Mole removal technique
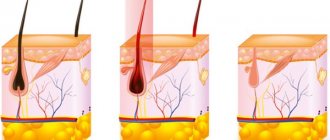
Coagulation is based on the use of high-frequency current, which serves as a scalpel.
With the help of such discharges, micro-incisions are made, cutting off the formation in small layers. Electric fields produce heat, preventing blood loss and minimizing the risk of infection. The device that generates the current for this procedure is called an electrocoagulator. It is quite expensive, so treating moles with an electric knife is not the most affordable method. The main advantage of the procedure is that it is done on the same day, when the doctor confirms the need to remove the mole and the absence of signs of a malignant tumor.
To prevent pain, the injection site is frozen with anesthetics. Next, a coagulator is used - a device for cauterization at the end with a special loop. Using an electric current, the required temperature is reached, and the device burns out the nevus. The entire procedure takes no more than a quarter of an hour.
Afterwards, a slight inflammation, hyperemia forms and a crust appears. It heals on its own within 10 days. It is recommended to lubricate the affected area with an antiseptic to prevent infection.
The procedure takes 15 - 30 minutes and consists of the following manipulations:
- the skin and area of the nevus are treated with an antiseptic solution;
- an injection of an anesthetic drug is given (if these are warts or very small formations, anesthesia can be in the form of a cream);
- a specialist burns out a mole or papilloma with an electrode;
- if necessary, stitches are applied to the wound;
- if the formation is small, the remaining stain is smeared with a solution of potassium permanganate.
The type of electrode used to remove a mole is selected according to its type and size. No pain is felt during the manipulation. The maximum that the patient can feel is the touch of the electrode and tingling.
general information
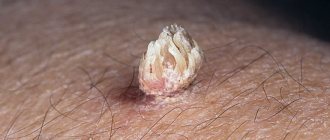
Removal of moles by electrocoagulation is a method of getting rid of age spots using an electric knife. Using an electric knife can only remove small pigments, papillomas and warts. The operation is safe to perform on the face. During the procedure, the nevus and the skin around it are cauterized, but there is no bleeding.
There will be a dark spot on the treated skin at first, which will disappear after 2 weeks. The procedure is one-time, which means that during the session one area of skin is cauterized, which does not need to be treated again. The skin that is removed is sent for examination to determine whether the growth was cancerous.
The electric knife plays the role of a scalpel, but it “cuts” with high-frequency current discharges. The discharges gradually make micro-incisions that cut off the mole layer by layer. The procedure produces heat, which traps blood and reduces the chance of infection. The electric knife was called an electrocoagulator because it generates a current during the movement of particles.
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation involves touching a heated electrode to the skin and is therefore more painful than laser. Flat tumors are cauterized with a ball electrode, and convex ones are cut off with a knife - a loop. This allows analysis after the procedure. Healing of the wound takes about two weeks. Often, pits remain at the site of exposure. To avoid scars, the wound requires special care. Scarring will also occur if the mole was located in the deep layers of the skin.
Electrocoagulation is recommended for flat formations up to 10 mm in size, and for convex “pedunculated” formations. Removing moles using electrocoagulation or laser is a medical cosmetology practice and has contraindications. Therefore, before the procedure, consultation with a specialist is required.
Recovery period, skin care after
When the skin is exposed to electricity, a dry crust forms at the site of a small mole or papilloma. This is a scab under which new tissue is forming. To ensure that nothing interferes with the process, it is necessary to adhere to some rules of the recovery period:
- Do not wet the scab with water or try to pick it off. After some time it will disappear on its own.
- If stitches were placed on the wound, they are treated with antiseptics. This could be brilliant green or a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
- After the anesthesia wears off, the patient may feel pain in the area of the removed lesion. It can be treated with pills, but in most cases they can be managed without them.
- Do not apply decorative cosmetics to the wound or seam. Electrocoagulation of moles can also have negative consequences if conventional care products are used prematurely.
- Until the scab falls off, you should not visit the bathhouse, go to the pool, or swim in open water. This can cause infection in the wound.
- It is worth limiting physical activity for a while, even if the formation was removed on the face. Avoid excessive sweating, which can cause infection.
- Care after mole removal by electrocoagulation does not allow prolonged exposure to the sun. Ultraviolet rays can cause increased pigmentation or hypertrophic development of the scar.
After the completion of the rehabilitation period, many prohibitions disappear. But even later, you should not spend a lot of time in the sun or expose your skin to mechanical, physical or chemical influences.
During the recovery period, avoid sunlight, do not wet or touch the area where the nevus was removed. Be sure to take care of the damaged surface and avoid contact with cosmetics.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with the Diet after tonsil removal in adults
After some time, the crust that has formed in this place will fall off on its own. Sometimes a pink spot remains at the site of the mole after the crust falls off, but it goes away quite quickly. You should not be alarmed if an area of the skin turns yellow; it will soon acquire a normal shade if electrocoagulation of moles was carried out correctly.
If inflammatory processes occur, you should consult a doctor. Sometimes a scar remains - this is a consequence of improper exposure, care or low qualifications of the doctor. Therefore, before removing a mole using electrocoagulation, it is necessary to spend time finding a good doctor, reading reviews and making sure of his competence.
The dense crust that appears on the surface creates optimal conditions for skin regeneration. It is also an obstacle to the penetration of infection, so you should not remove it. At the initial stage, it is necessary to treat the wound with an antiseptic, for example, chlorhexidine, an alcohol-based solution or potassium permanganate.
If the formation is removed from the face, slight swelling and soreness are observed within a few days, they go away on their own after some time, there is no need to treat them. A mole on the body may hurt, but not so much that painkillers are needed. The formation of new epithelium under the crust occurs within 1-2 weeks, after which it disappears and a pink or whitish spot remains. If the dermis has been affected, the spot will remain white forever.
Complications:
- Wound infection. Early removal of the crust from the wound leads to an increased risk of infection and suppuration. It happens that an infection occurs during the removal, then pus forms under the crust and it peels off. Then the wound requires special care so that the purulent process does not lead to scar formation.
- Scarring. Sometimes the white patches cannot be avoided and a significant proliferation of fibrous tissue occurs, especially in people who have a tendency to form scars.
For some time after the procedure, the patient feels discomfort and observes swelling at the cut site. Such consequences are not considered dangerous and should not be treated. It is rare to prescribe painkillers during the rehabilitation period, since the discomfort does not cause noticeable pain. If you remove the scab yourself before the wound heals, the likelihood of infection increases. The infection causes suppuration and tends to spread throughout the body.
Dangerous consequences
For some time after the procedure, the patient feels discomfort and observes swelling at the cut site. Such consequences are not considered dangerous and should not be treated. It is rare to prescribe painkillers during the rehabilitation period, since the discomfort does not cause noticeable pain. If you remove the scab yourself before the wound heals, the likelihood of infection increases. The infection causes suppuration and tends to spread throughout the body.
After excision of the mole, a small spot remains - a burn of the surrounding tissue. It is covered with a crust that serves as a protective barrier so that infection does not penetrate into the wound and healing occurs without complications. For small moles, coagulation leaves no traces. With large diameter growths, exposure to electric current will leave a scar.
If the face is cauterized, the area near the wound swells and hurts. In rare cases, similar symptoms are observed after removal of a mole using electrocoagulation on the body. The discomfort goes away after a few days. The pain is mild, not excruciating. After the crust falls off, new light skin appears. It will gradually heal and darken, matching the color with the surrounding tissues. With a large depth of exposure, a white mark may remain.
Care, which the doctor will tell you about, will help reduce the consequences and complications to a minimum. It consists of observing the following rules:
- Treat the wound daily with an antiseptic - medical alcohol, potassium permanganate, brilliant green, chlorhexidine. If indicated, an antibiotic-based ointment is prescribed. Apply strictly according to the schedule indicated by the doctor.
- Instead of a mole, after cauterization, a crust remains, which is prohibited from getting wet for 4-5 days.
- It is important to avoid contact with household chemicals and cosmetics on the wound.
- Until healing occurs, you cannot swim in open water, visit the pool, sauna, or bathhouse.
- Avoid injury. The crust should come off on its own. This is an important stage of recovery, preventing skin scarring.
- After the crust comes off, the new skin should be carefully protected from exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Failure to comply with the rule will provoke pigmentation. Sunscreens with an SPF of 50 or more will help you care for young skin in the summer.
After the removal procedure, people who have a tendency to grow hypertrophied and keloid scars may develop a scar that will have uneven edges and a constant tendency to increase. In this case, the patient needs the help of a doctor who will prescribe special ointments and help prevent severe tissue growth. In some cases, the skin can grow at such a rate that surgical removal is required.
After thermal exposure to papilloma, dry crusts form in the operated area, which eventually fall off on their own. Independent removal of crusts or papilloma tissue is unacceptable unless they are immediately rejected. Dry crusts or remnants of “evaporated” papilloma are a biological dressing, and their early removal often causes bleeding, and in the future can lead to the formation of scars and/or age spots.
Therefore, proper care of the wound after removal of these cosmetic defects is considered an important factor. At first (several hours or days) after electrocoagulation, slight discomfort or pain may be observed in the wound area, but this should not cause concern - they go away on their own and do not require treatment .
The crusts that form after the procedure are rejected on their own after the wound heals, on average after 8-10 days. The crust and the area around it must be treated 3 times a day with a weak solution of potassium permanganate (5% potassium permanganate solution) or another antiseptic (furacillin solution, chlorhexidine) - this is not only the prevention of secondary infection, but also an opportunity to avoid the appearance of a scar.
The decisive role in electrocoagulation of papillomas is played by the qualifications, experience and professionalism of the doctor or cosmetologist who carries out the procedure, the type, size and location of the tumor being removed, proper care of the wound, as well as prevention of relapses. All complications during the procedure or during the recovery period arise as a result of violation surgical techniques, incorrect choice of nozzle or current strength, incomplete examination of the patient or ignoring contraindications:
- bleeding from the wound in case of trauma to a large vessel or in the presence of blood diseases with problems with the blood coagulation system;
- allergic reaction (if you are allergic to painkillers and/or intolerant to electrical procedures).
Complicated course in the recovery period after removal of papilloma can be observed with improper care of the postoperative wound:
- suppuration (with early forcible removal of the crust and infection entering the wound);
- the formation of pigment spots or depigmented whitish scars;
- the formation of large connective tissue scars in those cases with a genetic predisposition to the proliferation of connective tissue;
- proliferation of atypical cells at the site of electrocoagulation (in case of injury, burn or constant exposure to aggressive chemical and physical agents), their malignancy (malignancy);
- recurrence of papilloma.
If any signs of a complicated course appear after electrocoagulation, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Risk factors
Often a person does not notice the degeneration of a nevus into melanoma. But melanoma is life-threatening, and it is almost impossible to cure it at an advanced stage. Therefore, it is advisable to remove the mole before it becomes malignant. The first symptoms of degeneration:
- change in the shape and size of the spot;
- violation of color uniformity;
- changes in texture, such as wrinkling or peeling;
- painful sensations;
- microbleeding.
Two or more of these signs serve as a reason for medical consultation and removal of the mole. It is worth getting the spot examined as soon as possible, because melanoma quickly spreads to healthy cells. Reasons why nevus degenerates:
- heredity;
- birthmark injuries;
- hormonal imbalance;
- excess ultraviolet rays.
Contraindications
So that after electrocoagulation of a mole there are no undesirable consequences,
Contraindications should also be taken into account.
- suspicion that the formation has degenerated into malignant;
- patient intolerance to electric current;
- pathologies that interfere with blood clotting;
- allergy to local anesthetics;
- tendency to form keloid scars.
There are also relative contraindications:
- acute period of a chronic disease.
This method is chosen if the indications for removal are purely aesthetic. The cosmetic effect is quick, affordable and almost without a trace. Removal of a mole with an electric knife is performed in cases in which the spot is not malignant. To replace electrocoagulation, when the spot is malignant, surgical operations or a method of removal using microloops are offered. The medical procedure is called electroexcision. Removing moles with an electric knife has the following contraindications:
- malignant nature of the mole;
- poor blood clotting;
- allergic reactions to anesthetic drugs;
- skin hypersensitivity;
- viral diseases.
Contraindications and restrictions
The malignant nature of the mole is not the only contraindication to the use of the described technique for removing nevi. It should not be used if the patient has:
- poor blood clotting;
- allergy to anesthesia drugs;
- viral diseases in the acute phase;
- skin hypersensitivity.
Electrocoagulation is not used even when the size of the formation is more than one centimeter.
Common Questions
- The procedure is painful. The electrode heats up to 80 degrees, so its impact causes pain. But before the procedure, a painkiller is injected into the area near the birthmarks. This results in the patient experiencing mild discomfort as much as possible.
- The choice between a coagulator and a laser. If we talk about eliminating moles, then each method has its own strengths, so the decision is made for each specific case separately.
- Many people are interested in whether it is possible to remove a mole using coagulation during pregnancy. The answer to this question is: if there is no intolerance to local anesthesia, then there are no other contraindications to removing a mole in the position.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with what moles on the body are for
Pros and cons of electrocoagulation of moles
Advantages of the procedure using an electric knife among other methods:
- Suitable for all areas of the body, even the face.
- Allowed for all skin types, in contrast to laser removal of moles, which is contraindicated for dark skin.
- Does not depend on the patient's age. Both young and old skin respond equally well to the influence of an electric knife.
- The operation is completely painless because local anesthesia is used.
- Held all year round. Unlike salon whitening procedures, they are carried out in the cold season, with inactive solar radiation.
- There is no need for special preparation on the part of the patient.
- One procedure is enough to completely get rid of the stain.
- The skin recovers quickly after the electric knife procedure.
- More affordable than laser mole removal.
- The principles of preventing bleeding and infection are observed.
The method of removing moles with an electric knife does not exclude the formation of scars.
Disadvantages of the procedure with an electric knife:
- Local anesthesia is mandatory for the procedure. The patient may have an allergic reaction to the anesthetic drug.
- Anesthesia is not performed on the skin around the eyes, so a patient with a mole in this area will feel severe pain during surgery.
- After the procedure, it is recommended to treat the wound surface for 2 weeks.
- There is a possibility of postoperative scar formation. But its appearance is due to unprofessional performance of surgical procedures or non-compliance with doctor’s recommendations during rehabilitation.
Weaknesses and strengths of electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation is a simple operation that allows you to remove moles on any part of the body, including the face. It has no age restrictions, and there are no contraindications based on skin type. The operation can be performed at any time of the day, at any time of the year. A small mole (up to one centimeter) is removed in just one session. Afterwards, a crust forms on the wound, which performs protective functions and helps prevent bleeding and infection. Electrocoagulation is characterized by a short recovery period.
The weaknesses of the method include:
- the need for local anesthesia (for many it can cause an allergic reaction);
- the need to properly and daily treat the wound;
- the possibility of spreading thermal effects to surrounding tissues (electrical burn);
- presence of risks of postoperative scar formation.
A highly qualified specialist allows you to minimize all existing risks.
Weaknesses and strengths
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=77b5B9vzrqU
Since electrocoagulation is a simple operation, it has its advantages and disadvantages. The benefits include:
- High degree of effectiveness. The likelihood of relapse if all rules of procedure and care are followed is minimized.
- It is possible to examine the material for histology.
- Removing adjacent skin reduces the risk of nevus growth.
- Availability and security.
Disadvantages include the possibility of scar formation. But this happens due to non-compliance with the rules of the mole removal process and its improper processing.
The procedure does not require special preparation and takes 25 minutes. The doctor numbs the affected area with an injection of lidocaine. Using an electrode made of tungsten, only one movement is made to completely remove the mole. At the moment of dissection of the jumping tissue, the vessels are cauterized.
Mechanism of the procedure
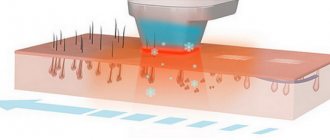
Electrocoagulation begins with local anesthesia. Anesthesia is administered under the skin by injection or by applying a numbing cream. When the anesthesia begins to take effect, the doctor selects the power of the electrode and cuts off the spot. When cut, the skin near the mole is burned with high temperatures, and the blood vessels are “sealed.”
Due to this, there is no swelling, bleeding and no risk of infection. No more than two moles are removed at a time. All surgical procedures take up to 15 minutes. The results and speed of recovery after a stain removal procedure are directly proportional to the level of skill of the doctor.
Algorithm for the procedure
The patient enters the doctor's office and is placed on the couch. He chooses the position based on what part of the body the nevus is located on (for example, if it is in the abdomen, the person lies on his back and frees the necessary area from clothing).
Methodology of the procedure (a photo of electrocoagulation of a mole is presented below):
- The doctor treats the nevus and the tissue around it with an antiseptic solution.
- The specialist injects an anesthetic subcutaneously. If the mole is very small in size, the doctor uses drugs in the form of a cream.
- The specialist burns out the mole entirely or layer by layer using an electrode.
- The doctor treats the resulting wound with a solution of potassium permanganate.
Immediately after the procedure, the patient can begin his daily activities. According to numerous reviews, electrocoagulation of a mole is well tolerated in most cases. This is due to the fact that no pain occurs during nevus removal. The patient can only detect a faint smell of burnt skin.
What else is electrocoagulation used for?
The procedure can be used to remove dilated vessels, hemangioma, spider veins, keratosis, complicated acne, molluscum contagiosum, viral papillomas, warts, genital warts and other diseases. The essence of the action is this: volumetric thermal damage occurs to the tissues around the object due to exposure to electric current.
Removing a mole using an electrocoagulator is quick and painless. Does the wound left after removal heal quickly? and almost never leaves scars, provided proper care is taken. The procedure makes sense when the mole is in a visible place or causes discomfort.
Recovery
Recovery after the procedure for excision of moles with an electric knife is at least 1.5 weeks.
When tumors are removed with an electric knife, a scab remains on the skin area, which minimizes the likelihood of infection entering the body through the wound and prevents blood loss. The minimum rehabilitation period after removing a stain is 10 days, but not all types of skin regenerate quickly.
Lighter, more sensitive skin extends the recovery phase to 21 days. Throughout the entire rehabilitation period, the area of the skin where the stain was removed requires specific care. It is worth treating the surface with antiseptic agents in the form of lotion. The doctor will prescribe specific medications. It is also recommended to protect the wound area from the influence of sunlight, aggressive cosmetics, household chemicals, and for the first few days from moisture.
Do not pick off the scab under any circumstances, as this is an additional natural protection. This crust disappears on its own when the wound is completely healed. New epithelium forms under the crust within two weeks. After the scab falls off, the skin will take on a pinkish tint, which will disappear over time.
We invite you to read: What treatment is provided after removal of an endometrial polyp?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MyWYv8INkZA
After a session of electrical coagulation, a crust appears at the site of the removed mole. Beneath it, new tissue is actively forming. During this time, it is important to properly care for your skin:
- Treat the wound daily with an antiseptic composition (manganese or alcohol-containing).
- Avoid getting the wound wet. To do this, you need to postpone trips to baths, saunas, and swimming pools for 2 weeks.
- “Hide” the crust from direct sunlight.
- For 14 days after the procedure, postpone the use of cosmetics and lotions.
Care after removal of moles by electrocoagulation also includes lubricating the problem area with sunscreen emulsions or baby cream without adding fragrances or other harmful additives.
Removal of moles by electrocoagulation will be carried out quickly, without pain and complications at the Laser Surgery Clinic. To get a free consultation with a doctor, call the phone number listed on the website.
Lyudmila Sergeevna Amyokhina
Head of the Laser Medicine Clinic Physician of the highest category, cardiologist, gastroenterologist, reflexologist
We provide a professional range of procedures in the laser medicine segment. We use modern equipment and widely use effective treatment methods. The staff is staffed by professional doctors of the highest category. Still have questions? Just call us and get a free consultation 7(812)244-36-58.
Work experience over 30 years
Rehabilitation period
After removing a mole using electrocoagulation, a dry crust forms on the skin. This is a scab under which new healthy tissue is forming.
Rules for patient behavior during the recovery period:
- Do not wet the crust with water or try to tear it off yourself.
- In the first days after electrocoagulation of a mole, minor painful sensations may appear. In this case, it is permissible to stop them with anesthetic drugs.
- It is forbidden to apply decorative cosmetics to the scab, especially for patients who have had a nevus removed from their face. If the wound is on the torso or limbs, it is not advisable to even use shower gel. Recommendations regarding skin care are provided by a dermatologist. Typically, your doctor will recommend showering with baby soap.
- Until the crust falls off, it is prohibited to visit swimming pools, saunas and steam baths. Swimming in open water is also prohibited.
- Reduce the intensity of physical activity to a minimum. This is due to the need to reduce the amount of sweat produced.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to sunlight for two months. This can cause hyperpigmentation.
The duration of the recovery period is, on average, 1 month. During this time, the scab disappears, and in its place remains smooth skin of a slightly pinkish tint. Over time, the fabrics acquire a natural color.
Recovery after the procedure for excision of moles with an electric knife is at least 1.5 weeks.
When tumors are removed with an electric knife, a scab remains on the skin area, which minimizes the likelihood of infection entering the body through the wound and prevents blood loss. The minimum rehabilitation period after removing a stain is 10 days, but not all types of skin regenerate quickly.
Lighter, more sensitive skin extends the recovery phase to 21 days. Throughout the entire rehabilitation period, the area of the skin where the stain was removed requires specific care. It is worth treating the surface with antiseptic agents in the form of lotion. The doctor will prescribe specific medications. It is also recommended to protect the wound area from the influence of sunlight, aggressive cosmetics, household chemicals, and for the first few days from moisture.
Do not pick off the scab under any circumstances, as this is an additional natural protection. This crust disappears on its own when the wound is completely healed. New epithelium forms under the crust within two weeks. After the scab falls off, the skin will take on a pinkish tint, which will disappear over time.
During the first few days after the procedure, the cauterized mole site will be painful, red and swollen; it is important not to expose it to sunlight or ultraviolet rays, or to get it wet. If you treat this with carelessness and cause an infection, dangerous suppuration will form under the crust. If the pain does not disappear over the course of several days, or worsens, you should immediately see a doctor.
With successful electrocoagulation of a shallow mole, a pale pink spot should remain in place of the former crust, which will soon pass and the skin will return to its natural color. High-quality mole removal using electrocoagulation and properly performed postoperative care ensure the absence of complications and scars at the intervention site.
Care after removal of a mole by electrocoagulation consists of maintaining hygiene of the place where the nevus was located. To do this, regularly treat the area with a disinfectant. The average recovery period is two to three weeks. It depends on the size of the nevus and the state of the person’s immune system. After the crust falls off and heals, there will be no trace left on the body that the mole was removed with an electron.
It is necessary to follow several rules that promote speedy healing:
- Do not subject the removal site to mechanical stress.
- Do not wet the area of skin where the nevus was located for two days after removal.
- Do not stay under the scorching sun for a long time.
- Limit visits to the solarium and swimming pool.
- Do not apply cosmetics.
After the protective crust spontaneously falls off, you can observe the skin having a light red tint. After two or three weeks the color will return to flesh. An important condition is the absence of exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Otherwise, a light brown stain may form that cannot be removed.
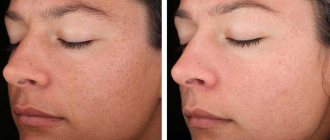
Before and after removal
Before and after removal