Any person is afraid not so much of the operation itself as of the anesthesia.
With all its types, an artificially induced reversible state of inhibition of the central nervous system occurs, sleep occurs, pain relief, muscle relaxation occurs, and some reflexes are inhibited.
They often ask: “Doctor, will I wake up? How will I feel?”
How long it will take and how you recover from general anesthesia, what sensations you experience - everything is very individual. This directly depends on the patient’s initial condition: his age, weight, gender, and concomitant diseases. Particular attention should be paid to which organ is being operated on:
- Cavity in the abdomen: on the stomach, intestines, appendicitis, etc.;
- Thoracic - that is, thoracic surgery, on the lungs, esophagus, trachea;
- Heart surgery;
- Neurosurgical;
- Burn injury;
- Polytrauma with damage to internal organs and the musculoskeletal system.
Also directly affects:
- Duration of the operation and its complexity;
- Qualification of an anesthesiologist;
- What drugs are used.
How many people recover from general anesthesia after elective abdominal surgery?
If it lasts no more than one or one and a half hours, (as a rule) a preliminary diagnosis was established before the operation and confirmed during it, then usually the patient wakes up, or rather the anesthesiologist wakes him up already on the operating table. If everything is normal, reflexes are restored, breathing is adequate, sufficient, the patient has regained consciousness, consciously answers questions, is oriented in place and time, then the patient is transferred to a regular ward under the supervision of a nurse and the attending physician. We also recommend reading: Venipuncture: technique and indications
How long does it take to recover after anesthesia?
Almost everyone who is about to undergo surgery asks themselves and doctors this question, but it is unlikely that anyone will be able to answer unequivocally how long the anesthesia takes to wear off and how it is removed. Recovery lasts from a few minutes to a certain number of hours. Therefore, how to quickly recover from anesthesia depends on several factors:
- Duration of the operation. If it is complex and lasts several hours, then coming out of anesthesia will be more difficult.
- Dosage of anesthetics. It is directly related to the time spent on the operation: with a multi-hour surgical intervention, the amount of the administered drug is correspondingly greater and its tolerability may be more difficult.
- General health of the patient. A strong body is able to tolerate anesthesia more easily and recover from it faster.
- Patient's age. Older people usually have a more difficult time with anesthesia.
Recovery from anesthesia is accompanied by the restoration of vital processes and the return to functioning of all functions. On average, this takes from 1.5 to 5 hours. The anesthesiologist continues to observe the patient after the intervention is completed, monitoring how the person returns to normal and whether there are any complications.
Folk remedies for recovery after anesthesia
In combination with drug support, the patient can use folk remedies. Arnica officinalis extract helps the patient recover faster and improves cerebral circulation after major surgery. Passionflower (passion flower) and chamomile have a relaxing and calming effect. It is better to buy the necessary herbs at the pharmacy - they come in the form of filter bags, convenient for use; you just need to pour boiling water over them and leave for a few minutes.
(Ratings: 9 , average: 4.89 )
Possible side effects of anesthesia
How the body will cope with anesthetics and how the patient will recover from their influence is of particular concern to the patient. Everyone has their own reaction to the administered drugs: some come out of this state almost immediately, while others experience side effects:
- Headache, dizziness. Anesthetics sometimes lower blood pressure, which leads to dizziness. Head pain is common after an epidural, but it goes away within a few hours.
- Sore throat. If you had to use a breathing tube or intubate the patient, then this side effect is possible. Usually goes away within 2 days.
- Nausea, sometimes with vomiting. The most common occurrence. The feeling of nausea directly depends on the drugs administered.
- Confused consciousness. This usually affects older people.
These are the main, most common side effects of anesthesia. There are several more severe reactions of the body, but they are less common:
- hallucinations;
- speech or hearing impairment;
- chills;
- slow thinking;
- numbness of the limbs;
- sleep disturbance.
In any case, it is not at all a fact that the listed reactions to anesthesia will necessarily occur. Most of them can be avoided if you take into account a number of simple conditions.
How to ensure an easy recovery from anesthesia?
Anesthesia is a general anesthesia of the body, which is accompanied by medicinal sleep. Its goal is to relieve the patient of pain during surgery. Proper preparation for anesthesia will help to easily remove the patient from this state.
Before an operation, the patient is often overcome by fears: will he wake up after the operation, what will be the consequences, and how will the anesthesia affect his future life? Therefore, the anesthesiologist must not only choose the right effective and safe pain relief, but also prepare the person psychologically. The patient's recovery from anesthesia requires special attention, because at this stage the restoration of all vital processes begins.
For patients with an unstable nervous system, sedatives are prescribed a day before surgery.
General rules: how not to aggravate the effects of anesthesia, prevention
To help yourself and more easily survive the so-called “coming-off” from anesthesia, you need to follow several rules that doctors always warn about:
- The day before surgery, you should absolutely not eat heavy foods. Dinner should be light, and no later than 18-19 hours (the doctor will say more precisely, it depends on the type of operation and its expected duration).
- On the day of the operation (before the start), you can eat 6 hours (no later), and drink at least 2 hours or more. In each specific case, the possible time of eating will be more accurately determined by the anesthesiologist.
- The anesthesiologist must know absolutely everything about the patient’s condition in order to select the correct dose of the drug or cancel the operation. This is especially true in cases where the patient’s well-being suddenly changed shortly before the intervention. It is very important!
- You can drink no earlier than an hour later, and only with your doctor’s permission. You should not drink sweet or carbonated drinks: this can cause bloating or vomiting. It is better to drink plain boiled water or warm tea.
- If drinking does not cause vomiting, after a few hours, with the consent of the doctor, you can eat some light and liquid food: fermented milk products, cream soup, jelly, vegetable puree. It is especially important to adhere to such a diet for those who have undergone surgery on the abdominal or pelvic region: these patients will experience disturbances in peristalsis for 2-3 days, so the food should be as gentle as possible and made from easily digestible foods.
- If the operation was long and difficult, then in order to avoid memory impairment you will need to drink a lot of fluid: from 1.5 to 3 liters per day. This will help remove the drug from the body faster.
- There is no point in enduring severe pain in the operated area, so you can always ask the doctor to prescribe a painkiller injection. But usually the patient who wakes up is given an injection immediately.
What you need to know from your anesthesiologist
During a consultation with an anesthesiologist, you need to find out what restrictions to observe after surgery, as well as:
- When to stop eating and drinking Usually, the last meal is allowed no later than 18:00 on the eve of surgery. On the morning of the operation you should not even drink water. This rule was established to prevent life-threatening complications during anesthesia - vomiting and entry of vomit into the respiratory tract.
- When to Stop Taking Medications There are a number of medications that you should limit or stop taking before surgery. The exact list of these medications can be checked with an anesthesiologist.
- How long before surgery to quit smoking Patients who smoke often experience rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and increased blood pressure. To avoid complications during anesthesia, it is worth checking with the anesthesiologist about how long before and after surgery you should not smoke.
Particular attention should be paid to preparing children for anesthesia.
The patient must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations, even if they seem excessive or unnecessary to him. When starting anesthesia, the doctor expects understanding and willingness to cooperate on the part of the patient. Even a slight violation of the recommendations can become an unpleasant surprise during anesthesia and complicate the operation. Anesthesiologists use modern objective methods to monitor the level of consciousness, so the risk of waking up during surgery is minimized.
Dear patients! We recommend that you refrain from driving vehicles for 24 hours after anesthesia.
Prevention of complications
In addition to the sometimes difficult condition after anesthesia, there is also a risk of postoperative complications. But they can be avoided if you follow simple conditions.
After surgery, the patient cannot always breathe deeply, which is usually fraught with depression of respiratory function, congestion in the lungs and subsequent pneumonia. Therefore, in order to catch his breath, the patient needs to perform breathing exercises. An exercise that simulates inflating a balloon will be useful.
2 hours after the surgeon finishes his work, you need to start turning over (with the doctor’s permission), after 5-6 hours you should try to sit up on the bed, and after half a day or a day you can walk. Physical activity is necessary to avoid the formation of blood clots due to a long lying position. Perhaps the doctor will prescribe physical therapy.
How do you recover from anesthesia?
During the early period of awakening, the patient feels:
- Pain in the area of the postoperative wound. Usually it is felt 5-6 hours after the end of the operation. This is good and normal, it means alive.
- A sore throat. This is not fatal and is also absolutely normal. Everything goes away without treatment in 1-2 days! Infrequently, but irritation with the endotracheal tube occurs, it is associated with difficulties in tracheal intubation or inconsistency in the size of the endotracheal tube (for women it is No. 7-8, for men No. 8-9-10). For children under 5 years of age, there are special tubes without an inflatable cuff. Although children are different, so everything is individual.
- Dizziness.
- Weakness.
- Chills. This is a violation of thermoregulation, drugs for anesthesia cause a decrease in body temperature, but today this is rare.
- Rarely nausea, even less often, even extremely rarely, vomiting. Nausea and vomiting often occur after operations on the abdominal cavity, stomach, and intestines. All these peculiarities of awakening are easily dealt with by anesthesiologists and resuscitators in the intensive care unit.
We also recommend reading: Neuroleptanalgesia: what drugs are used?
Special categories of citizens: in the postoperative period, persons suffering from alcoholism or drug use often experience agitation, aggressiveness, and an inadequate reaction to the environment. But these reactions are not directly related to anesthesia; it is rather a withdrawal syndrome! They can be treated quite easily with sedatives and infusion therapy, as well as symptomatic treatment.
Conclusion
The fear of going under the influence of anesthetics is understandable for many people. But this greatest invention gives doctors a unique opportunity to carry out any, even the most complex, operations and other actions without the threat of painful shock in the patient. Drugs that put the patient into a state of artificial sleep are constantly being improved, and perhaps someday a drug will be invented that does not cause negative reactions in the body.
But for now, it is important to understand that there are basic requirements to alleviate your condition after anesthesia:
- thorough preliminary examination and compliance with the doctor’s recommendations before surgery;
- correct actions after surgery regarding physical activity, breathing and nutrition;
- a conversation with an anesthesiologist if there is panic or worsening of the condition before the operation, which will help the specialist select the appropriate drug depending on the health and psychological state of the patient, the anesthesiologist can also advise you how to quickly recover from anesthesia if you ask him about it.
Prevention of anesthesia complications
Immediately after completion of the operation, the patient may experience headaches and hallucinations, which disappear in the next few hours after anesthesia. Vomiting is one of the most common consequences of anesthesia, which can be prevented by abstaining from food and drink for the first 2-3 hours.
To prevent thromboembolic complications and bedsores, the patient is recommended to move more, turning from side to side. Keeping a patient under anesthesia for too long can lead to memory impairment. To avoid this, you need to drink at least 2.5 liters of water daily for 7-10 days. This will speed up the body's cleansing of painkillers and reduce their negative effects.
Features of local anesthesia
Local anesthesia is understood as temporary anesthesia of a small area of the body due to the effect of external drugs on it or injection of a medicinal solution. In the definition one can immediately see a large classification of types of local anesthesia: superficial and internal. The latter, in turn, is divided into several more subtypes depending on the area of influence (epidural, conduction, spinal, infiltration).
Local anesthesia has found use in almost all areas of medicine, but the most striking example is dentistry. Today, almost all manipulations are performed with anesthesia. And if previously the patient had to endure 10-20 minutes while the doctor drills the tooth, cleans the canals, and puts a filling, now all pain is reduced to a second tingling sensation from the insertion of a thin needle.
How is it carried out?
All types of local anesthesia have their own characteristics, but on average it is something like this: a person is injected with medicine into a specific area. After a few minutes, sensitivity in this area is lost, and doctors can begin manipulation. The patient remains conscious, but he does not feel anything, not even the touch of a cold instrument. The general condition is also stable, although some admit to experiencing mild nausea and dizziness. But doctors attribute this more likely to anxiety than pain relief.
By the way! Sometimes, before inserting a needle, the skin is first numbed with external anesthetics to reduce pain from puncturing soft tissue. The result is a combined local anesthesia. It is used, for example, during epidural anesthesia.
How does anesthesia wear off?
The amount of anesthetic administered and the choice of its type are calculated based on the complexity of the operation and the patient’s physique. But the medicine is always taken with a reserve so that the anesthesia does not suddenly wear off during medical procedures if they require more time. Accordingly, after the end of the operation, the patient has a few more minutes (sometimes even a little more than an hour) for the anesthetic to stop working.
Sensitivity returns gradually, but quite quickly. First, a person begins to feel the touch, and after a minute or two he feels pain at the site of the manipulation. If it was a dental procedure, then the area where the gum was punctured or the hole after the extracted tooth may ache.
When treating caries, as a rule, no pain is felt after the anesthesia wears off. If it was a more complex operation, for example, to remove an ingrown nail, then the operated finger may begin to hurt quite severely because there was a violation of the integrity of the tissue. But these pains can be relieved with analgesics.
Possible complications
Some people are allergic to certain types of medications. Local anesthesia involves the use of Lidocaine, Novocaine, Bupivacaine, etc. And a person may experience a reaction to them in the form of:
- hives;
- itchy skin;
- difficulty breathing;
- swelling;
- anaphylactic shock.
These reactions appear immediately after administration of the drug. And if the first two are quite tolerable, then the last three require termination of the operation and hospitalization of the patient. You can find out if you are allergic to anesthetics by first conducting an allergy test.
Some people note certain reactions after the local anesthesia wears off: dizziness or headache, weakness, sleepiness, and fever. But it is impossible to say for sure whether this is an allergy to the medicine or consequences after the operation.
Features of general anesthesia
A more complex type of anesthesia, which involves immersing the patient in a narcotic sleep and completely depriving him of not only sensitivity, but also consciousness. It is difficult for people who have never been exposed to this in their lives to imagine such a state. Therefore, many people are afraid of their first operation under general anesthesia.
General anesthesia is also successfully used today in all areas of medicine. Moreover, sometimes this is the only chance to perform the operation. In dentistry, this type of pain relief is also used when a person (usually a child) is unable to overcome his fear of going to the dentist.
There are two main types of general anesthesia: inhalation (through a mask) and intravenous. Sometimes combined anesthesia is used. What it will be in a particular case is decided by the doctor, depending on the specifics of the operation and the physiology of the patient.
What is it made up of?
General anesthesia consists of three “components”: drug-induced sleep, analgesia and muscle relaxation. In essence, a person simply falls asleep, but in fact completely different changes occur in his body. During normal sleep, breathing is calm, the body is relaxed, but reflexes are preserved.
And if you prick a person with a pin or simply pat him, he will wake up. And narcotic sleep also implies analgesia - suppression of the body’s autonomic reactions to all types of interventions: punctures, incisions, manipulation of internal organs, etc.
The third “component” of general anesthesia – muscle relaxation – is necessary to facilitate the work of surgeons during surgery. Due to the presence of muscle relaxants in the medicinal solution, the patient’s muscles are as relaxed as possible and also cannot reflexively react to interventions (contract, tense).
How is it carried out?
If this is general anesthesia of the inhalation type, then a mask is put on the patient’s nose and mouth, through which a gas-narcotic mixture is supplied. A person is required to breathe evenly and not resist the onset of sleep. Using sensors connected to the body, the anesthesiologist determines when the anesthesia has fully taken effect and signals this to the surgeons.
Intravenous general anesthesia involves the administration of drugs through the skin. This anesthesia is considered deeper and more reliable, while inhalation anesthesia is used for simple operations. If a difficult and lengthy intervention is ahead, then combined anesthesia is used: first intravenous, then a mask is added.
By the way! During general anesthesia, doctors must monitor the main indicators of the body’s vitality, thanks to equipment and external signs. The patient’s skin color, body temperature, heart function, pulse - all this allows you to monitor the course of anesthesia and the person’s condition.
How long does it take to recover from general anesthesia?
People sometimes fear for their well-being when they come out of general anesthesia after surgery because it is a complex process. Although, it is difficult for the anesthesiologist, but rather unpleasant for the patient. It's like waking up from a very heavy sleep. In this case, the following sensations may be noted:
Absolute contraindications
This list is conditional. In some cases, as mentioned above, deep anesthesia is used even if they are present. We list the main contraindications to anesthesia:
- The patient has a disease such as bronchial asthma in severe or progressive form. This condition is directly related to the danger of laryngeal intubation during deep anesthesia. This manipulation can cause closure of the glottis or bronchospasm, which is life-threatening. That is why bronchial asthma and general anesthesia are a rather dangerous combination.
- Pneumonia. After surgery, pulmonary edema may develop in this case.
- Serious diseases of the cardiovascular system. These include myocardial infarction suffered earlier than six months, acute heart failure, as well as uncompensated heart failure. The latter is often accompanied by severe sweating, swelling and severe shortness of breath. Atrial fibrillation, in which the heart rate reaches one hundred beats per minute, is also an unacceptable condition.
- Epilepsy, schizophrenia and some other psychiatric and neurological diseases. Contraindications for such diagnoses are associated with an unforeseen reaction of the sick person’s body to the use of anesthetics.
- Temporary but absolute contraindications, in which surgery is usually not performed under anesthesia, is a state of alcohol or drug intoxication. The point here is that anesthetics will not work, so this procedure is impossible. Surgical intervention for a patient who is under the influence of alcohol or drugs can only be performed after complete detoxification of the body. Often in this case, the help of a narcologist is necessary. General anesthesia is used for patients under the influence of alcohol or drugs only for emergency medical reasons. However, in this case, large doses of anesthetics and narcotic analgesics are introduced into the body, which can subsequently lead to an unpredictable effect.
We also recommend reading: Various methods of pain relief
Is it possible to make recovery from anesthesia easier?
You can reduce the intensity of discomfort if you properly prepare for surgery. To do this, you need to openly tell your doctor about the illnesses you have suffered and your concerns, follow a diet, and conscientiously take the prescribed medications. If the patient is self-willed in preoperative preparation, eats in secret from doctors, runs around smoking or takes some pills, then this will create problems during surgery. Moreover, they will be associated not only with immersion in and recovery from anesthesia, but also with the course of the operation itself.
It is necessary to follow medical recommendations even after general anesthesia has stopped working. If your doctor allows you to get up and walk, you need to do this to prevent thromboembolism (blockage of the venous vessels). Some people are advised to simply move their legs for the same reason. It is not recommended to grab a book or smartphone immediately after waking up: it is better to rest and think about something good, for example, that everything is behind. And under no circumstances should you ignore the doctor’s instructions, which may vary depending on the type of anesthesia and the operation performed.
The main types of anesthesia used during operations
Anesthesia is a very deep sleep, which is induced with the help of special drugs for various operations. It provides analgesia (decreased sensitivity), amnesia (no memory of the operation), relaxation (relaxation of body muscles).
In medical practice, 2 types of anesthesia are used:
- General anesthesia.
- Local anesthesia.
General anesthesia is divided according to the method of drug administration:
- Inhalation – this is intubation or endotracheal, mask.
- Non-inhalation – intravenous, intramuscular, rectal.
Medicines that are used for general anesthesia are called anesthetics, and they are introduced into the body in several ways:
- Inhalation – through a face mask.
- Parenteral – intravenous (a catheter is installed).
- Combined – pain relief is achieved by sequential use of different methods and means.
Depending on how the respiratory organs react to drugs, a distinction is made between drug pain relief, artificial ventilation and spontaneous breathing. The first type requires incubation of the trachea or the use of other methods to help the passage of oxygen to the lungs.
Everything you need to know about anesthesia!
Anesthesia is an unconscious state of a person caused artificially in order to disable currently undesirable body functions. But the unconscious state is only one part of the effects of anesthesia. Its other task is to prevent the body from automatically reacting to pain. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for them, and it cannot be controlled by consciousness and works even in its absence.
And the final goal of anesthesia is to relax muscle tissue in order to provide full access to the problem area and create favorable conditions for the surgeon to work. Managing anesthesia is a difficult job, since the doctor can never predict what the reaction of a particular organism will be to certain substances. But recovery from general anesthesia is an equally important moment. It poses many dangers to the health and sometimes the life of the patient.
Please note that the term “anesthesia” assumes that the patient is in an unconscious state, therefore it is referred to only as general anesthesia. If pain relief is achieved in a specific area of the body, while the patient retains the ability to perceive the outside world, then it is incorrect to use the term “local anesthesia” here, since this is local anesthesia.
What kind of anesthesia is there?
Anesthesia is characterized by many parameters: by the potent substance used and the method of its entry into the body, by duration and depth, and by the purpose of use. Each of these groups has its own tasks, its own characteristics and advantages, as well as its own dangers, so:
Local anesthesia is intended to turn off sensitivity in specific areas of the body. And it is achieved through medicinal effects on certain areas of the nerves, which ensures loss of sensitivity of the tissues innervated by them. At the same time, the patient retains clear consciousness, as well as respiratory activity. This type of pain relief is used for patients with severe concomitant pathologies or in cases where the patient must be conscious. It does not have a general effect on the body, so removal from it is difficult and its consequences are minimal. The main disadvantage of this anesthesia is that the technique for performing it is quite complex and requires experienced specialists to perform it.
Inhalation anesthesia is achieved by inhaling anesthetic drugs using a special mask. It uses special “volatile” liquid substances, which include inhalational anesthetics and gas-like narcotic substances. Among them are nitrous oxide, fluorothane, methoxyflurane, and cyclopropane.
In its pure form, this method is used only in pediatrics, and for adult patients, mainly as one of the components of complex anesthesia. It is quite easy to use, has no serious side effects, is inactivated in the liver and is easily excreted from the body. That is why it is preferred in pediatric practice.
A very significant point is that the surgeon has the opportunity to freely control the anesthesia during the operation. This is especially important when the patient has concomitant pathology of the circulatory system and respiratory system.
Non-inhalation anesthesia - involves the administration of anesthetic drugs using one of the parenteral routes (intramuscular, intravenous, rectal). Its advantages are that it is technically simple, passes without a period of excitement, has a good relaxing effect, and its effect occurs quickly. The disadvantage of this method of pain relief is that its effect is short-lived, which makes it impossible to use it during long-term operations. Its area of application is many diagnostic procedures or minor surgical interventions. Recovery from this type of anesthesia is simple and lasts no more than one to two hours.
Techniques
When a person learns that he needs to undergo an operation, he is most often interested in the questions: “What anesthesia will the manipulations be performed under?” “How dangerous is this?” “Are there any contraindications?”
It must be said right away that what kind of anesthesia will be, the method of its implementation completely depends on the person’s condition and the complexity of the surgical intervention. The anesthesiologist's arsenal includes a wide variety of drugs and means for putting the patient into medicated sleep. Conventionally, anesthesia can be divided into minor and major. The first method includes:
- Hardware mask or inhalation. A person receives a dose of the drug along with an inhaled inhalation mixture. Anesthetics are introduced into the body: fluorothane, isoflurane. This type of anesthesia is used during short operations and invasive studies.
- Sleep induced by intramuscular injection is increasingly used by anesthesiologists. It is difficult for doctors to control the time of awakening, and this type of pain relief is quite poorly tolerated.
The big view is a multi-stage, not single drug effect on the body. Non-narcotic analgesics are used for children. These drugs help relax the muscles, the body does not tense in the area of the operation. Sleeping pills of various groups and a complex of intravenous infusions can also be used. These drugs can be administered either intravenously or by inhalation, but the child is given artificial ventilation during the operation.
Additionally: diet 6 according to Pevzner after a heart attack.
Staged action of general anesthesia
Once in the human body, narcotic substances affect the functioning of all systems and organs. At each of the four stages of anesthesia, these changes vary.
- Analgesia – when anesthetic substances enter the body
- Excitement – characterized by short-term activation of all systems, followed by long-term relaxation.
- Surgical intervention is the time of the operation when the functioning of the internal organs is maintained at the required stable level.
- Awakening is when consciousness returns and sensitivity is restored.
How does a person recover from general anesthesia?
The moment of removing the patient from the state of general anesthesia should be considered the most crucial, when the anesthesiologist should focus on the patient and his condition. How long does it last? From the moment the anesthetic is stopped, the patient begins to recover from anesthesia. How long it will last depends on several factors:
- Duration of surgery (the longer the operation took, the longer it will take to recover from anesthesia)
- The dose of the anesthetic received (in addition to the duration of the operation, it is affected by the patient’s weight and his sensitivity to the drug)
- Health status. People exhausted by the disease with many concomitant pathologies have a harder time recovering.
- Patient's age. At a young age, general anesthesia is tolerated more easily than at an older age.
At this point, the patient gradually returns to sensitivity and consciousness. At the first stage, muscle tone and their reflex reactions are restored, later the nervous system comes into an excited state, this is noticeable by incoherent speech and the presence of motor restlessness. Only after this consciousness fully returns, then the patient awakens. At first, he is lethargic and inhibited, cannot navigate in space, has difficulty speaking and expressing emotions.
At this point, the anesthesiologist performs a series of tests to give a correct assessment of the degree of breathing restoration. Only after ensuring a stable positive result is the patient allowed to be extubated and transported to the ward.
How do you wake up after anesthesia?
The stage of recovery from general anesthesia after surgery is considered very important and requires the anesthesiologist to fully focus on the patient’s condition. Recovery from anesthesia begins the moment the anesthetic supply stops. Consciousness and sensitivity begin to return to the patient: first, muscle tone and reflex muscle reactions return, and the nervous system is excited, which can manifest itself as incoherent speech and motor restlessness. After this, consciousness slowly returns and the patient wakes up - in the first minutes he is disoriented in space, lethargic, inhibited, speech and expression of emotions are difficult.
At the awakening stage, the anesthesiologist performs a series of tests that allow you to correctly assess the restoration of respiratory function. Only after a positive result is the patient extubated and given permission to be transported to the ward.
In most cases, after surgery, the patient is transported to the ward of his department, where he was before surgery. The exception is those situations when the patient is in serious condition - in this case he is transferred to the intensive care unit.
Transporting the patient after surgery
What a person may feel when coming out of general anesthesia
Until the narcotic drugs are completely removed from the patient’s body, he will feel their effects. On average, this process takes about four hours. When anesthetics are removed from the body, sensitivity to pain returns, so the first day after the operation, or even two (depending on the degree of complexity of the surgical intervention), the patient is administered strong painkillers, sometimes tranquilizers, according to the schedule, this makes the patient lethargic and lethargic. Typically, the infusion of medications continues at this time.
For the first hours after the end of the operation, the patient is prohibited from drinking; you can only wet your lips or rinse your mouth. After 3-6-10 hours, water is allowed to be drunk, starting with a few sips, gradually this dose increases and after a day or two reaches the usual volume.
On the first day the patient may complain:
- For dizziness and headache. It is associated with the effect of anesthetic drugs on the central nervous system. In addition, medications used to suppress pain can lower blood pressure, which is manifested by dizziness of varying degrees of intensity. Another cause of headache is the use of epidural anesthesia, but it goes away after a few hours.
- For painful sensations in the throat when swallowing and breathing. These phenomena may be caused by injury to the pharyngeal mucosa during intubation. As a rule, it takes two to three days to recover.
- For nausea and vomiting. These are the most common complaints upon recovery from anesthesia; they directly depend on the type of drug used. To prevent this condition, you need to take your time to drink water, and if this happens, then there are medications that can cope with this problem. You just need to ask the nurse to give you an injection.
- For chills. Very often, after regaining consciousness, patients complain of trembling; this is a consequence of a thermoregulation disorder. To normalize the condition, it is enough to cover the patient warmly and cover him with warm heating pads.
Ways to quickly recover from anesthesia
It takes some time for the body to fully recover from general anesthesia. It is difficult to name the exact timing of withdrawal of anesthesia from the body, since the speed depends on many factors. These include the length of time and the traumatic nature of the operation, the type of anesthesia used, the individual properties of the patient’s body, his gender and state of health before the operation - older people have a harder time recovering from anesthesia.
As a rule, modern drugs for general anesthesia are eliminated from the body quite quickly - within several hours, so the recovery stage itself is short. Older drugs take a little longer to eliminate, causing more unpleasant side effects such as nausea, vomiting, headache and severe tremors throughout the body. There are steps you can take to relieve these symptoms.
Nausea and vomiting
The most common side effects of anesthesia. To reduce discomfort, you should follow a fasting diet; it is not advisable to even drink water. Nausea and vomiting respond well to drug therapy, so you can ask the nurse to give an injection of an antiemetic drug - this will help get out of the unpleasant condition.
Shiver
During anesthesia, the body's thermoregulation system malfunctions, so after waking up the patient may feel chills. To prevent this condition, it is recommended to cover yourself with a warm blanket immediately upon arrival in the ward.
Headache
Severe headaches are often caused by the drug's effect on the brain. To relieve a pain attack, you can use conventional analgesics.
As a rule, the body needs about 4 hours to remove anesthetics and recover from anesthesia. In the postoperative period, the patient is often given tranquilizers and analgesics, so for the first 12 hours after the operation he is half asleep. If the patient feels satisfactorily and is not bothered by nausea and vomiting, drug withdrawal can be accelerated by taking large amounts of fluid. This should be done after consultation with the doctor - in some cases it is contraindicated to put extra stress on the kidneys.
Accelerating recovery from anesthesia is possible with the help of medications that promote the rapid metabolism of anesthesia drugs and neutralize the toxic effect of the drug on the body.
Visiting patients after surgery
Rapid recovery from anesthesia is facilitated by early activation - if the patient is feeling well, he should start moving and eating as soon as possible. It is recommended to ventilate the room as often as possible; saturating the body with oxygen promotes rapid recovery.
After surgery, you should stop smoking, as nicotine causes a sharp constriction of blood vessels, which slows down the elimination of the anesthetic drug. The same applies to alcohol - in addition to constricting blood vessels, it puts extra stress on the liver and kidneys, which are already overloaded.
How to remove anesthesia from the body quickly after surgery?
There are several possibilities for this. Firstly, toxic substances will be eliminated faster if you use medications that accelerate metabolism. Secondly, the faster the patient begins to lead an active lifestyle, the faster the effects of the administration of general anesthetics will disappear. Thirdly, drinking plenty of fluids, preferably vitamin drinks (rosehip decoction, sea buckthorn, compotes), and frequent ventilation contribute to a speedy recovery. Fourthly, anesthesia will wear off faster if you give up nicotine and alcohol. Since they cause vasospasm, which causes all metabolic processes to slow down. In addition, alcohol has a destructive effect on the liver, and in order to fully remove the remains of potent substances, the function of this organ should not be impaired. For the same reason, after undergoing a major operation, preventive courses of drug therapy with hepatoprotective action and maintenance of kidney function should be carried out.
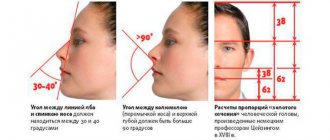
Surgery on the nasal septum under local anesthesia and general anesthesia
At the initial stage of development of the pathology, the patient may not notice any symptoms. However, after some time he may be disturbed by such unpleasant sensations as:
- labored breathing;
- headache;
- nosebleeds;
- dryness in the nasal cavity;
- frequent colds.
If you have such signs, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Modern diagnostics and treatment methods help a person get rid of all these unpleasant symptoms and return to a normal lifestyle. Most often, experts resort to septoplasty. This technology makes it possible to eliminate almost any defect without causing consequences.
Before surgery, the patient must adhere to important rules that will help avoid complications. A few weeks before surgery, the patient needs:
- stop using hormonal contraceptives;
- stop smoking, alcohol;
- stop exercising;
- Healthy food.
7 days before the operation, you should stop taking medications that have blood-thinning properties. If you do not follow all the doctor's instructions, the consequences can be unpredictable. The day before the procedure, you should stop eating solid food. In this case, the patient is prescribed an enema or other methods of cleansing the intestines.