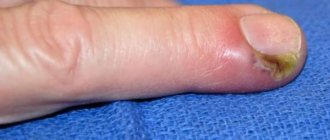
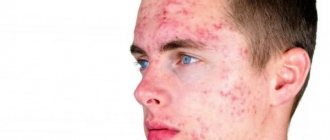
The source of the epidermal cyst is clogging of the hair follicle, high formation of sebum and filling of the cavity with horny masses. Acne precedes cystic formation.
General information
Atheroma - what kind of formation is this?
Atheroma (trichodermal cyst or steatoma) refers to fairly common tumor-like neoplasms of the pilosebaceous apparatus of the skin. It is one of the varieties of the group of epithelial skin cysts and is a rounded encapsulated neoplasm filled with thick yellowish-white contents, which may have an unpleasant odor. ICD-10 code: D23. Other benign skin neoplasms. Atheromas occur in 7–10% of the population. At the same time, atheromas occur more often in women compared to men, and in people of the older age group more often than in people under 30 years of age. Often found in patients with acne and seborrhea.
It occurs predominantly in areas of the skin with a high concentration of sebaceous glands (scalp, breast, face, back), therefore it is often found in the literature as a sebaceous gland cyst. In most cases, the size of atheromas is 1-3 cm, less often they reach 5 cm, but in practice there are cases of large atheroma formations. The localization of atheromas may vary.
The most common are atheroma of the scalp and atheroma on the back in different places, as well as atheroma on the face (usually on the cheek and skin of the forehead, in the chin area). Less common are atheroma behind the ear, on the ears (atheroma of the earlobe or pinna), on the neck (lateral/back surface), and atheroma of the mammary gland. And much less often - on the leg, atheroma on the penis, on the scrotum or atheroma on the labia and on the skin in the groin in women.
Photo. Atheroma on the back
Photo of atheroma on the head
Photo of atheroma behind the ear
Atheroma on the leg photo
Atheroma (blockage of the sebaceous gland on the eyelid). Photo.
Often in everyday life, atheroma is called a wen. However, this is not true, since there is a fundamental difference between them. Externally, atheroma is certainly similar to lipoma, however, structurally they are fundamentally different. Lipoma consists of altered cells of adipose tissue and develops in the layer of subcutaneous connective tissue, while atheroma is a cyst of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland.
Depending on the histomorphological structure, the sebaceous gland cyst of the skin is divided into several types:
- Epidermal cyst - occurs very rarely, is formed from the skin epithelium, which, due to disturbances in the embryonic period, was subdermally transferred, that is, submersible growth of epithelial elements occurs, their proliferation and desquamation, which leads to the formation of a cyst cavity, which is filled with keratin and components of the skin lard This type of atheroma is characterized by slower growth, occurs predominantly in females, the predominant localization is the scalp (atheroma on the head) and the perineal area (in the groin in women, atheroma on the penis).
- Retention - formed due to blockage of the excretory duct of the gland. It is characterized by faster growth and occurs in both sexes with equal frequency; in addition to the scalp, it can occur on the skin of the face, back, mammary glands, and external genitalia. They can be single or multiple, often of the same size. They tend to become inflamed and coalesce into lumpy conglomerates.
Atheromas are a pronounced cosmetic defect, which causes psychological discomfort and becomes the main reason for contacting a surgeon. Also, if an infection enters the internal cavity of the atheroma, there is a high probability of its suppuration, since the contents of the tumor are a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacterial microflora with the development of the inflammatory process and the formation of an abscess (cavity with pus).
Suppurating atheroma (there is no code according to ICD-10), since the atheroma code according to ICD-10: D23 does not provide for cyst complications. It often develops after mechanical damage to the atheroma, but in most cases the cause of its occurrence cannot be determined and therefore a diagnosis of “idiopathic purulent atheroma” is made.
Tumors of the sebaceous glands
Often, a photo of a sebaceous gland cyst on the face shows large abscesses in which a small amount of purulent or serous substance may be observed.
To understand what causes the disease, you need to determine what is its basis. A cyst is a capsule with purulent contents, which includes the following components:
- sebaceous gland;
- sebum;
- keratinized epithelium, hair follicle.
All of the above is involved in the emergence of education. It appears when the gland for releasing sebaceous secretions becomes clogged, and instead of coming out, it accumulates in a capsule under the skin. As the volume of such content increases, a significant growth of the tubercle on the skin can be noticed. Blockage of the sebaceous glands is caused by:
- various injuries;
- metabolic disease;
- hormonal imbalance;
- failure to comply with hygiene standards;
- excessive use of cosmetics;
- poor ecological environment;
- thickening of the epidermis.
It is worth noting that healthy people with strong immunity, as a rule, are not at risk of sebaceous cysts. This disease is more common in oily and mixed skin types. It is also possible to develop multiple cysts, especially along the hair growth contour. Experts in the field of dermatology do not exclude a hereditary factor as a common cause of the appearance of a neoplasm. There have been repeated cases where the disease occurred in blood relatives.
Sebaceous cysts and epidermoid cysts are terms often used interchangeably. But in reality they are different. The former often arise from hair follicles, while the latter develop from skin cells. Sebaceous cysts arise from an inflamed hair follicle, which sometimes becomes swollen. Symptoms include:
- small round bump under the skin
- soft to the touch
- sensitivity, redness, swelling, if there is inflammation
- bumps that are painless unless they are infected or damaged
- small blackheads covering the central opening of the cyst.
Classification
A cyst is a benign cavity formation. It can occur on any part of the body, including the face. Based on morphological features, true and false cysts are distinguished. The former have their own capsule (inner shell), while the latter lack it. True cutaneous cysts are represented by the following:
- Epidermal (atheromas).
- Dermoid.
- Implantation.
- Retentional (milia).
False cystic formations (without internal epithelial lining) are synovial, have the appearance of calcification, or are represented by pseudomilium. Each of the presented forms has its own origin, morphological and clinical features.
Depending on the origin there are:
- Congenital atheromas (primary, true) are a hereditary disease and develop from detached epidermal cells during the embryonic development of the fetus.
- Acquired (secondary, false) - are formed due to blockage of the sebaceous gland duct or difficulty in the outflow of its secretion, which contributes to the accumulation of secretion in the lumen of the gland and the formation of a sac filled with atheromatous masses (altered sebum).
Therapy methods (4 options)
There is no hope that atheroma will disappear on its own. If your doctor recommends laser, radio wave or surgical treatment, you must follow all instructions.
Treatment of atheroma on the face without surgery does not imply obtaining a quick positive result. The effectiveness of folk recipes and pharmaceutical drugs is low, and the patient’s condition will worsen.
Experts do not recommend conservative treatment. If the tumor has opened on its own, it is necessary to treat it with disinfectants, cover it with a band-aid and contact a medical facility.
It is considered the most common method. The procedure involves cutting the skin and removing the cyst along with the pus.
A cosmetic suture is placed on the wound, which is removed after 14 days. Removal of atheroma on the face is surgically performed under local anesthesia.
Laser removal
Suitable for combating small wen in the absence of an inflammatory process. A small incision is made in the skin where the LED is inserted.
Under the influence of a laser beam, the tumor is burned out. The duration of the procedure is 20 minutes.
If the tumor is removed from the scalp, the hair in the treatment area is first shaved off. The use of a laser protects the patient from recurrence of the disease.
Radio wave method
This method is similar to the previous one, the main difference is faster restoration of the affected tissues.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Yellow spots on the scalp of a child
The procedure involves evaporating the tumor. It is carried out only in the absence of inflammation. If infection occurs, the abscess is incised and drainage is installed. The patient is prescribed antibacterial drugs.
The procedure is considered the safest, since the effect is carried out with high precision. There are no scars left on the skin, and signs of the disease do not reappear.
Which doctor should I contact?
surgeon
Before starting the examination, the doctor will try to find out the possible reasons that caused the problems. If they are not eliminated, the risk of relapse of the pathology will significantly increase. In addition, the specialist must make sure that there are no contraindications for surgery. The patient will need to answer several questions:
- How long ago did the cyst appear?
- Does it hurt when touched or pressed?
- Has the patient had inflammatory dental diseases recently?
- Have you had any oral injuries within two to three months?
- Does the patient suffer from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or endocrine system?
- What medications has he taken recently?
- Is he allergic to any medications?
For a cyst on the cheek, treatment consists of mechanical removal of the formation. The operation does not pose any particular difficulties due to easy access to the affected area. It is performed under local anesthesia and does not require long-term rehabilitation.
Causes and mechanisms
The most common is an epidermal cyst or atheroma. It occurs as a result of blockage of the excretory duct of the sebaceous gland and the accumulation of secretions there. The mechanism for the formation of such a state has three components:
- Increased secretion.
- Hyperkeratosis of the excretory duct.
- Imbalance of neuroendocrine regulation.
Sebaceous cysts can occur in people with oily or combination skin types, but under certain conditions. It is known that the glands and epithelium are under the influence of sex hormones (primarily androgens). And if the balance with estrogen is disturbed (for example, during menopause or ovarian tumors), then the risk of developing atheroma increases. They usually occur in places where the glands are most dense: on the back, face, upper chest.
Compensatory hyperkeratosis of the excretory ducts accompanies not only sebaceous gland cysts on the face, but also occurs during trauma or inflammatory processes (acne, seborrhea). Mechanical damage can lead to the penetration of the epidermis into the skin, which will become the source of an implantation cyst.
Milia or retention cysts, unlike atheroma, are filled not with sebaceous secretions, but with horny masses. Therefore, their main development mechanism will be hyperkeratosis with increased division of epidermal cells. If we talk about dermoid cysts, they most often arise when embryogenesis processes are disrupted, i.e. they are congenital in nature.
Complications
The most common complication of a cystic formation on the face is infection. This leads to the beginning of an inflammatory process in it, which causes the appearance of pus. Next, the tumor begins to thicken and cause pain. Also, the skin of the affected area of the face becomes red, and the body temperature rapidly rises.
If the cyst opens on its own, it must be disinfected to prevent the development of more serious complications. If the formation breaks into the dermis, this will lead to the appearance of a purulent abscess or phlegmon. These diseases will already need to be treated surgically, while taking strong antibiotics. Therefore, if an inflammatory process appears in a cyst on the face, doctors try to open it, after which the cavity is drained. This is necessary in order to prevent intradermal anomalies from developing into more serious pathologies.
Pathogenesis
The formation of atheroma occurs as a result of the cessation/impairment of the release of the secretion of the sebaceous gland. As the secretion accumulates, it expands the duct of the sebaceous gland, forming a cavity in it with contents of a dough-like consistency, which includes particles of fat, detritus (a product of the breakdown of necrotic tissue) and keratinized cells of the epidermis.
The skin above the gradually enlarging cyst rises, and a round-shaped compaction with a soft-elastic consistency is formed. As it grows, a capsule of connective tissue begins to form around the overstretched walls of the sebaceous gland. At the same time, the inner surface of the cyst produces secretion.
Symptoms
The standard complaint of patients is the presence of a superficial tumor-like neoplasm with a dense elastic consistency, often easily movable when pressed with a finger and painless when palpated. In uncomplicated cases, the skin over the cyst remains unchanged; less often, on the most elevated part of the skin above the cyst, an enlarged obstructed duct of the sebaceous gland is noticeable.
In this case, there is severe pain during palpation and the patient’s general condition suffers (weakness, general malaise, increased body temperature). If the outcome is favorable, the pus breaks through the capsule or comes out through the ducts of the sebaceous glands. However, in some cases, pus can escape into the subcutaneous layer with the development of an abscess.
In a normal course, when there is no infection by microorganisms, the formation does not bother the person in any way. Upon careful examination, a yellow-pink color will be visible, but when pressed, a person will not feel anything.
When the color of the atheroma changes to dark red or brown, the formation will be accompanied by symptoms such as pain, inflammation of the tissue around the formation, and also if there is a large amount of pus inside the tissue, the tissue may not be able to withstand, so some of the contents come out.
Atheromas do not manifest pronounced clinical manifestations. The main sign of a cavity is enlargement and compaction. Visually, a hollow node appears in the form of a dense wen. In most cases, formations are formed in areas where hair follicles are present: head, ear area, back and neck, facial area, groin.
The main signs of a cyst include:
- The formation has a dense elastic structure;
- Mobility of the capsule is observed;
- Placed on the surface of the skin;
- A cyst on the face or body has clear contours;
- The gland duct may be located in the center of the formation;
- The occurrence of an inflammatory process and suppuration of atheroma. Severe redness of the borders of the formation, pain when palpating, and swelling appears. Possible rupture of the capsule and eruption of purulent contents.
Symptoms of cystic formation of the sebaceous gland are visual signs. Cavity neoplasms are identified quickly, at the first appointment with a dermatologist during examination and palpation.
A mass formation on the skin of the face (even a small one) is not a cyst on the leg, which no one will pay attention to. And when a similar problem arises in a child, it brings even more anxiety. But only a doctor can dispel all doubts regarding the benignity of the tumor and methods for its elimination. After conducting an examination, the specialist will give answers to all your questions.
Atheroma
An epidermal cyst of the facial skin is a closed formation containing horny masses mixed with sebum. The epithelium above it remains unchanged, probably only the expansion of the pores and the appearance of a vascular mesh. The size of the atheroma is usually in the range of 5–10 mm, but can also be significantly larger.
Atheroma develops gradually over quite a long time. Such a cyst is localized in various areas: on the head under the hair, on the forehead, cheeks, in the area of the lower or upper eyelid. The latter is also called atheroma of the eye, although the apple itself, of course, is not affected.
An epidermal cyst does not cause physical discomfort. But there are two situations when a tumor is cause for concern: when it becomes large and becomes inflamed. In the first case, there is likely to be pressure on neighboring structures, including vessels and nerves, and in the second, an abscess (microabscess) may form. Then other signs appear in the clinical picture:
- Redness of the skin.
- Swelling.
- Soreness.
An infected atheroma proceeds like a boil, only without a necrotic core. Despite this, pus accumulates in the center of the tumor, which can break out or, much worse, spread to neighboring tissues. Therefore, if you suspect an inflammatory process, you should not hesitate to consult a doctor.
Dermoid
Another subcutaneous cyst is a dermoid. It has an oval or spherical shape, has a dense capsule and can be multi-chambered. The contents of the cyst are various elements of the skin and its appendages:
- Epidermal cells.
- Sebum.
- Hair.
- Nails.
We suggest you read: When is the best time to cleanse your face?
Dermoid cysts are usually found in children or young adults. This is a painless and fairly dense tumor, not fused with surrounding tissues. It grows slowly, but under certain conditions (heredity, the influence of carcinogens) it can degenerate into malignant.
The forehead and bridge of the nose, behind the ear area, and neck are most susceptible to the formation of such cysts. But dermoid can also appear in other areas: on the back, abdomen, lower extremities, above the sacral spine, in internal organs (ovaries).
Milia
White spots on the face, especially common in adolescents and adults, but also common in the newborn period, are milia. These are intradermal cysts containing horny masses, not sebaceous secretions. They do not connect to the ducts of the glands, and therefore cannot empty themselves spontaneously.
Small nodules up to 3 mm in size are white or yellowish in color and rise slightly above the surface of the skin. Usually they are located in groups, but never merge with each other. Milia are prone to spontaneous disappearance, which is associated with the natural renewal of the skin.
Danger level
Regardless of how exactly the cysts were formed, they have the same clinical course and appearance. As a rule, epidermal cysts are not dangerous, since even if they are large, they are not able to compress any vital organs and cannot grow deep into underlying tissues.
The only factor that makes atheroma a potentially dangerous formation is the possibility of its inflammation. This manifests itself in the development of edema, redness, soreness and suppuration. In such cases, an abscess often forms.
If the inflammatory contents are removed, this is considered a favorable outcome, since the surrounding tissues will not melt, and toxic substances will not penetrate the bloodstream. If the contents of the atheroma are released into the surrounding tissues, then this will be an unfavorable outcome, since toxic substances and pathogenic microbes enter the bloodstream and can also cause infectious and inflammatory diseases of the subcutaneous fatty tissue, muscles, and bones.
Folk recipes
The use of traditional methods for the treatment of atheroma is possible only with mild symptoms of the pathology and only after consultation with a specialist.
The most effective are ointments, rubs and compresses made from natural ingredients.
Burdock ointment
The plant must be thoroughly washed with running water, passed through a meat grinder, and then mixed with pork fat.
For 3 days, the product is infused in a cool, dark place. After this, the ointment is applied in a thin layer to the wen, no more than 3 times a day.
Onion compress
The onion is baked in the oven, cooled, crushed and mixed with the same amount of laundry soap (pre-grated).
The resulting mass is applied to the wen and secured with a sterile bandage. The compress is changed 2 times a day.
A small amount of the product must be melted, then gently rubbed into the surface of the new growth until completely absorbed.
How to treat dermatitis on the face
Facial dermatitis is an inflammatory reaction of the skin that is expressed by red spots. Unbearable itching forces a person to comb the skin, which leads to a deterioration in their appearance.
The disease develops due to the influence of various factors. It can be a holistic allergic reaction or a separate sign of pathology. The disease is divided into allergic, contact, atopic, seborrheic and oral dermatosis.
Allergic type of disease
According to the allergic type, dermatitis develops due to sensitization of the body when it has to react to components of incoming food or substances touching the skin. At a mild stage, the disease is diagnosed by bright red spots, rashes, and swelling. In advanced conditions, the picture is complemented by the following symptoms:
- weakness;
- headache;
- tearfulness.
Scars may take the place of the blisters. The process is characterized by a slow flow. The problem on the face appears a few days after contact with the irritant.
All signs of dermatitis on the face are shown in the photo; its treatment with ointments and creams will be described below.
To develop a therapeutic course against allergic dermatitis, specialists take skin tests to facilitate the identification of the allergen. Creams for treatment are selected from those drugs that have antihistamine properties. Facial ointments are prescribed to eliminate symptoms and strengthen local immunity.
Among the desensitizing medications, a 10% solution of calcium gluconate is indicated - it is administered intravenously. The patient is also asked to switch to a diet excluding foods containing potential allergens. Cosmetic facial care products are also selected by a doctor. It is recommended to wash with special solutions.
Contact dermatitis
This form of the disease is manifested by tissue inflammation caused by allergens and irritants. They can be household chemicals, products containing nickel, medicines, latex.
The path of pathology development is simple:
- the irritant hits the face;
- an allergic reaction to contact occurs;
- the inflammatory process starts.
A striking symptom of contact dermatitis is severe itching, redness of the skin, peeling and blistering.
How to treat such dermatitis on the face? Once an allergen has been identified, it should be excluded from contact with the skin. Dermatologists prescribe Erius, Zyrtec, and Telfast among antihistamines. They are consumed orally or applied topically. Erius is prescribed at the rate of 1 tablet per day. The drug is suitable for the treatment of adults and children over 12 years of age.
The condition of skin covered with ulcers and blisters is improved with the help of corticosteroids. The problem is well solved by Advantan cream and Lokoid ointment. Use them once a day, lubricating the affected areas on the face for 3 to 5 days.
Chamomile and linden blossom are used in the fight against facial dermatitis. Take 4 tbsp of both components. l. and pour over a liter of boiling water. Boil the mixture over low heat for about 20 minutes, then leave for 4 hours. The product is filtered and used warm to wash the face.
Atopic form of dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis on the face is a common pathology known as eczema. Science has not been able to reveal the exact causes of its occurrence, so the disease develops into a chronic form.
Typical symptoms of facial atopy are:
- itching;
- burning;
- blistering;
- redness;
- peeling of the integument;
- thinning and breaking of eyebrows;
- deepening of the folds on the eyelids.
Mechanical impact on the problem area triggers the process of inflammation, leading to roughness of the skin. Scratching the skin tissue can cause an infection in the body, which will make the picture more vivid.
To treat atopic dermatitis on the face, doctors prescribe special antihistamine creams and ointments:
- Elokom, which relieves swelling and provides an antipruritic effect. In the form of an ointment, it is used to eliminate peeling, and in the form of a cream - for inflammatory infiltration.
- Afloderm is an antipruritic anti-inflammatory ointment that constricts blood vessels and reduces swelling. Treatment is carried out for 3 weeks.
- Trixera is a cream that reduces the hypersensitivity of the facial skin. To moisturize and restore the lipid layer, apply it 2 times. per day. The skin must be pre-cleansed.
- Solcoseryl is a gel and ointment that heals irritated tissues and accelerates recovery processes in the depths of inflamed areas. Skin treatment is carried out 1 - 2 times. in a day.
To normalize the emotional background, dermatologists prescribe tablets Persen, Tofisopam, Atarax. To maintain the gastrointestinal tract, it is recommended to take Smectite, Lignin, Hilak Forte, Bifidumbacterin.
Eczema is not a dangerous disease. However, severe itching and burning deprive a person of sleep, make him irritable and quickly tired.
Seborrheic dermatitis of the face
As a chronic inflammatory process, seborrheic dermatitis on the face develops due to the activation of the fungus of the saprophytic flora. An opportunistic microorganism inhabits the skin of every person and does not reveal itself in any way until circumstances favorable for reproduction occur.
The reasons for the surge in parasite activity are:
- increased skin oiliness;
- decreased immunity;
- endocrine disruptions;
- chronic lack of sleep;
- low stress resistance;
- bad habits;
- vitamin deficiency;
- diabetes;
- thinning of the protective barrier of the facial dermis.
The disease is recognized by irritated, reddened areas, white and yellow scales, and patient complaints of itching and burning.
Numerous papules on the face can be localized in the nasolabial area, on the forehead, cheekbones, and eyebrows. All symptoms of the pathology do not appear immediately. From the initial itching, the picture gradually changes for the worse.
How to cure seborrheic dermatitis on the face? To relieve itching and redness, doctors prescribe corticosteroids. In order to avoid the formation of rosacea and thinning of the skin, they are used in short courses. Salicylic acid and an antifungal agent for internal use are also prescribed.
Constant itching, nervous irritation and insomnia are treated with sedatives. Special products are indicated for skin care. To strengthen the immune system, the body is provided with vitamin support. For this purpose, take vitamins A, E, and fish oil.
Ointment for dermatitis on the face, mash, cream must contain zinc. The substance dries the skin, gives an antifungal effect and relieves inflammation. It is contained in zinc ointment and Tsindol. Physiotherapeutic procedures against SB include cryotherapy and ultraviolet irradiation.
Oral dermatitis
Perioral dermatosis develops around the mouth for various reasons. During pregnancy, the disease occurs due to the combination of certain foods. It also appears against the background of gastrointestinal dysfunction and long-term use of hormonal drugs.
Characteristic signs of the pathology are itching and burning, red spots of varying intensity, flaky areas around the mouth. It has been noticed that depending on the weather, the spots change tone. Also, vasodilating medications and certain foods can affect the intensity of the color of the lesions. Unfavorable facial changes cause aesthetic discomfort to people.
Treatment of oral dermatitis on the face begins with avoiding the use of fluoride-containing toothpastes, detergents and cosmetic products, and steroid preparations for external skin treatment. Courses of Metronidazole and Trichopolum are being developed as drug therapy. Patients with pustular rosacea are advised to take antibiotics:
- Erythromycin;
- Metacycline;
- Oxacillin;
- Oleandomycin.
Vitamin therapy against oral dermatitis involves the use of ascorutin, riboflavin, nicotinic acid and vitamin B6. For patients with pathological lesions located around the eyes, periodic visits to an ophthalmologist are recommended to prevent diseases of the visual organs. To alleviate the condition, the doctor prescribes Prednisolone, hydrocortisone drops, antihistamines, and riboflavin phosphate injections.
At the last step in the fight against perioral dermatosis, the patient is offered physiotherapeutic procedures. A good effect in treatment is achieved by using snow obtained from liquid nitrogen or carbonic acid. In special cases, electrolysis is prescribed. The patient is reminded that he should not be exposed to direct sunlight for a long time and stay in stuffy rooms.
Diet to relieve facial dermatitis
For dermatitis on the face, the diet involves excluding carbohydrate products from the diet in the form of sweets, sweet drinks, semolina, baked goods made from premium flour, baked goods, and jam.
By enhancing fermentation processes in the intestines, they impair digestion and promote the activation of pathogenic microorganisms. Due to the fact that harmful substances remain in the tract, proteins do not have time to be absorbed and lead to the development of dermatitis.
Canned food, pickled foods, and homemade pickles are strictly excluded from the menu. Spices are allowed to be consumed in limited quantities, avoiding hot and fiery seasonings. You can eat high-quality products from semi-finished products, but you still shouldn’t abuse them. Fast foods are generally completely prohibited.
As for the technology of preparing dishes, for dermatitis on the face they need to be baked, boiled or stewed. During heat treatment, vegetable oil should be replaced with olive oil. Meat dishes cooked over an open fire or coals are prohibited.
The ban is also imposed on:
- caviar;
- fatty fish;
- seeds and nuts;
- strawberries;
- bee products;
- citrus fruits.
Fruits and vegetables with orange and red skins should be peeled before eating. It is recommended to replace tomatoes and red peppers with yellow varieties.
Additional diagnostics
Diagnosis of atheromas in the presence of characteristic clinical symptoms does not present any particular difficulties. If necessary, an ultrasound examination of soft tissues can be performed, which allows visualization of the cavity and capsule with curd contents. Additional histological diagnosis is carried out during surgery by taking atheroma tissue for histological examination.
What caused the atheroma on the face or what the nature of the other cyst is - all this will become known based on the results of additional diagnostics. After a visual examination, the doctor must make sure that the formation is benign and make a final conclusion. They will help him with this:
- Complete blood count (leukocyte count, ESR).
- Blood biochemistry (hormonal spectrum, immunogram).
- Content analysis (microscopy, culture).
- Histological examination.
- Ultrasound of soft tissues.
When a cyst suppurates, it should be distinguished from acne or boils, and nodes under the skin require differential diagnosis with lipomas. But each case requires individual consideration.
Prevention
The main types of hollow neoplasms include:
- Secondary formations (retention follicular cyst). These neoplasms are formed as a result of complications of acne and acne. In most cases, these formations are localized on the facial area, back, neck;
- Congenital benign formations (epidermoids). This type of neoplasm is formed from epidermal cells. In most cases, epidermoids are multiple formations that are localized in the area where hair follicles are present;
- Trichodermal cystic nodules;
- Steacystoma;
- Various unspecified follicular formations of the skin and tissue.
Neoplasms arise due to a violation of the outflow of sebum, which occurs due to blockage of pores, therefore the prevention of atheroma on the face should be based on regular cosmetic procedures for cleansing the skin. These include:
- visiting the sauna;
- steam baths;
- cleansing masks;
- massages.
To reduce facial skin oiliness, you should use special tonics and cleansers. In addition, preventing the development of tumors on the skin of the face should include proper, balanced nutrition. So, with high fat content of the skin, you need to exclude fatty and carbohydrate-rich foods from your diet.
Atheroma in a child is a fairly rare occurrence, since the sebaceous glands in young children still function poorly. If adult patients require surgical removal of atheroma, then in most cases children under three years of age do not undergo surgery at all. An operation to remove atheroma in a child is undesirable, since general anesthesia is required, which is harmful to a still fragile body.
- There is rapid aggressive growth of the cyst.
- The surrounding tissues/vessels swell and are compressed.
- Signs of inflammation of the cyst appeared.
- The tumor is disturbing the child.
In rare cases, the neoplasm may disappear without surgical intervention, but you should not hope that the atheroma will resolve on its own. If your doctor advises you to remove the tumor, you should listen to him. A tumor under the skin can be removed in one of three ways: radio wave, surgical excision or laser.
A subcutaneous cyst can form after injury to the skin, inflammation of the hair follicles, improper squeezing of acne, and other circumstances. The fact is that the sebaceous duct becomes increasingly constricted, and the glands continue to produce deposits. Since the duct to the outside for sebaceous deposits is closed, it turns into a cyst, gradually increasing in size. It is in this way that the formation of a subcutaneous tumor occurs.
Prerequisites for the appearance of atheroma:
- Seborrhea caused by hormonal or inflammatory imbalance;
- Pimples and blackheads;
- Tendency to sweat heavily;
- Metabolism;
- Diseases caused by genetics;
- Rare adherence to hygiene standards, improper application of cosmetics;
- Injury to the skin.
In addition to the above prerequisites, a cyst can be a complication of the clinical manifestation. Thus, the auxiliary factors contributing to the appearance of atheroma include the following:
- Skin injuries;
- Diabetes mellitus, the protective functions of the skin in this case are weakened;
- Inflammatory lesion of the epidermis;
- Irregular structure of the sebaceous glands;
- Applying excessive amounts of cosmetics to the skin;
- Congenital diseases that affect the synthesis of fats in the body.
As a result of the increased work of the exocrine glands and their low permeability from the excretory duct, the secretion is retained and, as a result, the glands become swollen, which become like sacs filled with curdled contents.
It is possible to minimize the risk of atheroma formation by following simple rules:
- compliance with hygiene requirements;
- use of high-quality hypoallergenic cosmetics;
- conducting systematic vitamin therapy;
- including only healthy foods in the diet;
- careful care of delicate facial skin, prevention of injury and irritation;
- timely elimination of any diseases of the endocrine and hormonal systems, as well as pathologies of the skin.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Effective face cream Russia
At the same time, self-medication is unacceptable, since it often aggravates the situation. Atheromas are diagnosed and treated only by qualified doctors.
One of the types of cysts on the face are mammary cysts, or so-called milia. They are also called whiteheads or milletheads. They occur in children and infants. The main reason is that the child’s hormonal background has not yet been formed. A certain amount of hormones enters the baby’s body with mother’s milk, which intensifies the work of the sebaceous glands and clogs the pores.
In any case, it is recommended to show the baby to a doctor, who will make the correct diagnosis and recommend treatment if necessary. It is important not to confuse milia with allergies or heat rash. It is strictly forbidden to scratch or pierce the milia, as in the process of these manipulations it is possible to introduce an infection.
Breast cysts in adolescents and adults are recommended to be treated by cosmetologists. There are many procedures to help eliminate this cosmetic skin defect.
The most important rule that will help avoid the appearance of tumors on the face is personal hygiene, as well as regular visits to the doctor. In addition, the following prevention methods may help:
- Steam baths, with which you can easily remove sebum.
- Vitamin therapy.
- Proper nutrition (reducing the consumption of spicy, fatty and smoked foods; it is better to add foods that contain fiber, vitamins and minerals to the diet).
- Removing makeup before bed is mandatory.
Monitor the health of your skin and use preventative methods.
A cyst on the face is not a malignant tumor, so you should not worry too much if you have one.
The main thing is to consult a doctor in time for professional help to avoid complications.
Where do birthmarks come from in newborns?
It is generally accepted that a newborn's skin is clean and free of any marks. But sometimes, looking at their child, attentive parents identify changes in the skin. It is not surprising that birthmarks in newborns are such a concern for loved ones. After all, skin is an indicator of the condition of a person, even a recently born toddler.
Why moles appear in newborns
A mole is a specific formation on the human skin. Birthmarks in newborns occur for various reasons. One of them is hormonal imbalance in the mother’s body. Another reason is the presence of a pregnant woman in an unfavorable external environment - with radioactive radiation, sudden climate change, which is also manifested by changes in the skin.
Provoking factors include:
- oxygen starvation;
- Caesarean section, during which a sudden drop in blood pressure occurs;
- genetic predisposition.
Parents are often concerned about the problem of why spots appear on the head, in particular on the back of the child’s head. The causes are the same: heredity, hormonal imbalance.
The appearance of peculiar marks on the body of a newly born baby should not cause unnecessary anxiety to the mother. However, to make a decision regarding the spot, a professional opinion is needed, for which a dermatologist is consulted. You should consult as soon as possible after birth.
Types of birthmarks
There are different types of birthmarks in a newborn. These neoplasms are divided into two large groups:
- Nevi, represented by moles and various other pigmented spots that have a brown, or less often, other color.
- Angiomas, which are red spots that are of vascular origin.
Nevi appear in many people. When handled correctly, they are not dangerous, and their appearance occurs throughout a person’s life. A nevus is an accumulation of cells in the epidermis - melanocytes. Due to the natural brown pigment - melanin, they differ from other cells. In most cases, their occurrence occurs closer to two years, as well as during adolescence, when puberty becomes the cause. The number of marks, as well as their location, for example, on the back of the head, is individual and depends on the genetic factor.
There are 4 types of nevi:
- A giant pigmented nevus is distinguished by the presence of hairs.
- Halo-nevus is characterized by a round shape, brown color, surrounded by lighter skin.
- A fiery nevus is a dark-colored spot that requires monitoring by a dermatologist.
- Blue nevus is often located on the arms or the front of the head. It is distinguished by its small size and bluish-gray color.
Photos of the described birthmarks can be found in specialized literature. Angiomas are also divided into two large groups.
Hemangiomas are formations located in the dermal layer and consisting of small vessels. By their nature, they are congenital birthmarks. Often appear on the back of the head.
Lymphangiomas are formations consisting of vascular cells of the lymphatic system. They are formed during intrauterine development, but appear on the skin at the age of three.
There are 3 common types of angiomas:
- Strawberry - comes in different sizes, got its name due to its strawberry-red color. The reasons for the appearance lie in the underdevelopment of vascular cells that separated from the child’s circulatory system during intrauterine development. It can be seen on the back of the baby's head.
- Wine (capillary) penetrates the deep layers of the skin, distinguished by a bluish-red hue and a rough surface. A peculiarity is its gradual disappearance after a year.
- Cavernous or cavernous is a pulsating formation of a purple hue, consisting of cavities filled with blood. It is located under the skin and rises as a rounded spot. When pressed, it shrinks, but then returns to its previous form.
There are several other types of neoplasms; they are less common, but also differ in their red color and different location on the child’s body. Only a doctor can determine their type and make the correct diagnosis.
The danger of birthmarks
Birthmarks in newborns are not dangerous if handled properly. Parents need to know where skin changes come from and follow some rules. From the very beginning, if you notice a mark on your baby's skin, you should consult a dermatologist.
Upon examination, a specialist will determine the type of formation, the reasons for its appearance and make predictions. It is the parents’ responsibility to inform the doctor about all the peculiarities of the education and the presence of discomfort in the child from its presence. The birthmark cannot be exposed: neither mechanical nor chemical. They don’t rub it, don’t comb it, don’t get rid of it on their own.
It is contraindicated to cover it with an adhesive plaster, which can create a greenhouse effect. If hair grows in the affected area, it should not be pulled out or shaved, causing the degeneration of skin cells. It is always necessary to remember that skin formations are delicate phenomena and, if exposed, can become a malignant skin disease.
Removal of birthmarks in newborns
Appearing birthmarks can cause discomfort to the child, for example, if they are located in an area that often comes into contact with clothing and is subject to friction. Their number may increase. Only a doctor can answer the question of where the spots appear on a baby. If there is a danger to the newborn, the skin lesion is removed. Medicine offers four ways:
- laser removal;
- cryotherapy;
- removal through medicinal injection;
- surgical intervention.
The doctor will explain the reasons why one method or another is chosen. This is due to the specifics of the neoplasm, the age of the child and his state of health. In some cases, a birthmark is a cosmetic defect that worries parents, located on the head or open area of the child’s skin. Sometimes this spoils the first photo of the baby. In this case, it is necessary to remember about health, and not about the external component. Birthmarks should be removed only if necessary after consultation with a doctor.
Preventive actions
Diagnosis of formations occurs already at the first appointment with a dermatologist. The presence of a cyst is determined visually; the doctor feels it to determine its density and degree of mobility. The most important point of the examination is to identify the excretory duct. This indicator is the dominant sign of atheroma, allowing it to be distinguished from other formations of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
In cases of emergency need to remove skin formations, during the operation, the tissue of the capsule and the secretion contained inside are taken for histology.
Histological examination allows one to accurately differentiate cavity formation, since the symptomatic manifestations are similar to various neoplasms:
- Fibroids;
- Hygromas;
- Lipomas;
- Hemangiomas.
The analysis is of particular importance for differentiating formations in the axillary region, groin area, and scalp, since in these areas the risk of degeneration of a benign formation into a malignant tumor is highest.
Histology allows us to determine the nature and nature of the formation, because it is externally similar to the syphilitic gumma that forms on the knees and forehead area. In the area of the reproductive organs, bartholinitis may form, resembling a cavitary node at the initial stage. At the initial stage of development, lymphadenitis can be confused with a cyst.
Histological examination allows one to accurately determine the nature and form of the pathology and determine the treatment direction.
The main signs of neoplasms, allowing to identify the cavity formation of the sebaceous gland
| Dominant trait | Lipoma | Fibroma | Lymph node | Cyst | |
| External manifestations | In most cases, they appear visually in the case of an increase in size or growth of large formations. | Visualizes well. It appears as an elevation above the skin. Visually it is a round formation of regular shape. | |||
| The degree of mobility of the skin over the formation | The skin is characterized by good mobility, which is due to the location of the formation: it is formed deeper. | The displacement of the formation occurs along with the skin, due to the fact that the atheroma is formed in its thickness. It is impossible for the skin and formation to move relative to each other. | |||
| Formation Density | Soft to the touch | Have a dense structure | The formation is quite soft to the touch. | ||
| Presence or absence of pain on palpation | No pain is felt | Painful | In the absence of inflammatory processes, there is no pain. The inflammatory process, suppuration of the formation is manifested by pain on palpation. | ||
These signs make it possible to differentiate a cyst already at the first appointment with a dermatologist, to separate it from skin formations that have similar signs.
In some cases, an ultrasound examination of a neoplasm similar to atheroma is performed. If a cavity is detected during the examination, the possibility of a sebaceous gland formation is high.
Various methods of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are not used due to their low information content.
It is within the power of every person to reduce the risk of pathology; to do this, all you need to do is follow simple hygiene requirements, properly care for your skin, and use high-quality cosmetics.
Dermatologists recommend periodic professional facial cleansing, but a home procedure is also suitable: using scrubs and mud masks.
For complete prevention, additional tips are needed:
- regular visits to the dermatologist’s office, especially when skin diseases appear;
- periodic steam baths;
- healthy diet, supplement the menu with fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs and other foods high in vitamins;
- avoidance of fried and spicy foods;
- using sunscreen in the summer and nourishing creams in the winter;
- strengthening the body’s protective functions: taking vitamins, physical activity, giving up bad habits;
- daily removal of decorative cosmetics.