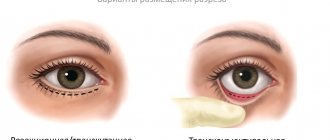
Ptosis of the eyelid is a pathology of the location of the upper eyelid, in which it droops down and partially or completely covers the palpebral fissure. Another name for the anomaly is blepharoptosis.
Normally, the eyelid should overlap the iris of the eye by no more than 1.5 mm. If this value is exceeded, they speak of pathological drooping of the upper eyelid.
Ptosis is not only a cosmetic defect that significantly distorts a person’s appearance. It interferes with the normal functioning of the visual analyzer, as it interferes with refraction.
Causes and symptoms of ptosis
Upper eyelid ptosis or blepharoptosis can be expressed by the following symptoms:
- noticeably drooping upper eyelid;
- with bilateral lesions, sleepy facial expression;
- rapid fatigue of the visual organs during exercise (reading, working on a computer, watching TV, etc.);
- excessive lacrimation, discomfort, pain;
- discomfort when closing the eyelids;
The mechanics of development of the above-described symptoms directly depends on the tone, contractions and width of the palpebral fissure during the motor function of the upper eyelid.
Thus, the levator palpebral muscle controls its vertical position. The orbicularis muscle allows you to close the eye. And the frontalis muscle provides compression and contraction of the eyelid when looking up.
Tone and contraction occur under the influence of nerve impulses that arrive to the frontal and circular muscles from the facial nerve, equipped with a nucleus located in the stem section on the corresponding side of the brain.
The muscle that raises the upper eyelid is innervated by a group of neurons - the left and right bundles of the caudal nucleus of the oculomotor nerve, which is also located in the brain.
Anatomy of the century
To understand the mechanism of ptosis formation, let us turn to the anatomy of the upper eyelid.
Muscles
The orbicularis oculi muscle is the main mover of the eyelid. Contraction of this muscle, which is innervated by cranial nerve VII, narrows the palpebral fissure.
The retractors of the upper eyelid are the levator muscles (which are innervated by cranial nerve III) and its aponeurosis and the upper part of the tarsus (Müller muscle). In the lower eyelid, the retractors are the capsulopalpebral fascia and the inferior talus muscle.
Closing and opening of the eyelids is achieved through the response of the levator palpebra and the eyeball.
Leather
The skin of the eyelid is the thinnest area and is also involved in the movement of the eyelid. Attached dorsally to the orbicularis of the upper eyelid and more loosely to the preseptal orbicularis.
Orbital septum
The orbital septum closes the entrance to the orbit, acting as a barrier.
The orbital septum varies anatomically and can be thick or thin.
The orbital septum is an important structure. With blepharochalasis, subcutaneous fat slides down due to a weakening of the septum.
Tarsal plate and upper eyelid fold
The superior tarsal plate is located on the lower edge of the upper eyelid under the orbicularis oculi muscle, and is usually 30 mm in length and 10 mm in width. The inferior tarsal plate is located on the upper edge of the lower eyelid, is usually 28 mm long and 4 mm wide, and is attached to the orbicularis muscle, capsulopalpebral fascia and conjunctiva.
Intraorbital fat
Acts as a shock absorber and surrounds the eyeball on all sides. Portions of the upper and lower intraorbital fat are divided into internal, central and external. Next to the upper outer portion is the lacrimal gland.
Types of Upper Eyelid Ptosis
Ophthalmologists divide ptosis according to the type of localization into unilateral (occurs in 70% of cases) and bilateral. Also, such a disease of the upper eyelid can be true and false. The second type may be associated with the presence of excess eyelid skin and subcutaneous tissue, endocrine pathology of the visual organs, eyelid hernia, loss of elasticity of the eyeballs, and strabismus.
In addition, a distinction is made between pathological and physiological drooping of the upper eyelids. The first occurs in connection with mechanical injuries, inflammatory processes of motor muscles, eyeballs or brain membranes, as well as anomalies at various levels (hemispheric, supranuclear, nuclear) in the nervous system after heart attacks and brain tumors, damage to the brachial plexus and others.
Physiological drooping of the upper eyelids can be associated with the sympathetic system, retina, hypothalamus, occipital and temporal cortex. Then the muscle tone and width of the palpebral fissure will depend on the emotional state of the person - fatigue, reaction to pain, surprise, anger and others. In this case, eyelid ptosis is short-lived.
According to the degree of the pathological condition in practice, ptosis of the upper eyelid is:
- partial - the upper eyelid covers only 1/3 of the pupil;
- incomplete - the eyelid covers 2/3 of the pupil;
- full - the eyelid completely covers the pupil.
Due to development, pathology is divided into congenital and acquired.
Treatment of ptosis
Elimination of ptosis of the upper eyelid can only be done after determining the root cause
Treatment of ptosis of the upper eyelid is possible only after determining the root cause. If it is neurogenic or traumatic in nature, its treatment necessarily includes physical therapy: UHF, galvanization, electrophoresis, paraffin therapy.
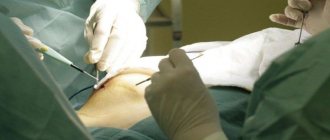
Operation
As for cases of congenital ptosis of the upper eyelid, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention . It is aimed at shortening the muscle that lifts the eyelid.
Main stages of the operation:
- An incision is made in the upper eyelid area.
- The levator palpebral muscle or its tendon is removed into the surgical wound.
- Part of the muscle fibers are removed in order to shorten them.
- Cosmetic stitches are applied.
The operation is also indicated if the upper eyelid still remains drooping after treatment of the underlying disease.
After the intervention, an aseptic (sterile) bandage is applied to the eye and broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are prescribed. This is necessary to prevent wound infection.
Medicine
Drooping upper eyelids can be treated conservatively. To restore the functionality of the extraocular muscles, the following therapy methods are used:
- Ultrahigh-frequency therapy is a method of physiotherapy in which the cornea is gently and effectively exposed to a high-frequency electromagnetic field;
- Medicines that nourish damaged nerve tissue;
- Gymnastic exercises tighten weakened extraocular muscles;
- Galvanization is a physiotherapeutic method in which the damaged area is exposed to a constant low-voltage electric current;
- Self-massage.
If the upper eyelid droops after a botulinum injection, then it is necessary to instill eye drops with alphagan, ipratropium, lopidine, and phenylephrine. Such drugs promote contraction of the extraocular muscles and, as a result, the eyelid rises.
Similar articles Chalazion of the upper and lower eyelid Chalazion removal operations: indications for surgery and recovery after surgery Hemophthalmos - what is it, causes and treatment Entropion or entropion of the eyelid in humans
You can speed up the lifting of the eyelid after Botox with the help of medical masks and creams for the skin around the eyelids. Professionals also recommend massaging your eyelids daily and visiting a steam sauna.
Exercises
A special gymnastic complex helps strengthen and tighten the extraocular muscles. This is especially true for involutional ptosis, which occurs as a result of natural aging.
Gymnastics for the eyes with ptosis of the upper eyelid:
- Direct your gaze forward, then make circular movements with your eyes clockwise. Repeat 5 times. Perform the exercise at a slow pace, moving only your eyes.
- Look up, then open your mouth and blink frequently. To begin with, perform the exercise for 30 seconds, and then gradually increase the time.
- Close your eyelids, count to 5, open your eyes wide and look forward. Repetition frequency: 6 times.
- Open your eyes, press your fingers to your temples, slightly stretch the skin. Blink frequently. Perform for 30 seconds, increasing the duration of the exercise over time. Make sure your fingers don't move.
- Close your eyes and use your fingers to lightly pull the skin near the outer corners. Overcoming resistance, try to raise your upper eyelids as much as possible.
- Tilt your head back, close your eyes.
Only with regular performance of a set of exercises for ptosis of the upper eyelid will you notice the effect.
Congenital blepharoptosis
The congenital form of the disease is less common in ophthalmological practice than the acquired form. Its reasons may be:
- Marcus syndrome is a drooping eyelid that is relieved by opening the mouth, chewing, yawning, or shifting the lower jaw to the opposite side. This is a syndrome with disruption of the nucleus of the oculomotor and trigeminal nerves.
- Congenital myasthenia or pathology of the levator innervation.
- Horner's syndrome is ptosis with accompanying constriction of the pupil, a more significant deepening of the eyeball, and dilation of the conjunctival vessels.
- Neural etiology with congenital paresis of the third pair of cranial nerves.
- Duane's syndrome is a rare congenital form of strabismus with a lack of motor ability of the eye to move outward.
- Isolated ptosis of the upper eyelid is caused by abnormal development or complete absence of development of the levator or its tendon. This congenital form of the disease is most often hereditary and, as a rule, is bilateral.
Folk remedies
Treatment of ptosis of the upper eyelid, especially at the initial stage, is possible at home. Folk remedies are safe, and there are practically no side effects.
Folk recipes for combating ptosis of the upper eyelid:
- Make a decoction of any medicinal herb that suits you, freeze it and wipe the skin around your eyes with ice cubes daily. Repeat morning and evening after washing with warm water.
- Make a herbal decoction (chamomile, parsley, birch leaves are suitable), soak gauze in it and apply to the sore eyelid for 10 minutes. Apply compresses every day.
- Beat the egg yolk, add 5 drops of sesame or olive oil, mix. Treat the upper eyelid, rinse with warm water after 20 minutes.
- Grate raw medium-sized potatoes, put them in the refrigerator, after 20 minutes, apply the mixture to the eyelid and leave for 15 minutes. Rinse off with warm water.
With regular use, folk remedies not only strengthen muscle tissue, but also smooth out fine wrinkles.
Amazing results can be achieved with the combined use of masks and massage. Massage technique:
- Treat your hands with an antibacterial agent;
- Remove makeup from the skin around the eyes;
- Treat your eyelids with massage oil;
- Perform light stroking movements on the upper eyelid in the direction from the inner corner of the eye to the outer. When treating the lower eyelid, move in the opposite direction;
- After warming up, lightly tap the skin around the eyes for 60 seconds;
- Then continuously press on the skin of the upper eyelid. Do not touch your eyeballs when doing this;
- Cover your eyes with cotton pads soaked in chamomile infusion.
Acquired ptosis
Acquired ptosis or drooping of the upper eyelid is often unilateral. The disease occurs due to levator paresis or palsy. This may be a consequence of mechanical damage, tumors, age-related changes in the body, or diseases such as herpes zoster, stroke and others.
The most common forms of acquired eyelid drooping include:
- Myogenic - manifests itself in muscular dystrophy, myasthenia gravis, blepharophimosis, or is a consequence of ocular myopathy.
- Aponeurotic - most often associated with dystrophic age-related changes and weakness of the muscle aponeurosis. Less often it becomes a consequence of mechanical damage and trauma, and is treated with corticosteroid-type drugs.
- Neurogenic - the result of abnormal innervation of the oculomotor nerve in Horner's syndrome, aplasia syndrome, paresis, ophthalmic migraine, diabetic neuropathy or stroke.
- Mechanical - can be caused by severe swelling, inflammatory processes, isolated levator pathology, abnormal changes in the orbit (tumor, damage to the anterior orbital region, etc.), unilateral facial dystrophy after a stroke.
How long will it take to recover?
The recovery period after ptosis takes varying amounts of time. For some clients, rehabilitation of the upper eyelids after Botox takes a couple of weeks, while others have to wait up to five to six months until the drug is completely absorbed in the body.
The duration of elimination of the problem with Botox depends on what type of ptosis the woman suffers from (partial, incomplete or complete), facial structure and muscle tone. The healing process occurs faster if you help with massage, compresses and medication.
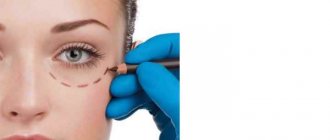
Blepharoplasty: indications and contraindications
It is important to understand that blepharoplasty is a surgical intervention, usually of a cosmetic type, but it can also be of a therapeutic nature. The operation is performed to change the shape of the eyelid, helps eliminate its overhang, and relieves the patient of ptosis.
Experts identify the following indications, in addition to the overhanging upper eyelid, for blepharoplasty:
- the patient has large bags under the lower eyelids;
- severe form of blepharoptosis, in which a person experiences discomfort;
- the appearance of severe dark circles under the eyes (it is important to remember that this symptom is characteristic of many diseases, so you first need to establish the cause of its occurrence);
- wrinkles at the outer edges of the eyes.
Before the operation is performed, the doctor identifies the causes of ptosis. For example, the congenital form of the pathology looks symmetrical, and its cause is abnormal muscle development. Therefore, as a consequence, “lazy eye” syndrome appears. If blepharoptosis of the upper eyelid is acquired, it is usually the result of a muscle strain, injury or nerve disease.
Contraindications in the presence of which blepharoplasty should not be performed include:
- pronounced pigmentation of the skin in the area around the eyes;
- tattooing in the eyelash area;
- systemic diseases during the period of decompensation;
- acute forms of inflammatory diseases of any origin;
- menstrual period in women.
How to fix: step-by-step instructions on what to do
What to do if your eyelids are drooping? There are several ways to eliminate unwanted consequences using:
- Medicines. Their action is often aimed at strengthening nerve fibers, restoring eyelid mobility and accelerating the dissolution of botulinum toxin.
Such drugs are injections of Proserin, Neuromedin, mesotherapy cocktails, eye drops (Vizin, Apraclonidine), Neromultivit - a vitamin complex for oral administration. Typically, eyelid lifting occurs after a few weeks of drug therapy, and only by a couple of millimeters. Therefore, pharmaceutical drugs are included in complex therapy.
Repeated Botox procedure. If the drug is injected into the fibers that cause drooping, muscle strength is balanced and the eyes begin to open and close steadily. Another option is to inject botulinum toxin into the other eyelid (with minimal drooping) - the appearance of the face will be symmetrical, albeit a little tired. But this is clearly better than a complete disproportion of the palpebral fissures.- Special procedures. You can apply warm compresses, visit the sauna, or do facial inhalations with herbs. A bag of salt or heated cereal, or a boiled egg in the shell helps a lot - you need to apply it to the area between the eyebrows or forehead. The procedure is done daily for 15-20 minutes.
However, warming will only help if there is no swelling. At home, you can also resort to a small massage. First, you should apply a tightening cream (lifting) to the eyelids and around the eyes to enhance the effect and provide additional hydration. After this, you need to perform circular strokes clockwise, then lightly pinching and patting.Using massage movements, the Botox drug is quickly removed from the cells, so you can massage the entire face, and not just the area around the eyes. Another remedy for ptosis is paraffin eye masks. To do this you need:
- Melt the paraffin.
Add a couple of drops of essential oil (lavender, tea tree or almond) to it.
- Wait until it cools down a little (to a temperature that is pleasant to the skin).
- Then soak thick napkins in this mixture and apply them to your eyelids, avoiding getting the product on your eyelashes.
- Wait until it hardens completely and carefully remove the paraffin compress.
Types of blepharoplasty: how to choose?
For a patient with a problem with a drooping upper eyelid, a specialist can offer several surgical options. The choice of method for carrying out the procedure will depend on the physiological characteristics of the person, the degree of impact of the pathology on the visual organs and the nature of its origin.
The following types of blepharoplasty are distinguished:
- Traditional upper eyelid surgery - the surgeon removes a little fat layer through a micro-incision, and then sagging skin. Subsequently, the skin is fixed with anatomical “anchors”.
- Laser correction - using a laser beam, a specialist makes several miniature incisions and removes not only hernias, but also existing fat deposits. The peculiarity of this type of blepharoplasty is minimal trauma.
- Transconjunctival intervention is a sutureless technique that is indicated for patients with slight drooping of the upper eyelid and congenital type of ptosis. That is, in the case when the regenerative abilities of the patient’s body are normal.
- Injection blepharoplasty - by injecting special substances that help get rid of drooping upper eyelids and dark circles under the eyes.
It is important to understand that the choice of type of operation is made individually after examining the patient.
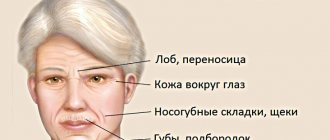
Manifestations and consequences
If eyelid ptosis were a purely cosmetic defect, there would be less talk about it. Unfortunately, this pathology can significantly affect vision, especially if it manifests itself in childhood. Being a purely mechanical defect, in children it leads to strabismus and amblyopia (lazy eye). The facial part as a whole suffers: you have to raise your chin, your forehead wrinkles - “stargazer pose”.
The consequences are inflammation of the conjunctiva, irritation, dry eye (in the case when the eye does not close completely), muscle tension.
And always - visual impairment. Any age. It is more dangerous in children than in adults, because the body is just developing. The slightest violation in one place breaks the entire chain and gradually each link is broken. That is, not only the eyes can be damaged, but also the cervical spine, spine, etc.
Preparing for surgery
Before starting the procedure, the specialist conducts a comprehensive examination of the patient. It is important for the doctor to know whether he has had chronic pathologies, whether there are diseases in the active stage, whether surgical interventions have been performed previously, what is the plasticity of the skin and the depth of wrinkles, and whether there are allergies to specific medications.
In addition, a patient with a drooping upper eyelid must undergo a number of instrumental and laboratory tests, including an ECG, general urine and blood tests, blood biochemistry, and a clotting test.
Most often, blepharoplasty is performed under local anesthesia, since general anesthesia is a serious stress for the body.
If the operation is complex, not only on the upper but also on the lower eyelid, the patient is offered general anesthesia. Because this type of procedure is more traumatic.
Causes of breast ptosis
The volume and appearance of a woman’s bust is determined by: the condition of the pectoralis major muscle and ligaments, the ratio of fatty and glandular tissue formed into lobules.
- Age-related changes - over time, after about 45 years, the process of fibro-fatty involution of the mammary glands begins in a woman’s body. It consists in the degradation of glandular tissue and its gradual replacement with adipose tissue. This occurs against the background of hormonal changes, which are especially active during menopause. These changes lead to a deficiency of the sex hormones estrogen and the gradual “fading” of the body. The synthesis of collagen and elastane, which are structural components of connective tissue, dermis and ligaments, slows down. As a result of fibrofatty involution, a woman’s breasts lose their aesthetically attractive appearance and, under the influence of the natural gravitational forces of the Earth, droop.
- Hereditary factor - congenital features of the synthesis of collagen and elastin determine the rate of tissue aging and predisposition to gigantomastia, and therefore to mastoptosis.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding - during pregnancy, a woman’s breasts increase in volume due to the filling of the glandular lobules with milk. At the same time, the load on the ligaments increases, and the skin stretches. After completion of lactation, the volume of the gland gradually decreases. Due to stretching of the skin, the breasts look “empty” and saggy. In addition, uneven distribution of milk, as well as feeding a baby from one breast, can lead to noticeable asymmetry.
- Rapid weight loss or weight gain - fatty tissue not only actually determines the shape of the mammary glands. In case of rapid weight loss, part of the breast volume is lost, and the skin does not have time to recover. Adipocytes in adipose tissue store and synthesize hormones that are responsible for metabolism. On the contrary, rapid weight gain leads to an increase in the volume of the mammary glands and stretching of the skin.
- Endoprosthetics of the mammary glands with implants that are too large - breast ptosis after mammoplasty occurs the faster, the larger the prosthesis and the less elastic the skin.
- Smoking and alcohol abuse.
Blepharoplasty: stages
Upper eyelid correction surgery includes several stages:
- applying markings to the eyelid using a marker;
- applying a plate to the visual organs to protect against injury;
- an incision in the eyelid in the area designated by markings;
- moving the skin of the eyelid to the side to remove the fat layer;
- removal of excess skin;
- suturing;
- treatment with an anesthetic anti-inflammatory solution and application of a cold bandage.
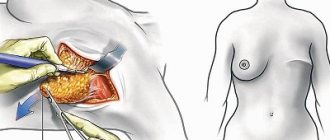
How to correct ptosis with a surgical lift (mastopexy)
In case of breast ptosis of the 1st degree, the bust can be restored to its beautiful shape with the help of endoprosthetics - an operation to enlarge it with implants. The problem of more advanced ptosis of the 2nd or 3rd degree is solved by mastopexy (mammopexy), that is, a breast lift. The essence of this plastic surgery is the resection of excess skin, fat and glandular tissue, as a result of which it is possible to raise the nipple-areolar complex. If there is insufficient volume of breast tissue, mastopexy can be combined with endoprosthetics and thus increase breast size. If a woman has noticeable asymmetry, it can be eliminated by combining a lift with reduction mammoplasty or endoprosthetics. In general, mastopexy is performed under general anesthesia for 1-3 hours.
There are three main methods of breast lift:
Periareolar mastopexy
It is used to eliminate mild and uncomplicated ptosis of 1st or 2nd degree. The plastic surgeon makes an incision around the areola to remove excess skin.
Vertical mastopexy
The method is used for breast ptosis of 2 and 3 degrees. The plastic surgeon makes two incisions: one around the areola, and the other vertically downwards from the circumference by 7-8 cm.
Anchor (or “T-shaped”) mastopexy
The most effective way to eliminate advanced stage 3 breast ptosis. The technique involves a composition of three neat incisions: vertical, around the areola and along the contour of the inframammary fold.
Rehabilitation
Healing of the eyelid after blepharoplasty proceeds without serious consequences if all the doctor’s recommendations are followed. Necessary:
- observing the prescribed regularity, take anti-inflammatory and painkillers;
- apply cold compresses;
- exclude physical activity;
- apply a special softening ointment to the postoperative suture;
- stop using a smartphone, working on a computer, and watching TV for at least 10 days.
If you adhere to the rules described above, you can minimize the risk of complications and speed up the rehabilitation process.
If blepharoplasty uses suture material that does not dissolve on its own, then, as a rule, the patient needs to visit a specialist 5-7 after the operation to remove the threads.
Diagnostics
Computer syndrome Appearance of dark spots before the eyes Warm-up for the eyes when working at the computer
A routine examination is sufficient to diagnose this disease. To determine its degree, it is necessary to calculate the MRD indicator - the distance between the center of the pupil and the edge of the upper eyelid. If the eyelid crosses the middle of the pupil, then the MRD is 0, if higher, then from +1 to +5, if lower, from -1 to -5.
A comprehensive examination includes the following studies:
- Determination of visual acuity;
- Determination of visual fields;
- Ophthalmoscopy with examination of the fundus;
- Examination of the cornea;
- Study of tear fluid production;
- Biomicroscopy of the eyes with assessment of the tear film.
It is very important that while determining the extent of the disease, the patient is relaxed and does not frown. Otherwise, the result will be unreliable.
Children are examined especially carefully, since ptosis is often combined with eye amblyopia. Be sure to check visual acuity using Orlova's tables.
Treatment prognosis and probability of disability
In general, after blepharoplasty surgery and subsequent drug treatment, the prognosis is favorable. However, there are conditions in which the effect after therapy may be only partial. These include, for example, paralysis of the eye muscles. In case of congenital ptosis, when blepharoplasty is performed on a 3-4 year old child, regular examinations by a specialist are required for several years in order to observe how the operated muscle will behave as the patient grows.
Lack of effect after surgical treatment can only be present in extremely advanced cases. Such patients receive the second or third group of disability. In case of complete unilateral ptosis, the second group is assigned, in case of partial ptosis, the third group is assigned.
Treatment of drooping eyelid
If the cause of drooping eyelid is a neurological disease, such as myasthenia gravis or neuropathy, then the underlying disease is treated first. Since ptosis is a symptom, it also goes away when the underlying disease is cured.
However, in some cases, complete recovery is impossible, and then surgical treatment is carried out for cosmetic purposes or, if ptosis leads to significant disruption of life due to deterioration of vision, then for therapeutic purposes.
Children undergo this operation no earlier than 3 years of age, but it should be done as soon as possible to prevent decreased vision and the development of strabismus.
In order to eliminate a cosmetic defect (when vision is not impaired), the operation is recommended to be performed after puberty, when the bony facial skeleton is finally formed.
If the prolapse is caused by injury, the operation can be performed directly during the initial treatment of the wound surface by the surgeon, or after healing, that is, after 6-12 months.
One way or another, the doctor makes a decision on the timing of the operation depending on the specific case.
Breast ptosis
Even the most luxurious and firm bust loses its attractiveness over time. Pregnancy and subsequent breastfeeding become a particularly difficult test for him. The mammary glands lose their volume, stretch and droop. You can correct this in our clinic with a surgeon who will perform breast lift surgery (mastopexy). Some of the stretched skin is simply removed, and the bust again becomes neat and elastic. If you wish, a breast lift will be combined with the installation of implants.
Hand ptosis
The inner surface of the forearms is a problem area for many people. The skin gradually stretches and begins to sag, forming unaesthetic flabby “wings”. And if there is also excess adipose tissue, the hands are simply disfigured.
A plastic surgeon successfully performs an operation in which an incision is made from the armpit to the elbow, excess skin and fat are removed, after which the tissue is pulled up to the muscles and a suture is placed (brachioplasty). Gravitational ptosis is an inevitable phenomenon. But modern methods and the professionalism of specialists make it possible to outwit nature and win back a few more years of youth and beauty from time.
Preventing the development of drooping eyelids
An important point in the prevention of eyelid drooping is the timely treatment of any diseases that can provoke this pathology. For example, neuritis of the facial nerves must be immediately treated by a neurologist, and the possibility of drooping eyelids after Botox injections should be discussed with the specialist performing the manipulation.
If you notice weakness of the eyelids associated with age-related changes, then cosmetics and folk remedies can help you. Prevention methods include the use of tightening masks, oils and massage treatments.
Massage of the skin of the eyelids should be carried out with drooping eyelids. Before the procedure, the eyelids can be wiped with lotion to remove sebaceous scales and open the excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands. Massage using a cotton swab or disk soaked in an antiseptic solution or special ointment. Use stroking with light pressure, making circular and linear movements, moving from the inner corner of the eye to the outer corner. You can lightly tap your eyelids with your fingertips.
There are special gymnastics for weakness of the eye muscles.
Starting position – standing, sitting or lying down.
- We look up, without raising our heads, then sharply down. We repeat the movements 6-8 times.
- We look up and to the right, then diagonally down and to the left. We repeat the movements 6-8 times.
- We look up and to the left, then down and to the right. We repeat the movements 6-8 times.
- We look as far as possible to the left, then as far as possible to the right. We repeat the movements 6-8 times.
- We stretch our arm forward and keep it straight. We look at the tip of the index finger and gradually bring it closer, without stopping looking until the picture begins to “double.” We repeat the movements 6-8 times.
- Place your index finger on the bridge of your nose. We look at the finger alternately with the right and left eyes. Repeat 10-12 times.
- We move our eyes in a circle to the right and left. We repeat the movements 6-8 times.
- We blink quickly for 15 seconds. Repeat blinking up to 4 times.
- We close our eyes tightly for 5 seconds, then sharply open our eyes for 5 seconds. Repeat 10 times.
- Close your eyes and massage your eyelids with your finger in a circle for 1 minute.
- We shift our gaze from the nearest point to the far one and vice versa.
Movements of the eyeball during exercises should be as wide as possible, but not to the point of pain. The motor tempo can be made more difficult over time. The duration of such prophylaxis is at least 3 months.
It is worth noting that in case of myasthenia gravis and myopathy, such exercises are contraindicated, as they contribute to the worsening of drooping eyelids due to “exhaustion” of the muscle. Therefore, before engaging in any treatment, you must consult a specialist.
Classification: congenital and acquired ptosis
In congenital pathology, the hereditary factor plays a major role. According to medical research, it has been noted that intrauterine underdevelopment of the muscles that lift the eyelid most often occurs in those children whose parents suffered from the same defect.
Congenital ptosis has the following features:
- When looking straight, the upper eyelid blocks the view, which forces the child to raise his head high, and when looking down, on the contrary, it is higher than the normal position.
- Blepharophimosis is a congenital anomaly consisting of a very short palpebral fissure, underdevelopment of the levator muscles of the upper eyelids and eversion of the lower eyelids. This condition is caused by unfavorable heredity, is only congenital and occurs infrequently.
- Dependence of the movement of the upper eyelid on the masticatory muscles. The fact is that chewing movements have a stimulating effect on the trigeminal nerve, which transmits impulses to the levator muscle of the upper eyelid. Often this type of congenital ptosis is accompanied by severe strabismus.
Acquired ptosis is more common than congenital ptosis; there are many more reasons for its occurrence.
- Neurogenic ptosis is a condition caused by problems with the nerves that control eye and eyelid movements. This could be paralysis, a pinched nerve due to the development of a tumor in the brain, or diabetic neuropathy.
- Myasthenic, or myogenic ptosis, is a condition that occurs with excessive stress. Most often it is bilateral and increases over the years. In this case, endorphin can help to correctly identify the pathology, which for a short time removes the manifestations of ptosis.
- Senile, or aponeurotic ptosis - develops in older people due to the fact that the muscle that moves the upper eyelids loses its elasticity and lags behind the plate it holds on to. In this case, the precise fixation of the eyelids disappears. It is often bilateral.
- Mechanical ptosis - occurs after injuries with blunt or sharp objects, in the presence of a tumor.
- Artificial ptosis is a condition in which doctors put a patient on purpose to speed up the treatment of certain eye diseases, such as corneal ulcers.
- False ptosis is an excess of skin folds of the upper eyelid. Also, this phenomenon can be either isolated or observed with strabismus and hypotony of the eyeball.
Ptosis can also be unilateral or bilateral, that is, spreading to one or both eyes. The bilateral form is in most cases congenital. Unilateral prolapse is most often acquired, but there are also cases of congenital pathology.
Consequences after Botox
Botox injections have become a fairly common procedure these days. Most often, they are done by public people over 50 years of age in order to smooth out wrinkles and acquire a more youthful appearance.
Ptosis often appears as a side effect of non-professional Botox lifting
Wrinkles around the eyes are formed due to overactivity of the periocular muscles. If the cosmetologist correctly determines the area for injection, muscles will relax and wrinkles will smooth out.
Ptosis is one of the most common complications after this procedure. It can be caused by an excessive dose of Botox, an incorrect injection site, or low qualifications of the specialist who performs the procedure.
Often the actions of patients lead to the fact that after Botox injections they experience drooping eyelids. The point is that such procedures should not be abused. Trying to shorten the interval between injections in order to look even younger can lead to complications.
Ptosis accounts for one-fifth of complications after Botox. Usually this condition is temporary, and after a few months the eyelid returns to its normal position. But for people whose profession involves frequent appearances in public, for example, artists, the complication can cause significant trouble.
Botox injections are strictly contraindicated for people diagnosed with the first stage of ptosis, as they can aggravate the condition.
Causes of prolapse
The eyelid opens with the help of a special muscle called the levator, which controls the oculomotor nerve. It follows from this that the main reason for drooping eyelids can be called abnormalities of this muscle or changes in the oculomotor nerve.
With congenital prolapse, the levator may be poorly developed or may not exist at all. Sometimes aplasia of conductive tracts or nuclei occurs. The congenital form is a genetic pathology. But this can happen due to the pathological course of pregnancy and during labor. Often the birth defect is accompanied by other eye diseases and abnormalities.
Forecast of drooping eyelid
As a rule, ptosis requires either treatment of the disease that caused it, or purely cosmetic correction, or both.
When treated for cosmetic purposes, the prognosis is favorable. If surgical treatment was performed on a child, then he is monitored periodically throughout his growth period. For myasthenia gravis, the selection of adequate therapy or complete cure for myasthenia gravis can eliminate ptosis. With the exception of cases where, due to prolonged drooping of the eyelid, overstretching of the muscle tendon has occurred, then the defect becomes purely cosmetic and is eliminated surgically.
In all other cases of neurological pathology (syncinesia, neuropathy, facial nerve paralysis, myopathy), the prognosis depends entirely on the initial disease and the prognosis for its treatment.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions