How does oxidative (or oxidative) stress affect the skin?
When, under the influence of negative external and internal factors, the balance of the oxidative and reductive systems is disturbed towards oxidation, a large number of radicals are formed in the skin, participating in lipid peroxidation. This leads to damage to nucleic acids, cellular proteins and lipids. Such processes have an extremely negative effect on the condition of the epidermis and its functions. Ceramides are damaged - lipid molecules, which are the main building component of the outer layers of the skin, forming a lipid barrier (protecting the skin from dehydration, peeling, irritation, penetration of foreign substances, etc.).
By oxidizing lipids, free radicals provoke a lack of moisture, inflammatory reactions, and the risk of developing bacterial infections and pollution. As a result, damage to the cell membranes of the epidermis and dermis may occur, which will weaken the protective function of the skin and may cause the formation of various cosmetic defects. Proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid are destroyed (which accelerates skin aging).
In addition, free radicals destroy the skin framework, damaging collagen and elastin fibers and preventing their synthesis. (Oxidized collagen molecules become free radicals and bind to each other, forming dimers: the so-called “cross-linked” collagen is formed, less elastic and resistant to the action of enzymes.) As a result, the firmness and elasticity of the skin suffers, wrinkles are easily formed, and tissue ptosis appears.
To prevent (or promptly eliminate) such consequences, doctors recommend maintaining a healthy lifestyle: this includes physical exercise, healthy sleep, avoiding stressful situations, limiting alcohol and quitting smoking, protection from excessive ultraviolet radiation (it is recommended to use products with SPF during the active sun season -protection). In addition, it is important to monitor your diet: it must be properly balanced.
Nina Vitalievna Levushkina, brand technologist at PLEYANA:
“A well-balanced diet will contain adequate amounts of vegetables and fruits. It is recommended to include sea fish and cold-pressed vegetable oils. All this is necessary to replenish the supply of vitamins E, C, A, F, bioflavonoids, coenzyme Q10 and other antioxidants important for the body.”
Also, to protect and restore healthy skin functions, today there is a wide range of cosmetics containing various types of antioxidants.
Antioxidants: protecting cells from destruction
The human body is equipped with a multi-level system of protection against the destructive effects of harmful radicals. It is called the antioxidant system, or AOS. The components of this body's defense system are called antioxidants.
Antioxidants are natural or synthetic substances that can slow down or stop the oxidation process of organic compounds. At their core, antioxidants are also radicals (particles with a missing or extra electron) that are ready to react with “harmful” radicals in order to break (or slow down) the oxidation chain.
The mechanism of action of the main part of antioxidants is as follows: antioxidant molecules interact with active radicals (which leads to the formation of low-active radicals) or destroy intermediate reaction products (as a result of which oxidation slows down, as the rate of formation of free radicals decreases). So, the main task of antioxidants is to break branched chain oxidation.
This is done in two ways. In the first, an antioxidant molecule containing a mobile hydrogen atom interacts with an active particle - a radical leading the oxidative chain - and oxidizes it, resulting in the formation of a low-active radical. Derivatives of secondary aromatic amines and phenols work according to this principle. In the second method, the antioxidant molecule reacts with the intermediate oxidation product, which leads to its decomposition and chain branching, thereby forming a stable compound. This is how organic derivatives of phosphites and sulfides act.
There are three main levels of antioxidant protection in the body: anti-oxygen (prevents “electron leakage” in mitochondria), anti-radical (prevents the formation of radicals) and anti-peroxide (protects cell membranes and enzyme systems of the cell).
A whole complex of enzymes is involved in the work of AOS, among which superoxide dismutase, catalase, peroxidase, and various reductases (glutathione reductase, methionine sulfoxide reductase, diascorbate reductase, etc.) are especially well known. In addition to enzymes, AOS also includes a number of cell metabolites: lipoic, ascorbic and uric acids, the tocopherol family, about 500 carotenoid compounds, flavonoids, polyphenols (4000–5000 compounds), urates and others. Also directly related to the protective system are: the amino acid taurine, the dipeptide carnosine, the catabolism product of heme-containing proteins - bilirubin, melatonin (a multifunctional antioxidant, one of the pineal gland hormones). Often, individual components of AOS work in synergy, enhancing each other’s actions (the process of studying this kind of interaction continues).
The discovery of antioxidants and their first use were associated with an attempt to preserve food for a longer period of time. After the war, the food problem was acute in the Soviet Union: scientists had to solve the pressing issue of extending the service life of products in order to avoid their spoilage. Research by B.N. Tarusov in the 1950s showed that changes in the surface properties of butter are the result of lipid peroxidation. Then vitamins (including E and C) began to be added to products to protect against oxidation. In 1961, biophysicist A.I. Zhuravlev discovered antioxidant activity in living organisms.
There is no uniform classification of antioxidants. However, they are usually divided:
- by molecular structure: they distinguish enzymes (superoxide dismutase, catalase, peroxidase, phospholipase, etc.) and organic compounds with non-enzymatic activity, which are macromolecular (melatonin, transferrin, cerruloplasmin, ferritin, serum albumin) and low molecular (ascorbic acid, glutathione, urea, bilirubin, sulfur-containing amino acids, adrenaline, steroid hormones, some vitamins, ubiquinone, flavonoids, some types of trace elements);
- according to the ability to act in the aqueous or lipid phase: polar (water-soluble) and non-polar (fat-soluble);
- by localization of action in cellular structures: membrane, intracellular and extracellular.
Antioxidants also differ in their mechanism of action:
- “scavengers” - react with all free radicals and neutralize them, restoring them to stable forms;
- “traps” - have an affinity for certain substances with which they react;
- “antioxidants that break biochemical chains” are substances that are even more active than free radicals: by reacting with the latter, these antioxidants make the radicals weakly active.
According to the classification of antioxidants according to A.V. Kudrin and O.A. Gromova (Russian scientists who have published a number of works on the role of microelements in medicine), they can be endogenous (originally present in the body) and exogenous (coming from the outside).
The first include:
- enzymes: superoxide dismutase (SOD) – zinc-, copper- and manganese-dependent, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione-S-transferase, etc.;
- metabolites: glutathione-GSH (oxidized and reduced), glutathione cell cycle, ubiquinone Q10.
The second ones include:
- vitamins and provitamins: alpha-, beta-, gamma-carotenes, vitamin A, retinoids, alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E), phylloquinone (vitamin K), vitamin C, rutin;
- plant substances: ubiquinone (coenzyme Q10), quercetin, polyphenolic compounds, catechins, chlorophylls, pigment complexes, glycosides, essential oils, bioflavonoids, gallic acids, thiol compounds;
- antioxidant cofactors: riboflavin, vitamin B6, pantothenic acid, omega-3, omega-6;
- trace elements: selenium, zinc, cobalt, manganese;
- medications.
We can conditionally distinguish three levels of antioxidant protection of the skin: surface (membrane or barrier protection), extracellular and intracellular.
Surface protection is located in the upper layers of the skin and is the first stage of protection against harmful factors (mainly acting from the outside). These include large amounts of fat-soluble beta-carotene, alpha-tocopherol and squalene.
Extracellular – implies protection mainly of the intercellular space from damage. It includes: alpha-tocopherol, vitamin C, glutathione, superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase (containing selenium), catalase.
Intracellular protection contains all types of antioxidants. It is carried out due to fat-soluble antioxidants located in the cell membrane (structural component - lipids) and water-soluble antioxidants (located in the cell membrane and membranes of its organelles in those areas where free radicals are formed and where they come into contact with the cell (outer cell membrane). One of the water-soluble antioxidants in this protection is tripeptide glutathione (its concentration here is much higher than other antioxidants).
Antioxidant mesotherapy
Despite the commercial hype around antioxidants in medicine, the question of whether or not to use them in mesotherapy is no longer asked. It is definitely necessary to appoint one. But how? The use of drugs with antioxidant properties in mesotherapy corresponds to the basic principles of antioxidant therapy, namely, preference is given to ready-made cocktails in which the functional synergism of various types of antioxidants is manifested. Studies have shown that the prescription of antioxidant therapy should be approached in a differentiated manner. To achieve good results, different tactics are required in the treatment of structures damaged due to sunburn, poorly healing wounds, inflammatory elements, etc. and to increase skin resistance to factors that activate free radical oxidation. The use of antioxidants in high concentrations can be considered as “first aid” for “tired,” aged, inflamed skin. In these cases, it is recommended to conduct short intensive courses or single sessions. For preventive purposes, it is better to use antioxidants of natural origin or preparations containing small doses of antioxidants.
You should not make antioxidant cocktails yourself, since in combination with certain ingredients, antioxidants lose their properties or trigger negative reactions. In addition, it is known that most compounds of this group are characterized by a two-phase effect - when a certain threshold value is exceeded, the antioxidant effect is replaced by a pro-oxidant one. In addition to their individual effects, antioxidants may act synergistically and protect each other from oxidative damage.
- Vitamin C restores the antioxidant activity of vitamin E by regenerating it into its active form after its interaction with free radicals.
- Beta-carotene supports vitamin E by scavenging reactive oxygen and breaking the free radical chain reaction. Vitamin E may protect beta-carotene from oxidation.
- Selenium is a component of the enzyme glutathione peroxidase, which protects cell membranes from fat peroxidation. Acts in synergy with vitamin E, reducing cell damage.
- Bioflavonoids restore vitamins C and E.
It is no coincidence that complex antioxidant therapy, which combines water- and fat-soluble antioxidants with a synergistic effect, has a great effect. In some cases, simultaneously with aesthetic procedures, it is necessary to take oral medications or natural antioxidants (fresh juices, fruits, vegetables, etc.).
Antioxidants in cosmetology and aesthetic medicine
The use of antioxidants in cosmetology (and in parallel in other areas of our lives) has become so popular over the past decades that today it is rare to find a cosmetic brand that does not use these ingredients at all in cosmetic compositions.
Skin care using products containing antioxidants was used long before the discovery of free radicals and antioxidants themselves as a separate group of substances. It is about using the valuable properties of plants to protect the skin and improve its overall properties. Some plants contain entire antioxidant complexes - these are natural cocktails that have found application due to their pronounced beneficial effects (confirmed by centuries-old practice). Scientific discoveries at one time were able to explain the value of such complexes by identifying vitamins of various groups in their composition: carotenoids, vitamin C, flavonoids (polyphenols) and other valuable substances.
Today, in addition to plant extracts, cosmetic preparations include a number of other ingredients with antioxidant properties: vitamins, organic and inorganic salts, superoxide dismutase, peroxidases. Antioxidants in cosmetics perform a dual function: they not only prevent oxidative processes in skin cells, but also protect the product itself from oxidative damage.
Olga Ivanovna Domashova, commercial director of DOMIX:
“Unsaturated fats, which are often included in cosmetic products, are susceptible to oxidative reactions. Oxidation makes them rancid, which is manifested in the appearance of a specific odor and unpleasant taste. Some vegetable fats are partially protected from oxidation by the presence of natural antioxidants, but remain sensitive to photo-oxidation. In order to preserve commercial properties throughout the shelf life, antioxidant preservatives must be added to fat-containing cosmetic products: moisturizing and softening products for the skin, as well as decorative cosmetics.”
To maintain the stability of a cosmetic product, synthetic antioxidants (polyethylene glycol succinate, butylated hydroxytoluene, butylated hydroxyanisole, propyl gallate, etc.) are mainly used. Some types of antioxidants (“indirect antioxidants”) are used for sunscreen cosmetics: among them are glycine, arginine, and beta-glucans.
In cosmetology, antioxidants are actively used in the following types of products.
How does nutricosmetics affect the body?
Such drugs act comprehensively not only from the outside, but also from the inside. Thanks to its use, the condition of hair and nail plates improves. Nutricosmetics helps to cope with wrinkles and overcome dry skin. It becomes fresher, its tone is evened out, acne and dermatitis on the skin stop.
Nutricosmetics tighten enlarged pores. The skin becomes less oily. For skin diseases, it is recommended to take a course of vitamins C, K, B. Preparations with lipoic acid or vitamin C help cope with pigmentation.
About the author: Larisa Vladimirovna Lukina
Dermatovenerology (Internship in the specialty of dermatovenerology (2003-2004), Certificate of the Department of Dermatovenerology of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after academician I.P. Pavlov dated June 29, 2004); Confirmation of the certificate in the Federal State Institution "SSC Rosmedtekhnologii" (144 hours, 2009) Confirmation of the certificate in the Rost State Medical University of the Ministry of Health of Russia (144 hours, 2014); approved clinical protocols. Read more about me in the Doctors-Authors section.
Cosmetic care products
It includes all types of cosmetics for face and body skin care. This includes products for cleansing and toning the skin (thermal water, tonic, foam, makeup remover milk, gommages, peelings and scrubs), skin care products responsible for moisturizing, nourishing and protecting (serums, creams, masks, etc.) , oils for care and massage, care products for the skin of hands and feet (used including for manicure and pedicure procedures).
Care products can be applied manually or using some hardware procedures to more effectively penetrate the components of the products into the deeper layers of the skin.
It should be borne in mind that the use of antioxidants (whether in special foods, pharmaceutical or cosmetic products) requires a responsible approach, and it is recommended to follow the instructions of a cosmetologist in this matter. The fact is that an excess of some antioxidants or their improper use (here we can cite the use of tocopherol as an example) may not only not bring the expected effect, but, on the contrary, cause harm to health.
Mesotherapy and biorevitalization with antioxidant effects
In mesotherapy today, cocktails containing plant complexes with a high concentration of oligoelements and vitamins are actively used. Such complexes may contain “indirect antioxidants” (amino acids, B vitamins, etc.); they can be added to formulations to improve cellular metabolism.
Among the components of mesotherapy drugs, the following are often found: ascorbic acid, oligoelements, rutin, green tea extracts, ginkgo biloba, Asian centella and others. Such cocktails most often contain hyaluronic acid. Cocktails can be composed by a doctor independently (for example, by combining herbal complexes with hyaluronic acid). Some manufacturers of this type of product produce it in such a form that the doctor has “room for maneuver.” However, many experts prefer ready-made cocktails. There are many such complexes designed to achieve specific effects (they may include hyaluronic acid, antioxidants, and other valuable substances). Antioxidants are often included in medications designed for other purposes, such as acne or cellulite. In such compositions, antioxidants play a supporting role.
Indications for mesotherapy with the use of antioxidants include age-related skin changes, traces of photoaging, gray and dull skin (“smoker’s effect”, acne and post-acne, pigmentation disorders, rosacea), as well as rehabilitation after invasive procedures (laser exposure, peelings, plastic surgery and etc.). To solve various problems (aging, inflammation, hypersensitivity, etc.), meso-cocktails with various compositions are used. In order to quickly restore the effect for tired, aged or problematic skin, it is recommended to carry out a short intensive course (or a single session) of a meso-cocktail with a high content of antioxidants. And for the prevention of problems and for a long course, cocktails of less intense action (with a lower content of antioxidants or with natural mild antioxidants) are more likely to be suitable.
One of the areas of mesotherapy with antioxidants is the use of meso-cocktails to solve problems related to hair (this is the fight against various types of alopecia, increasing the thickness, strength and elasticity of hair, strengthening hair follicles, and improving the scalp).
Causes of Oxidative Stress
The main reasons leading to the activation of free radical oxidation in tissues:
- reducing the intake of exogenous antioxidants (tocopherol, ascorbic acid, bioflavonoids, etc.) into the body;
- stress of various origins;
- entry into the body of pro-oxidants (pesticides, oxidizing drugs, photochemical products of smog, etc.);
- excess consumption of fats and carbohydrates
- if they are not spent enough;
- hypokinesia;
- influence of physical factors (UV radiation, electromagnetic field, etc.);
- age-related decrease in the activity of antioxidant enzymes;
- congenital enzymopathies of antioxidant enzymes.
Some important antioxidants in cosmetics
Tocopherol (vitamin E)
It is the main reducer of lipid peroxyl radicals (formed during peroxidation processes) in mammalian cell membranes. It is not produced in the body (it enters the body along with food, the vast majority of which are unrefined vegetable oils). Tocopherol interrupts lipid oxidation reactions and thereby provides protection to lipid membranes, restoring the natural protection of the epidermis. Several forms of tocopherol are used in cosmetics. Provides UV protection, has an anti-inflammatory effect, moisturizes and softens the skin.
Retinol (vitamin A)
Strengthens the immune response of cells, maintains healthy skin and mucous membranes. Different forms of retinol are used in cosmetics: retinol palmitate and retinol acetate, retinol (natural retinoids, often used in cosmetics, including home use), retinaldehyde and retinoic acid (the most effective form, used for the purpose of anti-aging effect, used in almost all cosmetic products for face and body skin care). The effects of retinol are manifested in lightening pigmentation, stimulating collagen production, skin renewal, thickening the deep epidermal layers, and reducing hypersensitivity. Before using cosmetics with retinol, it is recommended to consult a cosmetologist.
Tatyana Nikolaevna Mozharovskaya, cosmetologist, chief physician of the Skin Health Cabinet clinic, certified trainer of the Dermagenetic Academy:
“Vitamin A is a fat-soluble acid - the only one that penetrates the cell membrane and enters the nucleus. It is involved in 32 skin functions. In cosmetology, this is a very multifunctional product that can be used, among other things, as a carrier of active substances into the cell nucleus (which significantly accelerates metabolic processes in it), and as a result we get visible rejuvenation.”
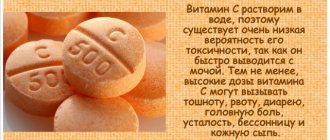
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
It is a water-soluble reducing agent that is synthesized in plants and some animals. The human body is not capable of producing ascorbate and is completely dependent on its timely intake from the outside. In addition to the ability to react with anionic superoxides, hydroxyl radicals and many lipid hydroperoxides, it also restores the antioxidant properties of tocopherol (which is why many cosmetic products contain both of these vitamins).
Tatyana Nikolaevna Mozharovskaya, cosmetologist, chief physician of the Skin Health Cabinet clinic, certified trainer of the Dermagenetic Academy:
“Vitamin C is involved in any cocktails of mesopreparations in anti-aging programs: it not only helps fight free radicals, but is also necessarily used in skin lightening programs. Among other things, in home care, vitamin C protects the skin from the negative effects of decorative cosmetics.”
Coenzyme Q10
It is a strong immunological stimulant. A fat-soluble antioxidant synthesized by the body (which decreases with age). Coenzyme Q10 (or ubiquinone) at the micro level protects three important components of the body from oxidation: the energy stations of mitochondrial cells, cell membranes (membranes) and blood plasma.
Fullerenes
Fullerenes (antioxidant sponges) are spherical carbon molecules with a closed surface (the structure resembles a soccer ball). Fullerene is significantly more active than many other antioxidants. It attracts and neutralizes free radicals, and its activity increases with the growth of free radicals: the more of them are formed in the body, the more actively fullerene neutralizes them. One fullerene molecule is capable of neutralizing an unlimited number of active radicals, which concentrate and recombine with each other, turning into neutral molecules. This is a kind of antioxidant catalyst: the fullerene molecule itself does not react and is not damaged; it is only a structure-forming element of the water cluster.
Anna Aleksandrovna Gertsovskaya, trainer-methodologist:
“The discovery of fullerenes made a real breakthrough in the field of biophysics, biochemistry, medicine and cosmetology, which was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1996. Fullerenes are 125 times more active than vitamin C. This active component, like diamond, is an allotropic carbon. Fullerene is capable of protecting and stabilizing biological structures for 40 hours without being perceived by a living organism as a foreign substance. The use of cosmetics with fullerenes helps to effectively combat all signs of skin aging, long-term and deep hydration and preserve youthful skin.”
Bioflavonoids (vitamin P)
The substances are of plant origin and are phenolic glycosides. Obtained from plants (apple fruits, citrus fruits, pomegranates, grapes, ginkgo biloba, black currants, green tea, etc.). They have pronounced antioxidant properties.
Selenium
The mineral is an important component of the enzyme glutathione peroxidase (which reacts with hydrogen peroxide to form water).
Zinc
Maintains normal concentrations of vitamin E and enhances the absorption of vitamin A. Zinc oxide is used in cosmetics as a physical UV filter.
Phytomelatonin, obtained from plants, has a photoprotective effect and helps maintain normal skin moisture. In the body, melanin provides “secondary photoprotection” of the skin, increasing its photoresistance: it protects against cell damage at all levels, including the dermis (as well as nerve fibers and blood vessels).
Antioxidant drugs used in mesotherapy
In mesotherapy, plant extracts with pronounced antioxidant properties are widely used: preparations containing oligoelements and vitamins. The effectiveness of antioxidant mesotherapy is increased by “indirect antioxidants” (B vitamins, amino acids, etc.), which are prescribed in addition to classical antioxidants to improve cell metabolism.
In antioxidant programs, it is recommended to use the following drugs: Ascorbic acid (Ascormax 10, Toskanicosmetics, Spain), Green tea extract (Camezin, Skinasil, Russia), Ginkgo biloba extract (Ghibilan, Skinasil, Russia), Rutin and melilot extract (Rutinel, Toskanicosmetics, Spain), Asian centella extract (Centazan, Skinasil, Russia), oligoelements (oligoelements Zn, Se, Si, ID-pharma, Spain; Cobre, Cobre-oroplata, Selenio, DIETBEL, Spain). All preparations contain vitamins, oligoelements, phenolic compounds, both in monotype and in the form of synergistic cocktails.
To create cocktails with antioxidants, it is good to use hyaluronic acid preparations: Hyalulite 1%, 2%, 3.5% (Skinasil, Russia), Hyaluform mesolift 1%, 1.8%, 2.5% (Tuscany, Russia) - the preparations contain hyaluronic acid of biotechnological origin, are used to create cocktails with organic silicon and antioxidants.
There are complex preparations containing hyaluronic acid and other antioxidants:
- Hyaluform M 1%* (Tuscany, Russia) – contains hyaluronic acid of biotechnological origin, vitamin C 0.2%, lysine 2 mg/ml.
- Hyaluform M 1.8%* (Tuscany, Russia) – contains hyaluronic acid of biotechnological origin, vitamin C 0.2%, cysteine 4 mg/ml. A drug with a pronounced antioxidant effect, since cysteine, being an antioxidant, also restores oxidized forms of vitamin C.
- Hyaluform M 2.5%* (Tuscany, Russia) – contains hyaluronic acid of biotechnological origin, vitamin C 0.2%, glycine 6 mg/ml, proline 3 mg/ml, lysine 3 mg/ml, valine 3 mg/ml.
- Revitacare Bio-Revitalization Complex (Revitacare Laboratory, France) – contains hyaluronic acid of biotechnological origin 1% (4 ml) and a vitamin-antioxidant complex (10 ml), which includes vitamins A, B1, B2, B5, B6, C, D, E, RR.
- Cytocare 40* (Revitacare Laboratory, France) – contains hyaluronic acid and a balanced antioxidant complex, which includes oligoelements (sodium, calcium, potassium, copper, magnesium, selenium, zinc, etc.), vitamins (B1, B2, B4, B5, B6, B8, B9, B12, H), basic amino acids (including sulfur-containing ones).
- Cytocare 50* (Revitacare Laboratory, France) – contains hyaluronic acid (in greater quantities than Cytocare 40) and a balanced antioxidant complex, which includes oligoelements (sodium, calcium, potassium, copper, magnesium, selenium, zinc, etc.) , vitamins (B1, B2, B4, B5, B6, B8, B9, B12, H), basic amino acids (including sulfur-containing ones). Indicated for severe signs of photoaging.
- NCTF 135 (Filorga Laboratory, France) – contains a complex of vitamins, nucleic acids, oligoelements, coenzymes and amino acids.
- Haircare (Revitacare Laboratory, France) – contains amino acids (arginine, cysteine, glutamine, glycine, ornithine), B vitamins (B3, B5, B6, B8, B9, B12), trace elements (zinc). The drug is used mainly in trichology, in addition, it has good antioxidant properties.
*Note (02/14/12): since the publication of the article, the “Hyaluform M” preparations have been renamed “Hyaluform Mesolift” and the assortment of the Revitacare Laboratory has also changed.
Cytocare 502, 516 and 532 are the closest to Cytocare 40 and 50 mentioned in this article. There are other complex preparations containing antioxidants that can be used not only to influence the effects of oxidative stress, but also as auxiliary ingredients to solve problems such as cellulite, excess fat deposits, acne, etc.