The mammary glands in boys and girls are identical before puberty. At the age of 12-13, the male body begins to synthesize the hormone testosterone, which should be used to build a male body and form secondary sexual characteristics. Where then does enlarged breasts come from - gynecomastia in adolescents?
The fact is that many boys enter adolescence overweight. Malnutrition - lack of a full breakfast and frequent consumption of fatty and sweet foods leads to excess deposition of fatty tissue in the hips, lower back, abdomen and chest. This is also facilitated by the refusal of sports activities and a sedentary lifestyle. As soon as puberty occurs, the male hormone testosterone can be converted in excess into the female sex hormone estradiol, which forms breasts in such a teenager according to the female type and develops gynecomastia.
There is another option - physiological gynecomastia, associated with a sharp increase in testosterone levels, which goes away on its own in adolescents within a short time after its onset.
Gynecomastia in adolescence
"Wait until you're 18..."
As a rule, parents of such children turn to an endocrinologist and are advised to wait indefinitely. This statement is paradoxical. If gynecomastia does not go away on its own within six months after its occurrence, it can no longer disappear. The growth of the rudimentary mammary gland is controlled by hormones, and it is estrogens that are responsible for this process. Figuratively speaking, the mammary glands do not care in which body they exist - male or female. They will behave as their hormones tell them to. That is, despite the fact that gynecomastia is a pathology in the male body, the growth of the mammary glands is a natural phenomenon in the event of an increase in estrogen levels. The formed mammary gland is essentially an organ that cannot disappear anywhere.
In our practice, there have been cases when desperate young people sought surgical help immediately after reaching adulthood due to a lack of mutual understanding with their parents, who were afraid to have surgery or hoped that gynecomastia would disappear.
Symptoms and causes
In recent years, enlargement of the mammary glands in children has been observed much more often than 9-10 years ago. Pediatric mastopathy causes serious concern among specialists, since medications that relieve adults from this disease are not suitable for a growing body. Side effects of these drugs can seriously affect the formation and functioning of organs.
Mastopathy in children has symptoms similar to those in adults:
- enlargement of one or two mammary glands at once;
- upon palpation, small balls or compactions are felt in the mammary glands;
- pain in the mammary glands;
- redness around the nipple;
- When you press on the circumference of the nipple, discharge appears from the milk duct.
The causes of breast enlargement in childhood partially overlap with those that provoke the disease in adults. Mastopathy in children occurs against the background of:
- drug therapy associated with hormonal components of drugs;
- serious metabolic disorders in the child’s body;
- disorder in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- serious disturbances in the functioning of the liver associated with its failure;
- severe liver diseases.
Leave breasts to women and be men!
Adolescent gynecomastia is not only a medical, but also a social problem. Female breasts in a young man can be a serious obstacle to the formation of his personality as a man. Sports activities, equal relationships with peers, and communication with the opposite sex can be difficult or even impossible for boys with gynecomastia. We know examples when teenagers became withdrawn, preferred “communication with the computer” to social contacts, fell into depression, lost motivation to study, develop physically and become men.
In addition to psychological complexes and social maladjustment, such adolescents experience poor posture. In an effort to hide women's breasts, they stoop for many years, which leads to curvature of the spine. Some young men are forced to bandage their breasts with elastic bandages or cover their areolas with a plaster. There is no point in hoping that gynecomastia will go away over time. It is impossible to get rid of breasts with the help of medications.
Possible complications and consequences
Gynecomastia that exists for more than 12 months may undergo scarring (fibrosis), which makes drug treatment extremely difficult.
Another complication of gynecomastia is psychological consequences; they most often occur in adolescents if breast enlargement is the cause of inferiority complexes.
Teenage gynecomastia usually goes away within the first two years after it occurs. This pathology only causes psychological discomfort in the boy. Young men with this problem are sometimes embarrassed to go to the swimming pool, gym, or use shared locker rooms.
But in some cases, the disease can cause serious problems in the socialization of a teenager. An increase in the volume of the mammary glands, which persists and develops for more than a year, can provoke fibrosis - scarring of tissue in the affected area. This significantly complicates drug therapy.
In extremely rare cases, gynecomastia can cause the development of carcinoma, a very serious disease. Therefore, if you experience severe chest pain, dark discharge from the nipples, or swelling, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Diagnosis of teenage gynecomastia
Diagnosing juvenile gynecomastia is not difficult. In most cases, an examination by a specialist is enough to make the correct diagnosis. Ultrasound can be an auxiliary diagnostic method.
The main task of the doctor is to exclude hormonal disorders, as well as genetic diseases, the symptom of which may be gynecomastia. If there are none, and gynecomastia is a manifestation of a hormonal imbalance noted during puberty or obesity in a teenager, treatment can only be surgical. Of course, such a young person needs to be oriented towards a healthy lifestyle, motivated to eat right and play sports. Often the first step on the path to physical rehabilitation is a surgical operation to get rid of female breasts.
Pubertal (youthful) gynecomastia
Pubertal gynecomastia in teenage boys is a benign enlargement of the mammary glands with a diameter of more than 1.5-2 cm during puberty.
More than half of all teenagers encounter this problem between the ages of 12 and 15.
In most cases, the disease goes away on its own, but, like protruding ears at an early age, it causes physical and mental discomfort to the child’s fragile body.
Symptoms and signs
The disease is typically asymptomatic, but with pronounced enlargement of the mammary glands, pathology can manifest itself.
This is expressed as follows:
- pressure, bloating and itching in the area of the mammary glands;
- upon palpation, a dense, painless formation is determined that is not fused with the surrounding tissues;
- the lymph nodes are normal, the general condition of the patient is not impaired.
Lymph nodes
At what age can it occur?
About 50-70% of healthy male adolescents aged 12-15 years experience gynecomastia..
For some, this process is observed even at 16 years of age.
How often does it occur?
Statistics about this problem are somewhat underestimated, since parents and doctors do not always pay attention to minimal changes in the mammary glands of a teenager, and the young man himself may not be psychologically ready to talk about his problem.
How long does it last?
In most cases, gynecomastia disappears on its own at the age of 15-16, in rare cases persisting until the age of 19.
In a number of patients, gynecomastia persists for a long time - then this condition is classified as a pathology and they begin to actively look for the cause of the disease.
Pubertal gynecomastia at 13 years of age
Causes
The common cause of gynecomastia is an excess of estrogen in the male body.
This condition may occur in the following cases:
Physiological reasons
- neonatal: an excess of estrogen is often observed in the blood of newborn boys. This condition is rarely permanent and goes away on its own within a few weeks.
- juvenile gynecomastia (micd 10): boys in adolescence may experience excessive activity of the enzyme aromatase, which converts testosterone into estrogen.
Estrogen and testosterone
Pathological causes
- taking certain medications that affect the amount and production of estrogens (antidepressants, anti-tuberculosis drugs, opiates, antiandrogens, etc.);
- regular use of alcohol, heroin, marijuana;
- tumors (hormone-producing tumors of the testicle or adrenal glands);
- endocrine pathology (Cushing's syndrome, acromegaly, etc.);
- systemic diseases (liver pathology, HIV infection, severe kidney disease);
- other conditions (injuries or herpes zoster in the mammary glands, excess body weight, etc.).
Hormone-producing testicular tumors
Gynecomastia in boys during adolescence is most often physiological and goes away on its own after some time.
To determine the exact cause of the development of pathology, consultation with one or more specialized specialists is required.
How dangerous is the disease?
The disease in adolescents has a favorable course and disappears spontaneously after a certain period of time.
Gynecomastia can lead to psychological trauma in a teenager, and severe enlargement of the mammary glands can cause a feeling of pressure, increased sensitivity and trauma to the nipples.
Increased nipple sensitivity
With unilateral enlargement of the mammary glands, the risk of developing a tumor process increases, so this condition requires dynamic monitoring and observation by a specialist.
Types of gynecomastia
In medical practice, gynecomastia is not an independent disease, but is a symptom of another disease.
There are several types of the disease:
- true;
- false;
- mixed.
True gynecomastia
The development of true gynecomastia is caused by an excess of the female hormone (estrogen) in the male body.
The mammary glands enlarge due to hypertrophy of the tissues of the gland itself and the milk ducts.
Depending on the causes of occurrence, there are two types of gynecomastia:
- Physiological: neonatal, familial, idiopathic and adolescent gynecomastia.
- Pathological: tumors, endocrine diseases, etc.
True gynecomastia in a teenager
False gynecomastia
Lipomastia (pseudogynecomastia) is an enlargement of breast tissue due to the proliferation and enlargement of fat cells.
Develops in patients who are overweight.
Mixed gynecomastia
This type of disease is caused by the proliferation of both adipose tissue and the breast’s own tissue.
It is classified depending on the severity of certain symptoms.
Degrees
There are 4 degrees of breast tissue hypertrophy:
- The first is minimal enlargement of the gland.
- The second is an increase in less than the diameter of the nipple areola.
- The third is compaction within the size of the areola.
- Fourth – the diameter of the seal exceeds the size of the areola.
Based on the size of the mammary glands, gynecomastia is conventionally divided into moderate (up to 6 cm), medium (6-10 cm) and severe (more than 10 cm).
Fourth degree of gynecomastia
How to determine it yourself?
You can independently suspect the development of gynecomastia in a teenager by carefully examining and palpating the mammary glands. They increase in diameter by 2-3 cm or more, the nipples become pigmented and enlarged in size.
The child may complain of a feeling of pressure in the chest and discomfort when wearing clothes due to severe nipple sensitivity.
Which doctor should I contact?
If you suspect teenage gynecomastia, you should contact a pediatric endocrinologist , who will conduct the necessary examination and prescribe additional examination.
Pediatric endocrinologist for gynecomastia
Survey
The examination includes several stages.
Objective examination, history taking and palpation of the mammary glands
In this case, the patient is asked about medications taken, sports activities, alcohol use, drugs and other significant points.
Doctors assess the degree of development of secondary sexual characteristics and exclude systemic pathology.
During palpation, they look at the size, consistency and tenderness of the mammary glands and regional lymph nodes.
Analyzes
They determine the level of testosterone, estradiol, liver transaminases, prolactin and other hormones.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound examination is carried out to differentiate true and false gynecomastia, as well as to exclude a tumor process in the mammary glands.
Ultrasound of the testicles is performed to exclude a tumor.
Other types of research
In difficult diagnostic cases, a puncture of the mammary gland is performed to study the cellular composition of the formation and exclude a tumor.
Treatment of gynecomastia in adolescents
Treatment depends on the degree of hypertrophy, hormone levels, the presence of concomitant diseases and other factors.
A moderate degree of gynecomastia without pathological causes is left without treatment, but under the constant supervision of a specialist.
Tablets and drugs
Medications are prescribed taking into account the level of certain hormones in the teenager’s body:
- "Bromocriptine" and its analogues: stimulate dopamine receptors and block prolactin synthesis. Suitable for hyperprolactinemic type of juvenile gynecomastia.
- Thiamine bromide: blocks the aromatase enzyme, which promotes the conversion of testosterone to estrogen.
- "Testosterone": used for low testosterone levels in a boy's body. In some cases, the opposite effect may be observed.
- antiestrogenic drugs: Clomiphene, Takmoxifen and others. Used when there is an excess of estrogen in the body.
- course of vitamins B, A and E
The drug "Bromocriptine"
Diet
Compliance with the principles of the diet will give a pronounced effect in the case of false gynecomastia.
If the enlargement of the mammary glands is due to excess body weight, then only reducing the calorie intake and regular physical activity will help cope with the problem.
Diet principles:
- exclude alcohol and low-alcohol drinks from the diet;
- give preference to “slow carbohydrates” (porridge, yeast-free bread, brown rice, etc.);
- count and observe the number of calories consumed (about 2500 kcal per day);
- drink up to 2 liters of water per day;
- limit or avoid eating fried, sweet and starchy foods;
- eat foods high in protein (cottage cheese, turkey meat, etc.), vitamins and microelements (broccoli, cauliflower, spinach, etc.).
In cases of true gynecomastia, following the principles of a healthy diet will not lead to the desired result, but will help strengthen the child’s immunity and mental state.
"Slow carbohydrates"
Exercises
For gynecomastia during puberty, experts recommend increasing physical activity.
In cases with false gynecomastia, this will help get rid of excess weight, and with true physiological gynecomastia, regular exercise contributes to the production of male hormones.
Effective exercises for gynecomastia:
Push ups
Banal push-ups will strengthen the pectoral muscles and help get rid of excess fat in the chest area.
Focus on slightly bent arms, wider than shoulder-width apart.
The body is straight, the toes rest on the floor.
Taking into account physical fitness, perform 15-20 push-ups in 3-4 sets.
Push ups
Reduction and extension of arms in a lying position
This exercise requires dumbbells and a firm horizontal surface.
It is performed in a lying position on a bench, arms slightly bent at the elbows.
From a position above your head, the dumbbells are moved to the sides as far as possible and then brought back to their original position.
Perform 4 sets 10-15 times, gradually increasing the weight of the dumbbells.
Reduction and extension of arms in a lying position
Folk remedies
Treatment of gynecomastia with traditional medicine is a highly controversial issue.
It is acceptable to use sedative and hypnotic herbal infusions (valerian, motherwort, lemon balm, etc.) if the patient is having a hard time with his condition and is tormented by neuroses and insomnia.
You can use folk remedies that increase testosterone levels in the body and reduce the production of female hormones.
Such plants are ginseng root, thyme and lovage.
- Recipe 1: grind 40 gr. ginseng root and pour 800 ml of alcohol. Infuse in a warm place for 14-15 days. Take a teaspoon of tincture 3 times a day for a month.
- Recipe 2: pour 2-3 tbsp. dry thyme with a liter of water and boil over low heat for 10 minutes. Cool the broth and take half a glass once a day for 2 weeks.
Treatment of gynecomastia with folk remedies
Removal (operation)
Severe gynecomastia in boys rarely reverses.
In such cases, doctors prepare the child and his parents for surgery, which is performed under general or local anesthesia.
The choice of anesthesia and the extent of surgical intervention depend on the degree of hypertrophy of the gland, the amount of adipose tissue and concomitant diseases.
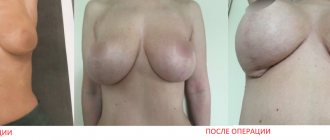
For true gynecomastia, a subcutaneous mastectomy is performed from an incision around the nipple areola.
For false gynecomastia, liposuction or lipectomy (removal of excess fatty tissue) is performed.
Important! It is prohibited to bandage or wrap the mammary glands with elastic bandages or other devices.
These methods lead to compression of lymphatic and blood vessels and can cause the development of malignant neoplasms.
Surgical removal of gynecomastia
Rehabilitation
During the rehabilitation period, it is recommended to use special compression garments to properly form the muscle corset and maintain skin elasticity.
The operation is well tolerated by the patients, and a month after surgery the patient returns to his usual lifestyle and sports.
Questions for the doctor
Question: How to treat gynecomastia in a 14-year-old son if the endocrinologist did not identify any significant abnormalities in the teenager’s body and advised him to simply monitor the child?
Answer: Moderate juvenile gynecomastia, in the absence of clinically significant causes, goes away on its own within several years. Your task is to listen to the doctor’s opinion and have an explanatory conversation with your son to prevent the formation of complexes and psychological problems in him.
Question: At the age of 23, the doctor diagnosed me with severe gynecomastia and insisted on surgical treatment. My father had the same problem when he was young, and he says that the tumor resolved itself at the age of 25. Does it make sense for me to wait for it to decrease or do I need to do something?
Answer: There is such a thing as familial gynecomastia, when breast enlargement occurs in several generations of men. In your case, the likelihood of reducing severe breast hypertrophy is very low, so it makes sense to listen to the opinion of a specialist and undergo surgery.
Source: https://proantiage.ru/lechenie-ginekomastii-u-podrostkov.html
Treatment of gynecomastia in adolescents
Treatment for gynecomastia is only surgical. Even in the case of a false form, when there is an excessive accumulation of fatty tissue in the chest area, it cannot be removed otherwise. Diets and exercise will, of course, lead to a decrease in breast volume, but this fat will not completely disappear, since it contains a fibrous component - a frame that forms the semblance of a woman’s breasts. As for mixed and true forms of gynecomastia, they contain a glandular component that can only be removed surgically.
Surgery to remove gynecomastia in adolescents is easily tolerated and rarely exceeds 30 minutes. At least we can say this based on 10 years of experience and more than 2,000 successfully completed operations. The procedure is performed through mini-accesses along the lower borders of the areolas, through which hypertrophied mammary glands, as well as excess fatty tissue, are removed. Smooth surfaces are formed. Sometimes areola plastic surgery is required - reducing them. Hospitalization in a hospital is 1-2 days. After surgery, it is recommended to use special compression garments, which are selected individually in the clinic. It is recommended to refrain from physical activity for 3 weeks.
Physiological form of the disease
Physiological mastopathy is not included in the group of diseases of newborns that would threaten their life or health. This is a passing disease that in most cases does not require special treatment.
While the baby is in the womb, he receives a large amount of estrogen from the woman with nutrients.
As soon as a child is born, the flow of hormones into the body abruptly stops, as a result of which, after a few days, the newborn experiences changes in the mammary glands and genitals due to a lack of this female hormone.
The so-called hormonal crisis is associated with the newborn’s adaptation to a new lifestyle, nutrition, cold or heat, bright light, loud sounds.
During this period, complex processes occur in the newborn’s body that are no longer associated with the mother’s body. And the most important thing is a sharp reduction in the child’s intake of estrogen.
The mother has an excess of these hormones in her blood, and when they enter the baby’s food through breast milk, they cause an imbalance in the baby’s body. Therefore, this disease in newborns is considered a normal condition without deviation from the norm.
The peak of symptoms appears after the 2nd day of the child’s life. It is on days 3-4 that signs of physiological mastopathy appear. By the 10th day of the baby’s life, they reach their maximum, and then begin to go away on their own. By the second month of life, the child has no signs of physiological mastopathy.
If the symptoms of the disease last more than 2 months, the newborn must be shown to a doctor.