended for removing a donor flap for large area burns. The cut graft is lubricated with surgical glue, after which it is transferred to the drum. During treatment, the outer layer of the epidermis is removed. The prepared skin piece is placed on the operated area. The edges are sutured with nylon thread, and the graft itself is secured with a plaster cast or medical splint.
After surgery, dressings are done using antimicrobial ointments. They prevent inflammation of the operated tissues and transplant rejection.
Recovery period
Whether the tissue has taken root will become clear within a week after transplantation. During this entire period, the bandage is not removed, it is simply changed regularly. If pus and inflammatory processes appear, this indicates that the body is rejecting the material. Even if it takes root, rehabilitation after skin grafting will be required for several months. The most severe cases require rehabilitation therapy for six months.
During this entire period, the patient will need to follow the doctor's instructions. First of all, several groups of drugs are prescribed to relieve various symptoms that arise during the rehabilitation period. Glucocorticosteroids are prescribed, as well as agents to eliminate inflammatory processes and tissue regeneration.
During the recovery period, the victim needs to use physical therapy. It is necessary to remember the possibility of deformation of joints and tendons during scar formation. Therefore, it is important to start rehabilitation as early as possible. The part of the body on which the transplant was performed must move frequently and a lot. The restorative course of procedures will be selected by the attending physician.
Physical therapy, electrophoresis, and magnetic therapy are used. During physical therapy, special medications are used to soften scars and relieve inflammation. In some cases, additional surgery may be required to correct remaining cosmetic imperfections.
For many patients, skin graft surgery after a burn is the only way to continue a normal life. Despite all the difficulties associated with its implementation, the benefits of transplantation are much greater. It improves the quality of life of burn victims and restores their ability to enjoy life.
Where do they come from and what types of transplants are there?
To cover the surface of the wound, artificial or natural grafts from one's own or donor skin are used. When preparing for dermatoplasty, the following tissue properties are taken into account:
- color;
- elasticity;
- blood supply;
- degree of hair growth.
When preparing for dermatoplasty, surgeons are guided by the principle: the closer the donor tissue is to the operated area, the higher the quality of the graft. For example, for facial burns, skin flaps from the supraclavicular area are usually used. They take root well and retain a pink tint that does not differ in color from the surrounding tissues. In turn, flaps from the subclavian zone often acquire an unnatural yellowish tint.
There are several areas for donor skin that are suitable for closing burn wounds:
- stomach;
- upper back;
- supraclavicular region;
- lateral surfaces of the chest;
- inner thighs.
When performing facial plastic surgery after burns, flaps from the following areas are used:
- in front and behind the ear;
- supraclavicular.
To cover large wound surfaces, split flaps are used, which consist of superficial layers of skin. They are taken from the buttocks, inner thighs, and abdominal wall.
Depending on the depth of the burn and the area of damage, grafting material of varying thickness is used:
- Thick – contains all of its epidermis and dermis. Its thickness reaches 0.8-1.1 mm.
- Middle - includes the main layer of the dermis (reticular layer), which contains many elastic fibers. The thickness of the flap does not exceed 0.3-0.7 mm.
- Thin - consists of germ and epidermal layers, therefore contains few elastic fibers. After the burn heals, the sewn-in flap of skin shrinks. Its thickness is no more than 0.3 mm.
The following are used as donor material:
- amnion – the embryonic membrane of vertebrates;
- xenoskin – pig skin;
- allo-skin – preserved skin of deceased people.
Also used for burns is explant material - living tissue that is cultured outside the body in a nutrient medium. In 2017, the Spanish company BioDan Group, with the support of a research institute, developed a technology for printing a bionic substitute for living tissue. Artificial leather is printed on a 3D bioprinter charged with cartridges with:
- keratinocytes;
- blood serum;
- calcium chloride;
- fibroblasts.
Scientists have obtained a multilayer matrix on a hydrogel that supports cell viability. Artificial skin “ripens” in the laboratory and only then is transplanted into the human body. But so far this technology has only been tested on mice and is not included in surgical practice.
How is the operation performed?
Any such intervention begins with the selection of healthy areas. Depending on the location where it is taken, the area is processed and the required layer is cut out. If tissue is taken from a living donor, anesthesia is used. The areas usually used are the hips, buttocks, back, and chest. The area is cut out using a special tool.
At this point, a second group of doctors prepares the patient for surgery. The affected area is further treated and dried. In this case, there should be no inflammatory processes. Then the transplant itself begins.
A piece of healthy skin is placed over the damaged area. If the damaged area is small, it is fixed using special glue or staples. Serious injuries require surgical sutures. After this, doctors secure the area with a tight bandage. The entire manipulation takes no more than an hour, so it is considered a fairly simple procedure.
On the first day after transplantation, the patient's condition is closely monitored. Bandages are changed regularly and the surface is treated with disinfectant solutions. During and after the procedure, the victim may experience unpleasant symptoms such as bleeding or infection of the surface. In addition, skin sensitivity decreases and there may be a risk of rejection.
The likelihood of complications is most often encountered by people with poor immunity and certain chronic diseases. Age is also a risk factor. Interventions should be used with caution in young children and the elderly.
Postoperative care
The rehabilitation period after surgical treatment of burns takes from 3 to 6 months. It includes three stages:
- adaptation – from the end of dermatoplasty to the first 2 days;
- regeneration – from 3 days after surgery to 2-3 months;
- stabilization – after 3 months. after skin transplantation.
To prevent complications, patients must follow all doctor’s recommendations:
- Dressings must be done within 1-2 weeks. Compliance with sanitary and hygienic rules prevents infectious complications.
- The bandage is not removed until the skin has healed. This stage takes from 4 to 6 days. But in order to prevent detachment of the flaps, dressings are performed for another 7-9 days.
- To restore the skin, the operated areas are lubricated with ointments. Moisturizing antiseptic preparations stimulate healing.
Operated patients complain of severe pain, so they are prescribed local or systemic analgesics. To prevent infectious inflammation and tissue rejection, they take vitamin and mineral complexes with retinol, tocopherol and other bioactive additives.
The transplanted skin is vulnerable for the first 2-3 months. She is practically incapable of self-healing. Therefore, patients are prohibited from visiting saunas, swimming pools, and solariums. You should also avoid prolonged exposure to the sun. The operation is considered successful if there are no complications after 3 months.
Operation methods
If there are serious skin lesions, surgery should be performed as quickly as possible. Only in this case can complications be avoided and the victim’s condition improved. The doctor prescribes a transplant after 1 month if the damage is not very serious, and after 2 to 3 months if the injuries are significant.
To speed up the healing process, dying tissue is removed, but this must be done with caution so as not to worsen the patient's condition. Manipulations are carried out when about 2 - 3 weeks have passed since the burn. Dead areas are removed gradually when the dressings are changed.
When carrying out the intervention, work is carried out by 2 groups of medical workers at once. The first takes tissue for transplantation, the second prepares the patient for surgery. Use one of several types of procedures:
- a thin layer of skin is transplanted, which promotes rapid survival and reduces the risk of rejection;
- Thick section transfer is usually applied to prominent areas (face, neck). Scars in this case are less noticeable;
- In addition to skin transplantation, cartilage or fatty tissue is also restored.
Possible complications
The procedure of skin grafting after burns is dangerous due to both early and delayed complications. The first include:
- bleeding from the operated area;
- rejection of donor skin;
- slow wound healing;
- infectious inflammation.
If the skin flap is detached, repeat dermatoplasty is performed.
Although necessary, the transplant procedure has some disadvantages. The main one is the risk of transplant rejection. If donor skin or synthetic material is used as a material, there are always concerns about tissue incompatibility.
If ulcers form at the site of damage, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. But even after successful engraftment, complications sometimes arise:
- decreased sensitivity of the skin;
- lack of hair growth in the transplanted areas;
- scarring, shrinkage of the graft;
- stiffness of movement due to tissue tension.
Lumps, insensitivity, and discoloration of the skin at the burn site are reasons to consult a doctor. The specialist will assess the severity of the situation and determine the least traumatic ways to eliminate complications.
Types of plastic surgery
Aesthetic surgery has the following types of operations:
- Free plastic . A skin flap completely separated from the donor area is used.
- Non-free plastic surgery . The defect is repaired with an adjacent skin graft or a piece of tissue on the feeding pedicle. The latter means that the transplanted flap is partially separated from the base. Its nutrition is carried out through an untouched area of skin through which blood supply occurs.
A) 3rd degree burn.
(B) Prompt surgery was performed. To eliminate the defect, material was taken from the skin of the thigh. (C) Six months after surgery. A finger separation procedure was performed. In turn, free plastic surgery can be:
- Vascularized , in which a skin flap with vessels is used. They connect to the general circulatory system.
- Nonvascularized when large areas of skin are transplanted. The transplanted material is taken split, that is, with the outer lobes of the epidermis, or layer-by-layer (for the entire thickness of the skin).
Depending on the time of transplantation, operations are:
- primary , when fresh wounds close;
- secondary , in which the scar tissue that formed several months after the burn is eliminated.
When not to have surgery
Reconstructive skin plastic surgery is contraindicated if there is a high risk of complications. Carrying out skin grafting procedures on burn wounds is prohibited when:
- secondary immunodeficiencies;
- purulent complications;
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- mental disorders;
- skin diseases.
Cosmetic plastic surgery is not prescribed during pregnancy, exacerbation of chronic diseases, or if damaged tissues are infected.
The operation is postponed in case of herpes zoster, trichophytosis, abscesses, acne, etc. Patients with vitamin deficiency undergo pre-vitamin therapy. It stimulates the immune system, thereby reducing the risk of infectious inflammation of transplanted tissues and their rejection.
Types of plastic surgery for scars on the face and body
Modern plastic surgery for scars and burns of the face and body today has various techniques for “removing” damage. They can be not only surgical, but also “non-surgical”.
Non-surgical methods of plastic surgery for burns and scars
Non-surgical methods today include laser, ultrasound and injection technologies. They are something between surgical interventions and cosmetic procedures. They are similar to the former in efficiency, and to the latter in their minimal invasiveness. The latter term means that this kind of manipulation is minimally traumatic, it does not affect nearby healthy tissue, does not require sutures and does not even require a hospital stay.
Laser and ultrasound methods involve smoothing out the scar either by removing the upper layers of the epidermis in the damaged area to bring it as close as possible in texture and color to the appearance of healthy skin, or by evaporating it, when under the influence of the energy of a laser beam the liquid contained in the damaged tissue is gradually heated and then removed . The indication in this case is scars that are not rough and relatively small in size.
Injection methods of scar plastic surgery are indicated in the case of retracted scars. Correction here occurs through the introduction of special preparations into the subcutaneous space, which, filling it, return the skin to an even and smooth surface. However, this procedure also involves laser resurfacing, which evens out the tissue in color.
In addition to non-surgical methods, plastic surgery of facial burns and scars also “operates” with endoscopic and classical surgical techniques.
Average cost of skin transplant in Moscow
Dermatoplasty is an expensive operation, the cost of which depends on:
- wound area;
- transplantation techniques;
- surgeon qualifications;
- type of transplant.
Autoplasty is cheaper because the person’s own tissue is used for transplantation. Prices for surgery in Moscow clinics vary from 100 thousand to 260 thousand rubles.
Skin grafting is one of the effective methods for treating serious burns and post-burn scars. During the operation, the area of the skin that has undergone changes is recreated. The success of dermatoplasty depends on following medical recommendations. To prevent complications, patients must take prescribed medications and undergo physical therapy.
Burn degrees
Based on the depth of tissue damage, burns are classified into 4 degrees.
- Damage to the surface layer (epidermis), accompanied by pain, redness and slight swelling of the burned area. Heals in a few days without special treatment.
- Damage to the epidermis and upper layer of the dermis, manifested by severe pain, swelling, redness, and the formation of blisters filled with clear serous fluid. With proper drug therapy, the injury heals in 10-14 days.
- A 3rd degree burn is classified into 2 types. Degree 3A is characterized by damage to the epidermis and dermis, the formation of large blisters with cloudy liquid inside, and a scab (crust) on the burned surface. Degree 3B is diagnosed when all skin layers are affected and subcutaneous fat is partially damaged. The resulting blisters are filled with bloody fluid.
- The most severe injury, accompanied by charring of the skin, muscle and bone tissue, and complete loss of sensitivity due to the destruction of nerve fibers.
Even a small but very deep burn is dangerous due to the penetration of infection and its spread through the bloodstream throughout the body. The results can be sepsis and death.
Difficulties of face transplantation
Transplantation of facial tissue is indicated only when reconstructive plastic interventions are impossible due to large tissue loss.
The first difficulty is the intervention itself. The essence is this: each organ (nose, eyelids, lips) is returned to its normal size and place, and in the absence of an organ, doctors form it anew. The operation is considered difficult for surgeons and risky for the patient. During transplantation, severed nerves, blood vessels, and transplanted parts of the face are connected, and the formations begin to work as if they were their own.
According to reconstructive surgery specialists, in the future, face transplantation will become a routine plastic intervention. Anyone can afford a transplant. However, other doctors believe that this operation is too complex to become routine.
The second difficulty is finding a suitable donor skin flap. It is taken from people who are related by blood to the patient, or it can be cadaveric material. If the lesion is deep, then not only skin flaps are required, but also bone flaps (i.e., bone fragments). Bone tissue is collected only from corpses.
Donor organs and tissues must be compatible with the tissues of the recipient (patient). Otherwise, rejection will begin.
The third difficulty, which is also the main one, is the process of transplant rejection. The host's immune system recognizes the transplanted tissue as foreign and attacks it. As a result, all the painstaking work of doctors goes down the drain. To avoid this, the tissue compatibility of the donor and recipient is carefully examined.
The fourth difficulty: even with close to ideal compatibility, the patient will take drugs that suppress his immune system for life in order to prevent immune aggression against the transplanted tissue.
Price
The cost of skin grafting is determined by various factors: the area of the damaged surface and the complexity of the specific operation, the type of materials and anesthesia used for transplantation, other pharmacological agents, the qualifications and professionalism of the surgeon, the location and reputation of the clinic. Depending on these factors, the price of the operation can range from 10,000 to 200,000 rubles.
Skin plastic surgery after a burn is not a complex or lengthy operation. But in some situations, graft engraftment after transplantation proceeds poorly, even if the donor material is one’s own skin. Detailed preparation for plastic surgery, correct calculation of the timing of its implementation, and appropriate care during the rehabilitation period are mandatory conditions for successful skin plastic surgery and help minimize the likelihood of developing postoperative complications.
Pros and cons of skin plastic surgery
Skin transplantation after a burn, like all other types of plastic surgery, has its advantages and disadvantages. The first include:
- protection of the wound from infection and mechanical damage;
- preventing moisture evaporation and loss of nutritional compounds through the open surface of the wound;
- more aesthetic appearance after healing of the wound surface.
The disadvantages of surgical intervention include:
- the possibility of rejection of the transplanted material (when transplanting your own skin, the risks are much lower);
- the likelihood of developing other complications;
- psychological discomfort of the patient (for example, if the donor material is cadaveric skin or tissue taken from an amputated limb).
Artificial leather "Stratagraft": treatment of severe thermal burns
Mallinckrodt has developed an effective alternative to autodermoplastic procedures.
Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals rose by a quarter after announcing the success of a pivotal clinical trial of its experimental regenerative therapy StrataGraft, which was studied in the treatment of thermal burns. The registration dossier is scheduled to be submitted to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the first half of 2020.
"Stratagraft" has been tested in the task of regenerating skin affected by a thermal burn, which led to incomplete necrosis with preservation of the growth zone. Typically, in such cases, autodermoplasty is performed, when the patient is transplanted with his own healthy skin from undamaged areas. And although the technique is considered very effective, it often leads to problems with increased wound load and healing of donor sites, which are painful, itchy and prone to infection and scarring. Again, if the burn area is large, there are not enough free flaps of skin, and therefore it is necessary to transplant tissue from the same area several times, each time waiting for its integrity to be restored. At such moments, the burn surface is protected, for example, with cadaver skin, pig skin or synthetic material, which act as a temporary protective barrier.
The Stratagraft, the equivalent of healthy human skin tissue, comprises dermal fibroblasts and fully stratified (multilayered) bioactive epidermis derived from the NIKS cell line, an infant tissue-derived keratinocyte progenitor cell that is immortalized, genetically stable, nontumorigenic, and pathogen-free. “Stratagraft”, which actually replicates the structure of natural skin, is assembled from two layers: an internal one, similar to the dermis, and an external one, similar to the epidermis. "Stratagraft", devoid of acute immunogenicity, does not cause rejection and does not lead to immune responses against NIKS. Mallinckrodt took over Stratagraft after purchasing its originator, Stratatech, in August 2020. The development is being carried out with financial assistance from the government's Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA).
Despite the extensive efforts of the industry, to date no cellular or synthetic product has been proposed that independently shows the same effectiveness in wound healing of burns as autodermal grafting does.
Clinical trials STRATA2016 (NCT03005106) phase III (randomized, open, multicenter) tested the safety and effectiveness of "Stratagraft" among adult patients (n=71) in the task of autologous regeneration of skin tissue in complex thermal skin lesions, burns of which affect the entire epidermis and more than two third dermis. Burns to the body, arms, or legs that still contained intact dermal elements had to be eligible for excision and autologous transplantation procedures. Randomization was carried out on each patient, when two similar burn areas of the same patient underwent either standard autodermoplasty therapy or Stratagraft treatment.
Within three months after therapy, 4% of burn areas to which Stratagraft was applied required an additional procedure of standard autodermoplasty - versus 2% of areas that initially underwent it. In other words, Stratagraft has reduced the need for traditional skin grafting of the patient's own skin by 98% (p