Chickenpox, or chickenpox
Pathogen: Varicella-Zoster virus (VZV).
Method of transmission: airborne. It is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person by talking, coughing, or sneezing.
Immunity to chickenpox: lifelong. Produced either as a result of illness or after vaccination. In children whose mothers had chickenpox or were vaccinated against it, immunity to chickenpox is transmitted from the mother in utero and persists for the first 6-12 months of life.
Incubation period: from 10 to 23 days.
Infectious period: the entire period of the rash + 5 days after the last rash.
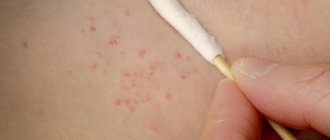
Manifestations: red dots appear simultaneously with a rise in temperature. However, sometimes the temperature may remain normal or rise slightly. The spots very quickly turn into single vesicles filled with a clear yellowish liquid. Soon they dry out and become crusty. A distinctive feature of chickenpox is a rash on the head under the hair and on the mucous membranes (in the mouth, on the eyelid, etc.). Very often this rash itches.
Treatment: chicken pox goes away on its own, so treatment can only be symptomatic: lower the temperature, treat the itchy rash with brilliant green (so that by scratching the blisters, the child does not introduce additional infection there), give an antihistamine to make itching less. You can swim if you have chickenpox! But at the same time, you should not rub the affected areas; instead, you need to gently blot them with a towel.
Important: you need to use brilliant green or other dyes (fucorcin, etc.) in order not to miss the next rash, because only old spots will be smeared. It is also easier to track the appearance of the last outbreak of the rash.
Herpes simplex
Causative agent: herpes simplex virus. There are two types: herpes simplex virus type I causes rashes in the mouth, type II - in the genital area and anus.
Method of transmission: airborne droplets and contact (kissing, shared household items, etc.).
Immunity: not developed, the disease occurs with periodic exacerbations due to stress or other infections (ARVI, etc.).
Incubation period: 4-6 days.
Contagious period: all the time of rash.
Manifestations: a few days before the rash appears, itching and soreness of the skin may occur. Then a group of closely spaced bubbles will appear in this place. The temperature rises extremely rarely.
Treatment: special antiviral ointments, for example with acyclovir, etc.
Important: use the ointment immediately after itching and pain occur, even before blisters appear. In this case, rashes may not occur at all.
Treatment
It is important to know what to do with certain green formations. If the cause is another, much more serious disease, they first fight it, and only then eliminate the formations on the skin. If the factor that caused the symptom is eliminated, then the stains themselves are removed using modern equipment and technology.
Dr. Evgeny Komarovsky about such spots in general: “In a civilized country, no one will approach you with a scalpel. They can discuss for a long time what it will be: cryodestruction, laser, sclerotherapy, systemic hormonal therapy, it even helps with white spots on the skin, mixed surgery...” Treatment is carried out in specialized centers, where there are the largest number of professionals in this field.
Before deleting, you need to ask a question that many people don’t ask. It is correct to ask how many similar operations or procedures the doctor has already performed before. Even doctors in the same field with the same academic degree may in fact have different degrees of professionalism in different areas, which is directly influenced by their experience.
“A collection of photos shows dynamics and gives a better idea to the doctor,” says Komarovsky. This applies to any stains: those that appear after sunbathing, those caused by diseases of internal organs, and others.
Other aspects of treatment
It is important to correctly determine initially what caused the green formations in order to understand whether it is scary. Then they decide what to do better. Coping with formations is not difficult, unlike the initial causes, the treatment of which will take time.
The underlying causes vary, and therefore the treatment varies. What is the shape, size and shade - all this indicates the disease. Therefore, if small spots have appeared on the body for now, this is a reason to take a camera and start chronicling, because later this information will be extremely important, and the doctor will not be able to build the dynamics of the disease based on assumptions alone.
A clear understanding of the reasons means that treatment will initially go in the right direction and at the right pace. Sometimes intervention does not require rush, and the problem can be gradually eliminated. But there are also diametrically opposite situations in which the patient’s life depends on the speed of the reaction.
Hand-foot-mouth syndrome
(from the English name Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease, HFMD), or enteroviral vesicular stomatitis with exanthema.
Pathogen: enteroviruses.
Mode of transmission: fecal-oral and airborne. The virus is transmitted from person to person through communication, conversation, and the use of common household items (dishes, toys, bed, etc.).
Immunity: after illness - lifelong.
Incubation period: from 2 days to 3 weeks, on average about 7 days. Infectious period: from the onset of the disease.
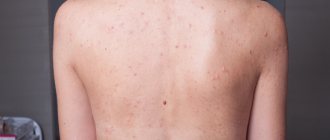
Manifestations: first the temperature rises and stomatitis begins: rashes on the oral mucosa, pain when eating, excessive salivation. The temperature lasts 3-5 days, often accompanied by diarrhea, and in some cases a runny nose and cough. On the second or third day of illness, a rash appears in the form of single blisters or small spots. The name of the disease comes from the location of the rash: it is located on the hands, feet and around the mouth. The rash lasts 3-7 days, after which it disappears without a trace.
Treatment: there is no specific treatment; symptomatic drugs are used to reduce fever and relieve pain during stomatitis. The disease goes away on its own; complications are possible only if a bacterial or fungal infection occurs in the oral cavity.
It is not easy to make a diagnosis of enteroviral vesicular stomatitis, because... The rash does not appear immediately and is very often regarded as a manifestation of an allergy.
Important: despite the active use of various painkillers in the treatment of stomatitis, the first few days it may be very painful for a child to eat. In such cases, it is good to use the most liquid food possible (milk, dairy products, milkshakes, baby food for babies, soups, etc.) and give it through a straw. Be sure to monitor the temperature of the food: it should not be cold or too hot - only warm.
What are skin spots
Rashes on the human body often have different appearance, size, shape (round, oval). A spot is a change in the shade of an area of the skin. The spots can take the form of a skin rash (small red dots) or large formations and occupy large areas, spreading over the entire back, abdomen, and legs. The rashes can be edged, scaly, of different colors, with shades of blue, orange, lilac, and white. Often, along with a change in color, the shape of the skin changes. This area rises above the rest of the surface, forming plaques, tubercles, and blisters.
The appearance of spots is often accompanied by itching, peeling, and pain. Sometimes their occurrence goes away without any alarming symptoms. If they are located in inaccessible places, a person may not immediately notice them. In many cases, skin lesions indicate the presence of some chronic diseases of the internal organs. Red spots on the body are often a sign of allergies. The occurrence of skin rashes sometimes indicates infectious diseases.
Roseola
(sudden exanthema, sixth disease)
Causative agent: another representative of the glorious family of herpes viruses is herpes virus type 6.
Method of transmission: airborne. The infection spreads through talking, socializing, sneezing, etc.
Immunity: after illness - lifelong. Children under 4 months have immunity received in utero from their mother. Incubation period: 3-7 days.
Infectious period: throughout the illness.
Manifestations: sudden rise in temperature and after 3-5 days its spontaneous decrease. Simultaneously with the normalization of the temperature, a pink, small- and medium-spotted rash appears. It is located mainly on the torso and, as a rule, does not cause itching. Goes away on its own after 5 days.
Treatment: only symptomatic therapy - drinking plenty of fluids, lowering the temperature, etc.
The herpes virus worsens due to stress or infections, such as ARVI.
The disease goes away on its own, there are practically no complications.
Roseola is often called pseudorubella, because. the skin manifestations of these diseases are very similar. A distinctive feature of roseola is the appearance of rashes after a drop in temperature.
Important: as in the case of enteroviral stomatitis, a rash that does not appear on the first day of illness is often regarded as allergic. Sometimes it is really difficult to distinguish them, but an allergic rash, as a rule, itches quite a lot, but with roseola there should be no itching.
Treatment
In order to remove stains from the body, it is necessary to find out the cause of their occurrence. Therapy is prescribed by a specialist based on laboratory data and information received from the patient. Treatment depends on the type, form, and nature of the disease that caused the spots to appear. The following types of medications can be used for therapy:
Treatment of serious diseases is carried out comprehensively, using several groups of drugs. If the disease is mild, only topical medications are often used. Medicines are available in the form:
- tablets;
- ointments, creams, sprays;
- solutions, tinctures.
Ketoconazole
Ketoconazole is an effective antifungal agent. The active substance of the drug powerfully suppresses the activity of fungi and destroys their cellular structure. The product is used to eliminate formations on the skin caused by dermatological diseases. It is prescribed for pityriasis versicolor, seborrhea, and various types of mycoses.
Ketoconazole is well tolerated by the body and has almost no contraindications. The course of treatment is 2-8 weeks. A distinctive feature of the drug is that it quickly eliminates skin rashes. A plus is the possibility of using the medicine for pregnant women. The disadvantages of this product include a large number of side effects.
Metronidazole
Metronidazole is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. This is one of the best modern medicines. It is a highly effective antimicrobial drug. The active substances of metronidazole destroy many types of bacteria and reduce the risk of recurrent diseases. It is used to treat complex infectious diseases and chronic diseases of internal organs.
The advantage of Metronidazole is the successful treatment of acne, lichen, and purulent formations on the skin. The disadvantages include the presence of many side effects. Among the undesirable manifestations are dysfunction of the nervous system, disorders of the esophagus, urinary tract, and allergic rashes on the body. The medicine has good reviews from doctors and patients.
Claritin
Claritin is an antihistamine that successfully eliminates allergy symptoms in adults and children. Used to treat urticaria, allergic dermatitis, and other skin diseases accompanied by rashes. In addition to the active substance - loratadine, it contains natural elements and flavorings. The medicine is not addictive, which is a big plus. It can be used for a long time without fear of harm to health.
A distinctive characteristic of the product is that it quickly relieves allergy symptoms without causing dryness of the dermis. The drug has many advantages: it can be prescribed to small children, has almost no contraindications, is well tolerated by the body, and side effects are rare. The only disadvantage is that it is recommended to avoid it during pregnancy and lactation.
«>
Rubella
Pathogen: rubella virus
Method of transmission: airborne. The virus is transmitted through communication, coughing, and talking.
Immunity: lifelong. It is produced either after an illness or after vaccination. For children whose mothers had rubella or were vaccinated against it, immunity to rubella is transmitted in utero and persists for the first 6-12 months of life.
Incubation period: from 11 to 24 days.
Infectious period: from the 7th day from infection until the rash completely disappears + another 4 days.
Measles
Pathogen: measles virus (Polinosa morbillarum)
Method of transmission: airborne. The unusually contagious and highly volatile measles virus can not only be transmitted through direct contact with a sick person, but also, for example, spread through ventilation pipes, infecting people in neighboring apartments.
Immunity: lifelong. It is produced either after an illness or after vaccination. For children whose mothers had measles or were vaccinated against it, immunity to measles is transmitted in utero and persists for the first 6-12 months of life.
Incubation period: 9-21 days.
Infectious period: From the last two days of the incubation period until the 5th day of rash/
Manifestations: fever, cough, hoarseness, conjunctivitis. On the 3-5th day of illness, bright, large, sometimes merging spots appear on the face, while the temperature remains. On the 2nd day, the rash appears on the torso, on the 3rd - on the limbs. Approximately on the fourth day from the moment of onset, the rashes begin to fade away in the same order as they appeared.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy: drinking plenty of fluids, darkened room (since conjunctivitis is accompanied by photophobia), antipyretics. Children under 6 years of age are prescribed antibiotics to prevent bacterial infection. Thanks to vaccination, measles has now become a fairly rare disease.
Green spots on the hand
Stains on the hands can make a person think that something is not going well with their health. The most common cause of spots is liver disease. Liver cirrhosis is usually accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased gas formation;
- disorientation;
- increased body temperature;
- bleeding gums;
- green skin pigmentation.
Such spots indicate that the disease has already become serious. Therefore, you should urgently consult a doctor.
Another reason for the appearance of green spots on the hands can be tinea versicolor. The causative agent of the disease is a fungus. People with oily skin often suffer from it. There are several ways to become infected with this fungus:
- Close contact with an infected person.
- Contact with an object that is contaminated.
After infection occurs, small dry spots begin to appear. The skin does not peel off. Each new spot turns green. Over time it darkens.
Sometimes, green spots appear on the skin as if from brilliant green. This problem is critical and should not be ignored. Pigmentation may be associated with problems with internal organs.
The trouble can be easily eliminated if you detect it in time and take action by contacting a competent doctor.
Erytherma infectiosum, or fifth disease
Pathogen: parvovirus B19
Method of transmission: airborne. Most often, the infection occurs in children in organized children's groups - nurseries, kindergartens and schools.
Immunity: after illness - lifelong.
Incubation period: 6-14 days.
Infectious period: incubation period + entire period of illness.
Manifestations: it all starts like a normal ARVI. Within 7-10 days, the child feels some discomfort (sore throat, slight runny nose, headache), but as soon as he “gets better,” a red, confluent rash appears on the cheeks, most reminiscent of mark from a slap. At the same time or after a few days, rashes appear on the torso and limbs, which form “garlands” on the skin, but do not itch. The red color of the rash quickly changes to bluish-red. Over the next two to three weeks, the temperature remains low, and the rash appears and disappears, depending on physical activity, air temperature, contact with water, etc.
Treatment: there is no specific treatment, only symptomatic therapy. The disease goes away on its own, complications are extremely rare.
Green spot on the body
The appearance of such unusual spots on the body can frighten a person. However, their green color may indicate some reasons for their occurrence:
- Hemorrhage of small vessels. When a vessel is damaged and blood gets under the skin, the spots acquire different shades upon contact with it.
- The appearance of such spots is caused by liver diseases.
- Pancreatic diseases.
- Cholecystitis.
- Skin diseases. For example, various types of lichen. The spots usually initially have a red tint, and after water procedures they acquire greenish colors.
- Hematomas of various origins.
- The presence of hemosederin in the skin. This is a special component of the circulatory system, which is obtained as a result of the division of hemoglobin. Its deposition under the skin can give the spot a green color.
Sometimes the spots go away on their own and do not require treatment. Do not forget that such spots can be the causes of hidden diseases in the body. If you find strange spots on your body, you should show them to a doctor.